A tea-flavor-producing Cystis xievasan and its application in liquor Daqu
A technology of loose capsule bacteria and fragrance type, which is applied in the biological field and can solve problems such as unapplied research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Embodiment 1 strain identification
[0017] (1) Morphological identification
[0018] The strain CICC 41587 (M9) was inoculated on the yeast extract medium (CYA medium), cultured at 25°C for 7 days, and the colonies were photographed, microscopic observation and scanning electron microscope observation of the bacteria. For detailed morphological characteristics, see figure 1 .
[0019] (2) Molecular biological identification
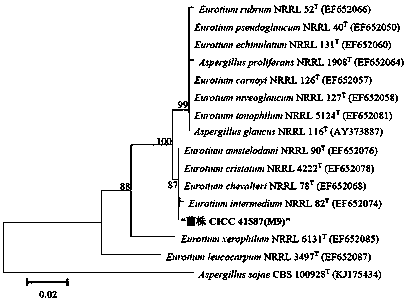
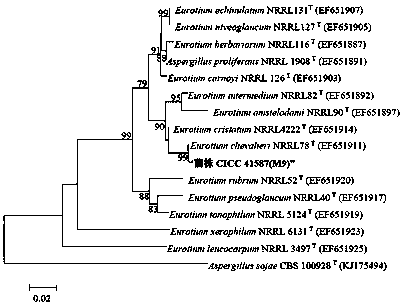
[0020] Strain CICC 41587 (M9) was accurately identified as a species through the phylogenetic analysis of ITS rDNA and β-tubulin gene sequences. For details on the phylogenetic tree, see Figure 2-Figure 3 .
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2 Determination of Flavor Substances in Fermented Broth of Cystis schevascens CICC 41587 (M9)
[0022] The 41587 (M9) serovar CICC 41587 (M9) was cultured in 4% glucose MEB medium at 28 ℃ for 30 days, and the olfactory senses of the fermentation broth were tea and green grass. The headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method was used to analyze the volatile substances in the fermentation broth of the strains, and the main aroma components were evaluated by combining the aroma threshold and relative odor activity value (ROAV).
[0023] A total of 42 volatile substances were detected (see Table 1 below), including 33 aroma substances. The evaluation of characteristic aroma components adopts relative odor activity value method (Relative odor activity value, ROAV) to evaluate the contribution of each volatile component to the overall aroma of the sample, namely: ROVAi≈100×Ci / Cmax×Tmax / Ti (1); where : Ci, Ti—the relative percenta...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3 Preparation of the powder of Cystis sievas CICC 41587 (M9)
[0029] (1) Wet bran and distilled water at a ratio of 1:1, weigh 20 g into a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask, a total of 15 bottles (No. 1-15), sterilize at 121 °C for 40 minutes, overnight, under the same conditions Sterilize again.
[0030] (2) After the bran medium was cooled, inoculate 5 mL of the fermentation broth of the M9 strain cultured at 28°C for 7 days, and cultivated at 28°C for 14 days, and observe whether there was any bacterial contamination during the culture period.
[0031] (3) After culturing for 10 days, randomly select bottle No. 3 and bottle No. 11 of the bran culture, weigh 2.5 g respectively, mix and dissolve in 50 mL normal saline, after mixing, draw 1 mL and spread it on a 20 cm diameter cell. On PDA plates (two plates in total), cultured at 28°C for 4 days, no growth of bacteria was observed;
[0032] (4) After culturing for 14 days, use a sterile long-handled spoon to buckle th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com