Gate driving circuit
A gate drive circuit, gate driver technology, applied in electrical components, electronic switches, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve problems such as current unbalance, and achieve the ideal of suppressing current unbalance and suppressing fluctuations in on-off loss. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
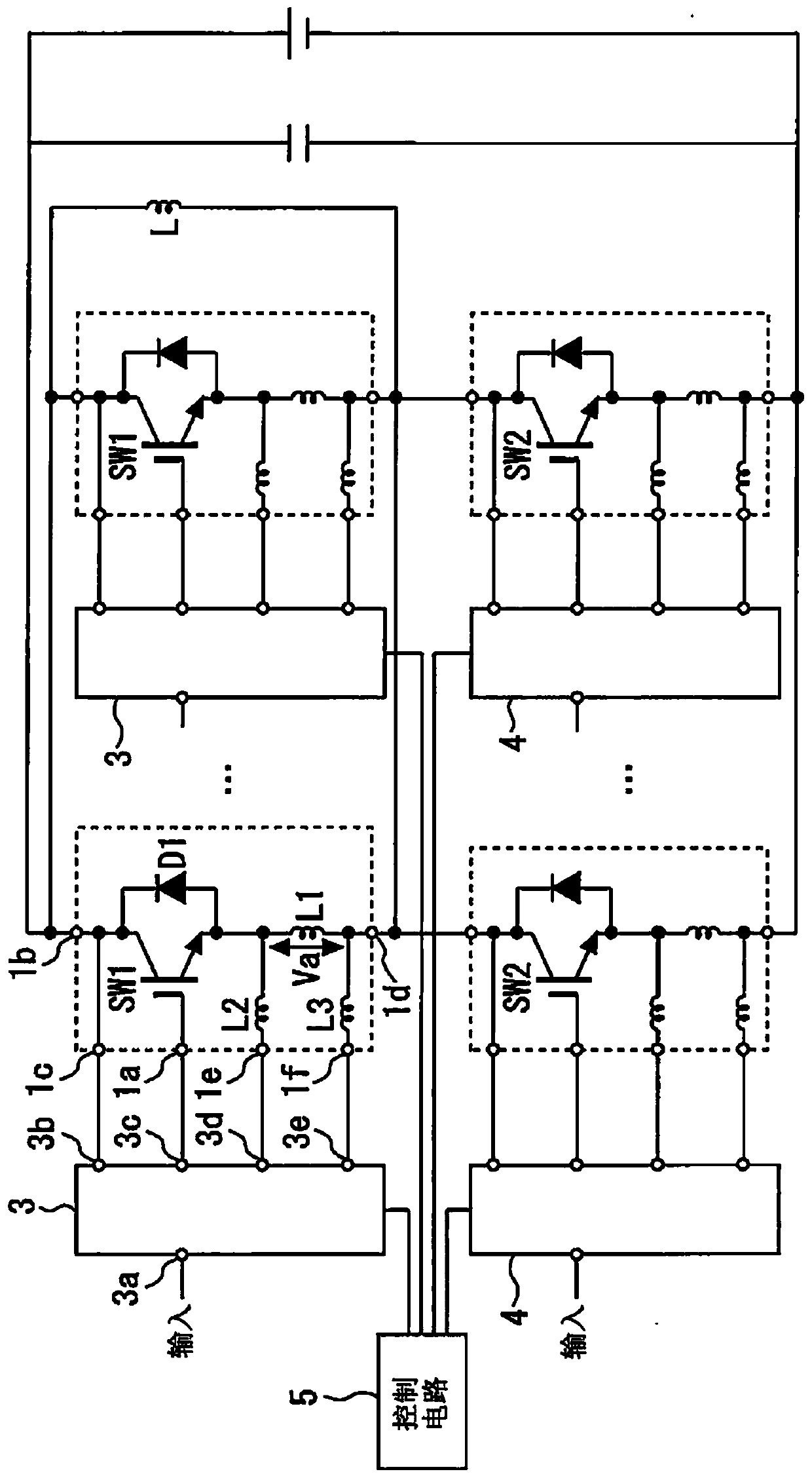
[0017] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the gate drive circuit concerning Embodiment 1 of this invention. The semiconductor switching elements SW1 and SW2 used for power conversion or control are connected in series with each other. A plurality of element pairs of the semiconductor switching elements SW1 and SW2 are connected in parallel. The plurality of gate driver units 3 and 4 respectively drive the plurality of semiconductor switching elements SW1 and SW2 connected in parallel. The inductance L is the load inductance when the semiconductor switching elements SW1 and SW2 are turned on and off. The control circuit 5 controls the plurality of gate driver units 3 , 4 .
