Traction characteristic test platform for miniature crawler mobile robot
A crawler robot and test platform technology, which is applied in the testing of machine/structural components, vehicle testing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to test soil subsidence, sliding rate and traction at the same time, so as to reduce sliding and improve movement ability , the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
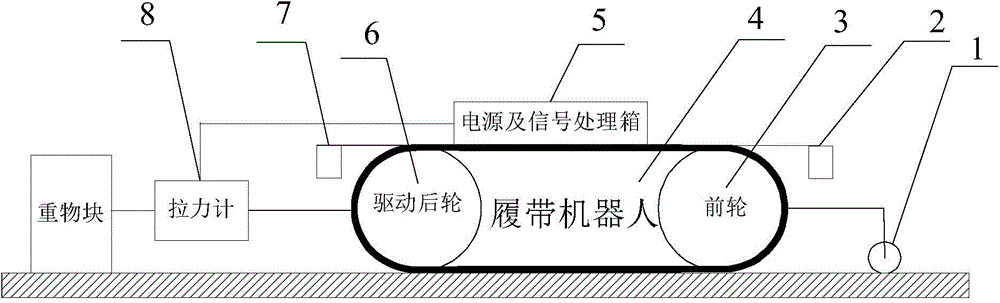
[0034] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the traction characteristic test platform of small crawler robot described in this embodiment, it comprises wheel 1 with encoder, front laser displacement sensor 2, power supply and signal processing box 5, rear laser displacement sensor 7 and pull gauge 8;
[0035] The power supply and signal processing box 5 are fixed on the car body of the crawler robot 4 under test,
[0036] The power supply and signal processing box 5 is used to supply power to the encoder in the front laser displacement sensor 2, tension gauge 8, rear laser displacement sensor 7 and wheel 1 with encoder,
[0037] The wheel 1 with the encoder is fixed on the front part of the car body of the tracked robot 4 under test through a floating connection system, and the tension gauge 8 is fixed on the rear part of the car body of the track robot 4 under test through a profile bracket.
[0038] The tension signal input end of power ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
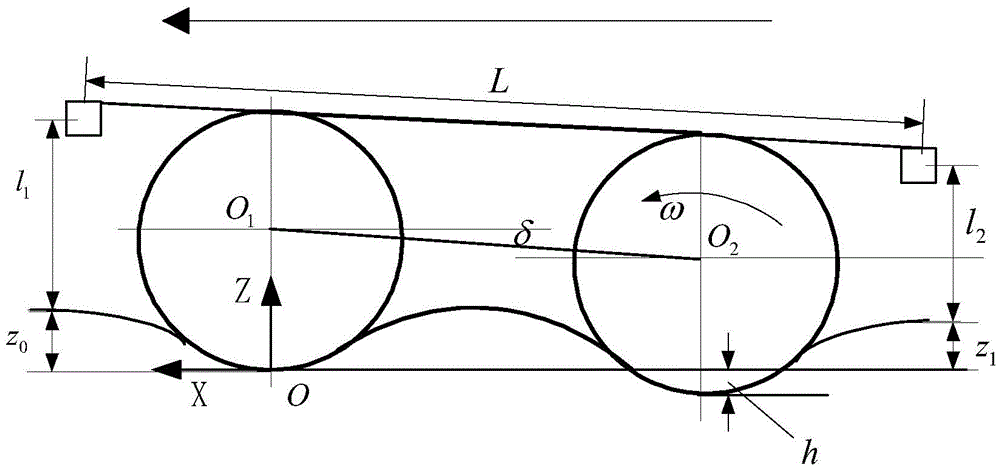
[0043] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the small crawler robot traction characteristic test platform described in the first embodiment is that the specific process of obtaining the sag of the crawler robot 4 under test by the power supply and signal processing box 5 is as follows:
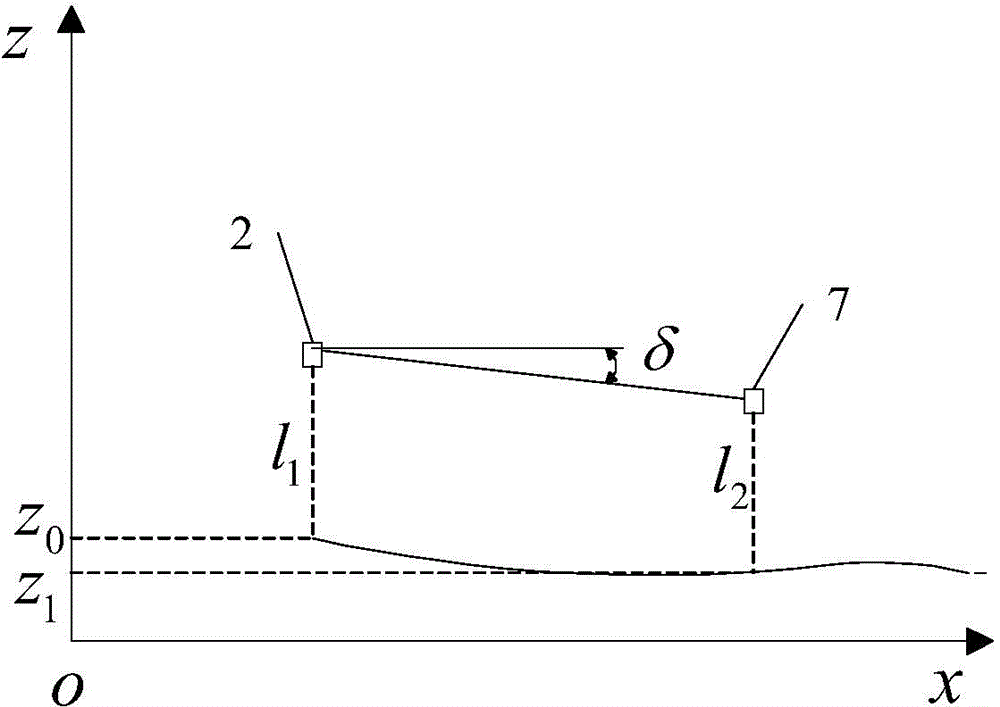
[0044] When the crawler robot 4 under test is in a static state, take the contact point between the front wheel of the crawler robot 4 and the ground as the origin, establish a coordinate system in the horizontal plane, take the forward direction of the crawler robot 4 as the X axis, and the vertical X axis direction as Z The axis establishes the plane,
[0045] In the coordinate system xoz, the distance between the laser displacement sensor 2 and the ground before the acquisition by the power supply and signal processing box 5 is l 1 mm, the distance between the rear laser displacement sensor 7 and the ground is l ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0054] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and the small crawler robot traction characteristic test platform described in specific embodiment one is that the specific process of obtaining the sliding rate of the tested crawler robot 4 by the described power supply and signal processing box 5 is:
[0055] During the movement of the crawler robot 4 under test, the angular velocity ω of the wheel 1 with the encoder is obtained through the encoder in the wheel 1 with the encoder, the power supply and the signal processing box 5 小轮 , the angular velocity ω 小轮 Substitute into the following formula to obtain the sliding rate i of the crawler robot 4 under test:
[0056]
[0057] Among them, ω 驱动轮 Indicates the angular velocity of the driving wheel of the tracked robot 4 under test, r 小轮 Indicates the radius of wheel 1 with encoder, r 驱动轮 Indicates the radius of the driving wheel of the crawler robot 4 under test.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com