Copper residue-slag based cementing material,preparation method and applications thereof
A technology for slag and copper slag, applied in the field of inorganic cementitious material preparation, can solve the problems of occupying land, environmental pollution, low utilization rate of copper slag, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The preparation method of above-mentioned copper slag-slag-based cementitious material comprises:
[0037] Step 1: After mixing and stirring copper slag powder, slag powder, quicklime, modification aid and light absorbing agent, add alkali activator and deionized water to form the first slurry, wherein the modification aid includes carbonization At least one of silicon, boron nitride, aluminum oxide or zinc oxide, the light absorbing agent includes chromium oxide, cadmium selenide, ferric oxide, titanium dioxide, lead sulfide, cobalt oxide and cadmium sulfide;
[0038] Step 2: Continue to add sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, Portland cement and deionized water to the first slurry, stir evenly and let it stand for 15-25 minutes for foaming treatment to obtain the second slurry;
[0039] Step 3: After adding heat-absorbing materials and fibers to the second slurry, continue stirring to obtain a third slurry, pour the third slurry into a mold and vibrate to form a rou...
Embodiment 1
[0055] A copper slag-slag-based cementitious material and a preparation method thereof, the cementitious material is composed of the following components in parts by weight, and the cementitious material comprises:
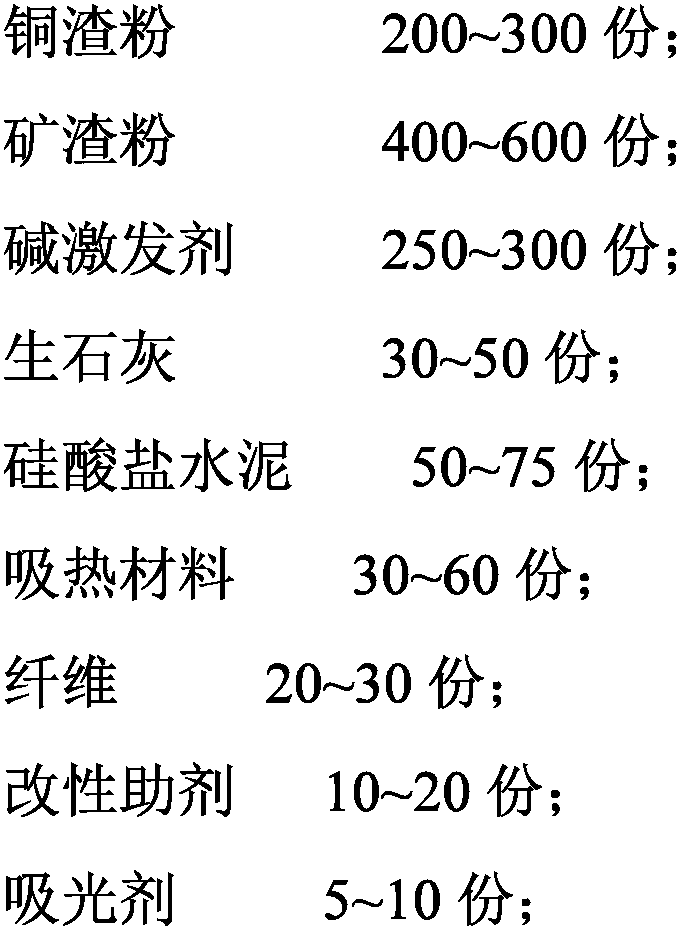
[0056] 200 parts of copper slag powder, 400 parts of slag powder, 250 parts of alkali activator (including 100 parts of potassium hydroxide and 150 parts of calcium hydroxide), 30 parts of quicklime, 50 parts of Portland cement, 30 parts of heat-absorbing material (including graphite 10 parts of alkene and 15 parts of graphite), 20 parts of fiber (including 10 parts of fluororubber fiber and 10 parts of polypropylene fiber); 10 parts of modification additives (including 5 parts of silicon carbide and 5 parts of boron nitride) and 5 parts of light absorbing agent share.
[0057] The preparation method of the copper slag-slag-based cementitious material in embodiment one is as follows:
[0058] Step 1: After mixing and stirring 200 parts of copper slag powder, 400 ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A copper slag-slag-based cementitious material and a preparation method thereof, the cementitious material is composed of the following components in parts by weight, and the cementitious material comprises:
[0069] 300 parts of copper slag powder, 600 parts of slag powder, 350 parts of alkali activator (including 150 parts of sodium hydroxide and 200 parts of calcium hydroxide), 50 parts of quicklime, 75 parts of Portland cement, 60 parts of heat-absorbing material (including graphite 30 parts of alkene and 30 parts of graphite), 30 parts of fiber (including 15 parts of fluororubber fiber and 15 parts of polypropylene fiber); 20 parts of modification additives (including 10 parts of silicon carbide and 10 parts of boron nitride) and 10 parts of light absorbing agent share.
[0070] The preparation method of the copper slag-slag-based cementitious material in embodiment two is as follows:
[0071] Step 1: After mixing and stirring 300 parts of copper slag powder, 600 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com