Dimethyl Ether's Contribution to Circular Economy Models
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Technology Background and Objectives
Dimethyl ether (DME) has emerged as a promising alternative fuel and chemical feedstock, gaining significant attention in recent years due to its potential to contribute to circular economy models. The technology behind DME production and utilization has evolved considerably over the past few decades, driven by the need for cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
DME's journey began in the early 20th century when it was first synthesized, but its potential as a fuel and chemical intermediate was not fully recognized until the late 1990s. Since then, research and development efforts have focused on improving production processes, expanding applications, and addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional fossil fuels.
The primary objective of DME technology in the context of circular economy models is to create a closed-loop system where waste materials and renewable resources are utilized to produce a versatile and environmentally friendly compound. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and promoting sustainable resource management.
One of the key technological advancements in DME production has been the development of efficient synthesis methods using various feedstocks. Traditional DME production relies on natural gas or coal as raw materials, but recent innovations have enabled the use of biomass, industrial waste gases, and even captured CO2. This diversification of feedstocks is crucial for enhancing the circular nature of DME production and reducing its environmental footprint.
The evolution of DME technology has also seen improvements in catalytic processes, reactor designs, and purification techniques. These advancements have led to increased production efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and higher product quality. As a result, DME has become more competitive with conventional fuels and chemicals in terms of both cost and performance.
In the context of circular economy models, DME technology aims to address several critical challenges. These include the need for carbon-neutral or carbon-negative fuel alternatives, the utilization of waste streams from various industries, and the development of flexible energy storage solutions. By tackling these issues, DME technology contributes to the broader objectives of sustainability and resource efficiency.
Looking ahead, the technological goals for DME in circular economy applications include further optimization of production processes, expansion of feedstock options, and development of novel applications. Researchers and industry players are exploring innovative approaches such as direct synthesis of DME from syngas, integration with carbon capture and utilization systems, and the use of renewable electricity for DME production through power-to-gas technologies.
DME's journey began in the early 20th century when it was first synthesized, but its potential as a fuel and chemical intermediate was not fully recognized until the late 1990s. Since then, research and development efforts have focused on improving production processes, expanding applications, and addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional fossil fuels.
The primary objective of DME technology in the context of circular economy models is to create a closed-loop system where waste materials and renewable resources are utilized to produce a versatile and environmentally friendly compound. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and promoting sustainable resource management.
One of the key technological advancements in DME production has been the development of efficient synthesis methods using various feedstocks. Traditional DME production relies on natural gas or coal as raw materials, but recent innovations have enabled the use of biomass, industrial waste gases, and even captured CO2. This diversification of feedstocks is crucial for enhancing the circular nature of DME production and reducing its environmental footprint.
The evolution of DME technology has also seen improvements in catalytic processes, reactor designs, and purification techniques. These advancements have led to increased production efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and higher product quality. As a result, DME has become more competitive with conventional fuels and chemicals in terms of both cost and performance.
In the context of circular economy models, DME technology aims to address several critical challenges. These include the need for carbon-neutral or carbon-negative fuel alternatives, the utilization of waste streams from various industries, and the development of flexible energy storage solutions. By tackling these issues, DME technology contributes to the broader objectives of sustainability and resource efficiency.
Looking ahead, the technological goals for DME in circular economy applications include further optimization of production processes, expansion of feedstock options, and development of novel applications. Researchers and industry players are exploring innovative approaches such as direct synthesis of DME from syngas, integration with carbon capture and utilization systems, and the use of renewable electricity for DME production through power-to-gas technologies.
Circular Economy Market Analysis for DME
The circular economy market for Dimethyl Ether (DME) is experiencing significant growth as industries and governments worldwide shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. DME, a clean-burning, non-toxic fuel and chemical feedstock, is increasingly recognized for its potential to contribute to circular economy models across various sectors.
