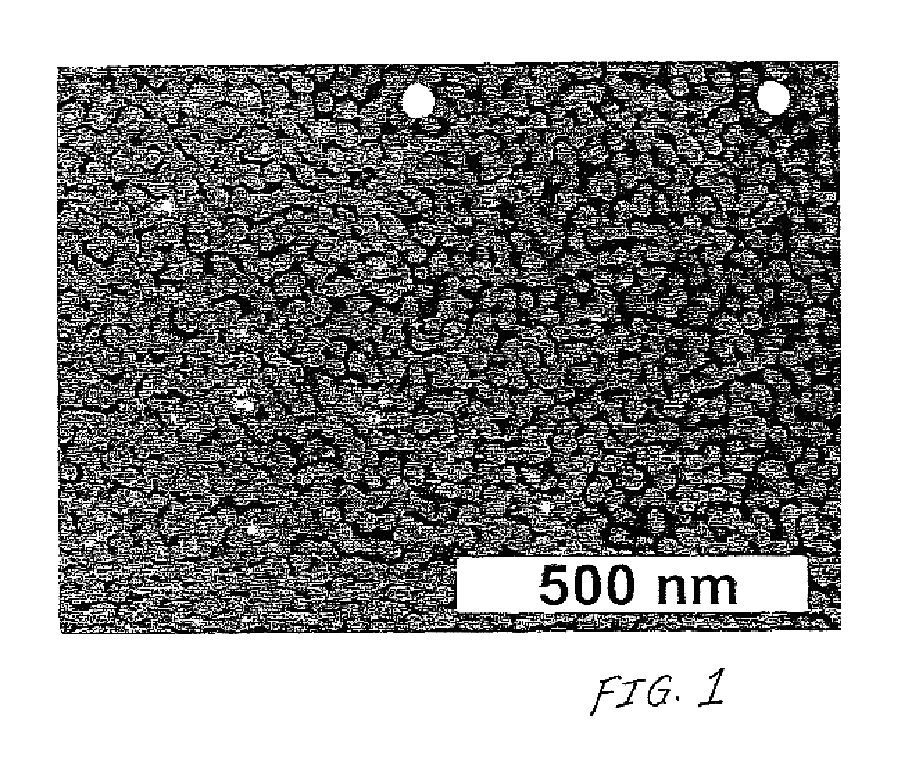
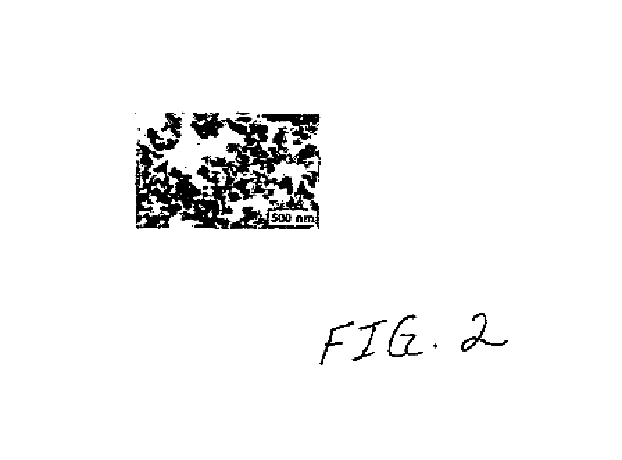
Ammonium hydroxide's role in the production of advanced ceramics
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Ceramics: Background and Objectives
Ammonium hydroxide has played a pivotal role in the production of advanced ceramics, revolutionizing the industry over the past few decades. This compound, also known as aqueous ammonia, has become an indispensable component in various ceramic manufacturing processes, particularly in the synthesis of high-performance materials.
The journey of ammonium hydroxide in ceramics began in the mid-20th century when researchers discovered its potential as a pH regulator and complexing agent. Since then, its applications have expanded significantly, contributing to the development of ceramics with enhanced properties and performance characteristics.
The primary objective of utilizing ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production is to achieve precise control over the material's microstructure, composition, and properties. By manipulating the pH and chemical environment during synthesis, manufacturers can tailor the ceramic's attributes to meet specific requirements for diverse applications, ranging from electronics to aerospace industries.
One of the key advantages of ammonium hydroxide lies in its ability to facilitate the formation of uniform and fine-grained ceramic powders. This is particularly crucial in the production of advanced ceramics, where homogeneity and particle size distribution directly impact the final product's performance. The compound's role in controlling particle morphology and preventing agglomeration has led to significant improvements in ceramic quality and consistency.
