Developing Antiviral Materials with Sulphanilic Acid Derivatives
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Antiviral Materials Development Background and Objectives
The development of antiviral materials has become increasingly crucial in the face of global health challenges, with sulphanilic acid derivatives emerging as a promising avenue for research. This field has evolved significantly over the past decades, driven by the need to combat various viral threats, from seasonal influenza to more severe pandemics. The journey of antiviral material development began with simple chemical compounds and has progressed to sophisticated, targeted molecules designed to disrupt specific viral mechanisms.
Sulphanilic acid, a versatile organic compound, has garnered attention due to its potential in creating effective antiviral materials. Its derivatives offer a wide range of possibilities for tailoring antiviral properties, making it an attractive starting point for researchers. The exploration of these derivatives builds upon a rich history of sulfonamide drugs, which have been used in medical treatments since the 1930s.
The current technological landscape is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining insights from virology, materials science, and medicinal chemistry. This convergence of fields has accelerated the pace of innovation, allowing for more precise and effective antiviral strategies. Recent advancements in computational modeling and high-throughput screening techniques have further enhanced the ability to design and test potential antiviral compounds derived from sulphanilic acid.
The primary objective of developing antiviral materials with sulphanilic acid derivatives is to create a new generation of materials capable of inhibiting viral replication, attachment, or entry into host cells. These materials aim to offer broad-spectrum antiviral activity while maintaining low toxicity and minimal side effects. Additionally, researchers seek to develop materials that can be easily incorporated into various products, from personal protective equipment to surface coatings, thereby expanding the range of preventive measures against viral infections.
Another critical goal is to address the challenge of viral resistance, which has become increasingly problematic with existing antiviral drugs. By exploring novel sulphanilic acid derivatives, scientists hope to discover compounds that viruses are less likely to develop resistance against, ensuring long-term efficacy of antiviral treatments and preventive measures.
The development of these materials also aims to contribute to global pandemic preparedness. By creating a diverse arsenal of antiviral compounds, researchers seek to establish a foundation for rapid response to emerging viral threats. This proactive approach aligns with the broader objective of enhancing public health resilience and reducing the economic and social impacts of future outbreaks.
Sulphanilic acid, a versatile organic compound, has garnered attention due to its potential in creating effective antiviral materials. Its derivatives offer a wide range of possibilities for tailoring antiviral properties, making it an attractive starting point for researchers. The exploration of these derivatives builds upon a rich history of sulfonamide drugs, which have been used in medical treatments since the 1930s.
The current technological landscape is characterized by a multidisciplinary approach, combining insights from virology, materials science, and medicinal chemistry. This convergence of fields has accelerated the pace of innovation, allowing for more precise and effective antiviral strategies. Recent advancements in computational modeling and high-throughput screening techniques have further enhanced the ability to design and test potential antiviral compounds derived from sulphanilic acid.
The primary objective of developing antiviral materials with sulphanilic acid derivatives is to create a new generation of materials capable of inhibiting viral replication, attachment, or entry into host cells. These materials aim to offer broad-spectrum antiviral activity while maintaining low toxicity and minimal side effects. Additionally, researchers seek to develop materials that can be easily incorporated into various products, from personal protective equipment to surface coatings, thereby expanding the range of preventive measures against viral infections.
Another critical goal is to address the challenge of viral resistance, which has become increasingly problematic with existing antiviral drugs. By exploring novel sulphanilic acid derivatives, scientists hope to discover compounds that viruses are less likely to develop resistance against, ensuring long-term efficacy of antiviral treatments and preventive measures.
The development of these materials also aims to contribute to global pandemic preparedness. By creating a diverse arsenal of antiviral compounds, researchers seek to establish a foundation for rapid response to emerging viral threats. This proactive approach aligns with the broader objective of enhancing public health resilience and reducing the economic and social impacts of future outbreaks.
Market Analysis for Antiviral Materials
The market for antiviral materials has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing global health concerns and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The demand for effective antiviral solutions spans various sectors, including healthcare, consumer goods, and industrial applications. Sulphanilic acid derivatives, known for their potential antiviral properties, are emerging as promising candidates in this expanding market.
