Exploring Enhancements in Carboxylic Acid for Drug Efficacy
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid in Drug Development: Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acids have long been recognized as crucial components in drug development, playing a pivotal role in enhancing drug efficacy and pharmacokinetics. The journey of carboxylic acids in pharmaceutical research dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in recent decades. This field has evolved from simple modifications of existing molecules to sophisticated design strategies aimed at optimizing drug properties.
The primary objective of exploring enhancements in carboxylic acid for drug efficacy is to improve the overall performance of pharmaceutical compounds. This includes enhancing bioavailability, increasing potency, reducing side effects, and improving drug stability. By manipulating the carboxylic acid moiety, researchers aim to fine-tune the physicochemical properties of drug molecules, ultimately leading to more effective and safer medications.
One of the key trends in this field is the development of prodrugs, where carboxylic acid groups are modified to improve drug absorption and distribution. This approach has gained traction due to its ability to overcome limitations associated with the parent drug, such as poor solubility or permeability. Another emerging trend is the use of bioisosteres, where carboxylic acid groups are replaced with structurally similar moieties to maintain or enhance biological activity while addressing potential drawbacks.
The technological evolution in this area has been marked by advancements in computational chemistry and high-throughput screening methods. These tools have enabled researchers to predict and optimize the behavior of carboxylic acid-containing compounds in biological systems more efficiently. Additionally, progress in synthetic methodologies has expanded the repertoire of possible modifications, allowing for more diverse and targeted approaches to drug design.
As we look towards the future, the goals for carboxylic acid enhancements in drug development are becoming increasingly ambitious. Researchers are aiming to develop "smart" drugs that can selectively target specific tissues or respond to physiological conditions, utilizing the unique properties of carboxylic acids. There is also a growing interest in exploring the potential of carboxylic acids in combination therapies, where multiple drugs are designed to work synergistically for enhanced efficacy.
In conclusion, the exploration of carboxylic acid enhancements for drug efficacy represents a dynamic and promising field in pharmaceutical research. By building on past achievements and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, researchers are poised to unlock new possibilities in drug design, potentially revolutionizing treatment options for a wide range of diseases.
The primary objective of exploring enhancements in carboxylic acid for drug efficacy is to improve the overall performance of pharmaceutical compounds. This includes enhancing bioavailability, increasing potency, reducing side effects, and improving drug stability. By manipulating the carboxylic acid moiety, researchers aim to fine-tune the physicochemical properties of drug molecules, ultimately leading to more effective and safer medications.
One of the key trends in this field is the development of prodrugs, where carboxylic acid groups are modified to improve drug absorption and distribution. This approach has gained traction due to its ability to overcome limitations associated with the parent drug, such as poor solubility or permeability. Another emerging trend is the use of bioisosteres, where carboxylic acid groups are replaced with structurally similar moieties to maintain or enhance biological activity while addressing potential drawbacks.
The technological evolution in this area has been marked by advancements in computational chemistry and high-throughput screening methods. These tools have enabled researchers to predict and optimize the behavior of carboxylic acid-containing compounds in biological systems more efficiently. Additionally, progress in synthetic methodologies has expanded the repertoire of possible modifications, allowing for more diverse and targeted approaches to drug design.
As we look towards the future, the goals for carboxylic acid enhancements in drug development are becoming increasingly ambitious. Researchers are aiming to develop "smart" drugs that can selectively target specific tissues or respond to physiological conditions, utilizing the unique properties of carboxylic acids. There is also a growing interest in exploring the potential of carboxylic acids in combination therapies, where multiple drugs are designed to work synergistically for enhanced efficacy.
In conclusion, the exploration of carboxylic acid enhancements for drug efficacy represents a dynamic and promising field in pharmaceutical research. By building on past achievements and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, researchers are poised to unlock new possibilities in drug design, potentially revolutionizing treatment options for a wide range of diseases.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Drug Efficacy
The market for enhanced drug efficacy through carboxylic acid modifications is experiencing significant growth, driven by the pharmaceutical industry's constant pursuit of more effective and safer medications. This segment of the drug development market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, as pharmaceutical companies increasingly focus on improving existing drugs and developing new ones with enhanced efficacy profiles.
