Trench silicon carbide mosfet device with low power consumption and high reliability
A reliable, trench-type technology, applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as weak short-circuit capability, high switching loss, and large gate-to-drain capacitance, so as to reduce saturation current, reduce switching loss, and improve The effect of short circuit capability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
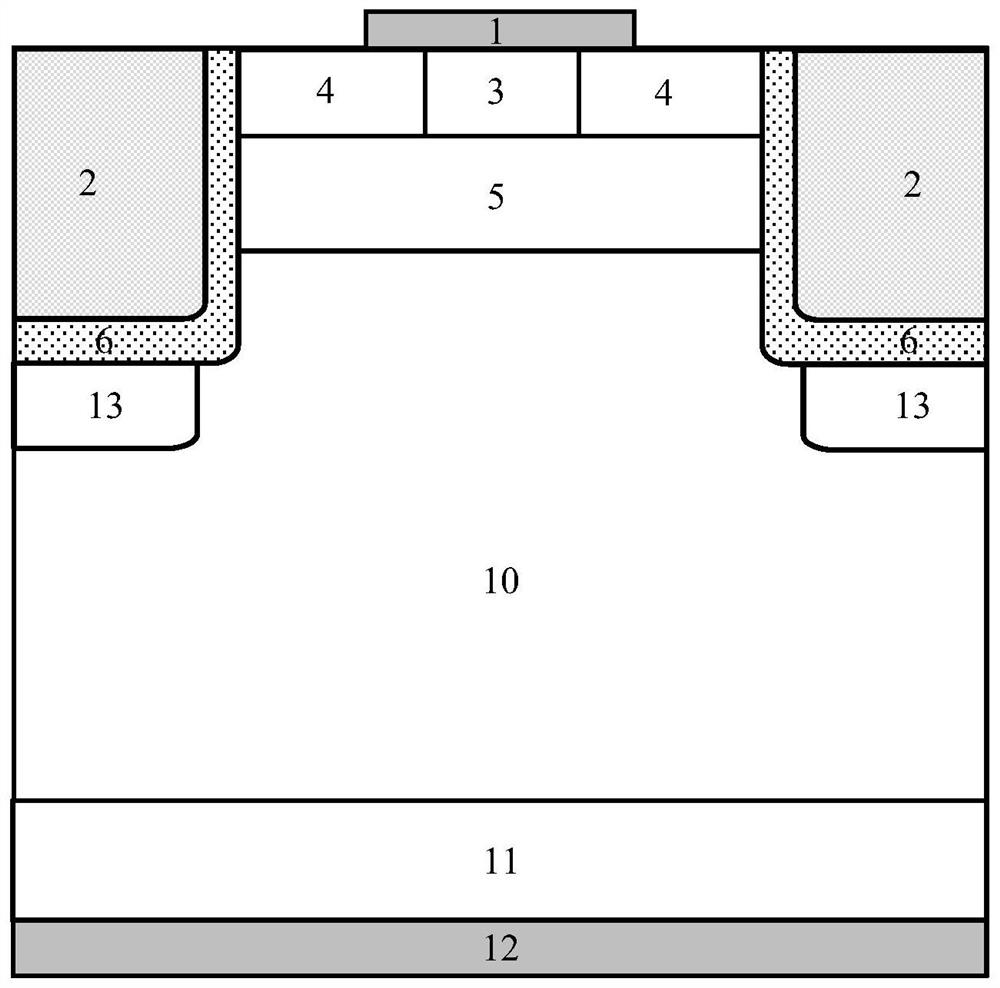
[0026] Such as figure 2 As shown, a trench type silicon carbide MOSFET device with low power consumption and high reliability in this embodiment includes: an N-type substrate 11, an N-type epitaxial layer 10 located above the N-type substrate 11, and an N-type epitaxial layer 10 located on the N-type epitaxial layer. The second P-body region 9 above the layer 10, the second P+ contact region 7 and the second N+ contact region 8 located inside the second P-body region 9, the second P+ contact region 7 and the second N+ contact region 8 The upper source electrode 1, the gate dielectric 6 above the second N+ contact region 8 and the groove gate 2 inside the gate dielectric 6, the first P-body region 5 between the gate dielectric 6, and the first P-body region 5 above the two first N+ contact regions 4, the first P+ contact region 3 between the two first N+ contact regions 4, the source electrode 1 above the first P+ contact region 3 and the first N+ contact region 4, The drain ...
