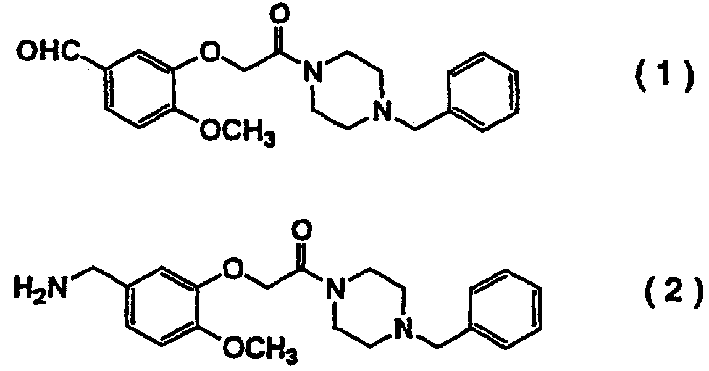
Process for producing benzylamine compound
A manufacturing method and compound technology, applied in organic chemistry and other fields, can solve the problems of many steps and complicated operation, and achieve the effect of good operability and good economy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Method for producing compound (2) using dl-valine in N,N-dimethylacetamide (case where low boiling point substances are not evaporated.)
[0039] In a 20 ml reaction vessel, add 1 g of the monohydrochloride salt of compound (1), 0.58 g of dl-valine, 6 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide and 2.5 ml of 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid-diox The alkane solution was stirred at an internal temperature of 150°C for 2 hours.
[0040] After cooling the reaction mixture to 40°C, 20 mg of seed crystals were added to precipitate crystals, and then the internal temperature was cooled to 10°C and maintained at this temperature for 1 hour.
[0041] Thereafter, the crystals were filtered and washed with 1 g of diisopropyl ether to obtain 0.74 g of dihydrochloride of benzylamine compound (2).
[0042] Melting point: 262°C (decomposition)
Embodiment 2
[0044] Method for producing compound (2) using 2-aminoisobutyric acid in N,N dimethylacetamide (case where low boiling point substances are not distilled off.)
[0045] In a 20 ml reaction vessel, add 200 mg of the monohydrochloride salt of compound (1), 57 mg of 2-aminoisobutyric acid, 1.2 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide and 0.2 g of 10% (w / w) Hydrochloric acid-ethanol solution was stirred at an internal temperature of 150°C for 2 hours.
[0046] The reaction mixture was cooled until crystallization occurred (ca. 40°C), then the internal temperature was allowed to cool to 10°C and held at this temperature for 1 hour.
[0047] Thereafter, the crystals were filtered and washed with 1 g of diisopropyl ether to obtain 0.16 g (yield 73%) of dihydrochloride of benzylamine compound (2).
[0048] Melting point: 262°C (decomposition)
Embodiment 3
[0050] Method for producing compound (2) using dl-valine in N,N-dimethylacetamide (case of evaporating low-boiling point substances.)
[0051] In a 100 ml reaction vessel, add 7 gram of compound (1) monohydrochloride, 3.04 gram of dl-valine, 28.89 gram of N,N-dimethylacetamide and 1.35% concentrated hydrochloric acid, at 110 The mixture was stirred for 2 hours while distilling off low boiling point substances at an internal temperature of -120°C.
[0052] 6.45 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide was distilled off under reduced pressure, and when the internal temperature was 75°C, 10.5 g of isopropyl ether was added, the internal temperature was cooled to 5°C, and this temperature was maintained for 1 hour.
[0053] The precipitated crystals were filtered and washed with a mixed solvent of 3.3 g of N,N-dimethylacetamide and 3.3 g of isopropyl ether to obtain 5 g of dihydrochloride of benzylamine compound (2).
[0054] Melting point: 262°C (decomposition)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com