The demand for enhanced drug efficacy is particularly strong in therapeutic areas such as oncology, neurology, and infectious diseases, where the need for more potent and targeted treatments is critical. Carboxylic acid modifications offer a promising avenue for achieving these improvements, as they can potentially enhance drug solubility, bioavailability, and target specificity.
Market research indicates that the global pharmaceutical industry is investing heavily in research and development efforts aimed at enhancing drug efficacy. A substantial portion of this investment is directed towards exploring novel chemical modifications, including those involving carboxylic acids. This trend is expected to continue, with the market for enhanced drug efficacy technologies projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall pharmaceutical market growth rate.
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing aging population worldwide are key factors driving the demand for more effective medications. As healthcare systems face mounting pressure to improve patient outcomes while managing costs, there is a growing emphasis on developing drugs that offer superior efficacy and reduced side effects. This trend is creating significant opportunities for technologies that can enhance drug performance through carboxylic acid modifications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for enhanced drug efficacy technologies, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical industries and robust research infrastructure. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in this sector, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing investment in pharmaceutical research and development.
The competitive landscape in this market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies, specialized biotechnology firms, and academic research institutions. Collaborations and partnerships between these entities are becoming increasingly common, as they seek to leverage complementary expertise and resources to accelerate the development of enhanced drug formulations.
In conclusion, the market for enhanced drug efficacy through carboxylic acid modifications presents significant growth potential. As pharmaceutical companies continue to prioritize the development of more effective medications, technologies that can improve drug performance are likely to see increasing demand and investment in the coming years.
The demand for enhanced drug efficacy is particularly strong in therapeutic areas such as oncology, neurology, and infectious diseases, where the need for more potent and targeted treatments is critical. Carboxylic acid modifications offer a promising avenue for achieving these improvements, as they can potentially enhance drug solubility, bioavailability, and target specificity.
Market research indicates that the global pharmaceutical industry is investing heavily in research and development efforts aimed at enhancing drug efficacy. A substantial portion of this investment is directed towards exploring novel chemical modifications, including those involving carboxylic acids. This trend is expected to continue, with the market for enhanced drug efficacy technologies projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall pharmaceutical market growth rate.
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing aging population worldwide are key factors driving the demand for more effective medications. As healthcare systems face mounting pressure to improve patient outcomes while managing costs, there is a growing emphasis on developing drugs that offer superior efficacy and reduced side effects. This trend is creating significant opportunities for technologies that can enhance drug performance through carboxylic acid modifications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for enhanced drug efficacy technologies, owing to their well-established pharmaceutical industries and robust research infrastructure. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in this sector, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing investment in pharmaceutical research and development.
The competitive landscape in this market is characterized by a mix of large pharmaceutical companies, specialized biotechnology firms, and academic research institutions. Collaborations and partnerships between these entities are becoming increasingly common, as they seek to leverage complementary expertise and resources to accelerate the development of enhanced drug formulations.
In conclusion, the market for enhanced drug efficacy through carboxylic acid modifications presents significant growth potential. As pharmaceutical companies continue to prioritize the development of more effective medications, technologies that can improve drug performance are likely to see increasing demand and investment in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Modifications
Despite the widespread use of carboxylic acids in drug development, several challenges persist in their modification and optimization for enhanced drug efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the limited solubility of many carboxylic acid-containing compounds in aqueous environments, which can significantly impair their bioavailability and, consequently, their therapeutic potential. This issue is particularly pronounced for drugs targeting lipophilic environments or those requiring oral administration.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of carboxylic acid moieties under various physiological conditions. The susceptibility of these functional groups to enzymatic degradation or chemical hydrolysis can lead to reduced half-life and diminished efficacy of the drug. This instability often necessitates higher dosages or more frequent administration, potentially increasing side effects and reducing patient compliance.