Furthermore, ammonium hydroxide has proven instrumental in the development of novel ceramic processing techniques. Its use in sol-gel synthesis, hydrothermal methods, and precipitation processes has enabled the creation of ceramics with unique properties, such as enhanced mechanical strength, improved thermal stability, and superior electrical characteristics.
The evolution of ammonium hydroxide's role in ceramics has been closely tied to the growing demand for advanced materials in various high-tech sectors. As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance, the importance of precise chemical control in ceramic synthesis has become increasingly apparent. This has driven ongoing research into optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide and exploring its potential in emerging ceramic technologies.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production are focused on further refining its application to address the challenges of next-generation materials. This includes developing more environmentally friendly processes, enhancing the scalability of production methods, and exploring new compositions that can meet the ever-increasing demands of cutting-edge technologies.
The journey of ammonium hydroxide in ceramics began in the mid-20th century when researchers discovered its potential as a pH regulator and complexing agent. Since then, its applications have expanded significantly, contributing to the development of ceramics with enhanced properties and performance characteristics.
The primary objective of utilizing ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production is to achieve precise control over the material's microstructure, composition, and properties. By manipulating the pH and chemical environment during synthesis, manufacturers can tailor the ceramic's attributes to meet specific requirements for diverse applications, ranging from electronics to aerospace industries.
One of the key advantages of ammonium hydroxide lies in its ability to facilitate the formation of uniform and fine-grained ceramic powders. This is particularly crucial in the production of advanced ceramics, where homogeneity and particle size distribution directly impact the final product's performance. The compound's role in controlling particle morphology and preventing agglomeration has led to significant improvements in ceramic quality and consistency.
Furthermore, ammonium hydroxide has proven instrumental in the development of novel ceramic processing techniques. Its use in sol-gel synthesis, hydrothermal methods, and precipitation processes has enabled the creation of ceramics with unique properties, such as enhanced mechanical strength, improved thermal stability, and superior electrical characteristics.
The evolution of ammonium hydroxide's role in ceramics has been closely tied to the growing demand for advanced materials in various high-tech sectors. As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance, the importance of precise chemical control in ceramic synthesis has become increasingly apparent. This has driven ongoing research into optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide and exploring its potential in emerging ceramic technologies.
Looking ahead, the objectives for ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production are focused on further refining its application to address the challenges of next-generation materials. This includes developing more environmentally friendly processes, enhancing the scalability of production methods, and exploring new compositions that can meet the ever-increasing demands of cutting-edge technologies.
Market Analysis for Advanced Ceramics
The advanced ceramics market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as electronics, aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. The global advanced ceramics market size was valued at approximately $75 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $130 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 8% during the forecast period.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics plays a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. As a key ingredient in the synthesis process, ammonium hydroxide contributes to the development of high-performance ceramic materials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation. This has led to a surge in demand for advanced ceramics in critical applications, particularly in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
The electronics sector remains the largest consumer of advanced ceramics, accounting for over 30% of the market share. The increasing adoption of advanced ceramics in electronic components, such as substrates, capacitors, and insulators, is driven by the need for miniaturization and improved performance in devices. The automotive industry is also emerging as a significant market for advanced ceramics, with applications in sensors, catalytic converters, and engine components.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the advanced ceramics market, holding a market share of approximately 40%. This is primarily due to the presence of major electronics and automotive manufacturing hubs in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow, with growing demand in aerospace and defense sectors contributing to market expansion.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Kyocera Corporation, CeramTec GmbH, and Saint-Gobain Ceramic Materials. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new products and improve manufacturing processes, including the optimization of ammonium hydroxide usage in ceramic production.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the advanced ceramics market faces challenges such as high production costs and complex manufacturing processes. The use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production also raises environmental concerns, prompting manufacturers to explore more sustainable alternatives and eco-friendly production methods.
