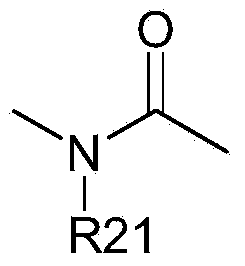
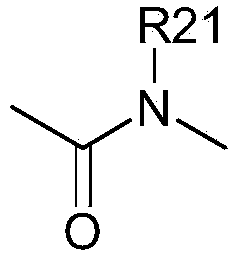
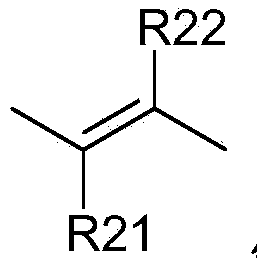
Chemical molecules that inhibit the slicing mechanism for treating diseases resulting from splicing anomalies
A disease, hydrogen atom technique, applied in the field of indole-derived compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0354] Example 1: Development of IDC16-derived compounds
[0355] The present inventors have demonstrated that the compound IDC16 (BAKKOUR et al., supra, 2007) functionally interacts with the SF2 / ASF complex, thereby helping to block alternative splicing during HIV replication, leading to a reduction in Tat protein production. termination.
[0356] Therefore, it is known that the family of polycyclic indoles to which the compound IDC16 belongs exhibits the properties of DNA intercalators. Such compounds thus present a risk of unwanted side effects.
[0357] The inventors thus attempted to develop new molecules that exhibit activity comparable to IDC16 in inhibiting HIV splicing, but at the same time do not exhibit the characteristics of a DNA intercalator.
[0358] In their original hypothesis, the inventors believed that the 2 polar heterocycles at the 2 ends of compound IDC16 were related to its activity, while the 2 middle rings were less important.
[0359] Based on t...
Embodiment 2
[0363] Embodiment 2: the method for synthesizing the compound of the present invention
[0364] [A1.] A list of compounds used in this study is provided in Table I below.
[0365]
[0366]
[0367]
[0368]
[0369]
[0370]
[0371]
[0372]
[0373]
[0374]
[0375]
[0376]
[0377]
[0378]
[0379]
[0380]
[0381]
[0382]
[0383]
[0384]
[0385]
[0386]
[0387]
[0388]
[0389]
[0390]
[0391]
[0392]
[0393]
[0394]
[0395]
[0396]
[0397]
[0398]
[0399]
[0400]
[0401]
[0402]
[0403]
[0404]
[0405]
[0406]
[0407]
[0408]
[0409]
[0410]
[0411]
[0412]
[0413] The synthesis of the compounds described in Table I is illustrated below.
[0414] Synthesis of stilbene (alkene) compounds
[0415]
[0416] 4-Chloropyridine 1 was obtained by neutralizing 4-chloropyridine hydrochloride with 10...
Embodiment 3
[0441] Embodiment 3: according to the selective inhibition of compound of the present invention to HIV-1mRNA ex vivo splicing
[0442] Using the pΔPSP plasmid (JACQUENET et al., J.Biol.Chem., vol.276, p.40464-40475, 2001) of the HIV-1 genome of the provirus containing the deletion of nucleotides 1511-4550, the test was performed in Example 2 Efficacy of the compounds described in . The pΔPSP plasmid contains all HIV-1 splice sites, and the relative use of these different sites is similar to that of the wild-type virus.
[0443] HeLa cells were cultured to 70-80% confluence in RPMI1640 medium (GIBCO) supplemented with fetal bovine serum on 3 cm diameter plates (NUNC). These cells were then transfected with the pΔPSP plasmid as described by JACQUENET et al. (2001).
[0444] HeLa cells transfected with pΔPSP were then treated with different concentrations (1.5 μM or 3 μM) of the compound described in Example 2 or IDC16 as a positive control. Cells transfected with pΔPSP but ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com