The reactivity of carboxylic acids also presents a double-edged sword in drug development. While their ability to form various derivatives is advantageous for creating prodrugs or improving pharmacokinetic properties, it can also lead to undesired interactions with other biomolecules in the body. This reactivity can result in off-target effects or unexpected metabolic pathways, complicating the drug's safety profile and efficacy.
Furthermore, the strong hydrogen-bonding capability of carboxylic acids, while beneficial for certain drug-target interactions, can hinder membrane permeability. This characteristic often poses a significant barrier to achieving optimal drug distribution, particularly for targets within cells or across the blood-brain barrier.
The synthesis and purification of complex carboxylic acid-containing compounds present additional challenges. Many synthetic routes involve harsh conditions or multiple steps, leading to low yields and increased production costs. The purification process can be equally demanding, especially when dealing with stereoisomers or closely related analogues.
Lastly, the formulation of carboxylic acid-containing drugs into stable, bioavailable dosage forms remains a persistent challenge. Issues such as pH-dependent solubility, potential for degradation during storage, and compatibility with other excipients often require extensive formulation studies and innovative delivery strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in medicinal chemistry, pharmaceutical technology, and drug delivery systems. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for unlocking the full potential of carboxylic acid modifications in enhancing drug efficacy and developing more effective therapeutic agents.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of carboxylic acid moieties under various physiological conditions. The susceptibility of these functional groups to enzymatic degradation or chemical hydrolysis can lead to reduced half-life and diminished efficacy of the drug. This instability often necessitates higher dosages or more frequent administration, potentially increasing side effects and reducing patient compliance.
The reactivity of carboxylic acids also presents a double-edged sword in drug development. While their ability to form various derivatives is advantageous for creating prodrugs or improving pharmacokinetic properties, it can also lead to undesired interactions with other biomolecules in the body. This reactivity can result in off-target effects or unexpected metabolic pathways, complicating the drug's safety profile and efficacy.
Furthermore, the strong hydrogen-bonding capability of carboxylic acids, while beneficial for certain drug-target interactions, can hinder membrane permeability. This characteristic often poses a significant barrier to achieving optimal drug distribution, particularly for targets within cells or across the blood-brain barrier.
The synthesis and purification of complex carboxylic acid-containing compounds present additional challenges. Many synthetic routes involve harsh conditions or multiple steps, leading to low yields and increased production costs. The purification process can be equally demanding, especially when dealing with stereoisomers or closely related analogues.
Lastly, the formulation of carboxylic acid-containing drugs into stable, bioavailable dosage forms remains a persistent challenge. Issues such as pH-dependent solubility, potential for degradation during storage, and compatibility with other excipients often require extensive formulation studies and innovative delivery strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in medicinal chemistry, pharmaceutical technology, and drug delivery systems. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for unlocking the full potential of carboxylic acid modifications in enhancing drug efficacy and developing more effective therapeutic agents.
Existing Strategies for Carboxylic Acid Enhancement
01 Carboxylic acid derivatives as drug candidates
Carboxylic acid derivatives are explored as potential drug candidates due to their diverse pharmacological properties. These compounds can be synthesized and modified to enhance their efficacy, bioavailability, and target specificity. Research focuses on developing novel carboxylic acid-based drugs for various therapeutic applications.- Carboxylic acid derivatives as drug candidates: Carboxylic acid derivatives are explored as potential drug candidates due to their diverse pharmacological properties. These compounds can be synthesized and modified to enhance their efficacy, bioavailability, and target specificity. Research focuses on developing novel carboxylic acid-based drugs for various therapeutic applications.
- Formulation strategies to improve carboxylic acid drug efficacy: Various formulation strategies are employed to enhance the efficacy of carboxylic acid drugs. These include the use of prodrugs, nanoparticle delivery systems, and controlled-release formulations. Such approaches aim to improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery, ultimately enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
- Structure-activity relationship studies of carboxylic acid drugs: Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies are conducted to understand how structural modifications of carboxylic acid drugs affect their efficacy. These investigations help identify key molecular features responsible for therapeutic activity and guide the design of more potent and selective drug candidates.