In the healthcare sector, antiviral materials incorporating sulphanilic acid derivatives are being explored for use in medical devices, personal protective equipment (PPE), and surface coatings for hospitals and clinics. The global healthcare PPE market, a key segment for antiviral materials, is projected to maintain steady growth in the coming years as healthcare facilities prioritize infection control measures.
The consumer goods industry has also shown increased interest in antiviral materials, particularly for household products, textiles, and packaging. Consumers are becoming more health-conscious and seeking products with added protection against viruses. This trend has led to the development of antiviral coatings and treatments for everyday items, creating new opportunities for sulphanilic acid derivative-based solutions.
In the industrial sector, antiviral materials are gaining traction in public spaces, transportation, and workplace environments. The need for enhanced safety measures in these areas has driven demand for antiviral coatings on high-touch surfaces, air filtration systems, and other applications where viral transmission is a concern.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be a key growth driver for the antiviral materials market, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices. North America and Europe also represent significant market opportunities, with established healthcare systems and stringent safety regulations driving adoption of advanced antiviral solutions.
However, the market for antiviral materials faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles, the need for extensive testing and validation, and competition from alternative technologies. Manufacturers developing sulphanilic acid derivative-based antiviral materials must navigate these obstacles while demonstrating the efficacy and safety of their products.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for antiviral materials remains positive. The ongoing research and development in sulphanilic acid derivatives for antiviral applications are likely to yield innovative products that address evolving market needs. As the global focus on health and safety continues, the demand for effective antiviral materials is expected to sustain growth across multiple industries in the foreseeable future.
In the healthcare sector, antiviral materials incorporating sulphanilic acid derivatives are being explored for use in medical devices, personal protective equipment (PPE), and surface coatings for hospitals and clinics. The global healthcare PPE market, a key segment for antiviral materials, is projected to maintain steady growth in the coming years as healthcare facilities prioritize infection control measures.
The consumer goods industry has also shown increased interest in antiviral materials, particularly for household products, textiles, and packaging. Consumers are becoming more health-conscious and seeking products with added protection against viruses. This trend has led to the development of antiviral coatings and treatments for everyday items, creating new opportunities for sulphanilic acid derivative-based solutions.
In the industrial sector, antiviral materials are gaining traction in public spaces, transportation, and workplace environments. The need for enhanced safety measures in these areas has driven demand for antiviral coatings on high-touch surfaces, air filtration systems, and other applications where viral transmission is a concern.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be a key growth driver for the antiviral materials market, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices. North America and Europe also represent significant market opportunities, with established healthcare systems and stringent safety regulations driving adoption of advanced antiviral solutions.
However, the market for antiviral materials faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles, the need for extensive testing and validation, and competition from alternative technologies. Manufacturers developing sulphanilic acid derivative-based antiviral materials must navigate these obstacles while demonstrating the efficacy and safety of their products.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for antiviral materials remains positive. The ongoing research and development in sulphanilic acid derivatives for antiviral applications are likely to yield innovative products that address evolving market needs. As the global focus on health and safety continues, the demand for effective antiviral materials is expected to sustain growth across multiple industries in the foreseeable future.
Current State and Challenges in Antiviral Material Research
The field of antiviral material research has seen significant advancements in recent years, particularly in the development of materials incorporating sulphanilic acid derivatives. Currently, researchers are exploring various approaches to enhance the efficacy and versatility of these materials in combating viral infections.
One of the primary focuses in this area is the synthesis and modification of sulphanilic acid derivatives to improve their antiviral properties. Scientists have made progress in developing compounds that exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity against both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. These materials show promise in inhibiting viral entry, replication, and release mechanisms.
However, several challenges persist in the development of effective antiviral materials. One major hurdle is the rapid mutation rate of viruses, which can lead to resistance against existing antiviral agents. Researchers are working on strategies to create materials that can adapt to viral mutations or target conserved regions of viral structures to overcome this challenge.
Another significant challenge lies in the biocompatibility and toxicity of antiviral materials. While sulphanilic acid derivatives have shown promising antiviral activity, ensuring their safety for human use remains a critical concern. Scientists are investigating ways to minimize potential side effects and improve the selectivity of these materials towards viral targets.
