A bacterial strain capable of producing DHA by high-temperature fermentation and its application
A technology of high-temperature fermentation and bacterial strains, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, microbial-based methods, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of limited application range of DHA oil commercialization, high fermentation production cost, and reduced DHA production, and achieves cell growth. The effect of shortening the fermentation period and increasing the growth rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] This example specifically illustrates the screening method for the strains of the present invention.
[0023] (1) Activating the original Schizochytrium strain at 30° C.; activating the original strain for 3 generations, each generation time is 24-48 hours.
[0024] (2) Insert the activated seeds into the seed medium with an inoculation amount of 1% (v / v), and the culture temperature is 32°C, 34°C, 34.5°C and 35°C, and the temperature can be raised according to the growth of the strain For acclimatization, for example, when the strain grows well at 32°C, the acclimatization temperature of the next generation can be set to 34°C, and so on, the rotation speed is 170rpm, and the shaking table is cultivated until the logarithmic growth phase of the strain is transferred to the next generation;
[0025] The composition of the seed medium is: glucose 30-60g / L, yeast powder 3-5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 4~6g / L, Na 2 SO 4 3~5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 4~6g / L,KH 2 PO 4 2~4g / L.
...
Embodiment 2
[0029] This example specifically illustrates the method for producing DHA by fermentation of Schizochytrium in the present invention.
[0030] (1) Seed cultivation
[0031] The composition of the seed medium is: glucose 30-60g / L, yeast powder 3-5g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 4~6g / L, Na 2 SO 4 3~5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 4~6g / L,KH 2 PO 4 2~4g / L, KCl 1~2g / L, sodium glutamate 18~20g / L.