- Combination therapies involving carboxylic acid drugs: Combination therapies involving carboxylic acid drugs are explored to enhance overall treatment efficacy. By combining carboxylic acid-based medications with other therapeutic agents, synergistic effects can be achieved, potentially leading to improved clinical outcomes and reduced side effects.
- Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of carboxylic acid drugs: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies are conducted to evaluate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of carboxylic acid drugs. These investigations help optimize dosing regimens, predict drug-drug interactions, and improve overall drug efficacy and safety profiles.
02 Formulation strategies to improve carboxylic acid drug efficacy
Various formulation strategies are employed to enhance the efficacy of carboxylic acid drugs. These may include the use of prodrugs, nanoparticle delivery systems, or controlled-release formulations. Such approaches aim to improve drug solubility, stability, and targeted delivery, ultimately enhancing therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Carboxylic acid drugs in combination therapy
Carboxylic acid drugs are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to achieve synergistic effects and improve overall treatment efficacy. This approach can help overcome drug resistance, reduce side effects, and enhance the therapeutic index of the combined treatment regimen.Expand Specific Solutions04 Structure-activity relationship studies of carboxylic acid drugs
Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies are conducted to understand the correlation between the chemical structure of carboxylic acid drugs and their biological activity. These investigations help in optimizing drug design, improving potency, and reducing unwanted side effects, ultimately leading to more effective therapeutic agents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations
The efficacy of carboxylic acid drugs is influenced by their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Research focuses on understanding and optimizing these parameters to improve drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. This knowledge is crucial for developing dosing strategies and maximizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pharmaceutical Carboxylic Acid Research
The field of carboxylic acid enhancements for drug efficacy is in a mature stage of development, with a diverse range of players contributing to its advancement. The market size is substantial, driven by the pharmaceutical industry's continuous need for improved drug formulations. Technologically, the field is well-established, with companies like Amgen, Bayer, and Sanofi leading in research and development. However, there's still room for innovation, as evidenced by the involvement of specialized biotech firms such as Innate Pharma and Ablynx. The presence of academic institutions like Johns Hopkins University and Huazhong Agricultural University suggests ongoing fundamental research, while the participation of chemical companies like BASF and Eastman Chemical indicates a robust supply chain for raw materials and intermediates.
Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH
Technical Solution: Bayer has made significant strides in enhancing carboxylic acid-based drugs through their proprietary "Acid Optimization Platform". This platform utilizes computational chemistry and high-throughput screening to identify optimal modifications to carboxylic acid groups. Their approach includes the strategic placement of electron-withdrawing or electron-donating substituents near the carboxylic acid moiety to fine-tune its pKa and lipophilicity[4]. Bayer has also developed novel linker technologies to create prodrugs of carboxylic acid-containing compounds, improving their pharmacokinetic profiles[5]. Additionally, they've explored the use of cyclic anhydrides as masked forms of dicarboxylic acids, which has shown promise in enhancing oral bioavailability for certain drug classes[6].
Strengths: Tailored approach to drug optimization, improved pharmacokinetic profiles, and potential for enhanced oral bioavailability. Weaknesses: Increased complexity in drug design and potential for unexpected metabolic products.
Amgen, Inc.
Technical Solution: Amgen has developed a novel approach to enhance carboxylic acid-based drugs for improved efficacy. Their method involves the use of prodrug technology, specifically targeting carboxylic acid moieties. By creating ester or amide derivatives of carboxylic acids, they've improved drug solubility and permeability[1]. This approach has shown particular promise in enhancing the bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs. Amgen's research has also focused on developing carboxylic acid bioisosteres, which maintain the desired pharmacological activity while potentially reducing side effects[2]. Their recent studies have explored the use of tetrazoles and oxadiazoles as carboxylic acid replacements in drug molecules, demonstrating improved metabolic stability and target affinity in several cases[3].
Strengths: Improved drug bioavailability, potential for reduced side effects, and enhanced metabolic stability. Weaknesses: Potential for altered drug-target interactions and increased complexity in drug synthesis and formulation.
