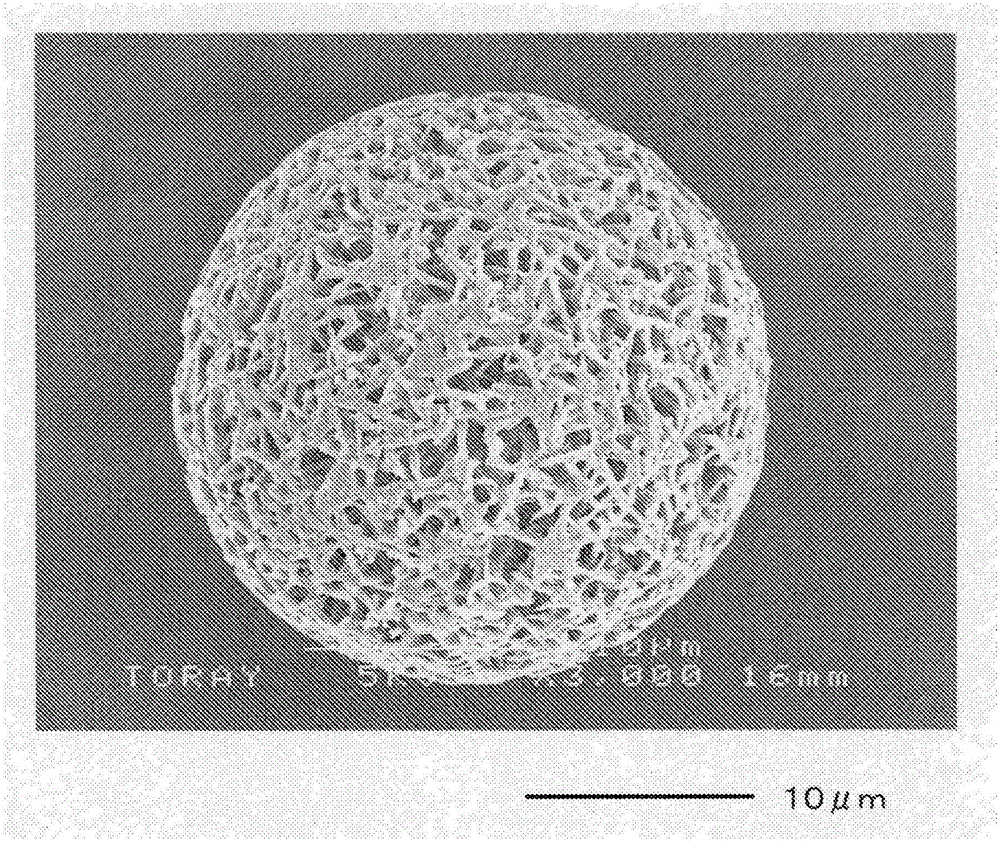
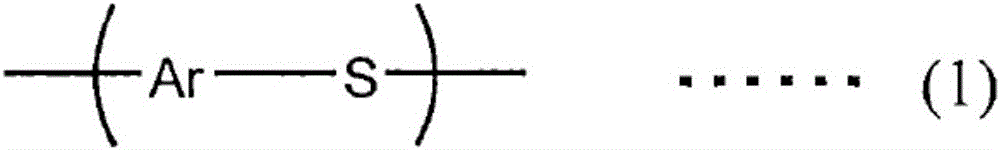
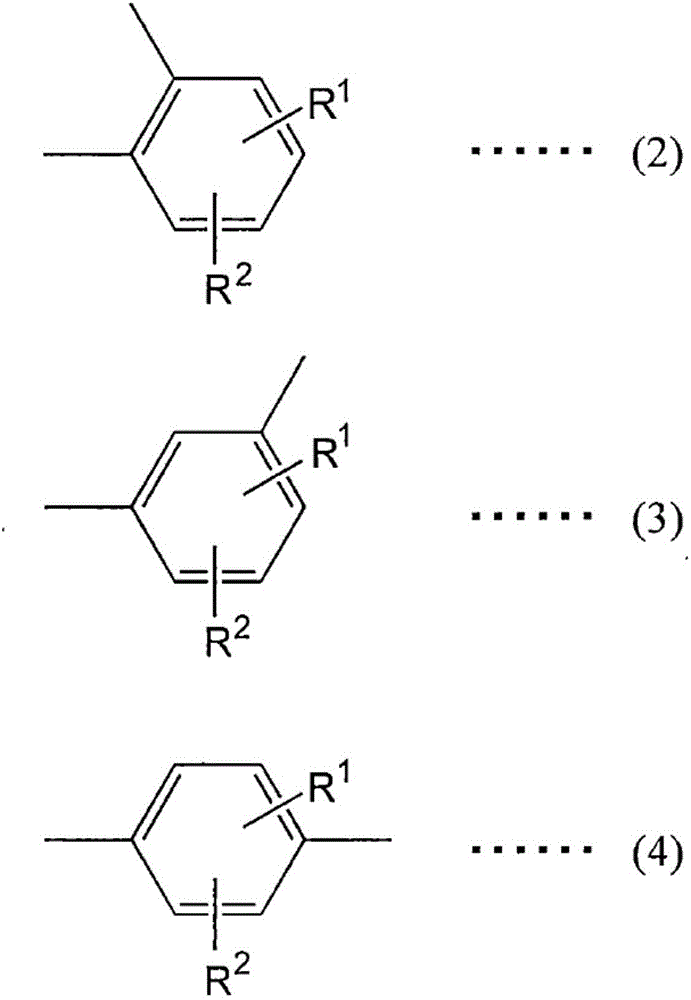
Polyphenylene sulfide microparticles
A technology of polyphenylene sulfide and polyphenylene sulfide resin, applied in the field of porous polyphenylene sulfide particles, can solve the problems of high demand and difficulty, and achieve the effect of promoting fusion and inhibiting specific reflection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0125] Hereinafter, although this invention is demonstrated based on an Example, this invention is not limited to this.
[0126] (Determination of oil absorption of linseed oil)
[0127] The oil absorption of linseed oil was measured according to the method described in Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) K5101-13-1:2004.
[0128] (Measurement of number average particle diameter)
[0129]The particle size of the porous PPS fine particles in the present invention is a number average particle size. Using a scanning electron microscope (Scanning Electron Microscope JSM-6301NF manufactured by JEOL Ltd.), the PPS microparticles were observed at 100 to 500 magnifications, and the diameter (particle diameter) of 100 PPS microparticles was measured. Next, the number average particle diameter was calculated by obtaining the arithmetic mean of the particle diameters of 100 particles according to the following formula. In addition, when the particles are not perfectly circular on the ...
reference example 1
[0179] [Reference Example 1] Modulation of p-PPS
[0180] (Dehydration process)
[0181] In a 70-liter autoclave with a stirrer and a bottom plug valve, add 47.5% sodium hydrosulfide 8.3kg, 96% sodium hydroxide 2.9kg, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone 11.5kg, sodium acetate 1.9kg and ion exchange 5.5kg of water, slowly heated to 245°C over about 3 hours while blowing nitrogen gas under normal