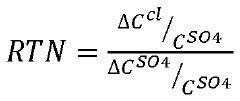Direct Lithium Extraction vs Evaporation Ponds: Environmental Impact
SEP 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Extraction Evolution and Objectives
Lithium extraction has undergone significant evolution since its commercial inception in the 1950s. Initially, lithium was primarily obtained from hard rock mining of spodumene deposits, a labor-intensive and environmentally disruptive process. The 1970s marked a pivotal shift with the development of evaporation pond technology in South America's "Lithium Triangle" (Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia), where lithium-rich brine could be concentrated through solar evaporation. This method became the dominant extraction approach due to its relatively low operational costs despite requiring extensive land use and water consumption.
The early 2000s witnessed growing environmental concerns regarding traditional extraction methods, coinciding with exponential growth in lithium demand driven by the rechargeable battery market. This market pressure catalyzed research into more sustainable extraction technologies, leading to the emergence of Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) techniques around 2010. These innovative approaches promised significantly reduced environmental footprints through selective lithium recovery from brines without extensive evaporation requirements.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving DLE efficiency and scalability, with notable progress in ion-exchange materials, membrane technologies, and electrochemical systems. The industry has gradually shifted from viewing lithium merely as a commodity to recognizing it as a strategic resource critical for the clean energy transition, necessitating more responsible extraction practices.
The primary objective of modern lithium extraction technology development is achieving a balance between meeting rapidly growing global demand and minimizing environmental impact. Specific technical goals include reducing water consumption by at least 70% compared to traditional evaporation methods, decreasing land footprint requirements by over 90%, and shortening extraction timeframes from months to days or hours.
Additional objectives include developing processes that can effectively extract lithium from lower-concentration sources previously considered uneconomical, improving recovery rates from the current industry average of 40-50% to potentially 80-90%, and reducing chemical reagent usage in processing. These advancements aim to support the projected quadrupling of lithium demand by 2030 while adhering to increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide.
The evolution trajectory suggests a future where hybrid approaches combining the economic benefits of traditional methods with the environmental advantages of newer technologies may become the industry standard, particularly as lithium becomes increasingly central to global decarbonization efforts and energy security strategies.
The early 2000s witnessed growing environmental concerns regarding traditional extraction methods, coinciding with exponential growth in lithium demand driven by the rechargeable battery market. This market pressure catalyzed research into more sustainable extraction technologies, leading to the emergence of Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) techniques around 2010. These innovative approaches promised significantly reduced environmental footprints through selective lithium recovery from brines without extensive evaporation requirements.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving DLE efficiency and scalability, with notable progress in ion-exchange materials, membrane technologies, and electrochemical systems. The industry has gradually shifted from viewing lithium merely as a commodity to recognizing it as a strategic resource critical for the clean energy transition, necessitating more responsible extraction practices.
The primary objective of modern lithium extraction technology development is achieving a balance between meeting rapidly growing global demand and minimizing environmental impact. Specific technical goals include reducing water consumption by at least 70% compared to traditional evaporation methods, decreasing land footprint requirements by over 90%, and shortening extraction timeframes from months to days or hours.
Additional objectives include developing processes that can effectively extract lithium from lower-concentration sources previously considered uneconomical, improving recovery rates from the current industry average of 40-50% to potentially 80-90%, and reducing chemical reagent usage in processing. These advancements aim to support the projected quadrupling of lithium demand by 2030 while adhering to increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide.
The evolution trajectory suggests a future where hybrid approaches combining the economic benefits of traditional methods with the environmental advantages of newer technologies may become the industry standard, particularly as lithium becomes increasingly central to global decarbonization efforts and energy security strategies.
Global Market Demand for Sustainable Lithium
The global lithium market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by the rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production and renewable energy storage systems. Annual demand for lithium is projected to increase from approximately 500,000 metric tons of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) in 2021 to over 3 million metric tons by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20%. This surge is primarily fueled by the automotive sector's transition to electrification, with major markets including China, Europe, and North America leading adoption rates.
Sustainability concerns have become increasingly central to lithium procurement strategies. Major automotive manufacturers including Tesla, Volkswagen Group, and BMW have publicly committed to sourcing lithium through environmentally responsible methods, with several implementing supplier certification requirements focused on water usage, carbon emissions, and land disturbance metrics. These corporate policies are reshaping supply chain dynamics and creating premium market segments for sustainably produced lithium.