In conclusion, the role of ammonium hydroxide in advanced ceramics production significantly influences market trends and product development. As industries continue to demand high-performance materials, the market for advanced ceramics is expected to expand further, with ongoing innovations in production techniques and materials science driving growth and competitiveness in the sector.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics plays a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. As a key ingredient in the synthesis process, ammonium hydroxide contributes to the development of high-performance ceramic materials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation. This has led to a surge in demand for advanced ceramics in critical applications, particularly in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
The electronics sector remains the largest consumer of advanced ceramics, accounting for over 30% of the market share. The increasing adoption of advanced ceramics in electronic components, such as substrates, capacitors, and insulators, is driven by the need for miniaturization and improved performance in devices. The automotive industry is also emerging as a significant market for advanced ceramics, with applications in sensors, catalytic converters, and engine components.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the advanced ceramics market, holding a market share of approximately 40%. This is primarily due to the presence of major electronics and automotive manufacturing hubs in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow, with growing demand in aerospace and defense sectors contributing to market expansion.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Kyocera Corporation, CeramTec GmbH, and Saint-Gobain Ceramic Materials. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new products and improve manufacturing processes, including the optimization of ammonium hydroxide usage in ceramic production.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the advanced ceramics market faces challenges such as high production costs and complex manufacturing processes. The use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production also raises environmental concerns, prompting manufacturers to explore more sustainable alternatives and eco-friendly production methods.
In conclusion, the role of ammonium hydroxide in advanced ceramics production significantly influences market trends and product development. As industries continue to demand high-performance materials, the market for advanced ceramics is expected to expand further, with ongoing innovations in production techniques and materials science driving growth and competitiveness in the sector.
Current Challenges in Ammonium Hydroxide Usage
The use of ammonium hydroxide in advanced ceramics production faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. One of the primary issues is the precise control of pH levels during the ceramic synthesis process. Ammonium hydroxide's volatile nature makes it difficult to maintain consistent pH conditions, which is crucial for achieving uniform material properties and reproducible results in ceramic manufacturing.
Another challenge lies in the environmental and safety concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide usage. Its strong odor and potential for releasing ammonia gas pose health risks to workers and require stringent safety measures in production facilities. This necessitates substantial investments in ventilation systems and personal protective equipment, increasing overall production costs.
The reactivity of ammonium hydroxide with certain ceramic precursors presents additional complications. In some cases, it can lead to undesired side reactions or the formation of unwanted byproducts, affecting the purity and quality of the final ceramic products. This reactivity issue limits the range of materials that can be effectively processed using ammonium hydroxide-based methods.
Furthermore, the scalability of ammonium hydroxide-dependent processes poses a significant challenge for large-scale industrial production of advanced ceramics. Maintaining uniform dispersion and reaction conditions becomes increasingly difficult as batch sizes increase, potentially leading to inconsistencies in product quality and properties.
The storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide also present logistical challenges. Its corrosive nature requires specialized storage containers and handling procedures, adding complexity to supply chain management and increasing operational costs for ceramic manufacturers.
Additionally, the varying concentration levels of commercially available ammonium hydroxide solutions can lead to inconsistencies in ceramic processing. This variability necessitates frequent adjustments to manufacturing protocols, potentially impacting production efficiency and product consistency.
Lastly, the disposal of ammonium hydroxide-containing waste streams presents environmental challenges. Proper treatment and neutralization of these wastes are essential to comply with environmental regulations, adding another layer of complexity and cost to the ceramic production process.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for advancing the role of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics. Innovations in process control, safety measures, and waste management are needed to fully harness the potential of this chemical in ceramic manufacturing while mitigating its associated risks and limitations.
Another challenge lies in the environmental and safety concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide usage. Its strong odor and potential for releasing ammonia gas pose health risks to workers and require stringent safety measures in production facilities. This necessitates substantial investments in ventilation systems and personal protective equipment, increasing overall production costs.
The reactivity of ammonium hydroxide with certain ceramic precursors presents additional complications. In some cases, it can lead to undesired side reactions or the formation of unwanted byproducts, affecting the purity and quality of the final ceramic products. This reactivity issue limits the range of materials that can be effectively processed using ammonium hydroxide-based methods.
Furthermore, the scalability of ammonium hydroxide-dependent processes poses a significant challenge for large-scale industrial production of advanced ceramics. Maintaining uniform dispersion and reaction conditions becomes increasingly difficult as batch sizes increase, potentially leading to inconsistencies in product quality and properties.
The storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide also present logistical challenges. Its corrosive nature requires specialized storage containers and handling procedures, adding complexity to supply chain management and increasing operational costs for ceramic manufacturers.
Additionally, the varying concentration levels of commercially available ammonium hydroxide solutions can lead to inconsistencies in ceramic processing. This variability necessitates frequent adjustments to manufacturing protocols, potentially impacting production efficiency and product consistency.