In the energy sector, DME is gaining traction as a renewable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. Its production from biomass and waste materials aligns with circular economy principles by utilizing resources that would otherwise be discarded. The market for DME as a transportation fuel is particularly promising, with several countries in Asia and Europe implementing policies to promote its use in heavy-duty vehicles and public transportation.
The chemical industry represents another key market for DME in circular economy models. As a versatile chemical intermediate, DME can be used to produce a wide range of products, including plastics, solvents, and aerosol propellants. The ability to synthesize DME from recycled carbon dioxide and renewable hydrogen further enhances its circular economy credentials, offering a pathway to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and close the carbon loop in industrial processes.
Agriculture and waste management sectors are also driving demand for DME in circular economy applications. The production of DME from agricultural residues and municipal solid waste not only provides a solution for waste valorization but also creates a valuable energy product. This dual benefit is attracting investment in biogas-to-DME technologies, particularly in regions with abundant biomass resources and stringent waste management regulations.
The global market size for DME in circular economy applications is projected to grow substantially over the next decade. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and growing consumer demand for sustainable products. Asia-Pacific currently leads the market, driven by strong government support and rapid industrialization in countries like China and India.
However, the market faces challenges that could impact its growth trajectory. These include the need for significant infrastructure investments, competition from other alternative fuels, and the current reliance on fossil-based feedstocks for a large portion of DME production. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in circular economy models.
Despite these challenges, the outlook for DME in the circular economy market remains positive. Technological advancements in production processes, coupled with supportive policy frameworks, are expected to drive innovation and market expansion. As industries continue to seek sustainable solutions, DME's versatility and environmental benefits position it as a key player in the transition towards a more circular and sustainable economy.
In the energy sector, DME is gaining traction as a renewable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. Its production from biomass and waste materials aligns with circular economy principles by utilizing resources that would otherwise be discarded. The market for DME as a transportation fuel is particularly promising, with several countries in Asia and Europe implementing policies to promote its use in heavy-duty vehicles and public transportation.
The chemical industry represents another key market for DME in circular economy models. As a versatile chemical intermediate, DME can be used to produce a wide range of products, including plastics, solvents, and aerosol propellants. The ability to synthesize DME from recycled carbon dioxide and renewable hydrogen further enhances its circular economy credentials, offering a pathway to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and close the carbon loop in industrial processes.
Agriculture and waste management sectors are also driving demand for DME in circular economy applications. The production of DME from agricultural residues and municipal solid waste not only provides a solution for waste valorization but also creates a valuable energy product. This dual benefit is attracting investment in biogas-to-DME technologies, particularly in regions with abundant biomass resources and stringent waste management regulations.
The global market size for DME in circular economy applications is projected to grow substantially over the next decade. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and growing consumer demand for sustainable products. Asia-Pacific currently leads the market, driven by strong government support and rapid industrialization in countries like China and India.
However, the market faces challenges that could impact its growth trajectory. These include the need for significant infrastructure investments, competition from other alternative fuels, and the current reliance on fossil-based feedstocks for a large portion of DME production. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in circular economy models.
Despite these challenges, the outlook for DME in the circular economy market remains positive. Technological advancements in production processes, coupled with supportive policy frameworks, are expected to drive innovation and market expansion. As industries continue to seek sustainable solutions, DME's versatility and environmental benefits position it as a key player in the transition towards a more circular and sustainable economy.
DME Production Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promising potential of dimethyl ether (DME) in circular economy models, its production faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the high energy consumption associated with DME synthesis. The conventional production process, which involves methanol dehydration or direct synthesis from syngas, requires significant thermal energy inputs, leading to increased production costs and carbon footprint.
Raw material availability and cost also pose significant challenges. While DME can be produced from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, the fluctuating prices and supply of these resources can impact the economic viability of DME production. Additionally, the use of fossil fuel-based feedstocks contradicts the circular economy principles, necessitating a shift towards more sustainable alternatives.
The catalysts used in DME production present another limitation. Current catalysts often suffer from rapid deactivation and limited selectivity, resulting in reduced efficiency and increased operational costs. Developing more stable and selective catalysts remains a critical area of research to enhance DME production processes.