The integration of sulphanilic acid derivatives into various material platforms is an active area of research. Efforts are being made to incorporate these compounds into polymers, nanoparticles, and surface coatings to create multifunctional antiviral materials. This approach aims to combine the antiviral properties of sulphanilic acid derivatives with other desirable characteristics such as durability, ease of application, and long-lasting effectiveness.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness present additional challenges in the development of antiviral materials. Researchers are exploring efficient synthesis methods and optimizing production processes to make these materials more accessible and economically viable for widespread use.
The current state of antiviral material research also involves the investigation of synergistic effects between sulphanilic acid derivatives and other antiviral agents. Combining these materials with existing antiviral drugs or natural compounds may lead to enhanced efficacy and reduced likelihood of viral resistance.
Lastly, the development of smart antiviral materials that can respond to specific environmental triggers or viral presence is an emerging area of interest. These materials could potentially offer targeted and controlled release of antiviral agents, improving their effectiveness and reducing unnecessary exposure.
One of the primary focuses in this area is the synthesis and modification of sulphanilic acid derivatives to improve their antiviral properties. Scientists have made progress in developing compounds that exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity against both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. These materials show promise in inhibiting viral entry, replication, and release mechanisms.
However, several challenges persist in the development of effective antiviral materials. One major hurdle is the rapid mutation rate of viruses, which can lead to resistance against existing antiviral agents. Researchers are working on strategies to create materials that can adapt to viral mutations or target conserved regions of viral structures to overcome this challenge.
Another significant challenge lies in the biocompatibility and toxicity of antiviral materials. While sulphanilic acid derivatives have shown promising antiviral activity, ensuring their safety for human use remains a critical concern. Scientists are investigating ways to minimize potential side effects and improve the selectivity of these materials towards viral targets.
The integration of sulphanilic acid derivatives into various material platforms is an active area of research. Efforts are being made to incorporate these compounds into polymers, nanoparticles, and surface coatings to create multifunctional antiviral materials. This approach aims to combine the antiviral properties of sulphanilic acid derivatives with other desirable characteristics such as durability, ease of application, and long-lasting effectiveness.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness present additional challenges in the development of antiviral materials. Researchers are exploring efficient synthesis methods and optimizing production processes to make these materials more accessible and economically viable for widespread use.
The current state of antiviral material research also involves the investigation of synergistic effects between sulphanilic acid derivatives and other antiviral agents. Combining these materials with existing antiviral drugs or natural compounds may lead to enhanced efficacy and reduced likelihood of viral resistance.
Lastly, the development of smart antiviral materials that can respond to specific environmental triggers or viral presence is an emerging area of interest. These materials could potentially offer targeted and controlled release of antiviral agents, improving their effectiveness and reducing unnecessary exposure.
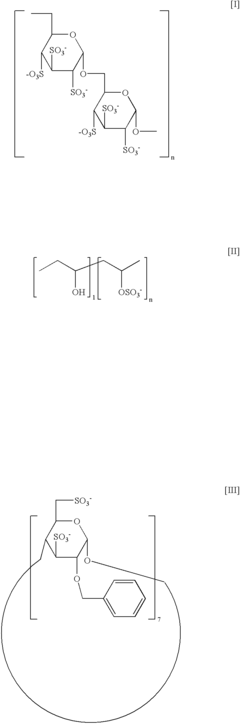
Existing Sulphanilic Acid Derivative Antiviral Solutions
01 Synthesis of sulphanilic acid derivatives
Various methods for synthesizing sulphanilic acid derivatives are described. These processes involve different reaction conditions, starting materials, and catalysts to produce a range of sulphanilic acid-based compounds with diverse applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and agrochemicals.- Synthesis of sulphanilic acid derivatives: Various methods for synthesizing sulphanilic acid derivatives are described, including different reaction conditions and starting materials. These processes aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of these compounds.
- Applications in dye industry: Sulphanilic acid derivatives are widely used in the dye industry as intermediates or precursors for the production of various dyes. These compounds contribute to the development of new colors and improved dyeing properties for different materials.
- Pharmaceutical applications: Certain sulphanilic acid derivatives exhibit pharmaceutical properties and are used in the development of drugs. These compounds may have potential applications in treating various diseases or conditions, showcasing their importance in medicinal chemistry.