Consumer awareness regarding battery material sourcing has shown significant growth, with recent market research indicating that 67% of potential EV buyers in developed markets consider environmental impact in purchasing decisions. This consumer preference is translating into market pressure for transparent supply chains and environmentally responsible extraction methods, creating differentiation opportunities for lithium producers employing sustainable practices.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to prioritize sustainable extraction methods. The European Union's proposed Battery Regulation includes mandatory carbon footprint declarations and responsible sourcing requirements, while Chile and Argentina have implemented stricter water usage regulations in lithium-rich regions. These regulatory developments are creating structural market advantages for low-impact extraction technologies.
Investment patterns reflect this sustainability focus, with venture capital and corporate investment in Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technologies reaching $1.2 billion in 2022, a threefold increase from 2020 levels. Major mining companies including Rio Tinto, Albemarle, and SQM have announced strategic investments in alternative extraction technologies, signaling industry recognition of both market demand and regulatory pressure for sustainable production methods.
Price premiums for sustainably produced lithium are emerging in certain market segments, particularly among premium automotive manufacturers and consumer electronics companies with strong environmental commitments. Early market indicators suggest price differentials of 5-10% for lithium produced with significantly reduced environmental footprints, though this remains an evolving market dynamic dependent on supply-demand balance and certification standards.
Sustainability concerns have become increasingly central to lithium procurement strategies. Major automotive manufacturers including Tesla, Volkswagen Group, and BMW have publicly committed to sourcing lithium through environmentally responsible methods, with several implementing supplier certification requirements focused on water usage, carbon emissions, and land disturbance metrics. These corporate policies are reshaping supply chain dynamics and creating premium market segments for sustainably produced lithium.
Consumer awareness regarding battery material sourcing has shown significant growth, with recent market research indicating that 67% of potential EV buyers in developed markets consider environmental impact in purchasing decisions. This consumer preference is translating into market pressure for transparent supply chains and environmentally responsible extraction methods, creating differentiation opportunities for lithium producers employing sustainable practices.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to prioritize sustainable extraction methods. The European Union's proposed Battery Regulation includes mandatory carbon footprint declarations and responsible sourcing requirements, while Chile and Argentina have implemented stricter water usage regulations in lithium-rich regions. These regulatory developments are creating structural market advantages for low-impact extraction technologies.
Investment patterns reflect this sustainability focus, with venture capital and corporate investment in Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technologies reaching $1.2 billion in 2022, a threefold increase from 2020 levels. Major mining companies including Rio Tinto, Albemarle, and SQM have announced strategic investments in alternative extraction technologies, signaling industry recognition of both market demand and regulatory pressure for sustainable production methods.
Price premiums for sustainably produced lithium are emerging in certain market segments, particularly among premium automotive manufacturers and consumer electronics companies with strong environmental commitments. Early market indicators suggest price differentials of 5-10% for lithium produced with significantly reduced environmental footprints, though this remains an evolving market dynamic dependent on supply-demand balance and certification standards.
DLE vs Evaporation: Technical Challenges
Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) and traditional evaporation pond methods represent contrasting approaches to lithium production, each facing distinct technical challenges. Evaporation ponds, while established technology, suffer from significant inefficiencies including lengthy processing times of 18-24 months, weather dependency, and low recovery rates typically between 30-50%. These systems also struggle with lithium purity, often requiring additional processing steps to remove contaminants like magnesium and boron.
Water consumption presents another major challenge for evaporation ponds, requiring approximately 500,000 gallons per ton of lithium produced. This intensive water usage becomes particularly problematic in arid regions where lithium brine deposits are commonly found, creating competition with agricultural and community needs in already water-stressed environments.
DLE technologies, though promising, face their own set of technical hurdles. Selectivity remains a primary challenge, as most extraction materials struggle to efficiently separate lithium from similarly sized ions like sodium and magnesium in complex brine compositions. This selectivity issue directly impacts economic viability by increasing processing costs and reducing output quality.
