Treatment process for recycling of nickel-cobalt hydrometallurgical waste residues
A technology for wet smelting and treatment process, applied in the field of treatment technology for recycling nickel-cobalt wet smelting waste residue, can solve the problems of high investment cost, environmental protection risks and high content of heavy metals, and achieves reduction of environmental pollution, acid consumption and The effect of sulfur dioxide consumption and improving sulfur utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
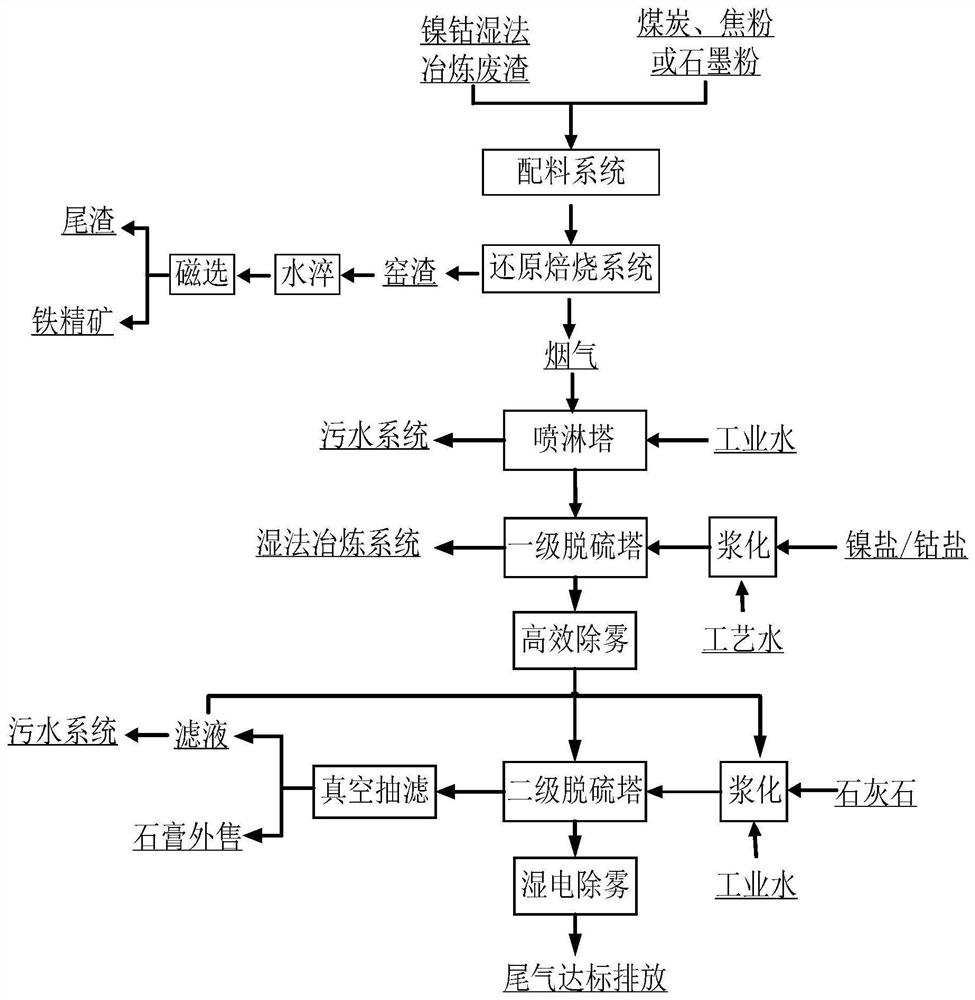
[0033] A process for recycling nickel-cobalt hydrometallurgy waste slag, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Add cobalt hydrometallurgy waste slag to additive coke powder for mixing; cobalt hydrometallurgy waste slag contains 4.62% sulfur, 27% iron, 0.19% cobalt, and 30wt% coke powder.
[0035] (2) Form a reducing atmosphere at 1200-1250°C in the high-temperature reaction zone of the additive in step (1) in the rotary kiln, so that the iron oxide in the cobalt hydrometallurgy waste residue undergoes a reduction reaction, and the reduction produces iron and four Ferric oxide; the cobalt in the cobalt wet smelting waste slag undergoes double salt decomposition and reduction reaction to form cobalt element and cobalt oxide, and after water quenching and magnetic separation to obtain iron and cobalt iron concentrate, cobalt in iron concentrate Enrichment; sulfate decomposition and reduction reactions occur, and sulfur oxides are precipitated and enter the desulfurizati...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A treatment process for recycling nickel hydrometallurgy waste slag, the specific steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) The nickel hydrometallurgy waste slag was mixed with additive coke powder; the sulfur content of the nickel hydrometallurgy waste slag was 3.98%, the iron content was 30%, the nickel content was 0.21%, and the coke powder addition amount was 35wt%.
[0041](2) The high-temperature reaction zone of the additive in step (1) in the rotary kiln forms a certain reducing atmosphere at 1150 ° C ~ 1200 ° C, so that the iron oxide in the nickel hydrometallurgy waste residue undergoes a reduction reaction, and the reduction produces iron elemental and ferroferric oxide; the nickel in the nickel hydrometallurgy waste slag undergoes double salt decomposition and reduction reaction to form nickel elemental and nickel oxide, and after water quenching and magnetic separation to obtain iron-nickel iron concentrate, nickel in iron Enrichment in the concentrate; decomposit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com