Application of NMR in Petrochemical Analysis
SEP 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
NMR Technology Evolution in Petrochemical Analysis
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has undergone significant evolution in its application to petrochemical analysis since its initial introduction to the field in the 1950s. The technology's journey began with simple one-dimensional proton NMR experiments that could only identify basic hydrocarbon structures. During this early period, NMR was primarily used for qualitative analysis of petroleum fractions, with limited resolution and sensitivity restricting its practical applications.
The 1970s marked a pivotal advancement with the introduction of Fourier Transform NMR (FT-NMR), dramatically improving signal-to-noise ratios and enabling the analysis of more complex petrochemical mixtures. This technological leap allowed researchers to begin quantitative analysis of petroleum components, though still with significant limitations in resolving complex mixtures.
By the 1980s and 1990s, the development of higher field strength magnets (moving from 60 MHz to 300 MHz and beyond) revolutionized NMR capabilities in petrochemical analysis. These stronger magnetic fields provided enhanced spectral resolution, allowing for more detailed characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures and the identification of trace components critical to petroleum processing.
The introduction of two-dimensional NMR techniques during this period represented another significant milestone. Techniques such as COSY (Correlation Spectroscopy), HSQC (Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence), and TOCSY (Total Correlation Spectroscopy) enabled scientists to unravel complex structural relationships within petrochemical compounds that were previously indecipherable.
The early 2000s saw the integration of NMR with advanced computational methods, giving rise to chemometric approaches for analyzing the vast datasets generated by modern NMR experiments. This computational revolution enabled automated identification of petrochemical components and prediction of fuel properties from spectral data.
Most recently, the development of benchtop NMR systems has democratized access to NMR technology in petrochemical settings. These compact, lower-field instruments, while offering reduced resolution compared to their high-field counterparts, provide sufficient analytical power for many routine petrochemical applications at a fraction of the cost and maintenance requirements.
The latest frontier in NMR technology for petrochemical analysis involves real-time monitoring capabilities, with specialized probes designed for in-line process analysis. These innovations allow for continuous quality control during petrochemical production, representing a shift from NMR as purely an analytical laboratory tool to an integrated process monitoring technology.
The 1970s marked a pivotal advancement with the introduction of Fourier Transform NMR (FT-NMR), dramatically improving signal-to-noise ratios and enabling the analysis of more complex petrochemical mixtures. This technological leap allowed researchers to begin quantitative analysis of petroleum components, though still with significant limitations in resolving complex mixtures.
By the 1980s and 1990s, the development of higher field strength magnets (moving from 60 MHz to 300 MHz and beyond) revolutionized NMR capabilities in petrochemical analysis. These stronger magnetic fields provided enhanced spectral resolution, allowing for more detailed characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures and the identification of trace components critical to petroleum processing.
The introduction of two-dimensional NMR techniques during this period represented another significant milestone. Techniques such as COSY (Correlation Spectroscopy), HSQC (Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence), and TOCSY (Total Correlation Spectroscopy) enabled scientists to unravel complex structural relationships within petrochemical compounds that were previously indecipherable.
The early 2000s saw the integration of NMR with advanced computational methods, giving rise to chemometric approaches for analyzing the vast datasets generated by modern NMR experiments. This computational revolution enabled automated identification of petrochemical components and prediction of fuel properties from spectral data.
Most recently, the development of benchtop NMR systems has democratized access to NMR technology in petrochemical settings. These compact, lower-field instruments, while offering reduced resolution compared to their high-field counterparts, provide sufficient analytical power for many routine petrochemical applications at a fraction of the cost and maintenance requirements.
The latest frontier in NMR technology for petrochemical analysis involves real-time monitoring capabilities, with specialized probes designed for in-line process analysis. These innovations allow for continuous quality control during petrochemical production, representing a shift from NMR as purely an analytical laboratory tool to an integrated process monitoring technology.
Market Demand for Advanced Petrochemical Characterization
The petrochemical industry is experiencing a growing demand for advanced analytical techniques that can provide comprehensive characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has emerged as a critical technology in this space, with market indicators showing significant growth potential. Current market analysis reveals that the global NMR spectroscopy market in petrochemical applications is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 5-6%, driven by increasing quality control requirements and process optimization needs.
The primary market drivers for advanced petrochemical characterization using NMR include the growing complexity of feedstocks, stricter environmental regulations, and the industry's push toward higher-value products. As refineries increasingly process unconventional crude oils, including heavy oils, oil sands, and shale oils, traditional analytical methods prove insufficient for detailed molecular characterization. This creates a substantial market opportunity for NMR technologies that can provide detailed structural information without extensive sample preparation.
Regulatory pressures represent another significant market force. Environmental agencies worldwide are implementing more stringent specifications for fuel products, particularly regarding sulfur content, aromatics, and other potentially harmful components. This regulatory landscape necessitates more sophisticated analytical capabilities, creating demand for NMR solutions that can accurately quantify these compounds at increasingly lower detection limits.
The economic value proposition of NMR in petrochemical analysis is compelling. Industry reports indicate that optimized refining processes based on better feedstock characterization can improve margins by 1-3%, representing millions in additional profit for large refineries. Furthermore, the ability to rapidly characterize catalysts and monitor catalyst degradation in real-time offers substantial operational benefits, with some facilities reporting maintenance cost reductions of 15-20% after implementing advanced NMR monitoring systems.
Regional market analysis shows varying adoption rates, with North America and Europe leading in NMR implementation for petrochemical applications, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market segment due to rapid industrialization and increasing refining capacity. China and India, in particular, are investing heavily in advanced analytical capabilities as they expand their petrochemical infrastructure.
The market is also witnessing a shift toward more accessible NMR solutions. Traditionally, high costs and operational complexity limited NMR adoption to major research centers and large corporations. However, recent technological advances have enabled the development of benchtop and process NMR systems that are creating new market segments among smaller refineries and petrochemical producers who previously could not justify the investment in conventional high-field NMR systems.
The primary market drivers for advanced petrochemical characterization using NMR include the growing complexity of feedstocks, stricter environmental regulations, and the industry's push toward higher-value products. As refineries increasingly process unconventional crude oils, including heavy oils, oil sands, and shale oils, traditional analytical methods prove insufficient for detailed molecular characterization. This creates a substantial market opportunity for NMR technologies that can provide detailed structural information without extensive sample preparation.
Regulatory pressures represent another significant market force. Environmental agencies worldwide are implementing more stringent specifications for fuel products, particularly regarding sulfur content, aromatics, and other potentially harmful components. This regulatory landscape necessitates more sophisticated analytical capabilities, creating demand for NMR solutions that can accurately quantify these compounds at increasingly lower detection limits.
The economic value proposition of NMR in petrochemical analysis is compelling. Industry reports indicate that optimized refining processes based on better feedstock characterization can improve margins by 1-3%, representing millions in additional profit for large refineries. Furthermore, the ability to rapidly characterize catalysts and monitor catalyst degradation in real-time offers substantial operational benefits, with some facilities reporting maintenance cost reductions of 15-20% after implementing advanced NMR monitoring systems.
Regional market analysis shows varying adoption rates, with North America and Europe leading in NMR implementation for petrochemical applications, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market segment due to rapid industrialization and increasing refining capacity. China and India, in particular, are investing heavily in advanced analytical capabilities as they expand their petrochemical infrastructure.
The market is also witnessing a shift toward more accessible NMR solutions. Traditionally, high costs and operational complexity limited NMR adoption to major research centers and large corporations. However, recent technological advances have enabled the development of benchtop and process NMR systems that are creating new market segments among smaller refineries and petrochemical producers who previously could not justify the investment in conventional high-field NMR systems.
Current NMR Capabilities and Technical Limitations
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has evolved into a powerful analytical tool in the petrochemical industry, offering unique capabilities for molecular structure determination and quantitative analysis. Current NMR systems can achieve resolution down to parts per billion, enabling detailed characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures without requiring prior separation. Modern instruments operate at field strengths ranging from 400 MHz to 900 MHz, with higher field strengths providing enhanced spectral resolution critical for analyzing complex petrochemical samples.
The application of multi-dimensional NMR techniques (2D, 3D) has significantly expanded analytical capabilities, allowing for the elucidation of molecular connectivity and spatial relationships in complex petrochemical compounds. These techniques have proven particularly valuable for characterizing asphaltenes and heavy crude oil fractions that resist analysis by conventional methods. Additionally, solid-state NMR has emerged as an essential tool for analyzing catalysts, coke deposits, and other solid materials encountered in petrochemical processing.
Despite these advancements, NMR spectroscopy faces several technical limitations in petrochemical applications. Sample preparation remains challenging, particularly for viscous or heterogeneous samples that may require dilution or special handling procedures that can potentially alter the sample's chemical composition. Signal overlap in complex mixtures continues to be problematic, especially in the analysis of crude oils containing thousands of different molecular species.
Sensitivity constraints represent another significant limitation, particularly when analyzing trace components or when working with nuclei having low natural abundance or small gyromagnetic ratios. This often necessitates extended acquisition times that may be impractical in industrial settings where rapid analysis is required. The quantitative accuracy of NMR can also be compromised by relaxation effects, requiring careful calibration and standardization procedures.
From an operational perspective, conventional NMR instruments demand specialized laboratory environments with controlled temperature and minimal electromagnetic interference. This requirement limits their deployment in field settings or harsh industrial environments. Additionally, the high cost of high-field NMR instruments and their maintenance represents a significant barrier to widespread adoption in routine petrochemical analysis.
Recent technological developments are addressing some of these limitations through innovations such as benchtop NMR spectrometers, which offer reduced field strength but greater portability and lower cost. Time-domain NMR and hyperpolarization techniques are also emerging as promising approaches to enhance sensitivity and reduce acquisition times. However, these technologies are still evolving and have yet to match the analytical power of traditional high-field NMR for complex petrochemical applications.
The application of multi-dimensional NMR techniques (2D, 3D) has significantly expanded analytical capabilities, allowing for the elucidation of molecular connectivity and spatial relationships in complex petrochemical compounds. These techniques have proven particularly valuable for characterizing asphaltenes and heavy crude oil fractions that resist analysis by conventional methods. Additionally, solid-state NMR has emerged as an essential tool for analyzing catalysts, coke deposits, and other solid materials encountered in petrochemical processing.
Despite these advancements, NMR spectroscopy faces several technical limitations in petrochemical applications. Sample preparation remains challenging, particularly for viscous or heterogeneous samples that may require dilution or special handling procedures that can potentially alter the sample's chemical composition. Signal overlap in complex mixtures continues to be problematic, especially in the analysis of crude oils containing thousands of different molecular species.
Sensitivity constraints represent another significant limitation, particularly when analyzing trace components or when working with nuclei having low natural abundance or small gyromagnetic ratios. This often necessitates extended acquisition times that may be impractical in industrial settings where rapid analysis is required. The quantitative accuracy of NMR can also be compromised by relaxation effects, requiring careful calibration and standardization procedures.
From an operational perspective, conventional NMR instruments demand specialized laboratory environments with controlled temperature and minimal electromagnetic interference. This requirement limits their deployment in field settings or harsh industrial environments. Additionally, the high cost of high-field NMR instruments and their maintenance represents a significant barrier to widespread adoption in routine petrochemical analysis.
Recent technological developments are addressing some of these limitations through innovations such as benchtop NMR spectrometers, which offer reduced field strength but greater portability and lower cost. Time-domain NMR and hyperpolarization techniques are also emerging as promising approaches to enhance sensitivity and reduce acquisition times. However, these technologies are still evolving and have yet to match the analytical power of traditional high-field NMR for complex petrochemical applications.
Mainstream NMR Methods for Hydrocarbon Analysis
01 NMR hardware and system design
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance systems require specialized hardware components including magnets, RF coils, and signal processing units. Innovations in this area focus on improving magnetic field homogeneity, enhancing signal-to-noise ratios, and developing more compact or portable NMR systems. These advancements enable more precise measurements and expand the applications of NMR technology in various fields.- NMR apparatus and hardware improvements: Advancements in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance hardware focus on improving the sensitivity, resolution, and reliability of NMR systems. These innovations include enhanced magnet designs, probe configurations, and signal processing components that allow for more precise measurements. Hardware improvements enable better analysis of complex molecular structures and can be applied across various fields including chemistry, medicine, and materials science.
- Portable and downhole NMR systems: Portable and downhole NMR technologies have been developed to enable in-situ measurements outside of traditional laboratory settings. These systems are designed to be compact, robust, and capable of operating in challenging environments such as oil wells, geological formations, or field locations. Applications include real-time fluid analysis, formation evaluation, and on-site quality control in various industries.
- NMR imaging and spectroscopy techniques: Advanced NMR imaging and spectroscopy techniques enable detailed analysis of molecular structures and dynamics. These methods include multi-dimensional NMR, pulse sequence optimization, and specialized data acquisition protocols that enhance the information obtained from samples. Such techniques are crucial for structural biology, pharmaceutical research, and materials characterization, providing insights into molecular interactions and properties.
- NMR data processing and analysis methods: Innovative data processing and analysis methods for NMR focus on extracting meaningful information from complex spectral data. These approaches include advanced algorithms for signal processing, noise reduction, peak identification, and automated interpretation of NMR spectra. Computational methods enhance the accuracy and efficiency of NMR data analysis, enabling faster and more reliable characterization of molecular structures and properties.
- Specialized NMR applications: Specialized applications of NMR technology have been developed for specific industries and research areas. These include NMR systems designed for medical diagnostics, food quality assessment, petroleum analysis, and materials testing. Custom NMR solutions address unique analytical challenges in various fields, providing targeted information about sample composition, structure, and properties that cannot be easily obtained through other analytical methods.
02 NMR pulse sequence and measurement techniques
Various pulse sequence methodologies are employed in NMR to extract specific information from samples. These techniques include specialized timing patterns for RF pulses, gradient applications, and signal acquisition strategies. Innovations in this area focus on developing new pulse sequences that can provide enhanced resolution, reduced measurement time, or access to previously undetectable parameters, thereby expanding the analytical capabilities of NMR spectroscopy.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMR applications in medical imaging
NMR principles form the foundation of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) used in medical diagnostics. Innovations in this field focus on improving image resolution, reducing scan times, and developing specialized imaging protocols for specific medical conditions. These advancements enable better visualization of soft tissues, functional imaging of organs, and early detection of pathological changes, significantly enhancing diagnostic capabilities in healthcare.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMR for material analysis and characterization
NMR spectroscopy is widely used for analyzing the composition, structure, and properties of various materials. This application area includes techniques for studying polymers, catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and other complex substances. Innovations focus on methods to extract more detailed molecular information, analyze heterogeneous samples, and characterize material properties at different scales, providing valuable insights for materials science and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Downhole and field NMR applications
NMR technology has been adapted for use in challenging environments such as oil wells, geological formations, and field settings. These specialized NMR systems are designed to operate under extreme conditions including high pressure, high temperature, and limited space. Innovations in this area focus on ruggedized equipment, simplified operation protocols, and data interpretation algorithms tailored for geophysical exploration, oil and gas characterization, and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in NMR Technology
The NMR application in petrochemical analysis market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by established technologies and steady expansion. The global market size is substantial, driven by increasing demand for precise molecular characterization in petroleum processing. Technologically, NMR spectroscopy has reached high maturity levels with major players like Sinopec, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and PetroChina leading adoption in Asia, while Western companies such as Baker Hughes, Schlumberger, ExxonMobil, and TotalEnergies drive innovation through R&D investments. Academic institutions including Peking University and Southwest Petroleum University collaborate with industry to advance applications in reservoir characterization, product quality control, and process optimization, creating a competitive ecosystem balancing established methodologies with ongoing technological refinements.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced NMR spectroscopy techniques for petrochemical analysis, focusing on high-resolution characterization of complex hydrocarbon mixtures. Their technology employs both 1D and 2D NMR methods to analyze crude oil compositions, with particular emphasis on identifying and quantifying aromatic compounds, asphaltenes, and resins. Sinopec has implemented pulse sequence optimization techniques that enhance signal-to-noise ratios for low-concentration components in petroleum samples. Their integrated NMR platform combines traditional hydrogen and carbon-13 NMR with more specialized techniques like DOSY (Diffusion Ordered Spectroscopy) to separate components based on molecular size and diffusion properties. This approach allows for detailed structural elucidation of complex petroleum fractions without requiring extensive sample preparation or separation procedures. Sinopec has also pioneered the application of solid-state NMR for analyzing catalysts used in refining processes, providing insights into catalyst deactivation mechanisms and optimizing regeneration protocols.
Strengths: Comprehensive integration of multiple NMR techniques provides more complete characterization of complex petroleum samples. Their methods excel at analyzing heavy oil components that are difficult to characterize by other analytical techniques. Weaknesses: Their systems typically require high-field magnets and specialized equipment, increasing operational costs. Some techniques have limited throughput, creating bottlenecks in high-volume testing environments.
Baker Hughes Co.
Technical Solution: Baker Hughes has developed the MagTrak™ LWD NMR service that utilizes nuclear magnetic resonance technology for real-time petrochemical analysis while drilling. Their system employs pulsed NMR techniques to measure hydrogen proton relaxation properties in formation fluids, providing continuous data on porosity, permeability, and fluid typing without requiring core samples. Baker Hughes' proprietary signal processing algorithms can distinguish between different hydrocarbon phases and identify water types based on their unique NMR signatures. The company has also created advanced interpretation models that convert raw NMR measurements into actionable reservoir quality indicators and fluid property estimates. Their technology includes specialized pulse sequences designed to minimize the effects of tool motion during measurement, enabling reliable data acquisition even in challenging drilling environments. Baker Hughes has integrated their NMR capabilities with other logging-while-drilling measurements to create comprehensive formation evaluation packages that optimize well placement and completion design. Their latest innovations include machine learning algorithms that enhance NMR data interpretation by recognizing complex signal patterns associated with specific reservoir conditions.
Strengths: Industry-leading capability for acquiring NMR measurements while drilling, reducing operational time and costs. Their technology provides immediate feedback for geosteering decisions, improving well placement accuracy. Weaknesses: Measurement quality can be affected by severe drilling vibrations and high-angle wellbores. Limited depth of investigation compared to wireline NMR tools, potentially missing features away from the wellbore.
Key Patents and Breakthroughs in Petrochemical NMR
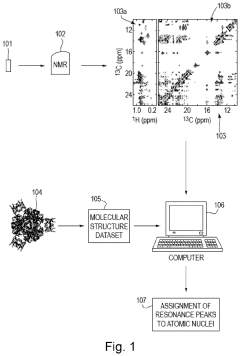
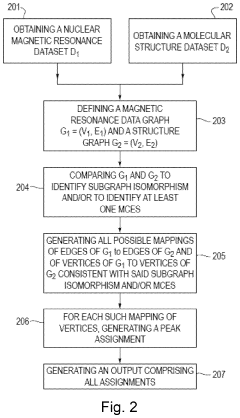
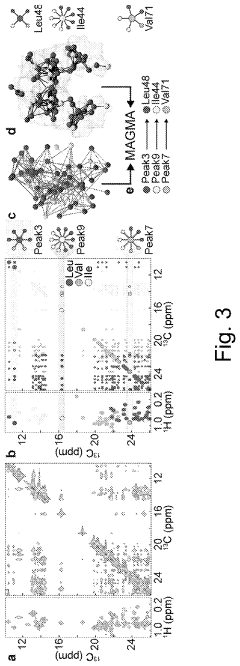
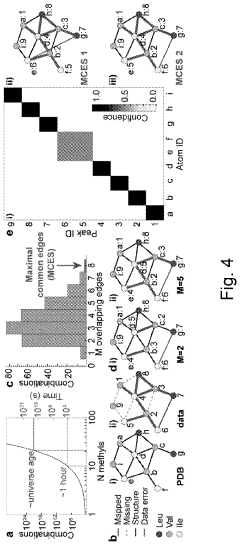
Method for processing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic data
PatentInactiveUS10866295B2
Innovation
- A graph-matching algorithm that combines structural models with experimental multidimensional magnetic resonance data to accurately identify confident and ambiguous peak assignments by comparing experimental distance restraints with structural models, reducing the need for laborious experiments and providing exact sets of plausible assignments.
Environmental Impact Assessment of NMR-Based Analysis
The environmental implications of NMR-based analysis in petrochemical applications represent a significant consideration for industry stakeholders. Traditional petrochemical analysis methods often involve hazardous chemicals, generate substantial waste, and consume large quantities of energy. In contrast, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy offers a more environmentally sustainable alternative with reduced ecological footprint.
NMR techniques require minimal sample preparation and significantly less solvent usage compared to conventional chromatographic methods. Quantitative studies indicate that NMR analysis can reduce solvent consumption by up to 90% for certain petrochemical applications. This dramatic reduction in chemical usage translates to decreased hazardous waste generation and diminished environmental contamination risks associated with disposal processes.
Energy efficiency represents another environmental advantage of modern NMR systems. While older NMR equipment was notorious for high energy consumption due to superconducting magnet requirements, technological advancements have yielded more efficient systems. Contemporary NMR spectrometers incorporate improved cryogenic technologies and power management systems, reducing electricity consumption by approximately 30-40% compared to previous generations.
The non-destructive nature of NMR analysis further enhances its environmental credentials. Samples remain intact after examination, eliminating the need for additional material extraction and processing. This characteristic is particularly valuable for rare or environmentally sensitive petrochemical samples, supporting conservation efforts while maintaining analytical rigor.
Life cycle assessments of NMR-based petrochemical analysis reveal favorable environmental profiles when compared with alternative techniques. The extended operational lifespan of modern NMR equipment—typically 15-20 years with proper maintenance—distributes the environmental impact of manufacturing across a longer period, reducing the cumulative carbon footprint per analysis.
However, challenges remain regarding the environmental impact of helium usage in traditional NMR systems. Helium is a finite resource, and its extraction and processing carry environmental consequences. The industry has responded with the development of helium recycling systems and nitrogen-cooled magnets, though these technologies have not yet achieved widespread implementation in petrochemical applications.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize the environmental benefits of NMR-based analysis. Several jurisdictions now offer incentives for adopting greener analytical technologies, including tax benefits and expedited regulatory approvals for facilities utilizing NMR as their primary analytical method for petrochemical characterization.
NMR techniques require minimal sample preparation and significantly less solvent usage compared to conventional chromatographic methods. Quantitative studies indicate that NMR analysis can reduce solvent consumption by up to 90% for certain petrochemical applications. This dramatic reduction in chemical usage translates to decreased hazardous waste generation and diminished environmental contamination risks associated with disposal processes.
Energy efficiency represents another environmental advantage of modern NMR systems. While older NMR equipment was notorious for high energy consumption due to superconducting magnet requirements, technological advancements have yielded more efficient systems. Contemporary NMR spectrometers incorporate improved cryogenic technologies and power management systems, reducing electricity consumption by approximately 30-40% compared to previous generations.
The non-destructive nature of NMR analysis further enhances its environmental credentials. Samples remain intact after examination, eliminating the need for additional material extraction and processing. This characteristic is particularly valuable for rare or environmentally sensitive petrochemical samples, supporting conservation efforts while maintaining analytical rigor.
Life cycle assessments of NMR-based petrochemical analysis reveal favorable environmental profiles when compared with alternative techniques. The extended operational lifespan of modern NMR equipment—typically 15-20 years with proper maintenance—distributes the environmental impact of manufacturing across a longer period, reducing the cumulative carbon footprint per analysis.
