Process for producing hydrogenated ester, hydrogenation catalyst for use therein, and processing for producing the catalyst
A technology of hydrogenation catalyst and production method, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, organic chemical method, etc., can solve problems such as undescribed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1A-1
[0203] (dilute raw material with inert solvent)
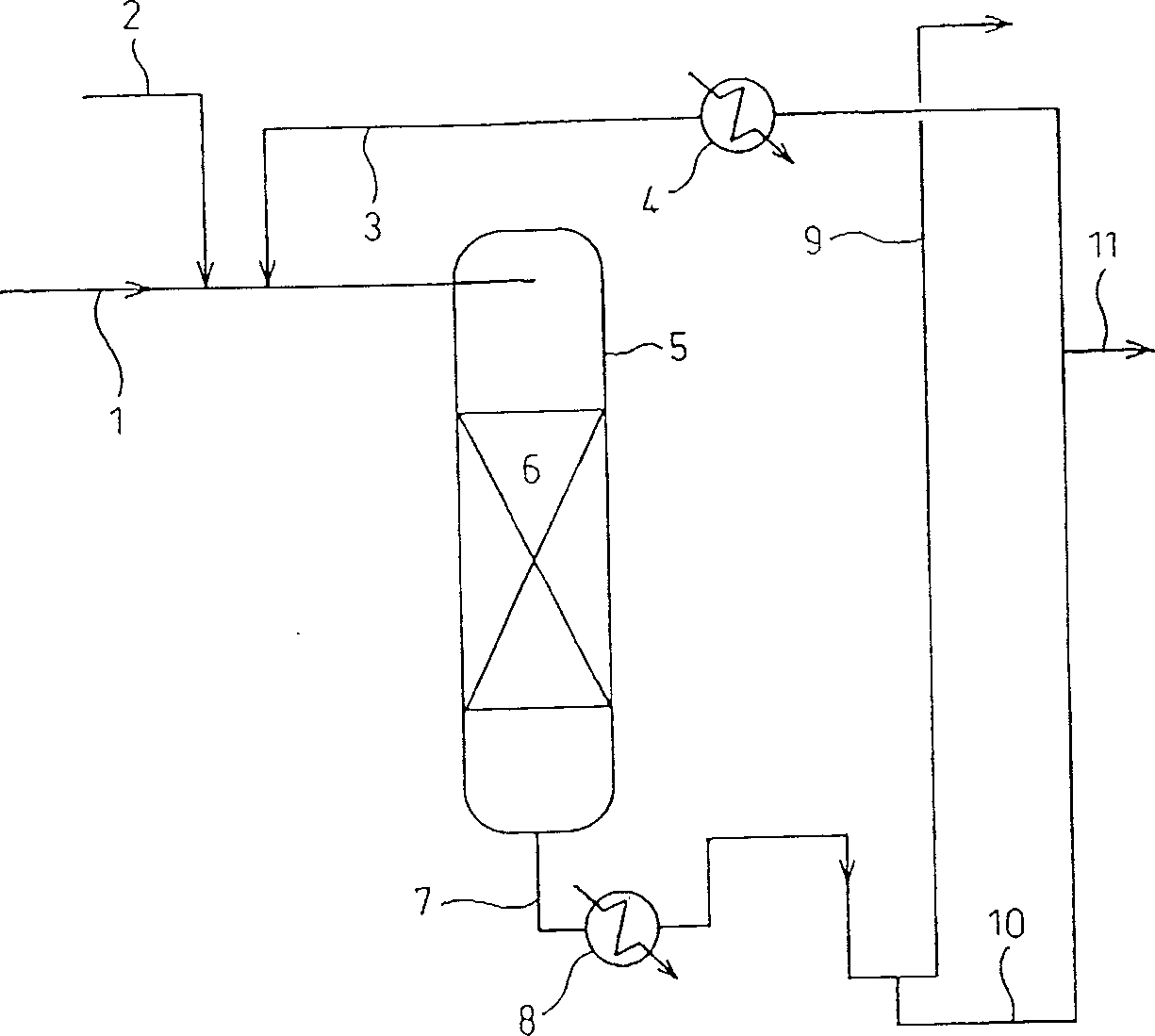
[0204] according to figure 1Shown flow process, with 130ml loaded palladium catalyst (3mm-diameter ball, silica carrier, palladium content 0.5%, specific surface area 300m 2 / g, produced by NE-Chem Cat K.K.) as a hydrogenation catalyst was filled into a stainless steel cylindrical reactor 5 with an inner diameter of 20 mmφ to form a catalyst packing layer 6, and the pressure of the reactor 5 was adjusted to 2.0 MPa (gauge pressure) with hydrogen. . From the upper part of the reactor 5, a liquid mixture comprising recycled n-propyl acetate (hydrogenated ester): allyl acetate (unsaturated group-containing ester) = 12.9: 1 (wt / wt) was transferred from The feed pipe 1 of the ester containing the unsaturated group is added therein and circulated in the reactor 5 at a speed of 550ml / hr, and the hydrogen from the hydrogen feed pipe 2 is also in the reactor at a speed of 18.6Nl / hr. 5 internal circulation (fixed bed type, gas-liquid ...
Embodiment 1A-2
[0209] The unsaturated group-containing ester was hydrogenated in the same manner as in Example 1A-1, but with 130 ml of supported palladium catalyst (alumina carrier, a sheet of 3 mm in diameter × 3 mm in length, with a palladium content of 0.3%, and a specific surface area of 100 m 2 / g, produced by NE-Chem Cat K.K.) to replace the 130ml supported palladium catalyst used in Example 1A-1 (silicon oxide carrier, 3mm-diameter ball, palladium content 0.5%, specific surface area 300m 2 / g, produced by NE-Chem Cat K.K.) as a hydrogenation catalyst; the pressure inside the reactor is 0.9MPa (gauge pressure) instead of 2.0MPa (gauge pressure) used in Example 1A-1. The temperature at the outlet of the reactor (the bottom of the catalyst layer) was 97.5°C.
[0210] The reaction mixture from the outlet of the reactor was condensed and analyzed by gas chromatography (GC-14B manufactured by Shimazu Kagaku K.K.; hydrogen flame ionization detector) under the above conditions. The result...
Embodiment 1A-3
[0212] Hydrogenation of esters containing unsaturated groups in the same manner as in Example 1A-1, but with 130 ml of supported ruthenium catalyst (alumina carrier, a sheet with a diameter of 3 mm × length of 3 mm, a ruthenium content of 0.5%, and a specific surface area of 100 m 2 / g, produced by NE-Chem Cat K.K.) to replace the 130ml supported palladium catalyst used in Example 1A-1 (silicon oxide carrier, 3mm-diameter ball, palladium content 0.5%, specific surface area 300m 2 / g, produced by NE-Chem Cat K.K.) as a hydrogenation catalyst; replace the mixture containing allyl acetate and n-propyl acetate as a raw material in Example 1A-1 with a mixture containing methallyl acetate and isobutyl acetate Esters mixture. The temperature at the outlet of the reactor (the bottom of the catalyst layer) was 95.5°C.
[0213] The reaction mixture from the outlet of the reactor was condensed and analyzed by gas chromatography (GC-14B manufactured by Shimazu Kagaku K.K.; hydrogen fla...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com