Lastly, the disposal of ammonium hydroxide-containing waste streams presents environmental challenges. Proper treatment and neutralization of these wastes are essential to comply with environmental regulations, adding another layer of complexity and cost to the ceramic production process.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for advancing the role of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics. Innovations in process control, safety measures, and waste management are needed to fully harness the potential of this chemical in ceramic manufacturing while mitigating its associated risks and limitations.
Existing Ammonium Hydroxide Applications
01 Use of ammonium hydroxide in chemical processes
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes as a reactant, catalyst, or pH adjuster. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste. Its alkaline properties make it useful for neutralizing acids and controlling pH in different applications.- Use of ammonium hydroxide in chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes as a reactant, catalyst, or pH adjuster. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste. Its alkaline properties make it useful for neutralizing acids and controlling pH in different applications.
- Application in cleaning and surface treatment: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It is effective in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces. In the semiconductor industry, it is used for etching and cleaning silicon wafers. Its ability to dissolve certain metals and oxides makes it valuable in metal surface treatment and electroplating applications.
- Role in textile and leather processing: Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in the textile and leather industries. It is used in dyeing processes to adjust pH and improve color fastness. In leather tanning, it helps in dehairing and liming operations. Its alkaline nature aids in breaking down proteins and preparing materials for further treatment.
- Use in agricultural and horticultural applications: In agriculture and horticulture, ammonium hydroxide is used as a source of nitrogen for plant nutrition. It can be applied directly to soil or used in the production of nitrogen-based fertilizers. Its ability to increase soil pH makes it useful for treating acidic soils. Additionally, it is used in composting processes to control odors and accelerate decomposition.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use of ammonium hydroxide requires careful handling due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods are essential to prevent accidents and minimize environmental risks. Safety measures, such as proper ventilation and personal protective equipment, are necessary when working with ammonium hydroxide. Efforts are being made to develop safer alternatives or improve its application methods in various industries.
02 Application in cleaning and surface treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It is effective in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces. In the semiconductor industry, it is used for etching and cleaning silicon wafers. Its ability to dissolve certain metals and oxides makes it valuable in metal surface treatment and electroplating applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Role in textile and leather processing
Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in the textile and leather industries. It is used in dyeing processes to adjust pH and improve color fastness. In leather tanning, it helps in the dehairing process and adjusting the pH of tanning solutions. Its alkaline nature aids in breaking down proteins and fats in these materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in agricultural and horticultural applications
In agriculture and horticulture, ammonium hydroxide is used as a source of nitrogen for plant nutrition. It can be applied directly to soil or used in the production of fertilizers. Its alkaline properties also make it useful for adjusting soil pH. In some cases, it is used as a preservative for silage and animal feed.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of ammonium hydroxide requires careful handling due to its corrosive nature and potential to release ammonia gas. Proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods are essential to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety. In some applications, alternatives or modified processes are being developed to reduce the environmental impact and improve safety profiles.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Advanced Ceramics Industry
The competitive landscape for ammonium hydroxide's role in advanced ceramics production is evolving rapidly. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-performance ceramic materials across various sectors. The global market size for advanced ceramics is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like NGK Insulators, CoorsTek, and Kyocera leading innovation. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to enhance the use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic processing, aiming to improve material properties and production efficiency. While the technology is maturing, there's still room for breakthroughs, particularly in sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
NGK Insulators, Ltd.
Technical Solution: NGK Insulators utilizes ammonium hydroxide in their advanced ceramic production process, particularly for their high-performance insulators and ceramic components. The company employs a sol-gel method where ammonium hydroxide acts as a pH regulator and precipitating agent[1]. This process allows for precise control of the ceramic microstructure, resulting in improved mechanical and electrical properties. NGK's technique involves the use of ammonium hydroxide to create a uniform dispersion of ceramic particles, which is crucial for the formation of homogeneous and dense ceramic bodies[3]. The company has also developed a proprietary process where ammonium hydroxide is used in the synthesis of ceramic precursors, enabling the production of complex ceramic shapes with high dimensional accuracy[5].
Strengths: Precise control of ceramic microstructure, improved mechanical and electrical properties, ability to produce complex shapes. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns due to ammonia emissions, higher production costs compared to traditional methods.
CoorsTek, Inc.