Durability of extraction materials represents another significant obstacle for DLE implementation. Many adsorbents and ion exchange materials degrade after multiple extraction cycles, particularly in harsh brine environments containing high concentrations of dissolved solids. This degradation necessitates frequent replacement, substantially increasing operational costs.
Energy requirements for DLE systems typically exceed those of traditional methods, with most technologies requiring significant electricity for pumping, pre-treatment, and regeneration processes. This energy intensity can undermine the environmental benefits of DLE unless powered by renewable sources.
Scalability remains perhaps the most pressing challenge for DLE technologies. While laboratory and pilot projects have demonstrated promising results, few systems have successfully scaled to commercial production levels. Engineering challenges include maintaining extraction efficiency at larger volumes, managing flow rates, and designing systems that can process variable brine compositions.
Waste management also presents technical difficulties for both methods. Evaporation ponds generate substantial salt waste that requires proper disposal, while DLE systems produce concentrated brine streams that must be managed to prevent environmental contamination. The development of closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation remains an active area of research for both approaches.
Water consumption presents another major challenge for evaporation ponds, requiring approximately 500,000 gallons per ton of lithium produced. This intensive water usage becomes particularly problematic in arid regions where lithium brine deposits are commonly found, creating competition with agricultural and community needs in already water-stressed environments.
DLE technologies, though promising, face their own set of technical hurdles. Selectivity remains a primary challenge, as most extraction materials struggle to efficiently separate lithium from similarly sized ions like sodium and magnesium in complex brine compositions. This selectivity issue directly impacts economic viability by increasing processing costs and reducing output quality.
Durability of extraction materials represents another significant obstacle for DLE implementation. Many adsorbents and ion exchange materials degrade after multiple extraction cycles, particularly in harsh brine environments containing high concentrations of dissolved solids. This degradation necessitates frequent replacement, substantially increasing operational costs.
Energy requirements for DLE systems typically exceed those of traditional methods, with most technologies requiring significant electricity for pumping, pre-treatment, and regeneration processes. This energy intensity can undermine the environmental benefits of DLE unless powered by renewable sources.
Scalability remains perhaps the most pressing challenge for DLE technologies. While laboratory and pilot projects have demonstrated promising results, few systems have successfully scaled to commercial production levels. Engineering challenges include maintaining extraction efficiency at larger volumes, managing flow rates, and designing systems that can process variable brine compositions.
Waste management also presents technical difficulties for both methods. Evaporation ponds generate substantial salt waste that requires proper disposal, while DLE systems produce concentrated brine streams that must be managed to prevent environmental contamination. The development of closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation remains an active area of research for both approaches.
Current DLE and Evaporation Pond Methodologies
01 Environmental impacts of evaporation pond lithium extraction
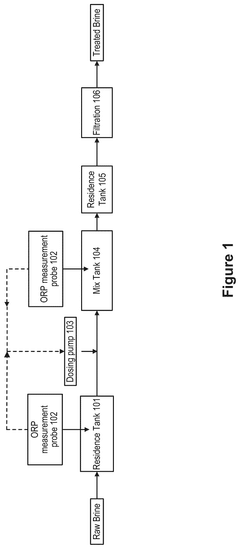
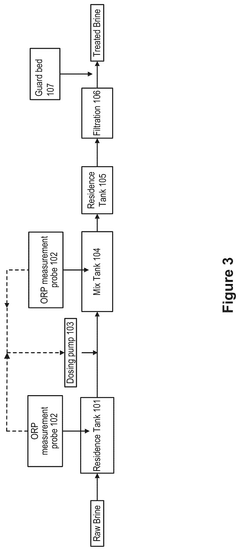
Traditional lithium extraction using evaporation ponds has significant environmental impacts including high water consumption in often water-scarce regions, land use disruption, and potential contamination of soil and groundwater. These methods typically require 18-24 months of solar evaporation and can alter local ecosystems. The extensive water usage can deplete aquifers and affect surrounding communities and wildlife habitats, while the chemical processes may introduce contaminants to the environment.- Environmental impacts of evaporation pond lithium extraction: Traditional lithium extraction using evaporation ponds has significant environmental impacts including high water consumption in often water-scarce regions, land use disruption, and potential contamination of surrounding ecosystems. These ponds require large surface areas and can take 18-24 months for evaporation to concentrate lithium, leading to habitat destruction and potential leakage of brine solutions containing chemicals that may harm local flora and fauna. The process also disrupts the natural water balance in sensitive areas like salt flats and can contribute to soil salinization.