Infrastructure constraints further hinder the widespread adoption of DME. The lack of dedicated distribution networks and storage facilities limits its accessibility and increases transportation costs. Retrofitting existing infrastructure or building new systems specifically for DME handling and distribution requires substantial investments.
Regulatory hurdles and policy uncertainties also impact DME production and utilization. The absence of clear standards and regulations for DME as a fuel or chemical feedstock in many regions creates barriers to market entry and commercialization. Harmonizing regulations and establishing consistent quality standards across different markets is essential for fostering DME adoption.
The competition from established alternative fuels and chemicals presents another challenge. DME must demonstrate clear advantages in terms of cost, performance, and environmental impact to displace incumbent products in various applications. Overcoming market inertia and gaining consumer acceptance requires extensive education and awareness campaigns.
Scaling up DME production to meet potential demand while maintaining economic viability remains a significant hurdle. Current production capacities are limited, and expanding them requires substantial capital investments. Balancing production scale with market demand and ensuring consistent product quality across different plant sizes pose ongoing challenges for manufacturers.
Addressing these challenges and limitations requires a multifaceted approach involving technological innovations, policy support, and market development strategies. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in contributing to circular economy models and sustainable development goals.
Raw material availability and cost also pose significant challenges. While DME can be produced from various feedstocks, including natural gas, coal, and biomass, the fluctuating prices and supply of these resources can impact the economic viability of DME production. Additionally, the use of fossil fuel-based feedstocks contradicts the circular economy principles, necessitating a shift towards more sustainable alternatives.
The catalysts used in DME production present another limitation. Current catalysts often suffer from rapid deactivation and limited selectivity, resulting in reduced efficiency and increased operational costs. Developing more stable and selective catalysts remains a critical area of research to enhance DME production processes.
Infrastructure constraints further hinder the widespread adoption of DME. The lack of dedicated distribution networks and storage facilities limits its accessibility and increases transportation costs. Retrofitting existing infrastructure or building new systems specifically for DME handling and distribution requires substantial investments.
Regulatory hurdles and policy uncertainties also impact DME production and utilization. The absence of clear standards and regulations for DME as a fuel or chemical feedstock in many regions creates barriers to market entry and commercialization. Harmonizing regulations and establishing consistent quality standards across different markets is essential for fostering DME adoption.
The competition from established alternative fuels and chemicals presents another challenge. DME must demonstrate clear advantages in terms of cost, performance, and environmental impact to displace incumbent products in various applications. Overcoming market inertia and gaining consumer acceptance requires extensive education and awareness campaigns.
Scaling up DME production to meet potential demand while maintaining economic viability remains a significant hurdle. Current production capacities are limited, and expanding them requires substantial capital investments. Balancing production scale with market demand and ensuring consistent product quality across different plant sizes pose ongoing challenges for manufacturers.
Addressing these challenges and limitations requires a multifaceted approach involving technological innovations, policy support, and market development strategies. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for realizing the full potential of DME in contributing to circular economy models and sustainable development goals.
Current DME Production Methods
01 Production of dimethyl ether
Various methods for producing dimethyl ether are described, including catalytic dehydration of methanol, direct synthesis from syngas, and conversion of other hydrocarbons. These processes often involve specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize yield and selectivity.- Production of dimethyl ether: Various methods for producing dimethyl ether are described, including catalytic dehydration of methanol, direct synthesis from syngas, and conversion of other hydrocarbons. These processes often involve specific catalysts and reaction conditions to optimize yield and selectivity.
- Catalysts for dimethyl ether synthesis: Different types of catalysts are used in the production of dimethyl ether, including zeolites, metal oxides, and composite catalysts. The choice of catalyst can significantly affect the reaction efficiency, product selectivity, and overall process economics.
- Applications of dimethyl ether: Dimethyl ether has various applications, including use as a fuel substitute, propellant, refrigerant, and chemical intermediate. Its properties make it suitable for use in diesel engines, aerosol products, and as a feedstock for other chemical processes.