- Use in polymer and material science: Sulphanilic acid derivatives play a role in polymer and material science, being used as monomers, additives, or modifiers in the production of various materials. They can enhance specific properties of polymers or contribute to the development of new materials with desired characteristics.
- Environmental and industrial applications: Some sulphanilic acid derivatives find applications in environmental and industrial processes, such as water treatment, catalysis, or as components in specialized industrial products. These compounds may contribute to improved efficiency or sustainability in various industrial sectors.
02 Use of sulphanilic acid derivatives in dye production
Sulphanilic acid derivatives are utilized as important intermediates in the production of dyes and pigments. These compounds contribute to the creation of various color shades and improve the stability and fastness properties of the final dye products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pharmaceutical applications of sulphanilic acid derivatives
Sulphanilic acid derivatives have been explored for their potential therapeutic properties. These compounds are investigated for their use in developing new drugs, particularly in areas such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic treatments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sulphanilic acid derivatives in agrochemical formulations
The use of sulphanilic acid derivatives in agrochemical formulations is described. These compounds are incorporated into pesticides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators, contributing to improved crop protection and agricultural productivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel sulphanilic acid derivatives and their applications
Research on developing new sulphanilic acid derivatives with enhanced properties is ongoing. These novel compounds are being explored for their potential applications in various fields, including electronics, materials science, and environmental remediation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Antiviral Material Industry
The development of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives is in a nascent stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is expanding due to increased demand for advanced antiviral solutions across various industries. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are making strides in research and development. Companies like BASF Corp., Ajinomoto Co., Inc., and Cipla Ltd. are leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing and pharmaceuticals to explore innovative applications. Academic institutions such as Oregon State University and the Ocean University of China are contributing to fundamental research. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical companies and emerging biotech firms vying for market share, indicating a dynamic and promising future for this technology.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed innovative antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives. Their approach involves incorporating these derivatives into polymer matrices to create functional coatings and films with enhanced antiviral properties. The company has utilized its expertise in chemical synthesis to modify sulphanilic acid, improving its compatibility with various polymers and increasing its antiviral efficacy[1]. BASF's technology focuses on creating stable, long-lasting antiviral surfaces that can be applied to a wide range of products, from medical devices to consumer goods. The company has also invested in advanced testing methods to validate the antiviral performance of their materials against different types of viruses, including enveloped and non-enveloped varieties[2].
Strengths: Extensive chemical expertise, large-scale production capabilities, and a diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges and the need for extensive safety testing of new materials.
Cipla Ltd.
Technical Solution: Cipla Ltd. has focused on developing antiviral drug formulations incorporating sulphanilic acid derivatives. Their approach leverages the company's pharmaceutical expertise to create novel antiviral compounds with improved efficacy and reduced side effects. Cipla's research has centered on modifying sulphanilic acid to enhance its antiviral properties while maintaining good bioavailability and safety profiles[3]. The company has explored various drug delivery systems, including nanoparticle formulations, to optimize the performance of these sulphanilic acid-based antivirals. Cipla has also conducted extensive clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness of their formulations against a range of viral infections, particularly focusing on respiratory viruses[4].
Strengths: Strong pharmaceutical R&D capabilities and established presence in global markets. Weaknesses: Lengthy drug approval processes and potential competition from other antiviral treatments.
Core Innovations in Sulphanilic Acid-Based Antivirals
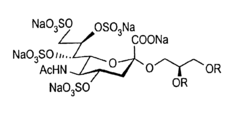
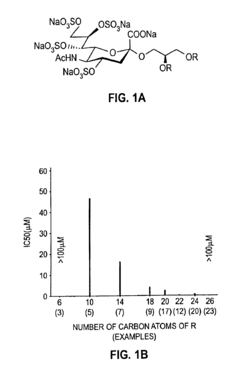
Compounds having antiviral activity
PatentInactiveUS6835720B2
Innovation
- Development of sulfated nonulonic acid derivatives with all hydroxyl groups sulfated, specifically targeting the anomeric position of monosaccharide-lipid or nonulonic acid moieties with O-glycosidic, S-glycosidic, or amide linkages, and branched lipid structures to create compounds with reduced anticoagulant activity and lower cytotoxicity for effective anti-HIV activity.