Innovative Approaches in Carboxylic Acid Modification
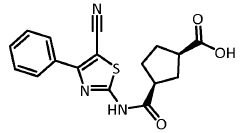
Cocrystals of (1r,3s)-3-(5-cyano-4-phenyl-1,3-thiazol-2-ylcabamoyl)cyclopentane carboxylic acid
PatentWO2021185748A1
Innovation
- The formation of cocrystals with gentisic acid, urea, and nicotinamide improves the physical and pharmacokinetic properties, including reduced hygroscopicity and enhanced bioavailability, by forming stable and less hygroscopic cocrystals that maintain therapeutic efficacy at lower doses.
Carboxylic acid derivative and medicine comprising salt or ester of the same
PatentWO2002098840A1
Innovation
- Development of a carboxylic acid derivative with a novel structure that acts as a dual or triple agonist on PPARα and PPARγ receptors, improving insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism, while minimizing toxicity and side effects.
Regulatory Considerations for Novel Drug Formulations
The regulatory landscape for novel drug formulations involving carboxylic acid enhancements is complex and multifaceted. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, have established stringent guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of new drug formulations. These agencies require comprehensive data on the chemical properties, stability, and bioavailability of the enhanced carboxylic acid compounds.
One key consideration is the impact of carboxylic acid modifications on the drug's pharmacokinetic profile. Regulatory authorities will scrutinize how these enhancements affect absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes. Manufacturers must provide robust evidence demonstrating that the modified formulation maintains or improves the drug's therapeutic efficacy without introducing new safety concerns.
Stability testing is another critical aspect of the regulatory process. Enhanced carboxylic acid formulations must demonstrate long-term stability under various environmental conditions. This includes accelerated stability studies to predict shelf life and identify potential degradation products. Regulatory bodies will require detailed information on storage conditions, packaging materials, and any special handling instructions.
Impurity profiling is a significant regulatory focus for novel formulations. Manufacturers must identify and characterize all impurities resulting from the carboxylic acid enhancement process. Regulatory guidelines specify acceptable limits for impurities, and any new or increased impurities must be thoroughly evaluated for safety.
Bioequivalence studies may be necessary if the carboxylic acid enhancement significantly alters the drug's bioavailability. Regulatory agencies will assess whether the modified formulation delivers comparable systemic exposure to the active ingredient as the original formulation. This may involve in vivo studies comparing pharmacokinetic parameters between the enhanced and reference formulations.
Manufacturing process changes associated with carboxylic acid enhancements will also face regulatory scrutiny. Authorities will review the proposed manufacturing methods, quality control procedures, and analytical methods to ensure consistency and reproducibility in production. Validation of these processes is essential to meet Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements.
Lastly, regulatory considerations extend to labeling and packaging. Any changes in drug formulation must be accurately reflected in product labeling, including updates to dosing instructions, storage requirements, and potential side effects. Clear communication of these changes to healthcare providers and patients is crucial for regulatory compliance and safe use of the enhanced formulation.
One key consideration is the impact of carboxylic acid modifications on the drug's pharmacokinetic profile. Regulatory authorities will scrutinize how these enhancements affect absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes. Manufacturers must provide robust evidence demonstrating that the modified formulation maintains or improves the drug's therapeutic efficacy without introducing new safety concerns.
Stability testing is another critical aspect of the regulatory process. Enhanced carboxylic acid formulations must demonstrate long-term stability under various environmental conditions. This includes accelerated stability studies to predict shelf life and identify potential degradation products. Regulatory bodies will require detailed information on storage conditions, packaging materials, and any special handling instructions.
Impurity profiling is a significant regulatory focus for novel formulations. Manufacturers must identify and characterize all impurities resulting from the carboxylic acid enhancement process. Regulatory guidelines specify acceptable limits for impurities, and any new or increased impurities must be thoroughly evaluated for safety.
Bioequivalence studies may be necessary if the carboxylic acid enhancement significantly alters the drug's bioavailability. Regulatory agencies will assess whether the modified formulation delivers comparable systemic exposure to the active ingredient as the original formulation. This may involve in vivo studies comparing pharmacokinetic parameters between the enhanced and reference formulations.
