Polypeptide self-assembled nano-drug as well as preparation method and application thereof
A nano-drug and self-assembly technology, which is applied in the preparation method of peptides, nano-drugs, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of fast metabolism, short half-life of polypeptide hormones, low bioavailability, etc., to achieve improved half-life, strong hydrophobicity, Improve the effect of microenvironment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] Based on the same inventive concept, the present invention also provides a preparation method of polypeptide self-assembled nanomedicine, the preparation method comprising:
[0049] dissolving the amphiphilic molecule in the organic phase;
[0050] Under ultrasonic conditions, the organic phase dissolved with amphiphilic molecules is dispersed in the water phase, and left to stand to obtain polypeptide self-assembled nanomedicine.
[0051] In this application, the self-assembly process of polypeptide self-assembled nano-medicine is simple, self-assembled through weak intermolecular interactions (hydrophobic interactions) to form uniform and stable nanoparticles, no covalent bond is generated, and there is no reverse reaction, the prepared nano-medicine Good biocompatibility and enzyme responsiveness.
[0052] Further, the organic phase includes dimethyl sulfoxide, and the aqueous phase includes deionized water or phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.4.
[0053] In this app...
Embodiment 1
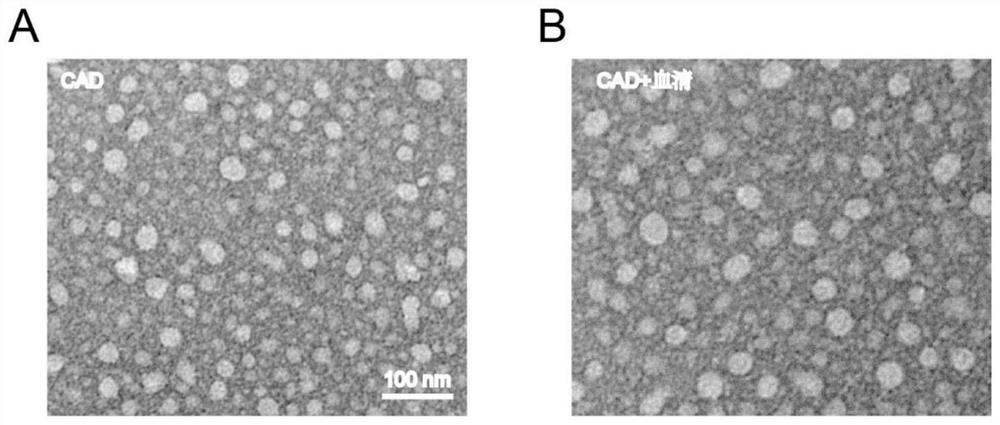
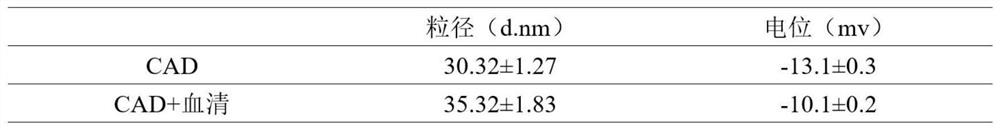
[0063] In this example, the nanomedicine was prepared by the following method: dissolving the amphiphilic molecule (with C18 at the hydrophobic end) in 10 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and dissolving the amphiphilic molecule under 120W ultrasonic conditions The dimethyl sulfoxide solution was slowly dispersed in 1 mL of deionized water, ultrasonicated for 20 minutes, and left to stand at room temperature for 1 hour. The morphology and particle size of the obtained nanomedicine (named CAD) were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and laser particle size analyzer. The result is as figure 1 A and figure 2 shown. figure 1 A is the electron micrograph of the nano-medicine. It can be seen from the figure that the prepared nano-medicine is spherical and the particle size is relatively uniform. figure 2 For the particle size distribution and potential change of the nano-medicine in serum, the particle size distribution of the obtained nano-medicine is 30-40nm, and...
Embodiment 2
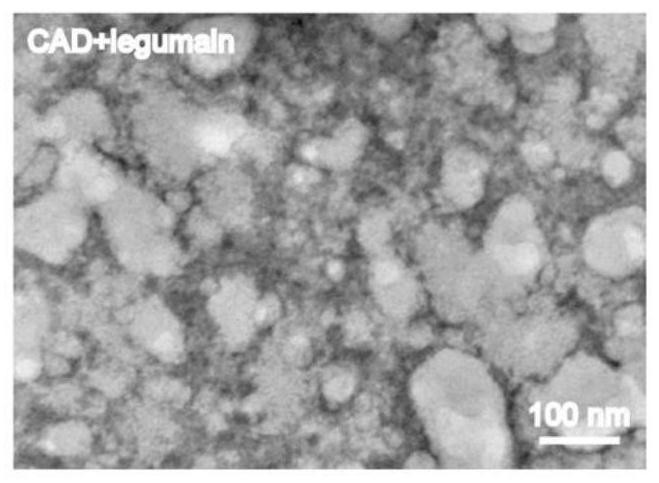
[0066] The purpose of this example is to determine the enzyme response of nanomedicine in pod protease solution.
[0067] The enzyme responsiveness was reflected by the morphology change after enzyme treatment. The nanomedicine obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in 1 ml of a buffer solution (pH 5.5) containing pod protease. Place in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C, incubate for more than two hours, take samples, and use transmission electron microscopy to characterize the nano-medicine after enzyme incubation, as shown in image 3 As shown, after the nanomedicine was treated with enzymes, the nanoparticles disintegrated and lost their spherical structure, reflecting the responsiveness of nanomedicines to enzymes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com