Embodiment 2
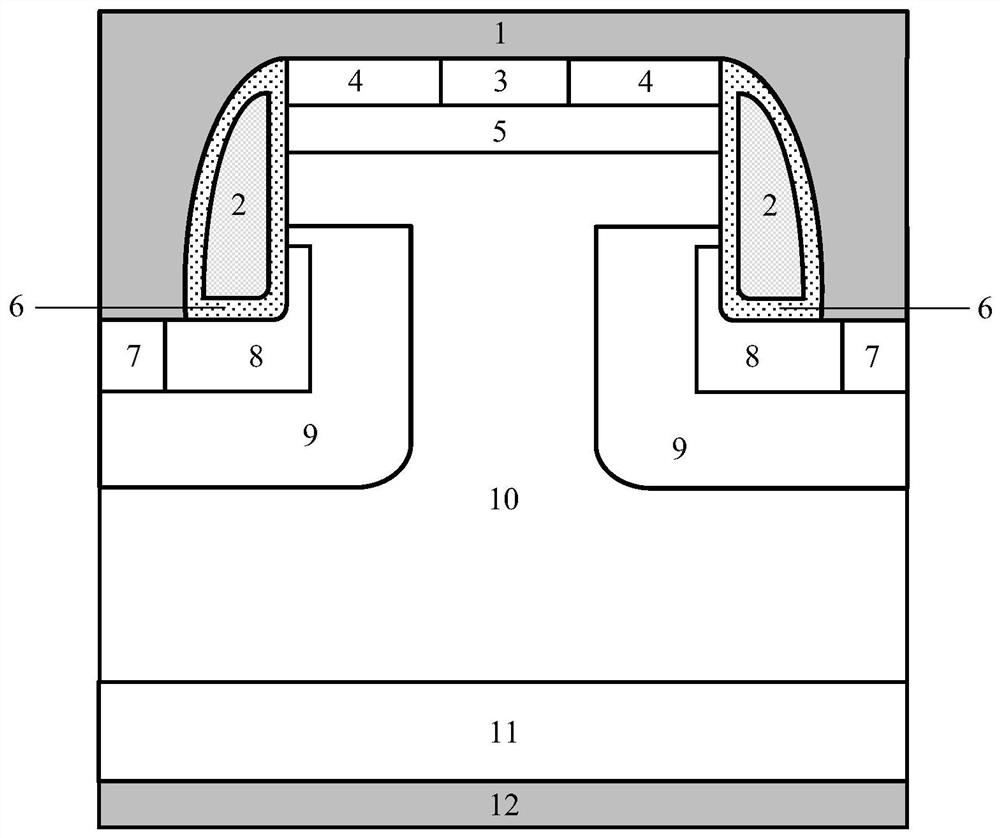
[0030] Such as image 3As shown, the difference between the device structure of this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the trench gate 2 and the gate dielectric 6 are in an inverted L shape, and the inverted L shape includes a horizontal section and a vertical section connected below the horizontal section. An N-type epitaxial layer 10 is provided between a P-body region 5 and gate dielectrics 6 on both sides, and the horizontal section of the trench gate 2 and gate dielectric 6 is located in the first N+ contact region 4, the first P-body region 5 and the N Above the N-type epitaxial layer 10 , a gate dielectric 6 is provided between the trench gate 2 and the first N+ contact region 4 , the first P-body region 5 , and the N-type epitaxial layer 10 .
Embodiment 3
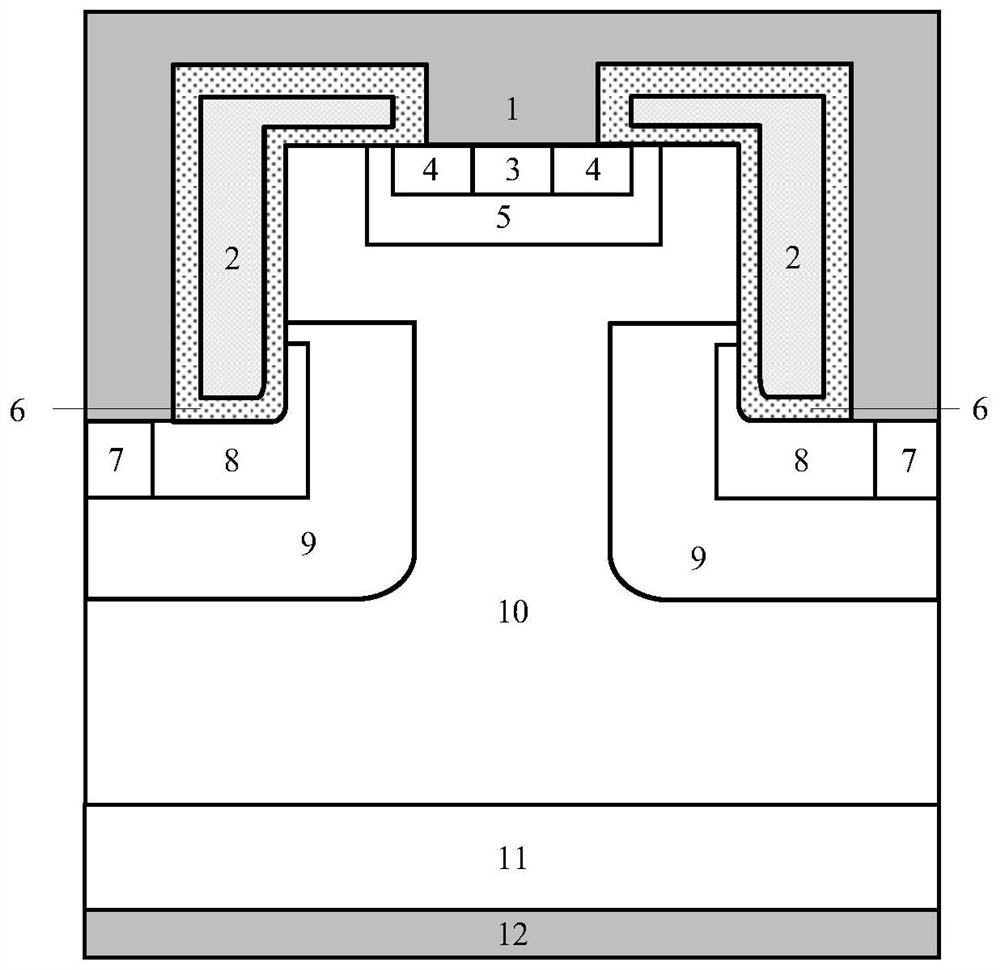
[0032] Such as Figure 4 As shown, two first P-body regions 5 are arranged between gate dielectrics 6, two first P+ contact regions 3 are arranged between two first N+ contact regions 4, and two first P+ contact regions 3 are arranged An N-type epitaxial layer 10 is provided between the first P-body regions 5 and between the two first P-body regions 5 , and the N-type epitaxial layer 10 forms a Schottky contact with the source electrode 1 . The advantage of doing this is that the performance of the third quadrant of the device is improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com