[0032] Insert the bacteria into the seed medium with 1% inoculum, cultivate for 24-48 hours, and the rotation speed is 170 rpm to complete the first-generation activation, and use the same method to activate the second-generation seeds to activate For three generations, the seeds were obtained.
[0033] (2) Fermentation culture
[0034] The components of the fermentation medium are: glucose 80-100g / L, yeast powder 4-6g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 3~5g / L, Na 2 SO 4 6~9g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2~4g / L,KH 2 PO 4 2~4g / L, KCl 0.1~0.5g / L, NaCl 5~8g / L, sodium glutamate 18~20g / L.
[0035] The seed solution i...
Embodiment 3
[0037] This embodiment specifically illustrates the comparison of the shake flask fermentation performance of domesticated bacterial strains and original bacterial strains
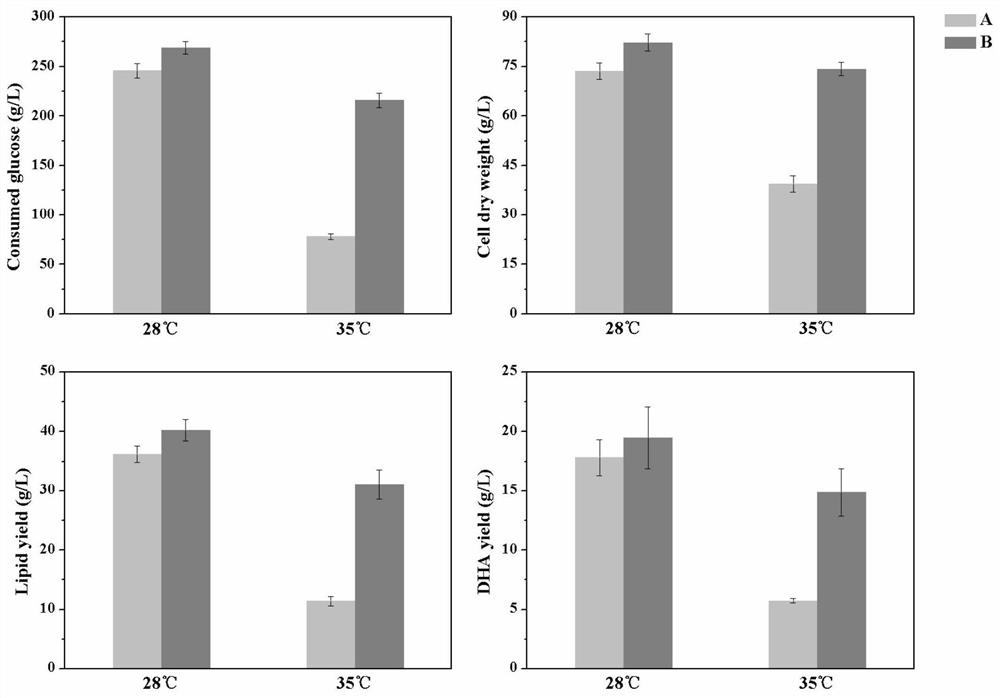
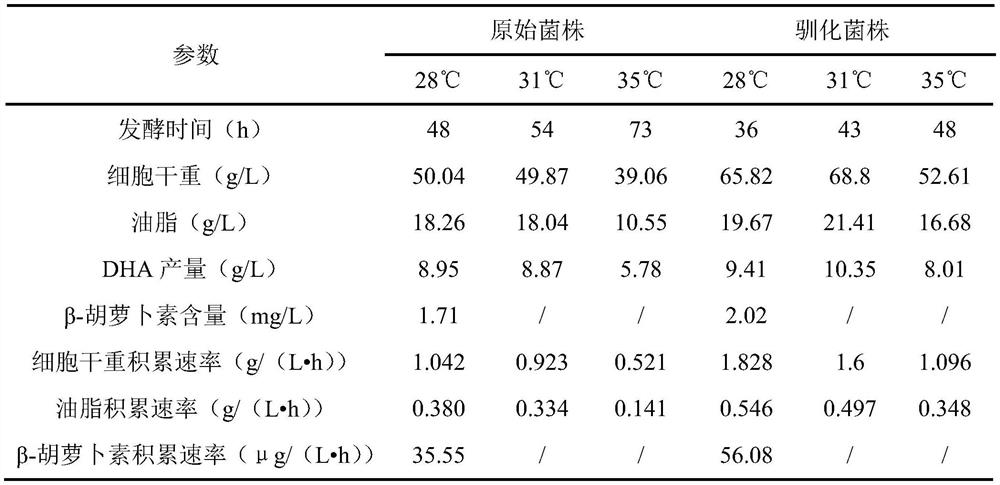
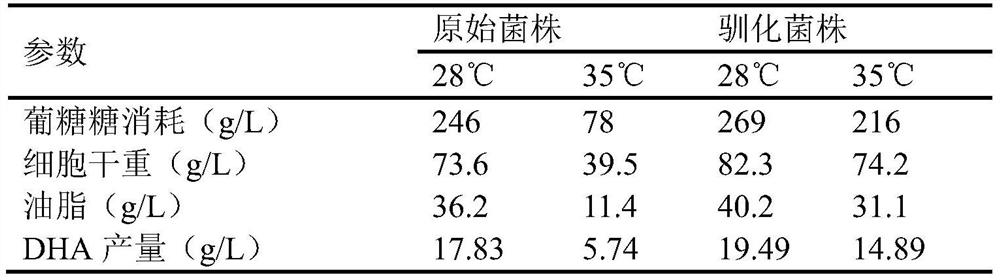
[0038]Select the strains with excellent growth at 35°C, adopt the fermentation method of Example 2, and ferment at 28°C, 31°C and 35°C respectively, to compare the fermentation performance of different domesticated strains and original strains at normal temperatures ( DHA production capacity). The fermentation time was recorded, and the dry cell weight, fatty acid production and DHA content were measured after the fermentation was completed. The comparison of fermentation parameters between different domesticated strains and original strains is shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1 Comparison of fermentation parameters between the original strain and the domesticated strain at different temperatures
[0040]
[0041] The data in the table shows that under certain initial sugar conditions, the fermentatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com