Technical Solution: CoorsTek incorporates ammonium hydroxide in their advanced ceramic manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of high-purity alumina ceramics. The company uses ammonium hydroxide as a key component in their chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process for creating thin ceramic films[2]. In this application, ammonium hydroxide serves as a source of nitrogen, which is crucial for the formation of certain nitride ceramics. CoorsTek also employs ammonium hydroxide in their colloidal processing techniques, where it acts as a dispersant and pH modifier to control the stability of ceramic suspensions[4]. This allows for the production of ceramics with enhanced uniformity and density. Additionally, the company has developed a novel process using ammonium hydroxide in the synthesis of nano-sized ceramic powders, which are essential for producing advanced ceramics with superior properties[6].
Strengths: Ability to produce high-purity ceramics, enhanced control over ceramic microstructure, capability to synthesize nano-sized ceramic powders. Weaknesses: Potential scalability issues for some specialized processes, higher raw material costs.
Innovations in Ammonium Hydroxide Utilization
Ceramic composite material consisting of aluminium oxide and zirconium oxide as main constituents
PatentInactiveEP2513009A1
Innovation
- A ceramic composite material with an aluminum oxide matrix and dispersed zirconium oxide, where the tetragonal phase of zirconium oxide is mechanically stabilized, reducing the need for chemical stabilizers and minimizing oxygen vacancies, resulting in improved fracture toughness and resistance to hydrothermal aging.
Method of producing aluminum oxides and products obtained on the basis thereof
PatentInactiveUS6841497B1
Innovation
- A process involving chlorine-free precursors, hydrolysis, aging, and controlled calcination followed by annealing at temperatures ≤950°C, using nuclei to promote corundum formation, resulting in redispersible nanocorundum with D50 <100 nm and nanoporous Al2O3 sintered products with tailored pore sizes.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process involving this compound can lead to various environmental impacts, primarily due to its chemical properties and the byproducts generated during ceramic production.
One of the main environmental concerns is the potential for ammonia emissions. Ammonium hydroxide, when used in ceramic processing, can release ammonia gas into the atmosphere. This can contribute to air pollution and potentially affect local air quality. Ammonia is a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Additionally, ammonia emissions can lead to the formation of secondary aerosols, contributing to smog and reduced visibility in affected areas.
Water pollution is another critical environmental aspect to consider. The use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production may result in the discharge of ammonium-rich wastewater. If not properly treated, this effluent can lead to eutrophication in receiving water bodies, causing algal blooms and disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, high levels of ammonia in water can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, potentially impacting biodiversity in affected waterways.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of ceramic manufacturing. The energy-intensive processes involved in producing this compound, as well as its transportation to ceramic manufacturing facilities, result in greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to climate change. This indirect environmental impact should be factored into comprehensive assessments of the ceramic production lifecycle.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with the use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production. Accidental spills or improper disposal of ammonium-containing waste can lead to soil acidification and alter soil chemistry. This can negatively affect soil fertility and potentially impact local flora and fauna.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, ceramic manufacturers employing ammonium hydroxide must implement robust environmental management systems. This includes installing effective air pollution control devices to capture and treat ammonia emissions, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies to remove ammonium from effluents, and adopting best practices for chemical handling and storage to prevent spills and leaks.
Regulatory compliance is crucial in managing the environmental impacts of ammonium hydroxide use in ceramic production. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations governing air and water quality, waste management, and chemical handling. Regular environmental monitoring and reporting are essential to ensure compliance and to identify areas for improvement in environmental performance.
In conclusion, while ammonium hydroxide plays a vital role in the production of advanced ceramics, its environmental impacts are significant and multifaceted. A comprehensive environmental impact assessment is necessary to fully understand and mitigate these effects, ensuring that the benefits of advanced ceramic production are balanced against environmental protection and sustainability goals.
One of the main environmental concerns is the potential for ammonia emissions. Ammonium hydroxide, when used in ceramic processing, can release ammonia gas into the atmosphere. This can contribute to air pollution and potentially affect local air quality. Ammonia is a precursor to particulate matter formation, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Additionally, ammonia emissions can lead to the formation of secondary aerosols, contributing to smog and reduced visibility in affected areas.
Water pollution is another critical environmental aspect to consider. The use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production may result in the discharge of ammonium-rich wastewater. If not properly treated, this effluent can lead to eutrophication in receiving water bodies, causing algal blooms and disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, high levels of ammonia in water can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, potentially impacting biodiversity in affected waterways.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of ceramic manufacturing. The energy-intensive processes involved in producing this compound, as well as its transportation to ceramic manufacturing facilities, result in greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to climate change. This indirect environmental impact should be factored into comprehensive assessments of the ceramic production lifecycle.