pressure, distilled 9.8kg of water and 0.3kg of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, and then cooled the reaction vessel to 200°C . The amount of water remaining in the system including the water consumed by the hydrolysis of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone was 1.1 mol per mol of the added alkali metal sulfide. In addition, the scattering amount of hydrogen sulfide was 0.02 mol per 1 mol of the added alkali metal sulfide.
[0182] (polymerization process)
[0183] Next, 10.4 kg of p-dichlorobenzene and 9.4 kg of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone were added, the reaction vessel was sealed under nitrogen, and the temperature was ...
reference example 2
[0186] [Reference Example 2] Preparation of p- / m-PPS Copolymer
[0187] (Dehydration process)
[0188] In a 1-liter autoclave with a stirrer, add 118g of 47% sodium hydrosulfide, 42.4g of 96% sodium hydroxide, 163g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, 32.0g of sodium acetate and 150g of ion-exchanged water. Next, it was heated slowly to 225°C over about 3 hours while blowing nitrogen gas, 210 g of water and 4 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone were distilled off, and the reaction vessel was cooled to 150°C. The scattering amount of hydrogen sulfide was 1.8 mol%.
[0189] (polymerization process)
[0190] Next, 125 g of p-dichlorobenzene, 22.1 g of m-dichlorobenzene, and 131 g of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone were added, the reaction vessel was sealed under nitrogen, and the temperature was raised at a rate of 0.8° C. / min while stirring at 400 rpm. to 227°C, then raised to 270°C / min at a rate of 0.6°C / min, and kept at 270°C for 170 minutes. During this time, 14.4 g of water was added over 10 minutes...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Number average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com