- Water conservation advantages of Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE): Direct Lithium Extraction technologies offer significant water conservation benefits compared to traditional evaporation methods. DLE processes can reduce water consumption by up to 90% through selective extraction of lithium from brines and potential water recycling systems. These methods typically return most of the processed brine back to its source, helping to maintain groundwater levels and hydrological balance in sensitive ecosystems. The reduced water footprint makes DLE particularly valuable in arid regions where lithium resources and water scarcity often coincide, potentially minimizing impacts on local communities and agriculture that depend on the same water sources.
- Chemical usage and waste management in lithium extraction: Both traditional and DLE lithium extraction methods involve chemical usage that presents environmental challenges. DLE often requires solvents, adsorbents, or ion exchange resins that must be properly managed to prevent contamination. The process generates waste streams containing various chemicals and metals that require treatment before disposal. Evaporation ponds produce substantial quantities of salt and magnesium waste that can accumulate in large quantities. Innovations in waste management include closed-loop systems that minimize discharge, recovery and recycling of chemicals, and methods to convert waste materials into useful byproducts, reducing the overall environmental footprint of lithium production.
- Land use and habitat disruption comparison: The land footprint of lithium extraction methods varies significantly, with traditional evaporation ponds requiring extensive surface area compared to DLE facilities. Evaporation ponds can span thousands of hectares, permanently altering landscapes and disrupting wildlife habitats, particularly in sensitive salt flat ecosystems that often host unique and endemic species. DLE technologies typically require much smaller land areas, potentially reducing habitat fragmentation and ecosystem disruption. Some advanced DLE systems are designed with modular, scalable components that can be installed with minimal surface disturbance, allowing for more responsible development in ecologically valuable areas.
- Carbon footprint and energy considerations: The energy requirements and resulting carbon footprint differ substantially between lithium extraction methods. Traditional evaporation relies primarily on solar energy for evaporation but requires fossil fuel-powered pumping and processing. DLE technologies typically demand more energy for operation, including electricity for pumping, heating, and running separation processes. However, innovations in DLE are increasingly incorporating renewable energy sources like geothermal, solar, and wind power to offset carbon emissions. Some advanced systems integrate with existing geothermal operations, using the same geothermal fluid as both an energy source and lithium feedstock, creating potential for near-zero carbon lithium production that could significantly improve the overall environmental profile of lithium supply chains.
02 Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) environmental advantages
Direct Lithium Extraction technologies offer environmental advantages over traditional evaporation methods, including significantly reduced water consumption, smaller land footprint, and faster extraction times. DLE methods can recover up to 90% of available lithium compared to 40-50% with evaporation ponds. These technologies often allow for the return of processed brine to aquifers, helping to maintain hydrological balance. The reduced processing time (hours or days versus months) and lower chemical usage contribute to a more sustainable extraction process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water management and conservation in lithium extraction
Advanced water management systems in lithium extraction focus on minimizing freshwater consumption and maximizing water recycling. These systems include closed-loop water circuits, brine reinjection technologies, and water treatment processes that remove contaminants before discharge or reuse. Some innovations allow for the separation of lithium from brine while returning the majority of water to its source, significantly reducing the net water consumption compared to traditional methods. These approaches help preserve local water resources and reduce potential impacts on surrounding communities and ecosystems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy consumption and carbon footprint considerations
The energy requirements and associated carbon footprint vary significantly between lithium extraction methods. While evaporation ponds rely primarily on solar energy for evaporation, they require extensive pumping operations and subsequent processing. DLE technologies often require more electricity for operation but can be powered by renewable energy sources to minimize carbon emissions. Some innovative extraction processes incorporate energy recovery systems, heat exchangers, and optimization algorithms to reduce overall energy consumption. The total lifecycle environmental impact depends on the energy sources used and process efficiencies implemented.Expand Specific Solutions05 Waste management and remediation strategies
Effective waste management is crucial in mitigating the environmental impact of lithium extraction. Advanced extraction methods incorporate strategies for handling and treating solid waste, managing chemical reagents, and preventing soil and groundwater contamination. Some technologies focus on valorizing extraction by-products such as magnesium, calcium, and potassium compounds, turning potential waste streams into valuable resources. Post-extraction site remediation techniques include soil restoration, native vegetation replanting, and long-term monitoring systems to ensure environmental recovery. These approaches help minimize the long-term ecological footprint of lithium production operations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) versus evaporation ponds market is in a transitional growth phase, with global lithium demand projected to increase significantly due to electric vehicle adoption. While traditional evaporation ponds dominate current production, DLE technologies are gaining momentum as more environmentally sustainable alternatives. Companies like Energy Exploration Technologies, International Battery Metals, and LiEP Energy are advancing commercial DLE solutions, while established players such as POSCO Holdings and Schlumberger are investing heavily in technology development. Traditional resource companies including Saudi Aramco and BYD are also entering this space, recognizing DLE's potential to reduce water consumption, minimize land footprint, and accelerate production timelines compared to conventional methods. The technology is approaching commercial viability with several pilot projects demonstrating promising results.