- Purification and separation of dimethyl ether: Methods for purifying and separating dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These processes may involve distillation, adsorption, or membrane separation techniques to obtain high-purity dimethyl ether.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of dimethyl ether production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on emissions reduction, handling procedures, and risk assessments associated with its storage and transportation.
02 Catalysts for dimethyl ether synthesis
Different types of catalysts are used in the production of dimethyl ether, including zeolites, metal oxides, and composite catalysts. The choice of catalyst can significantly affect the reaction efficiency, product selectivity, and overall process economics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether has various applications, including use as a fuel additive, aerosol propellant, and refrigerant. It is also being explored as an alternative clean fuel for diesel engines and power generation due to its favorable combustion properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and separation of dimethyl ether
Techniques for purifying and separating dimethyl ether from reaction mixtures or other compounds are crucial in its production process. These may include distillation, adsorption, and membrane separation methods to achieve high-purity dimethyl ether.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of dimethyl ether production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on emissions reduction, handling procedures, and storage requirements to ensure safe and sustainable utilization of dimethyl ether.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DME Industry
The dimethyl ether (DME) market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing interest in circular economy models and alternative fuels. The global DME market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with key players like DuPont de Nemours, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij BV leading innovation efforts. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with established processes for DME production from methanol, but ongoing research into direct synthesis from CO2 and biomass. Universities and research institutes, such as the University of Southern California and the Chinese Academy of Science Guangzhou Energy Research Institute, are actively contributing to advancing DME technologies, particularly in areas of sustainability and process efficiency.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has been actively researching and developing technologies to integrate DME into circular economy models. Their approach focuses on the production of bio-based DME from renewable feedstocks, particularly lignocellulosic biomass[18]. DuPont has developed advanced enzymatic and chemical processes to convert biomass into DME, potentially reducing the carbon footprint of DME production[19]. The company has also explored the use of DME as a green solvent in various industrial processes, aiming to replace more environmentally harmful solvents[20]. Additionally, DuPont has invested in research to use DME as a precursor for the production of other valuable chemicals, such as acetic acid and methyl acetate, which could lead to more sustainable chemical manufacturing processes[21]. The company has also been investigating the potential of DME in aerosol propellant applications, as a more environmentally friendly alternative to current propellants[22].
Strengths: Focus on bio-based DME production, exploration of DME as a green solvent, and potential for sustainable chemical manufacturing. Weaknesses: Possible challenges in scaling up bio-based DME production to meet large-scale industrial demands.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a comprehensive approach to integrating dimethyl ether (DME) into circular economy models. Their strategy involves producing DME from various feedstocks, including coal, natural gas, and biomass, thus promoting resource efficiency[1]. Sinopec has implemented large-scale DME production facilities, with an annual capacity exceeding 1 million tons[2]. The company has also focused on developing DME as a clean-burning alternative fuel for vehicles and household cooking, contributing to reduced emissions and improved air quality[3]. Furthermore, Sinopec has invested in research to explore DME's potential in chemical synthesis, particularly as a methanol alternative, which could lead to more sustainable production processes in the chemical industry[4].
Strengths: Diverse feedstock utilization, large-scale production capabilities, and multiple application areas. Weaknesses: Dependence on fossil fuel feedstocks for some production routes, potential competition with other alternative fuels.
DME Circular Economy Innovations
Energy supply method and system
PatentWO2006004140A1
Innovation
- The introduction of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a versatile energy circulation medium, which can be derived from biomass, waste, and petroleum residues, and used for power generation, transportation, and heating, allowing for efficient energy storage and distribution without relying on pipelines, and enabling the conversion of waste heat into usable energy.
