Method for treating waste lithium battery
A technology for waste lithium batteries and batteries, applied in the field of environmental protection, can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving split effect, and achieve the effect of reducing difficulty and reducing emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0047] Example 1
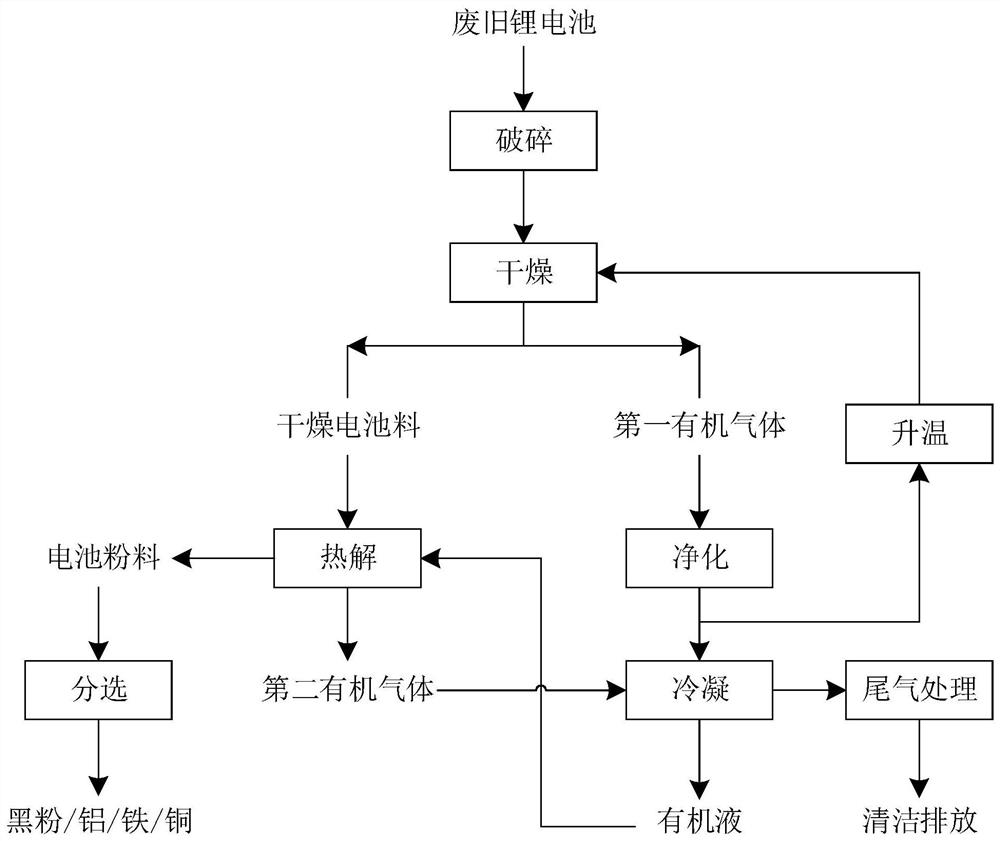
[0048] This embodiment provides a method for processing waste lithium batteries, and the process flow diagram of the method is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the waste lithium battery treated in this embodiment is a module battery in which the electrolyte contains dimethyl carbonate and ethylene carbonate, and the separator and the binder contain polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinylidene fluoride and other organic substances. The method includes the following steps:
[0049] (1) Dry the crushed waste lithium battery, and the operation interval between crushing and drying is 20s to obtain the dry battery material and the first organic gas; the drying method is hot air drying, and the drying method is hot air drying at an oxygen concentration of 0.08vol%. The drying temperature is 160 ℃, and the end point of drying is to make the electrolyte removal rate in the waste lithium battery 95%;
[0050] (2) The dry battery material obtained in the pyrolysis step ...
Example Embodiment
[0056] Example 2
[0057] This embodiment provides a method for processing waste lithium batteries, and the process flow diagram of the method is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the waste lithium battery treated in this embodiment is a single battery in which the electrolyte contains diethyl carbonate and ethylene carbonate, and the separator and the binder contain organic substances such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinylidene fluoride. The method includes the following steps:
[0058] (1) Dry the crushed waste lithium battery, and the operation interval between crushing and drying is 40s to obtain dry battery material and the first organic gas; the drying method is hot air drying, and the drying method is hot air drying at an oxygen concentration of 0.01vol%. The drying temperature is 150 ℃, and the end point of drying is to make the electrolyte removal rate in the waste lithium battery 90%;
[0059] (2) The dry battery material obtained in the pyrolysis step (1)...
Example Embodiment
[0065] Example 3
[0066] This embodiment provides a method for processing waste lithium batteries, and the process flow diagram of the method is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the waste lithium battery treated in this embodiment is a waste product containing dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate and ethylene carbonate in the electrolyte, and the separator and the binder containing hydrocarbon organics. The method includes the following step:
[0067] (1) Dry the used lithium battery after crushing, and the operation interval between crushing and drying is 30s to obtain dry battery material and the first organic gas; the drying method is hot air drying, and the drying method is hot air drying at an oxygen concentration of 0.05vol%. The drying temperature is 180 ℃, and the end point of drying is to make the electrolyte removal rate in the waste lithium battery 94%;
[0068] (2) The dry battery material obtained in the pyrolysis step (1) is used to remove the diaphragm and the...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap