Carboxylic Acid's Role in Energy-Efficient Materials Science
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Background and Research Objectives
Carboxylic acids have played a pivotal role in the field of materials science for decades, with their unique chemical properties making them invaluable in the development of energy-efficient materials. These organic compounds, characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH), have been the subject of extensive research due to their versatility and potential applications in various industries.
The history of carboxylic acids in materials science can be traced back to the early 20th century when scientists began exploring their potential in polymer synthesis. However, it was not until the late 1960s and early 1970s that researchers started to recognize the significance of carboxylic acids in developing energy-efficient materials. This realization coincided with the growing global awareness of energy conservation and environmental sustainability.
Over the past few decades, the field has witnessed significant advancements in understanding the structure-property relationships of carboxylic acid-based materials. These insights have led to the development of novel materials with enhanced energy efficiency, such as improved thermal insulation, better heat transfer properties, and more efficient energy storage capabilities.
The current research landscape focuses on several key areas where carboxylic acids show promise in energy-efficient materials science. These include the development of advanced polymer composites, smart materials for energy harvesting, and innovative coatings for energy conservation. Additionally, carboxylic acids are being explored for their potential in creating more efficient catalysts for energy-related chemical processes.
One of the primary objectives of ongoing research is to optimize the molecular structure of carboxylic acid-based materials to maximize their energy efficiency. This involves investigating various factors such as chain length, branching, and functional group modifications to tailor the properties of these materials for specific applications.
Another crucial research goal is to develop sustainable and environmentally friendly synthesis methods for carboxylic acid-based materials. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and the need to reduce the environmental impact of material production processes.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the integration of carboxylic acid-based materials with other advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart systems, to create multifunctional materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions and energy demands.
As we look towards the future, the role of carboxylic acids in energy-efficient materials science is expected to expand further. Emerging areas of interest include the development of bio-based carboxylic acids for sustainable materials, the exploration of carboxylic acid-based materials for energy storage applications, and the creation of self-healing materials that can enhance the longevity and efficiency of energy systems.
The history of carboxylic acids in materials science can be traced back to the early 20th century when scientists began exploring their potential in polymer synthesis. However, it was not until the late 1960s and early 1970s that researchers started to recognize the significance of carboxylic acids in developing energy-efficient materials. This realization coincided with the growing global awareness of energy conservation and environmental sustainability.
Over the past few decades, the field has witnessed significant advancements in understanding the structure-property relationships of carboxylic acid-based materials. These insights have led to the development of novel materials with enhanced energy efficiency, such as improved thermal insulation, better heat transfer properties, and more efficient energy storage capabilities.
The current research landscape focuses on several key areas where carboxylic acids show promise in energy-efficient materials science. These include the development of advanced polymer composites, smart materials for energy harvesting, and innovative coatings for energy conservation. Additionally, carboxylic acids are being explored for their potential in creating more efficient catalysts for energy-related chemical processes.
One of the primary objectives of ongoing research is to optimize the molecular structure of carboxylic acid-based materials to maximize their energy efficiency. This involves investigating various factors such as chain length, branching, and functional group modifications to tailor the properties of these materials for specific applications.
Another crucial research goal is to develop sustainable and environmentally friendly synthesis methods for carboxylic acid-based materials. This aligns with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and the need to reduce the environmental impact of material production processes.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the integration of carboxylic acid-based materials with other advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and smart systems, to create multifunctional materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions and energy demands.
As we look towards the future, the role of carboxylic acids in energy-efficient materials science is expected to expand further. Emerging areas of interest include the development of bio-based carboxylic acids for sustainable materials, the exploration of carboxylic acid-based materials for energy storage applications, and the creation of self-healing materials that can enhance the longevity and efficiency of energy systems.
Market Analysis for Energy-Efficient Materials
The market for energy-efficient materials is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing global awareness of environmental issues and the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions. Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in this expanding sector, particularly in the development of advanced materials for energy storage, conversion, and conservation.
In the energy storage domain, carboxylic acid-based materials are gaining traction in the production of high-performance batteries and supercapacitors. The global energy storage market is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, with a considerable portion attributed to materials incorporating carboxylic acids. These materials offer improved energy density, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features, making them attractive for both stationary and mobile energy storage applications.
The energy conversion sector, particularly in solar cells and fuel cells, is another area where carboxylic acid-based materials are making significant inroads. The photovoltaic market continues to expand rapidly, with carboxylic acid derivatives being used to develop more efficient and durable solar cells. Similarly, in fuel cell technology, carboxylic acid-functionalized materials are being explored for their potential to enhance proton conductivity and overall cell performance.
In the realm of energy conservation, carboxylic acids are finding applications in the development of advanced insulation materials and phase change materials (PCMs). The global insulation market is experiencing steady growth, driven by stringent building energy efficiency regulations. Carboxylic acid-based foam insulations and aerogels are emerging as promising alternatives to traditional insulation materials, offering superior thermal performance and reduced environmental impact.
The market for PCMs, where carboxylic acids play a significant role, is also expanding. These materials are increasingly being used in building materials, textiles, and thermal management systems to regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption. The growing demand for smart and energy-efficient buildings is a key driver for this market segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in the adoption of energy-efficient materials, including those based on carboxylic acids. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
Key market players in this space include both established chemical companies and innovative startups. Major chemical corporations are investing heavily in research and development of carboxylic acid-based energy-efficient materials, while startups are focusing on niche applications and novel synthesis methods.
The market for energy-efficient materials, particularly those utilizing carboxylic acids, faces some challenges, including high initial costs and the need for further technological advancements. However, ongoing research, supportive government policies, and increasing consumer awareness are expected to drive continued growth and innovation in this sector.
In the energy storage domain, carboxylic acid-based materials are gaining traction in the production of high-performance batteries and supercapacitors. The global energy storage market is projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, with a considerable portion attributed to materials incorporating carboxylic acids. These materials offer improved energy density, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features, making them attractive for both stationary and mobile energy storage applications.
The energy conversion sector, particularly in solar cells and fuel cells, is another area where carboxylic acid-based materials are making significant inroads. The photovoltaic market continues to expand rapidly, with carboxylic acid derivatives being used to develop more efficient and durable solar cells. Similarly, in fuel cell technology, carboxylic acid-functionalized materials are being explored for their potential to enhance proton conductivity and overall cell performance.
In the realm of energy conservation, carboxylic acids are finding applications in the development of advanced insulation materials and phase change materials (PCMs). The global insulation market is experiencing steady growth, driven by stringent building energy efficiency regulations. Carboxylic acid-based foam insulations and aerogels are emerging as promising alternatives to traditional insulation materials, offering superior thermal performance and reduced environmental impact.
The market for PCMs, where carboxylic acids play a significant role, is also expanding. These materials are increasingly being used in building materials, textiles, and thermal management systems to regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption. The growing demand for smart and energy-efficient buildings is a key driver for this market segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in the adoption of energy-efficient materials, including those based on carboxylic acids. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
Key market players in this space include both established chemical companies and innovative startups. Major chemical corporations are investing heavily in research and development of carboxylic acid-based energy-efficient materials, while startups are focusing on niche applications and novel synthesis methods.
The market for energy-efficient materials, particularly those utilizing carboxylic acids, faces some challenges, including high initial costs and the need for further technological advancements. However, ongoing research, supportive government policies, and increasing consumer awareness are expected to drive continued growth and innovation in this sector.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Applications
Despite the widespread use of carboxylic acids in materials science, particularly in energy-efficient applications, several challenges persist that hinder their full potential. One of the primary obstacles is the limited thermal stability of carboxylic acids, which restricts their use in high-temperature environments. This limitation is particularly problematic in applications such as heat storage materials and thermal insulation, where maintaining structural integrity under elevated temperatures is crucial.
Another significant challenge lies in the control of carboxylic acid reactivity. While their reactive nature is beneficial for many applications, it can also lead to undesired side reactions or degradation of materials over time. This issue is particularly evident in the development of durable coatings and long-lasting energy storage devices, where stability and longevity are paramount.
The solubility of carboxylic acids in various solvents presents both opportunities and challenges. While their solubility allows for easy processing and incorporation into materials, it can also lead to leaching and loss of functionality in certain applications. This is especially problematic in water-based systems or in environments with high humidity, where the acids may dissolve and migrate, reducing the effectiveness of the material.
Furthermore, the scalability of carboxylic acid-based materials remains a significant hurdle. Many promising laboratory-scale results have been difficult to translate into large-scale industrial production. This challenge is often related to issues of cost, process complexity, and maintaining consistent quality across larger batches.
The environmental impact of carboxylic acids and their derivatives is also a growing concern. While many are biodegradable, the production processes and potential release of these compounds into the environment during the lifecycle of materials need careful consideration. Developing greener synthesis routes and ensuring the safe disposal or recycling of carboxylic acid-containing materials are ongoing challenges.
Lastly, the optimization of carboxylic acid functionalities for specific energy-efficient applications remains a complex task. Tailoring the molecular structure to achieve the desired properties while maintaining overall material performance is a delicate balance. This challenge is particularly evident in the development of advanced phase change materials and energy storage systems, where precise control over melting points, enthalpy of fusion, and thermal conductivity is required.
Another significant challenge lies in the control of carboxylic acid reactivity. While their reactive nature is beneficial for many applications, it can also lead to undesired side reactions or degradation of materials over time. This issue is particularly evident in the development of durable coatings and long-lasting energy storage devices, where stability and longevity are paramount.
The solubility of carboxylic acids in various solvents presents both opportunities and challenges. While their solubility allows for easy processing and incorporation into materials, it can also lead to leaching and loss of functionality in certain applications. This is especially problematic in water-based systems or in environments with high humidity, where the acids may dissolve and migrate, reducing the effectiveness of the material.
Furthermore, the scalability of carboxylic acid-based materials remains a significant hurdle. Many promising laboratory-scale results have been difficult to translate into large-scale industrial production. This challenge is often related to issues of cost, process complexity, and maintaining consistent quality across larger batches.
The environmental impact of carboxylic acids and their derivatives is also a growing concern. While many are biodegradable, the production processes and potential release of these compounds into the environment during the lifecycle of materials need careful consideration. Developing greener synthesis routes and ensuring the safe disposal or recycling of carboxylic acid-containing materials are ongoing challenges.
Lastly, the optimization of carboxylic acid functionalities for specific energy-efficient applications remains a complex task. Tailoring the molecular structure to achieve the desired properties while maintaining overall material performance is a delicate balance. This challenge is particularly evident in the development of advanced phase change materials and energy storage systems, where precise control over melting points, enthalpy of fusion, and thermal conductivity is required.
Existing Carboxylic Acid-Based Solutions
01 Improved catalytic processes for carboxylic acid production
Advanced catalytic methods are being developed to enhance the energy efficiency of carboxylic acid production. These processes often involve novel catalyst designs or optimized reaction conditions to reduce energy consumption and improve yield. Such improvements can significantly decrease the overall energy footprint of carboxylic acid manufacturing.- Improved catalytic processes for carboxylic acid production: Advanced catalytic methods are being developed to enhance the energy efficiency of carboxylic acid production. These processes often involve novel catalyst designs or optimized reaction conditions that reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving yield. Such improvements can significantly lower the overall energy footprint of carboxylic acid manufacturing.
- Energy-efficient purification and separation techniques: Innovative purification and separation methods are being implemented to reduce energy consumption in carboxylic acid processing. These techniques may include advanced distillation processes, membrane technologies, or crystallization methods that require less energy input while effectively isolating and purifying carboxylic acids from reaction mixtures.
- Waste heat recovery and process integration: Integrating waste heat recovery systems and optimizing process flows can significantly improve the energy efficiency of carboxylic acid production. This approach involves capturing and reusing thermal energy from various stages of the production process, as well as designing more efficient heat exchange networks to minimize overall energy consumption.
- Renewable feedstocks and bio-based production routes: Exploring the use of renewable feedstocks and developing bio-based production routes for carboxylic acids can lead to improved energy efficiency. These approaches often involve fermentation processes or the conversion of biomass-derived precursors, which can be less energy-intensive than traditional petrochemical routes.
- Process intensification and continuous flow technologies: Implementing process intensification techniques and continuous flow technologies can enhance the energy efficiency of carboxylic acid production. These approaches often involve miniaturized reactors, improved mixing strategies, and optimized reaction conditions that allow for better heat and mass transfer, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved product quality.
02 Energy-efficient purification and separation techniques
Innovative purification and separation methods are being implemented to reduce energy consumption in carboxylic acid processing. These techniques may include advanced distillation processes, membrane separation, or crystallization methods that require less energy input while maintaining high product purity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Waste heat recovery and process integration
Integration of waste heat recovery systems and process optimization strategies are being employed to improve overall energy efficiency in carboxylic acid production. This approach involves capturing and reusing thermal energy from various stages of the production process, thereby reducing the need for external energy inputs.Expand Specific Solutions04 Renewable feedstocks and bio-based production methods
Research is focused on developing energy-efficient processes for producing carboxylic acids from renewable feedstocks. These bio-based methods often utilize enzymatic or microbial processes that operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to traditional petrochemical routes, resulting in reduced energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process intensification and continuous flow technologies
Implementation of process intensification techniques and continuous flow technologies is enhancing energy efficiency in carboxylic acid production. These approaches often involve miniaturized reactors, improved heat and mass transfer, and optimized reaction conditions, leading to reduced energy requirements and improved product yields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The field of carboxylic acid's role in energy-efficient materials science is in a growth phase, with increasing market potential as sustainability becomes a global priority. The market size is expanding, driven by demand for eco-friendly materials across industries. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Evonik Operations GmbH and Wanhua Chemical Group are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in specialty chemicals. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Tech University and East China Normal University contribute significantly to research and development. Collaborations between industry leaders like Toyota Motor Corp. and research institutions are accelerating innovation, pushing the boundaries of energy-efficient materials applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has made significant strides in utilizing carboxylic acids for energy-efficient materials. They have developed a range of specialty carboxylic acids for use in high-performance coatings and adhesives, which contribute to energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications[7]. Evonik's research also extends to carboxylic acid-based phase change materials for thermal energy storage, offering innovative solutions for energy management in construction and automotive sectors[8]. Furthermore, they have pioneered the use of carboxylic acid-functionalized silica nanoparticles in advanced lubricants, reducing friction and improving energy efficiency in mechanical systems[9].
Strengths: Diverse portfolio of specialty chemicals, strong focus on customer-specific solutions. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks for some products, potential environmental concerns.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has been at the forefront of utilizing carboxylic acid-based materials in energy-efficient automotive applications. Their research has led to the development of novel electrolyte additives containing carboxylic acid groups for lithium-ion batteries, significantly improving battery life and performance[4]. Toyota has also pioneered the use of carboxylic acid-functionalized carbon nanotubes in fuel cell catalysts, enhancing efficiency and durability[5]. Additionally, they have developed lightweight, high-strength composite materials incorporating carboxylic acid-modified fibers for vehicle body parts, contributing to overall fuel efficiency[6].
Strengths: Strong integration of materials science with automotive applications, extensive resources for research and development. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on automotive sector, potentially limiting broader applications.
Innovative Carboxylic Acid Technologies
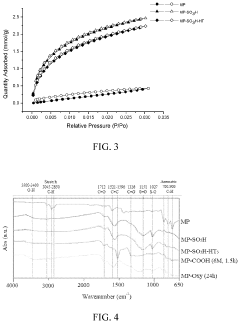
Carbon dioxide adsorbent
PatentActiveUS20240207814A1
Innovation
- A carbonaceous material with high surface coverage of acidic functional groups, specifically covalently linked to the edges of hexagonal carbon networks, enhancing hydrolytic efficiency and CO2 capture capabilities through modifications using sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or hypochlorite salt treatments, resulting in a nonporous structure with increased acid site density and specific surface area.
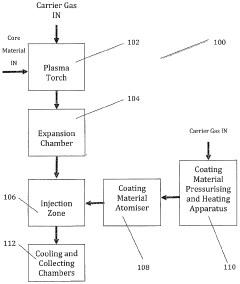
Fine particles
PatentWO2010073021A1
Innovation
- The production of fine particles with a core and a coating of organic molecules using thermal plasma processes, which reduces agglomeration and oxidation, maintaining high surface energy and purity, and allowing for efficient dispersion without the need for dispersants.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of carboxylic acid's role in energy-efficient materials science reveals both positive and negative implications. On the positive side, the development of energy-efficient materials incorporating carboxylic acids contributes significantly to reducing overall energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. These materials, when applied in construction, transportation, and industrial processes, lead to improved energy efficiency and decreased carbon footprints.
Carboxylic acid-based materials often exhibit enhanced durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing waste generation. This extended lifespan of products and structures translates to reduced resource extraction and manufacturing processes, further mitigating environmental stress.
However, the production and use of carboxylic acids in materials science are not without environmental concerns. The synthesis of these compounds often involves petrochemical feedstocks and energy-intensive processes, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from their application in energy-efficient materials.
Water pollution is another potential issue, as carboxylic acids can be water-soluble and may leach into aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. This necessitates careful consideration of disposal methods and potential environmental contamination throughout the lifecycle of carboxylic acid-based materials.
Biodegradability is a crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact. While some carboxylic acids are naturally occurring and readily biodegradable, others may persist in the environment, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and affecting wildlife. Research into developing more environmentally friendly alternatives and improving biodegradability is ongoing.
The use of carboxylic acids in energy-efficient materials also raises concerns about potential air quality impacts. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during production, application, or degradation of these materials may contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to humans and ecosystems.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) play a critical role in evaluating the overall environmental impact of carboxylic acid-based energy-efficient materials. These assessments consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life disposal. LCAs help identify areas for improvement and guide the development of more sustainable practices in the field.
In conclusion, while carboxylic acids offer significant potential for advancing energy-efficient materials science, their environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Balancing the benefits of improved energy efficiency against potential environmental risks requires ongoing research, innovation, and careful management throughout the entire lifecycle of these materials.
Carboxylic acid-based materials often exhibit enhanced durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing waste generation. This extended lifespan of products and structures translates to reduced resource extraction and manufacturing processes, further mitigating environmental stress.
However, the production and use of carboxylic acids in materials science are not without environmental concerns. The synthesis of these compounds often involves petrochemical feedstocks and energy-intensive processes, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from their application in energy-efficient materials.
Water pollution is another potential issue, as carboxylic acids can be water-soluble and may leach into aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. This necessitates careful consideration of disposal methods and potential environmental contamination throughout the lifecycle of carboxylic acid-based materials.
Biodegradability is a crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact. While some carboxylic acids are naturally occurring and readily biodegradable, others may persist in the environment, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and affecting wildlife. Research into developing more environmentally friendly alternatives and improving biodegradability is ongoing.
The use of carboxylic acids in energy-efficient materials also raises concerns about potential air quality impacts. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during production, application, or degradation of these materials may contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to humans and ecosystems.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) play a critical role in evaluating the overall environmental impact of carboxylic acid-based energy-efficient materials. These assessments consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life disposal. LCAs help identify areas for improvement and guide the development of more sustainable practices in the field.
In conclusion, while carboxylic acids offer significant potential for advancing energy-efficient materials science, their environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Balancing the benefits of improved energy efficiency against potential environmental risks requires ongoing research, innovation, and careful management throughout the entire lifecycle of these materials.
Intellectual Property Landscape
The intellectual property landscape surrounding carboxylic acid's role in energy-efficient materials science is characterized by a diverse array of patents and ongoing research initiatives. Major chemical companies and academic institutions have been actively filing patents related to the application of carboxylic acids in various energy-efficient materials and processes.
One significant area of patent activity focuses on the use of carboxylic acids in the development of advanced thermal insulation materials. These patents often describe novel formulations incorporating carboxylic acids to enhance the thermal properties of insulation, resulting in improved energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications. Companies like BASF, Dow Chemical, and 3M have been particularly active in this domain.
Another prominent trend in the patent landscape involves the application of carboxylic acids in energy storage technologies. Patents in this area typically cover innovations in battery electrolytes, where carboxylic acids are utilized to improve the performance and longevity of lithium-ion and other advanced battery systems. Key players in this field include Tesla, Panasonic, and LG Chem.
The use of carboxylic acids in the development of energy-efficient catalysts has also seen significant patent activity. These patents often describe novel catalyst designs incorporating carboxylic acid functional groups to enhance selectivity and reduce energy consumption in various chemical processes. Companies like ExxonMobil and Shell have been at the forefront of these innovations.
In the realm of renewable energy, patents related to carboxylic acids in solar cell technologies have gained traction. These innovations typically focus on using carboxylic acid derivatives to improve the efficiency and stability of organic photovoltaic materials. Universities and research institutions, such as MIT and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, have been particularly active in this area.
The geographical distribution of patent filings shows a concentration in the United States, Japan, and Europe, with China rapidly emerging as a significant player in recent years. This reflects the global nature of research and development efforts in energy-efficient materials science.
It's worth noting that many patents in this field are part of larger patent families, indicating the international scope of protection sought by inventors and companies. Cross-licensing agreements and patent pools are also becoming increasingly common, facilitating collaboration and technology sharing in this rapidly evolving field.
One significant area of patent activity focuses on the use of carboxylic acids in the development of advanced thermal insulation materials. These patents often describe novel formulations incorporating carboxylic acids to enhance the thermal properties of insulation, resulting in improved energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications. Companies like BASF, Dow Chemical, and 3M have been particularly active in this domain.
Another prominent trend in the patent landscape involves the application of carboxylic acids in energy storage technologies. Patents in this area typically cover innovations in battery electrolytes, where carboxylic acids are utilized to improve the performance and longevity of lithium-ion and other advanced battery systems. Key players in this field include Tesla, Panasonic, and LG Chem.
The use of carboxylic acids in the development of energy-efficient catalysts has also seen significant patent activity. These patents often describe novel catalyst designs incorporating carboxylic acid functional groups to enhance selectivity and reduce energy consumption in various chemical processes. Companies like ExxonMobil and Shell have been at the forefront of these innovations.
In the realm of renewable energy, patents related to carboxylic acids in solar cell technologies have gained traction. These innovations typically focus on using carboxylic acid derivatives to improve the efficiency and stability of organic photovoltaic materials. Universities and research institutions, such as MIT and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, have been particularly active in this area.
The geographical distribution of patent filings shows a concentration in the United States, Japan, and Europe, with China rapidly emerging as a significant player in recent years. This reflects the global nature of research and development efforts in energy-efficient materials science.
It's worth noting that many patents in this field are part of larger patent families, indicating the international scope of protection sought by inventors and companies. Cross-licensing agreements and patent pools are also becoming increasingly common, facilitating collaboration and technology sharing in this rapidly evolving field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!