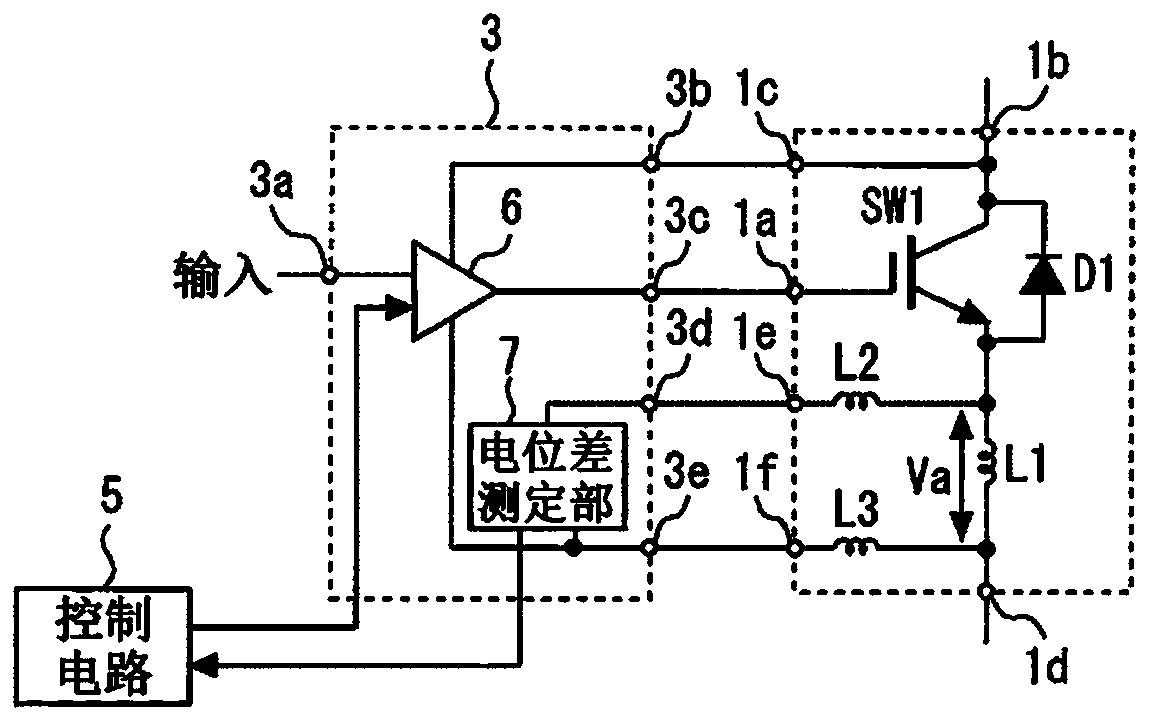
[0018] A diode D1 is connected in antiparallel to the semiconductor switching element SW1. A gate electrode 1a is connected to the gate of the semiconductor switching element SW1. A collector electrode (electrode) 1b and a collector auxiliary electrode 1c are connected to a collector of the semicondu...
Embodiment approach 2
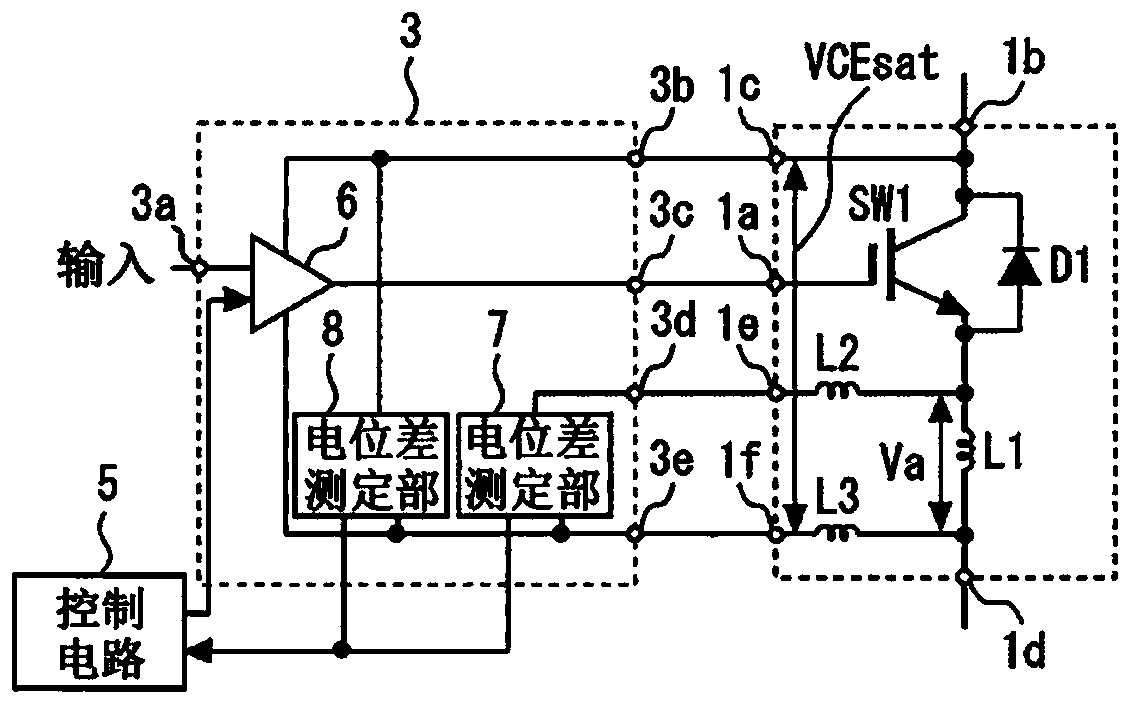
[0027] image 3 It is an enlarged view of a part of the gate drive circuit according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The gate driver unit 3 further includes a collector-emitter potential difference measuring unit 8 that connects the collector auxiliary electrode 1c and the emitter auxiliary electrode 1f of the corresponding semiconductor switching element SW1 to each other. The voltage between the collector and the emitter, VCEsat, is measured in units of one cycle of the output frequency. The same applies to the structure of the gate driver unit 4 .
[0028] The control circuit 5 controls the voltages VCEsat supplied from the gate drivers 6 of the respective gate driver units 3 and 4 so that the collector-emitter voltages VCEsat of the plurality of semiconductor switching elements SW1 and SW2 in the steady state are the same as each other. The gate voltage VGE is adjusted. Thereby, it is possible to suppress fluctuations in loss during steady-state ON.
[0029] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com