Sheath wave barrier for magnetic resonance (MR) applications
A magnetic resonance and barrier technology, which is applied in the directions of using nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum for measurement, using nuclear magnetic resonance image system for measurement, magnetic resonance measurement, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete symmetry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
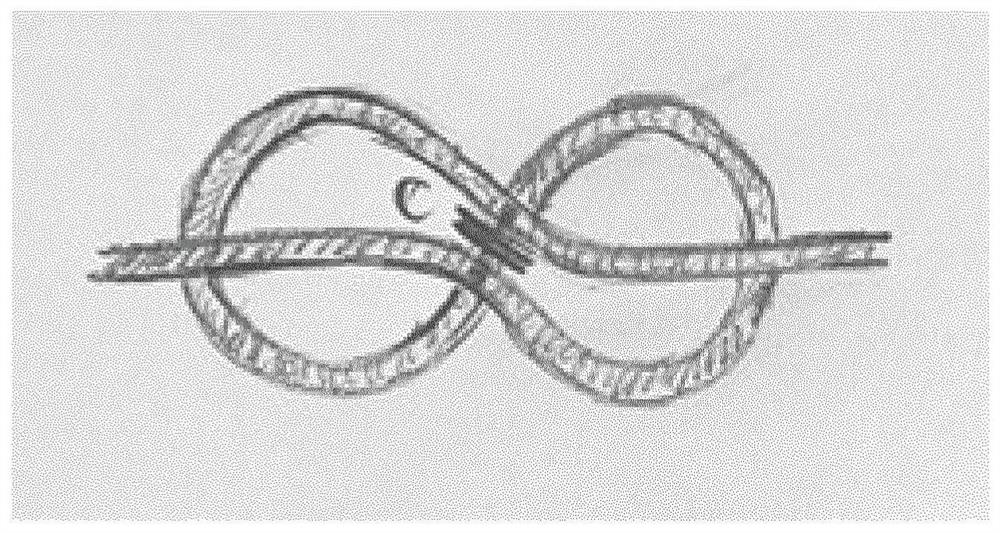
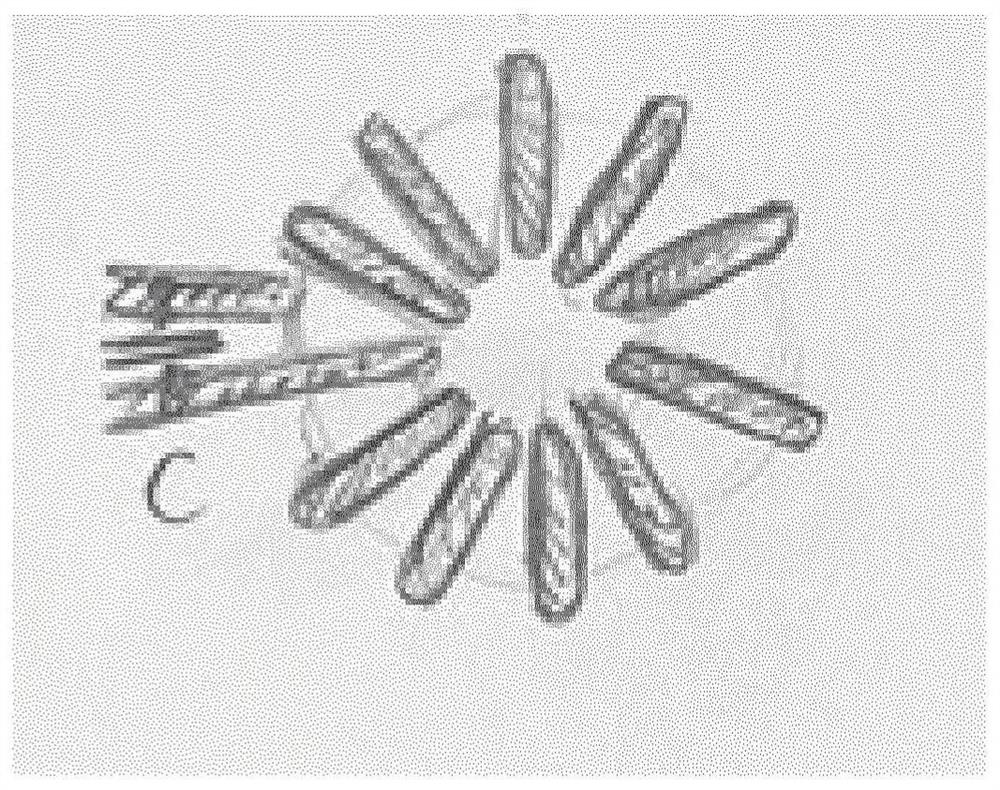
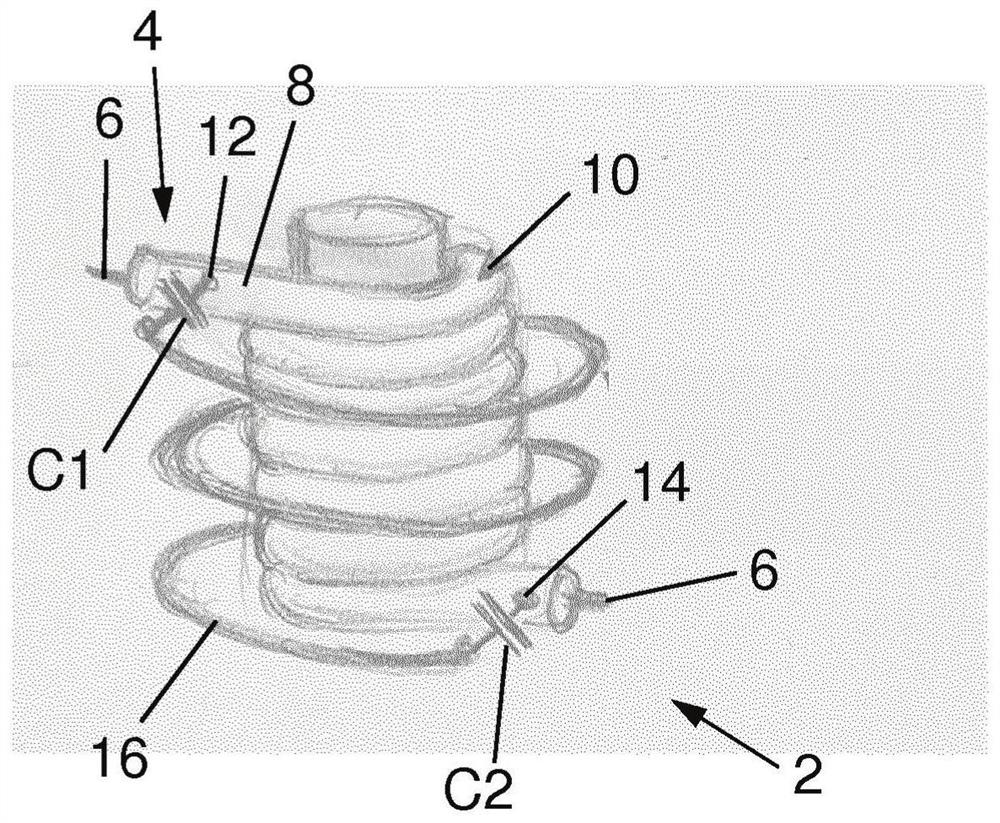
[0068] Figure 2a Shown for use in magnetic resonance (MR) imaging or spectroscopy setups with a predetermined suppression frequency (ω 0 ) A sheath wave barrier 2 that suppresses the electromagnetic RF coupling phenomenon of the cable 4 . The cable 4 is a shielded cable having an inner conductor 6 and a surrounding conductive cable sheath 8 . The sheath wave barrier 2 comprises a section of shielded cable, a primary inductor 10 formed by the shielded cable 4 between a first cable location 12 and a second cable location 14, and a secondary inductor 16 formed by a conductor. In the example shown, the secondary inductor 16 is made of a simple cable arranged concentrically around the primary inductor 10 and is electrically connected to the cable sheath 8 at said first and second cable connections 12 and 14 . Primary inductor 10 and secondary inductor 16 are configured as concentric and substantially coaxial solenoids. To be configured in a compensating manner, the two solenoid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com