Manufacturing process changes associated with carboxylic acid enhancements will also face regulatory scrutiny. Authorities will review the proposed manufacturing methods, quality control procedures, and analytical methods to ensure consistency and reproducibility in production. Validation of these processes is essential to meet Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements.
Lastly, regulatory considerations extend to labeling and packaging. Any changes in drug formulation must be accurately reflected in product labeling, including updates to dosing instructions, storage requirements, and potential side effects. Clear communication of these changes to healthcare providers and patients is crucial for regulatory compliance and safe use of the enhanced formulation.
Environmental Impact of Carboxylic Acid-Based Drugs
The environmental impact of carboxylic acid-based drugs is a critical consideration in the pharmaceutical industry, encompassing both their production and post-consumption effects. The manufacturing processes of these drugs often involve complex chemical reactions and the use of various solvents, which can lead to significant environmental concerns if not properly managed. Waste streams from production facilities may contain residual carboxylic acids, intermediates, and byproducts that require careful treatment before release into the environment.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with carboxylic acid-based drugs is their persistence in aquatic ecosystems. Many of these compounds are not fully metabolized by the human body and are excreted into wastewater systems. Conventional wastewater treatment plants may not be equipped to completely remove these pharmaceuticals, resulting in their release into rivers, lakes, and oceans. This can lead to potential bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and disruption of ecosystem balance.
The presence of carboxylic acid-based drugs in the environment has been linked to various ecological effects. Some studies have shown that these compounds can interfere with the endocrine systems of aquatic life, potentially affecting reproduction and development. Additionally, there are concerns about the development of antibiotic resistance in environmental bacteria due to the presence of antibiotic carboxylic acids in water bodies.
To address these environmental concerns, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on green chemistry principles in drug development and production. This includes the use of less harmful solvents, optimization of reaction conditions to reduce waste, and the development of more biodegradable drug formulations. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration, are being explored to improve the removal of pharmaceutical residues from effluents.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are also implementing stricter guidelines for the environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. This includes requirements for comprehensive ecotoxicological studies and the development of environmental fate models for new drug candidates. Such measures aim to minimize the potential negative impacts of carboxylic acid-based drugs on ecosystems and human health through environmental exposure.
Research into the development of more environmentally friendly carboxylic acid derivatives is ongoing. This includes the exploration of bio-based carboxylic acids and the design of molecules with improved biodegradability profiles. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance the efficacy of drugs, potentially reducing the required dosage and, consequently, the environmental burden.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with carboxylic acid-based drugs is their persistence in aquatic ecosystems. Many of these compounds are not fully metabolized by the human body and are excreted into wastewater systems. Conventional wastewater treatment plants may not be equipped to completely remove these pharmaceuticals, resulting in their release into rivers, lakes, and oceans. This can lead to potential bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and disruption of ecosystem balance.
The presence of carboxylic acid-based drugs in the environment has been linked to various ecological effects. Some studies have shown that these compounds can interfere with the endocrine systems of aquatic life, potentially affecting reproduction and development. Additionally, there are concerns about the development of antibiotic resistance in environmental bacteria due to the presence of antibiotic carboxylic acids in water bodies.
To address these environmental concerns, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on green chemistry principles in drug development and production. This includes the use of less harmful solvents, optimization of reaction conditions to reduce waste, and the development of more biodegradable drug formulations. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration, are being explored to improve the removal of pharmaceutical residues from effluents.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are also implementing stricter guidelines for the environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. This includes requirements for comprehensive ecotoxicological studies and the development of environmental fate models for new drug candidates. Such measures aim to minimize the potential negative impacts of carboxylic acid-based drugs on ecosystems and human health through environmental exposure.
Research into the development of more environmentally friendly carboxylic acid derivatives is ongoing. This includes the exploration of bio-based carboxylic acids and the design of molecules with improved biodegradability profiles. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance the efficacy of drugs, potentially reducing the required dosage and, consequently, the environmental burden.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!