However, challenges remain regarding the environmental impact of helium usage in traditional NMR systems. Helium is a finite resource, and its extraction and processing carry environmental consequences. The industry has responded with the development of helium recycling systems and nitrogen-cooled magnets, though these technologies have not yet achieved widespread implementation in petrochemical applications.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize the environmental benefits of NMR-based analysis. Several jurisdictions now offer incentives for adopting greener analytical technologies, including tax benefits and expedited regulatory approvals for facilities utilizing NMR as their primary analytical method for petrochemical characterization.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning Platforms
The integration of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy with artificial intelligence and machine learning platforms represents a transformative advancement in petrochemical analysis. This convergence enables automated interpretation of complex NMR spectra, significantly reducing analysis time while enhancing accuracy and consistency in molecular characterization of petroleum products.
Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep neural networks, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in pattern recognition within NMR data. These systems can be trained on vast libraries of reference spectra to identify molecular structures and quantify components in complex petrochemical mixtures without human intervention. The application of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has proven especially effective for spectral pattern recognition, while recurrent neural networks (RNNs) excel at analyzing time-domain NMR data.
Recent developments have focused on creating integrated platforms that combine NMR hardware with cloud-based AI processing. These systems enable real-time analysis and decision-making in petrochemical production environments. For instance, refineries can implement continuous monitoring of product quality through NMR analysis with AI interpretation, allowing for immediate process adjustments when deviations are detected.
Transfer learning techniques have emerged as particularly valuable in this domain, allowing AI models trained on general NMR datasets to be fine-tuned for specific petrochemical applications with minimal additional training data. This approach addresses the challenge of limited labeled data in specialized petrochemical contexts while maintaining high analytical performance.
The integration extends beyond mere spectral interpretation to predictive analytics. AI systems can correlate NMR spectral features with downstream product performance characteristics, enabling prediction of properties like octane ratings, viscosity indices, or thermal stability without additional testing. This predictive capability significantly accelerates product development cycles and quality control processes.
Automated workflow systems now incorporate NMR-AI integration for comprehensive sample management, from acquisition scheduling to results reporting. These platforms can prioritize analyses based on production needs, manage instrument parameters, and generate customized reports for different stakeholders in the petrochemical value chain.
Challenges remain in standardizing data formats and ensuring model interpretability. Efforts to develop open-source frameworks for NMR data processing with transparent AI decision pathways are gaining momentum within the industry. These initiatives aim to create explainable AI systems that provide not only analytical results but also confidence metrics and reasoning behind spectral interpretations, critical for regulatory compliance and scientific validation in petrochemical applications.
Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep neural networks, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in pattern recognition within NMR data. These systems can be trained on vast libraries of reference spectra to identify molecular structures and quantify components in complex petrochemical mixtures without human intervention. The application of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has proven especially effective for spectral pattern recognition, while recurrent neural networks (RNNs) excel at analyzing time-domain NMR data.
Recent developments have focused on creating integrated platforms that combine NMR hardware with cloud-based AI processing. These systems enable real-time analysis and decision-making in petrochemical production environments. For instance, refineries can implement continuous monitoring of product quality through NMR analysis with AI interpretation, allowing for immediate process adjustments when deviations are detected.
Transfer learning techniques have emerged as particularly valuable in this domain, allowing AI models trained on general NMR datasets to be fine-tuned for specific petrochemical applications with minimal additional training data. This approach addresses the challenge of limited labeled data in specialized petrochemical contexts while maintaining high analytical performance.
The integration extends beyond mere spectral interpretation to predictive analytics. AI systems can correlate NMR spectral features with downstream product performance characteristics, enabling prediction of properties like octane ratings, viscosity indices, or thermal stability without additional testing. This predictive capability significantly accelerates product development cycles and quality control processes.
Automated workflow systems now incorporate NMR-AI integration for comprehensive sample management, from acquisition scheduling to results reporting. These platforms can prioritize analyses based on production needs, manage instrument parameters, and generate customized reports for different stakeholders in the petrochemical value chain.
Challenges remain in standardizing data formats and ensuring model interpretability. Efforts to develop open-source frameworks for NMR data processing with transparent AI decision pathways are gaining momentum within the industry. These initiatives aim to create explainable AI systems that provide not only analytical results but also confidence metrics and reasoning behind spectral interpretations, critical for regulatory compliance and scientific validation in petrochemical applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!