Power conversion device and elevator using the power conversion device
A power conversion device and circuit technology, applied in the direction of irreversible DC power input conversion to AC power output, electrical components, AC motor control, etc., can solve the problems of promoting current imbalance and shortening the life of semiconductor switching elements, etc., to achieve Suppresses the effect of lifespan shortening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
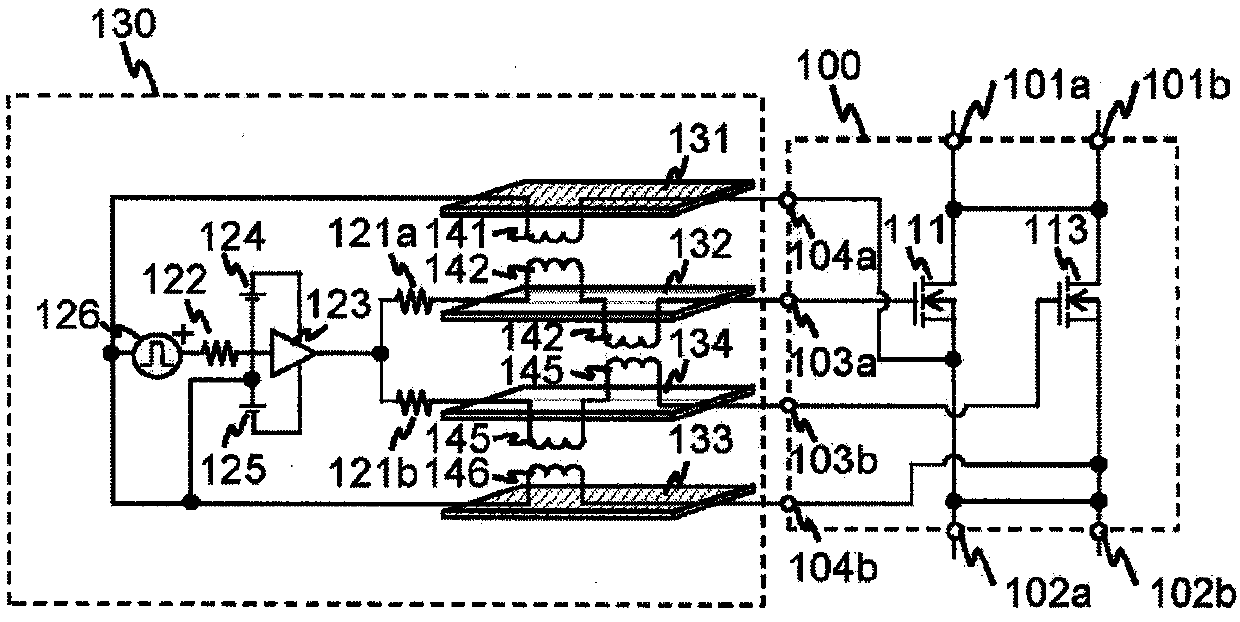
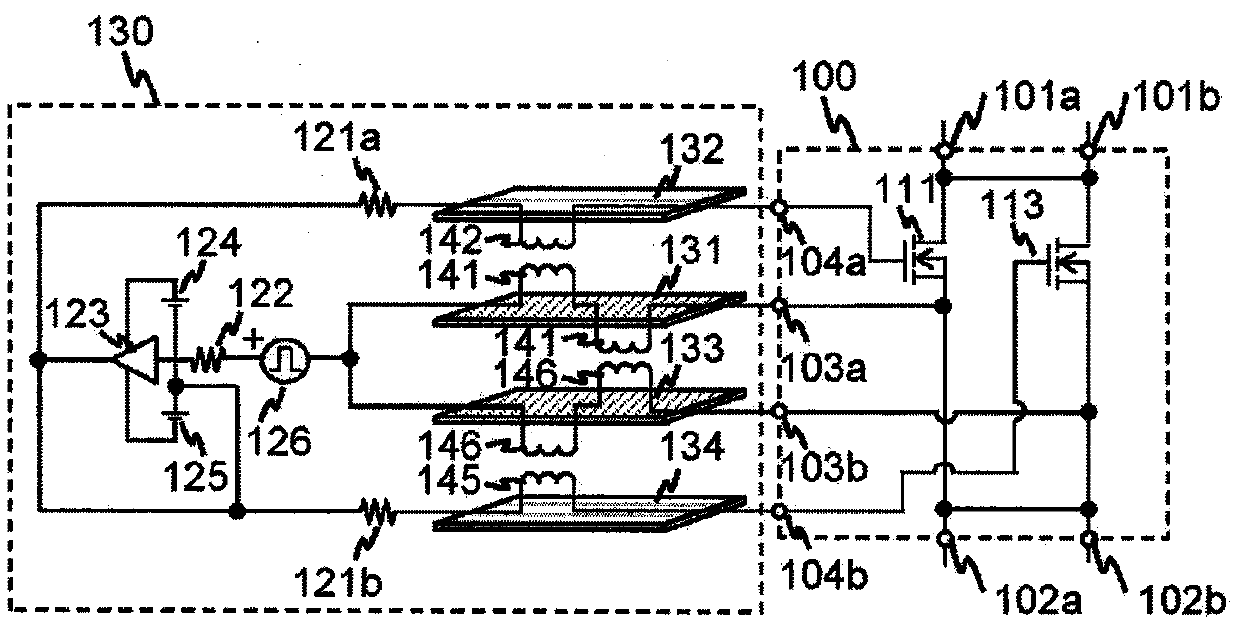
[0036] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the parallel circuit and the driving circuit of the first embodiment of the present invention. figure 1 the basic structure of Figure 13 as well as Figure 14 same, but in Figure 13 as well as Figure 14 IGBT is taken as an example as a semiconductor switching element in the description. In contrast, in figure 1 An example using a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is shown in . Hereafter, description will be made taking MOSFET as an example as a semiconductor switching element. For example, MOSFETs using silicon carbide (SiC) devices that can