Energy supply method and system
PatentInactiveEP1780859A1
Innovation
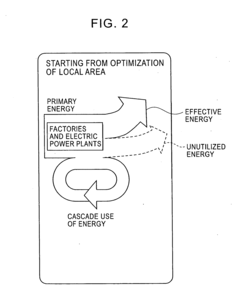
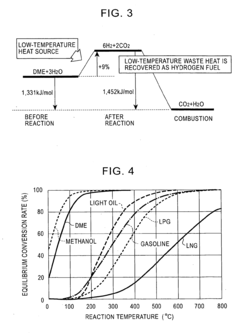
- The method involves recovering sensible heat from power generators and transport devices as H2 or CO + H2 through reforming dimethyl ether (DME) or methanol, and using these gases as fuel or chemical raw materials within an energy supply and demand grid, allowing for interconnection of grids and storage, thereby enabling efficient energy distribution and utilization.
Environmental Impact Assessment of DME
The environmental impact assessment of Dimethyl Ether (DME) as a contributor to circular economy models reveals both positive and negative aspects. On the positive side, DME production from renewable sources, such as biomass or captured CO2, can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels. When produced from waste materials or by-products, DME aligns well with circular economy principles by valorizing resources that might otherwise be discarded.
DME's clean-burning properties result in lower particulate matter and NOx emissions when used as a fuel, particularly in diesel engines. This characteristic makes it an attractive alternative for reducing air pollution in urban areas and improving overall air quality. Additionally, DME's potential as a hydrogen carrier for fuel cells offers a pathway to further reduce emissions in transportation and stationary power applications.
However, the environmental impact of DME production varies greatly depending on the feedstock and production method. When derived from fossil fuels, such as natural gas or coal, the lifecycle emissions can be comparable to or even higher than conventional fuels. The energy-intensive nature of some DME production processes also raises concerns about overall energy efficiency and associated emissions.
Land use changes and potential competition with food crops are significant considerations when DME is produced from biomass feedstocks. Large-scale production could lead to deforestation or displacement of food production, impacting biodiversity and food security. Water consumption and potential contamination during the production process are additional environmental factors that require careful management.
The infrastructure requirements for DME distribution and use also have environmental implications. While DME can utilize existing LPG infrastructure to some extent, widespread adoption would necessitate new or modified storage, transportation, and fueling systems. The environmental impact of these infrastructure changes must be weighed against the potential benefits of DME adoption.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, DME's relatively simple chemical structure allows for easier decomposition compared to more complex fuels. This characteristic potentially reduces the environmental burden of waste management and aligns with circular economy principles of designing out waste and pollution.
Overall, the environmental impact assessment of DME in circular economy models highlights its potential as a cleaner alternative fuel, particularly when produced from renewable or waste sources. However, careful consideration of production methods, feedstock selection, and infrastructure development is crucial to ensure that DME contributes positively to sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
DME's clean-burning properties result in lower particulate matter and NOx emissions when used as a fuel, particularly in diesel engines. This characteristic makes it an attractive alternative for reducing air pollution in urban areas and improving overall air quality. Additionally, DME's potential as a hydrogen carrier for fuel cells offers a pathway to further reduce emissions in transportation and stationary power applications.
However, the environmental impact of DME production varies greatly depending on the feedstock and production method. When derived from fossil fuels, such as natural gas or coal, the lifecycle emissions can be comparable to or even higher than conventional fuels. The energy-intensive nature of some DME production processes also raises concerns about overall energy efficiency and associated emissions.
Land use changes and potential competition with food crops are significant considerations when DME is produced from biomass feedstocks. Large-scale production could lead to deforestation or displacement of food production, impacting biodiversity and food security. Water consumption and potential contamination during the production process are additional environmental factors that require careful management.
The infrastructure requirements for DME distribution and use also have environmental implications. While DME can utilize existing LPG infrastructure to some extent, widespread adoption would necessitate new or modified storage, transportation, and fueling systems. The environmental impact of these infrastructure changes must be weighed against the potential benefits of DME adoption.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, DME's relatively simple chemical structure allows for easier decomposition compared to more complex fuels. This characteristic potentially reduces the environmental burden of waste management and aligns with circular economy principles of designing out waste and pollution.