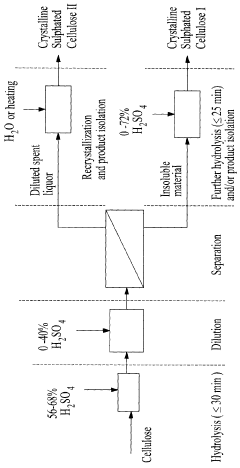
Crystalline sulphated cellulose ii and its production from sulphuric acid hydrolysis of celulose
PatentWO2010127451A1
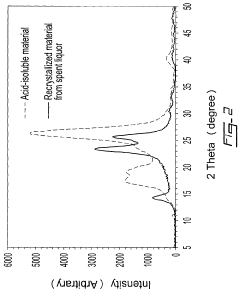
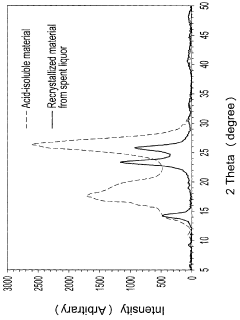
Innovation
- A process involving dilution of spent liquors from sulphuric acid hydrolysis, followed by separation and recrystallization, allows for the isolation of crystalline sulphated cellulose II and concurrently produces crystalline sulphated cellulose I, using dilution with an aqueous diluent and subsequent heating or addition to water to precipitate the cellulose materials.
Regulatory Framework for Antiviral Materials
The regulatory framework for antiviral materials, particularly those developed using sulphanilic acid derivatives, is a complex and evolving landscape. At the international level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provide guidelines that influence national regulatory policies. These guidelines cover various aspects of antiviral material development, including safety assessments, efficacy studies, and quality control measures.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating antiviral materials. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) oversees the approval process for new antiviral drugs and materials. For sulphanilic acid derivatives used in antiviral applications, developers must adhere to the FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, followed by New Drug Application (NDA) submissions. This process involves rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) governs the regulatory framework for antiviral materials in the European Union. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) evaluates applications for marketing authorization. Developers of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives must comply with the EU's Clinical Trials Regulation and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines.
In Asia, regulatory bodies such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) have their own specific requirements for antiviral material approval. These agencies often collaborate with international counterparts to harmonize regulatory standards, facilitating global development and distribution of antiviral materials.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the development of antiviral materials. Agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) impose strict guidelines on the production, use, and disposal of chemical compounds, including sulphanilic acid derivatives. Developers must ensure compliance with regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the US.
Intellectual property protection is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Patent offices worldwide, including the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and the European Patent Office (EPO), provide mechanisms for protecting novel antiviral materials and their manufacturing processes. Developers must navigate these systems to secure and maintain patent rights for their innovations in sulphanilic acid-based antiviral materials.
As the field of antiviral materials continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology and advanced materials science, may necessitate new regulatory approaches. Developers of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives must stay informed about these changes and adapt their development strategies accordingly to ensure compliance and successful market entry.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating antiviral materials. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) oversees the approval process for new antiviral drugs and materials. For sulphanilic acid derivatives used in antiviral applications, developers must adhere to the FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, followed by New Drug Application (NDA) submissions. This process involves rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) governs the regulatory framework for antiviral materials in the European Union. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) evaluates applications for marketing authorization. Developers of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives must comply with the EU's Clinical Trials Regulation and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines.
In Asia, regulatory bodies such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) have their own specific requirements for antiviral material approval. These agencies often collaborate with international counterparts to harmonize regulatory standards, facilitating global development and distribution of antiviral materials.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the development of antiviral materials. Agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) impose strict guidelines on the production, use, and disposal of chemical compounds, including sulphanilic acid derivatives. Developers must ensure compliance with regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the US.
Intellectual property protection is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Patent offices worldwide, including the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and the European Patent Office (EPO), provide mechanisms for protecting novel antiviral materials and their manufacturing processes. Developers must navigate these systems to secure and maintain patent rights for their innovations in sulphanilic acid-based antiviral materials.