Soil contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with the use of ammonium hydroxide in ceramic production. Accidental spills or improper disposal of ammonium-containing waste can lead to soil acidification and alter soil chemistry. This can negatively affect soil fertility and potentially impact local flora and fauna.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, ceramic manufacturers employing ammonium hydroxide must implement robust environmental management systems. This includes installing effective air pollution control devices to capture and treat ammonia emissions, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies to remove ammonium from effluents, and adopting best practices for chemical handling and storage to prevent spills and leaks.
Regulatory compliance is crucial in managing the environmental impacts of ammonium hydroxide use in ceramic production. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations governing air and water quality, waste management, and chemical handling. Regular environmental monitoring and reporting are essential to ensure compliance and to identify areas for improvement in environmental performance.
In conclusion, while ammonium hydroxide plays a vital role in the production of advanced ceramics, its environmental impacts are significant and multifaceted. A comprehensive environmental impact assessment is necessary to fully understand and mitigate these effects, ensuring that the benefits of advanced ceramic production are balanced against environmental protection and sustainability goals.
Safety Protocols and Regulations
The use of ammonium hydroxide in the production of advanced ceramics necessitates stringent safety protocols and adherence to regulations due to its corrosive and potentially hazardous nature. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive safety measures to protect workers and the environment throughout the production process.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling ammonium hydroxide. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, face shields, and appropriate protective clothing. Respiratory protection, such as approved respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus, may be required depending on the concentration and exposure levels.
Proper ventilation systems are essential in areas where ammonium hydroxide is used or stored. These systems should be designed to effectively remove vapors and maintain air quality within acceptable limits. Regular monitoring of air quality and exposure levels is necessary to ensure compliance with occupational health and safety standards.
Storage and handling protocols must be strictly followed. Ammonium hydroxide should be stored in cool, well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials and sources of heat or ignition. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed when not in use. Secondary containment systems should be in place to prevent spills from spreading.
Emergency response procedures must be established and regularly practiced. This includes spill containment and cleanup protocols, as well as evacuation plans in case of large-scale releases. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in all areas where ammonium hydroxide is handled.
Training programs are critical to ensure all personnel understand the hazards associated with ammonium hydroxide and are proficient in safe handling procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness.
Compliance with local, national, and international regulations is mandatory. This includes adherence to guidelines set by organizations such as OSHA, EPA, and REACH. Proper documentation and record-keeping of safety procedures, incident reports, and employee training are essential for regulatory compliance and audits.
Waste management protocols must be implemented to ensure proper disposal of ammonium hydroxide and related waste products. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized disposal methods in accordance with environmental regulations.
Regular safety audits and risk assessments should be conducted to identify potential hazards and improve safety measures continuously. This proactive approach helps in maintaining a safe working environment and ensures compliance with evolving safety standards and regulations in the advanced ceramics industry.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling ammonium hydroxide. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, face shields, and appropriate protective clothing. Respiratory protection, such as approved respirators or self-contained breathing apparatus, may be required depending on the concentration and exposure levels.
Proper ventilation systems are essential in areas where ammonium hydroxide is used or stored. These systems should be designed to effectively remove vapors and maintain air quality within acceptable limits. Regular monitoring of air quality and exposure levels is necessary to ensure compliance with occupational health and safety standards.
Storage and handling protocols must be strictly followed. Ammonium hydroxide should be stored in cool, well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible materials and sources of heat or ignition. Containers must be properly labeled and sealed when not in use. Secondary containment systems should be in place to prevent spills from spreading.
Emergency response procedures must be established and regularly practiced. This includes spill containment and cleanup protocols, as well as evacuation plans in case of large-scale releases. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in all areas where ammonium hydroxide is handled.
Training programs are critical to ensure all personnel understand the hazards associated with ammonium hydroxide and are proficient in safe handling procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness.
Compliance with local, national, and international regulations is mandatory. This includes adherence to guidelines set by organizations such as OSHA, EPA, and REACH. Proper documentation and record-keeping of safety procedures, incident reports, and employee training are essential for regulatory compliance and audits.
Waste management protocols must be implemented to ensure proper disposal of ammonium hydroxide and related waste products. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized disposal methods in accordance with environmental regulations.
Regular safety audits and risk assessments should be conducted to identify potential hazards and improve safety measures continuously. This proactive approach helps in maintaining a safe working environment and ensures compliance with evolving safety standards and regulations in the advanced ceramics industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!