Energy Exploration Technologies, Inc.
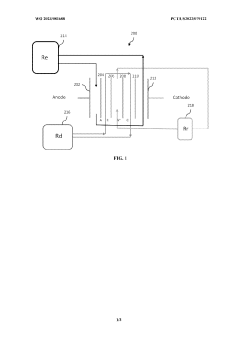
Technical Solution: Energy Exploration Technologies (EnergyX) has developed a proprietary Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technology called LiTAS (Lithium Ion Transport and Separation). This system utilizes advanced metal-organic framework (MOF) membranes and solid-state electrolyte materials to selectively extract lithium ions from brine solutions. The LiTAS technology employs a non-evaporative process that can extract lithium directly from brine regardless of magnesium or other metal content, achieving recovery rates of over 90% compared to traditional evaporation pond methods that typically recover only 30-50% of available lithium. The system operates in a continuous flow process rather than batch processing, significantly reducing the time required from 18+ months to just days. EnergyX's approach requires minimal land use and reduces water consumption by approximately 90% compared to evaporation ponds, making it particularly suitable for environmentally sensitive areas.
Strengths: High lithium recovery rates (>90%), dramatically reduced water consumption, minimal land footprint, and significantly faster extraction timeframe (days vs. months). Weaknesses: Requires more energy input than passive evaporation systems, higher initial capital expenditure, and the technology is still being scaled to commercial production levels.
POSCO Holdings, Inc.
Technical Solution: POSCO Holdings has developed an advanced Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technology called "PosLX" that utilizes a selective adsorption process with proprietary adsorbent materials. This technology can extract lithium directly from various brine sources, including low-concentration resources that would be uneconomical with traditional methods. The PosLX system employs a continuous adsorption-desorption cycle that selectively captures lithium ions while rejecting other elements like magnesium, calcium, and sodium. POSCO's process can extract lithium from brine in just 8 hours compared to the 12-18 months required for solar evaporation, achieving recovery rates of approximately 80-90%. The technology has been demonstrated at pilot scale in Argentina's lithium triangle and South Korea, processing various brine types. POSCO's approach significantly reduces water consumption by approximately 70% compared to evaporation ponds and requires less than 30% of the land area, making it substantially more environmentally friendly.
Strengths: High selectivity for lithium over competing ions, significantly reduced water footprint, smaller land requirements, and much faster extraction timeframe. The technology works with various brine compositions, including those with high Mg/Li ratios. Weaknesses: Higher energy consumption than passive evaporation methods, requires specialized adsorbent materials that need periodic replacement, and has higher operational complexity requiring skilled personnel.
Critical Patents in Lithium Extraction Technologies
Mitigation of contamination of lithium selective media in a direct lithium extraction process
PatentPendingUS20250250653A1
Innovation
- Adjusting the oxidative-reductive potential and/or pH of the aqueous lithium salt-containing solution to render foulants inert, followed by removing these inert foulants using filtration or chelating agents to protect the lithium-selective media.
Monovalent anion selective membrane enabled by high concentration brine
PatentWO2023081688A1
Innovation
- A monovalent anion selective membrane enabled by high concentration brine solutions is developed, utilizing an anion exchange membrane that enhances selectivity for monovalent anions, allowing for effective separation of lithium from divalent ions like Mg2+ and sulfate, thereby reducing lithium losses and improving recovery rates.