Overall, the environmental impact assessment of DME in circular economy models highlights its potential as a cleaner alternative fuel, particularly when produced from renewable or waste sources. However, careful consideration of production methods, feedstock selection, and infrastructure development is crucial to ensure that DME contributes positively to sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
Policy Framework for DME in Circular Economy
The policy framework for Dimethyl Ether (DME) in circular economy models is crucial for promoting its adoption and maximizing its potential benefits. A comprehensive policy approach should address multiple aspects of DME production, distribution, and utilization within the circular economy context.
Regulatory support is essential for establishing DME as a viable alternative fuel. Governments should implement policies that incentivize the production and use of DME, such as tax credits, subsidies, or mandates for blending DME with conventional fuels. These measures can help overcome initial market barriers and accelerate the transition to more sustainable energy sources.
Environmental regulations play a significant role in promoting DME adoption. Policies should focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality by encouraging the use of DME as a cleaner-burning fuel. This may include stricter emissions standards for vehicles and industrial processes, which can indirectly boost DME demand.
Infrastructure development is another critical area for policy intervention. Governments should invest in or provide incentives for the construction of DME production facilities, storage tanks, and distribution networks. This infrastructure support is essential for ensuring a reliable supply chain and making DME more accessible to end-users.
Research and development policies are vital for advancing DME technology and its applications in circular economy models. Funding programs, grants, and public-private partnerships should be established to support innovation in DME production methods, particularly those utilizing renewable feedstocks or waste materials.
Standardization and certification processes are necessary to ensure the quality and safety of DME products. Policymakers should work with industry stakeholders to develop and implement uniform standards for DME production, storage, and use across different applications.
Education and awareness campaigns should be part of the policy framework to inform businesses and consumers about the benefits of DME in circular economy models. This can include training programs for industry professionals and public outreach initiatives to increase acceptance and adoption of DME technologies.
International cooperation is essential for creating a global market for DME. Policies should promote cross-border collaboration in research, technology transfer, and trade agreements to facilitate the growth of the DME industry on a global scale.
By implementing a comprehensive policy framework that addresses these key areas, governments can create an enabling environment for DME to contribute significantly to circular economy models, fostering sustainable development and resource efficiency.
Regulatory support is essential for establishing DME as a viable alternative fuel. Governments should implement policies that incentivize the production and use of DME, such as tax credits, subsidies, or mandates for blending DME with conventional fuels. These measures can help overcome initial market barriers and accelerate the transition to more sustainable energy sources.
Environmental regulations play a significant role in promoting DME adoption. Policies should focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality by encouraging the use of DME as a cleaner-burning fuel. This may include stricter emissions standards for vehicles and industrial processes, which can indirectly boost DME demand.
Infrastructure development is another critical area for policy intervention. Governments should invest in or provide incentives for the construction of DME production facilities, storage tanks, and distribution networks. This infrastructure support is essential for ensuring a reliable supply chain and making DME more accessible to end-users.
Research and development policies are vital for advancing DME technology and its applications in circular economy models. Funding programs, grants, and public-private partnerships should be established to support innovation in DME production methods, particularly those utilizing renewable feedstocks or waste materials.
Standardization and certification processes are necessary to ensure the quality and safety of DME products. Policymakers should work with industry stakeholders to develop and implement uniform standards for DME production, storage, and use across different applications.
Education and awareness campaigns should be part of the policy framework to inform businesses and consumers about the benefits of DME in circular economy models. This can include training programs for industry professionals and public outreach initiatives to increase acceptance and adoption of DME technologies.
International cooperation is essential for creating a global market for DME. Policies should promote cross-border collaboration in research, technology transfer, and trade agreements to facilitate the growth of the DME industry on a global scale.
By implementing a comprehensive policy framework that addresses these key areas, governments can create an enabling environment for DME to contribute significantly to circular economy models, fostering sustainable development and resource efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!