As the field of antiviral materials continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology and advanced materials science, may necessitate new regulatory approaches. Developers of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives must stay informed about these changes and adapt their development strategies accordingly to ensure compliance and successful market entry.
Environmental Impact of Antiviral Material Production
The production of antiviral materials using sulphanilic acid derivatives presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of environmental impact. The synthesis process typically involves multiple steps, including sulfonation, nitration, and reduction reactions, which can generate significant amounts of waste and potentially harmful byproducts. However, advancements in green chemistry principles are driving efforts to minimize these environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the use of solvents in the production process. Traditional methods often rely on organic solvents, which can be toxic and contribute to air and water pollution. Recent research has focused on developing alternative solvent systems, such as aqueous or supercritical CO2-based processes, which offer reduced environmental footprints. These approaches not only decrease the release of volatile organic compounds but also improve the overall sustainability of the manufacturing process.
The energy consumption associated with antiviral material production is another critical factor. The synthesis of sulphanilic acid derivatives often requires elevated temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy demands. To address this issue, researchers are exploring catalytic methods that can lower reaction temperatures and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities can further mitigate the carbon footprint of these processes.
Waste management is a significant challenge in the production of antiviral materials. The generation of byproducts and unreacted starting materials necessitates effective treatment and disposal strategies. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane filtration and chromatography, are being employed to recover and recycle valuable components, thereby reducing waste streams. Furthermore, the development of closed-loop systems aims to minimize the release of pollutants into the environment.
The environmental impact of raw material sourcing for sulphanilic acid derivatives is also a consideration. Efforts are underway to identify sustainable feedstocks and develop bio-based alternatives to petrochemical precursors. This shift towards renewable resources not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also potentially decreases the overall environmental burden of antiviral material production.
Lifecycle assessment studies are increasingly being conducted to evaluate the full environmental impact of antiviral materials from cradle to grave. These assessments consider factors such as resource depletion, greenhouse gas emissions, and ecotoxicity throughout the entire product lifecycle. By identifying hotspots in the production chain, manufacturers can target specific areas for improvement and implement more sustainable practices.
As regulations surrounding environmental protection become more stringent, the antiviral material industry is adapting by investing in cleaner technologies and production methods. This includes the adoption of continuous flow chemistry, which offers improved process control and reduced waste generation compared to traditional batch processes. Such innovations not only address environmental concerns but also often lead to enhanced product quality and production efficiency.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the use of solvents in the production process. Traditional methods often rely on organic solvents, which can be toxic and contribute to air and water pollution. Recent research has focused on developing alternative solvent systems, such as aqueous or supercritical CO2-based processes, which offer reduced environmental footprints. These approaches not only decrease the release of volatile organic compounds but also improve the overall sustainability of the manufacturing process.
The energy consumption associated with antiviral material production is another critical factor. The synthesis of sulphanilic acid derivatives often requires elevated temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy demands. To address this issue, researchers are exploring catalytic methods that can lower reaction temperatures and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities can further mitigate the carbon footprint of these processes.
Waste management is a significant challenge in the production of antiviral materials. The generation of byproducts and unreacted starting materials necessitates effective treatment and disposal strategies. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane filtration and chromatography, are being employed to recover and recycle valuable components, thereby reducing waste streams. Furthermore, the development of closed-loop systems aims to minimize the release of pollutants into the environment.
The environmental impact of raw material sourcing for sulphanilic acid derivatives is also a consideration. Efforts are underway to identify sustainable feedstocks and develop bio-based alternatives to petrochemical precursors. This shift towards renewable resources not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also potentially decreases the overall environmental burden of antiviral material production.
Lifecycle assessment studies are increasingly being conducted to evaluate the full environmental impact of antiviral materials from cradle to grave. These assessments consider factors such as resource depletion, greenhouse gas emissions, and ecotoxicity throughout the entire product lifecycle. By identifying hotspots in the production chain, manufacturers can target specific areas for improvement and implement more sustainable practices.
As regulations surrounding environmental protection become more stringent, the antiviral material industry is adapting by investing in cleaner technologies and production methods. This includes the adoption of continuous flow chemistry, which offers improved process control and reduced waste generation compared to traditional batch processes. Such innovations not only address environmental concerns but also often lead to enhanced product quality and production efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!