Water Conservation Metrics and Resource Efficiency
Water conservation represents a critical metric when comparing Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) and traditional evaporation pond methods. DLE technologies demonstrate significant advantages in water efficiency, with some processes achieving up to 90% water recovery rates compared to the substantial water losses in evaporation ponds. Quantitative assessments indicate that evaporation ponds consume approximately 500,000 gallons of water per ton of lithium produced, while advanced DLE methods can reduce this figure to below 100,000 gallons, representing an 80% improvement in water conservation.
Resource efficiency extends beyond water to include land utilization metrics. Evaporation ponds require extensive surface area, typically 2-3 square kilometers per 1,000 tons of annual lithium carbonate production. In contrast, DLE facilities can achieve the same output with less than 10% of this land footprint, dramatically reducing ecosystem disruption and habitat fragmentation in sensitive desert environments.
Energy consumption metrics reveal another dimension of resource efficiency. While evaporation ponds rely primarily on solar energy for evaporation, they require significant energy inputs for subsequent processing. DLE technologies vary widely in their energy profiles, with adsorption-based systems generally demonstrating lower energy requirements (3-4 GWh per ton of lithium) compared to membrane or ion-exchange systems (5-7 GWh per ton). However, when considering the entire production cycle, including reduced transportation and processing needs, certain DLE implementations show 30-40% improvements in overall energy efficiency.
Chemical resource efficiency metrics also favor DLE approaches. Traditional evaporation methods require substantial quantities of soda ash, lime, and other reagents for precipitation and purification steps. Advanced DLE technologies can reduce chemical consumption by 40-60% through more selective extraction processes and closed-loop systems that regenerate and reuse key reagents.
Time efficiency represents another critical resource metric. Evaporation ponds require 18-24 months for brine concentration, while DLE processes can extract lithium in hours or days, enabling faster response to market demands and reducing working capital requirements. This temporal efficiency translates to improved capital utilization and reduced financial risk in volatile commodity markets.
When evaluating total environmental resource efficiency, lifecycle assessment data indicates that DLE technologies can reduce the overall environmental footprint by 30-50% compared to traditional methods, with water conservation representing the most significant contribution to this improvement. These metrics underscore the potential for DLE to transform lithium production into a more sustainable industry aligned with circular economy principles.
Resource efficiency extends beyond water to include land utilization metrics. Evaporation ponds require extensive surface area, typically 2-3 square kilometers per 1,000 tons of annual lithium carbonate production. In contrast, DLE facilities can achieve the same output with less than 10% of this land footprint, dramatically reducing ecosystem disruption and habitat fragmentation in sensitive desert environments.
Energy consumption metrics reveal another dimension of resource efficiency. While evaporation ponds rely primarily on solar energy for evaporation, they require significant energy inputs for subsequent processing. DLE technologies vary widely in their energy profiles, with adsorption-based systems generally demonstrating lower energy requirements (3-4 GWh per ton of lithium) compared to membrane or ion-exchange systems (5-7 GWh per ton). However, when considering the entire production cycle, including reduced transportation and processing needs, certain DLE implementations show 30-40% improvements in overall energy efficiency.
Chemical resource efficiency metrics also favor DLE approaches. Traditional evaporation methods require substantial quantities of soda ash, lime, and other reagents for precipitation and purification steps. Advanced DLE technologies can reduce chemical consumption by 40-60% through more selective extraction processes and closed-loop systems that regenerate and reuse key reagents.
Time efficiency represents another critical resource metric. Evaporation ponds require 18-24 months for brine concentration, while DLE processes can extract lithium in hours or days, enabling faster response to market demands and reducing working capital requirements. This temporal efficiency translates to improved capital utilization and reduced financial risk in volatile commodity markets.
When evaluating total environmental resource efficiency, lifecycle assessment data indicates that DLE technologies can reduce the overall environmental footprint by 30-50% compared to traditional methods, with water conservation representing the most significant contribution to this improvement. These metrics underscore the potential for DLE to transform lithium production into a more sustainable industry aligned with circular economy principles.