increase switching speed can be used. In addition, in the case of a MOSFET, since it has a built-in diode structure between the drain and the source, it is possible to omit an external anti-parallel connection diode necessary when using an IGBT, thereby omitting an external anti-parallel diode . exist figure 1 Here, only the semiconductor switching elements 1...
Embodiment 21
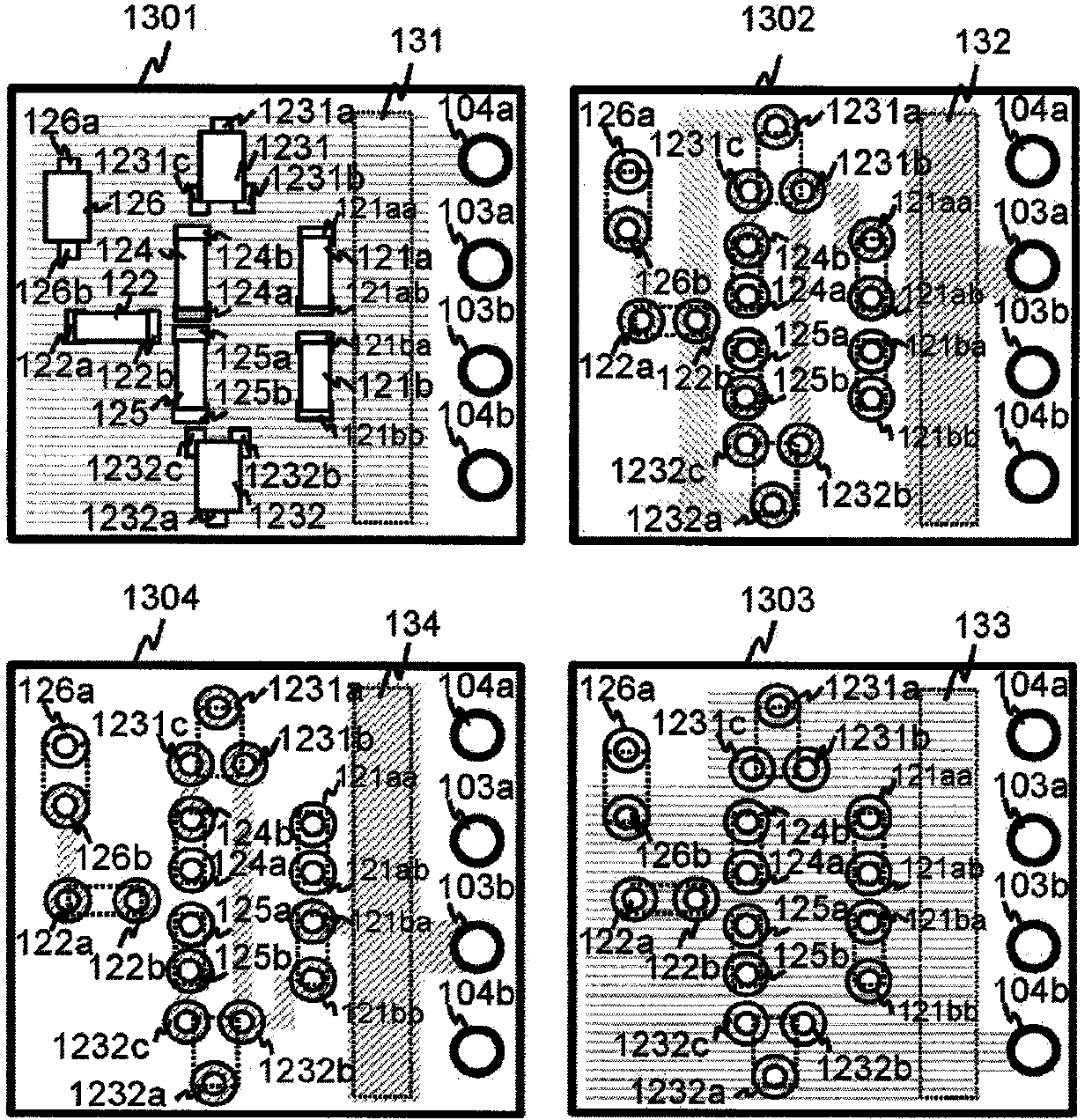
[0075] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram of the parallel circuit and the driving circuit of the second embodiment of the present invention. The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that the sensing source layers and gate layers are alternately arranged. Specifically, in the multilayer substrate, the sensing source layer 1301 , the gate layer 1302 , the sensing source layer 1303 , and the gate layer 1304 are arranged in sequence.
[0076] In the second embodiment, although the interlayer distance between the sensing source layer 1301 and the sensing source layer 1303 is shorter than that of the first embodiment, since the gate layer 1302 is sandwiched between the sensing source layer 1301 and the sensing source layer 1303 to maintain an interlayer distance, so although the effect is smaller than that of the first embodiment, the same effect can be obtained.
Embodiment 31
[0078] Figure 10 It is a schematic diagram of the parallel circuit and the driving circuit of the third embodiment of the present invention. In the third embodiment, the difference from the second embodiment is that the number of parallel circuits 100 connected in parallel is three.
[0079] To this end, a semiconductor switching element 115 connected in parallel to the semiconductor switching elements 111 and 113 is added. 101c, 102c, 103c, and 104c are drain terminals connected to the drain, source, gate, and source of the semiconductor switching element 115, respectively. terminal, source terminal, gate terminal, sense source terminal.
[0080] In addition, the driving circuit 130 has a multilayer substrate having 6 layers, in addition to the sensing source layer and the gate layer of the semiconductor switching elements 111 and 113, and also has a sensing source layer 1305, which is a conductive layer with the same potential as the source (sensing source) of the semicon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com