Regulatory Frameworks for Lithium Mining Operations
The regulatory landscape governing lithium mining operations varies significantly across regions, reflecting different environmental priorities, resource management approaches, and socioeconomic considerations. In countries with established lithium industries like Chile, Argentina, and Australia, comprehensive regulatory frameworks have evolved to address the specific environmental challenges posed by both traditional evaporation pond methods and emerging Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technologies.
Chile, as the world's second-largest lithium producer, has implemented a tiered regulatory system that classifies lithium as a strategic resource subject to special concession agreements. The Chilean Environmental Assessment Service (SEA) requires detailed Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) for all lithium projects, with particularly stringent water usage regulations in the water-scarce Atacama region. Recent regulatory updates have begun to differentiate requirements for evaporation ponds versus DLE methods, acknowledging their distinct environmental footprints.
Argentina has adopted a more decentralized approach, with provincial governments holding significant authority over mining regulations. The Federal Environmental Protection Law provides baseline standards, while provinces like Catamarca, Salta, and Jujuy have developed specific protocols for lithium operations in their salt flats. These regulations increasingly incorporate water management provisions and indigenous consultation requirements, though enforcement remains inconsistent across jurisdictions.
In North America, regulatory frameworks are evolving rapidly as domestic lithium production expands. The United States Bureau of Land Management and Environmental Protection Agency jointly oversee lithium projects on federal lands, with additional oversight from state-level agencies. Recent policy initiatives, including the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, have created incentives for environmentally responsible lithium production while maintaining regulatory compliance requirements under the National Environmental Policy Act and Clean Water Act.
The European Union has established the most comprehensive sustainability criteria for battery materials, including lithium, through its Battery Regulation framework. This regulation introduces mandatory carbon footprint declarations, due diligence requirements for raw material sourcing, and recycling targets that indirectly influence global lithium mining practices, even in non-EU producing regions.
Emerging lithium producers like Bolivia and Zimbabwe are developing regulatory frameworks that attempt to balance economic development with environmental protection. These frameworks often incorporate elements from established mining codes but lack specific provisions for the unique challenges of lithium extraction technologies.
International standards and voluntary initiatives, such as the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) and the Global Battery Alliance's Battery Passport, are increasingly influencing national regulatory approaches by establishing best practices for environmental management in lithium operations across both traditional and DLE extraction methods.
Chile, as the world's second-largest lithium producer, has implemented a tiered regulatory system that classifies lithium as a strategic resource subject to special concession agreements. The Chilean Environmental Assessment Service (SEA) requires detailed Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) for all lithium projects, with particularly stringent water usage regulations in the water-scarce Atacama region. Recent regulatory updates have begun to differentiate requirements for evaporation ponds versus DLE methods, acknowledging their distinct environmental footprints.
Argentina has adopted a more decentralized approach, with provincial governments holding significant authority over mining regulations. The Federal Environmental Protection Law provides baseline standards, while provinces like Catamarca, Salta, and Jujuy have developed specific protocols for lithium operations in their salt flats. These regulations increasingly incorporate water management provisions and indigenous consultation requirements, though enforcement remains inconsistent across jurisdictions.
In North America, regulatory frameworks are evolving rapidly as domestic lithium production expands. The United States Bureau of Land Management and Environmental Protection Agency jointly oversee lithium projects on federal lands, with additional oversight from state-level agencies. Recent policy initiatives, including the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, have created incentives for environmentally responsible lithium production while maintaining regulatory compliance requirements under the National Environmental Policy Act and Clean Water Act.
The European Union has established the most comprehensive sustainability criteria for battery materials, including lithium, through its Battery Regulation framework. This regulation introduces mandatory carbon footprint declarations, due diligence requirements for raw material sourcing, and recycling targets that indirectly influence global lithium mining practices, even in non-EU producing regions.
Emerging lithium producers like Bolivia and Zimbabwe are developing regulatory frameworks that attempt to balance economic development with environmental protection. These frameworks often incorporate elements from established mining codes but lack specific provisions for the unique challenges of lithium extraction technologies.
International standards and voluntary initiatives, such as the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) and the Global Battery Alliance's Battery Passport, are increasingly influencing national regulatory approaches by establishing best practices for environmental management in lithium operations across both traditional and DLE extraction methods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!