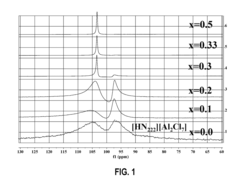
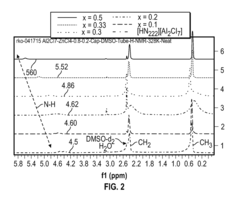
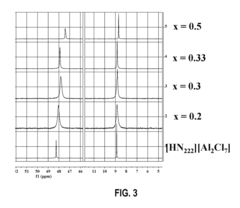
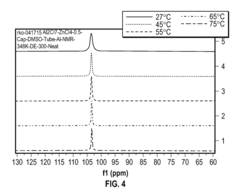
Fluoroantimonic Acid: Leading the Way in Acid Catalysis Innovation
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fluoroantimonic Acid Background and Objectives
Fluoroantimonic acid, often referred to as the world's strongest superacid, has emerged as a groundbreaking catalyst in the field of acid catalysis. Its discovery and development have revolutionized various industrial processes, particularly in the petrochemical and pharmaceutical sectors. The journey of fluoroantimonic acid began in the mid-20th century when researchers sought to create acids stronger than conventional mineral acids.
The primary objective of fluoroantimonic acid research is to harness its exceptional acidity for catalyzing reactions that were previously challenging or impossible with traditional acid catalysts. This superacid, formed by combining hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5), exhibits a Hammett acidity function (H0) of -28, making it over a billion times stronger than 100% sulfuric acid.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid technology has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and selective catalytic processes in the chemical industry. Its ability to protonate even extremely weak bases has opened up new possibilities in organic synthesis, isomerization reactions, and the cracking of hydrocarbons. The unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid have also sparked interest in its potential applications in materials science and nanotechnology.
One of the key technological goals in fluoroantimonic acid research is to develop more stable and manageable forms of the superacid. Due to its extreme reactivity and corrosive nature, handling and storage of fluoroantimonic acid pose significant challenges. Researchers are exploring ways to immobilize the acid on solid supports or develop ionic liquid analogues to mitigate these issues while retaining its catalytic prowess.
Another important objective is to expand the range of reactions that can be catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. This includes investigating its potential in asymmetric synthesis, C-H bond activation, and the formation of novel carbon-carbon bonds. The ability of fluoroantimonic acid to generate highly reactive carbocations has also led to studies on its use in polymerization reactions and the synthesis of advanced materials.
Environmental considerations have become increasingly important in recent years, prompting research into more sustainable and eco-friendly applications of fluoroantimonic acid. This includes exploring its role in the valorization of biomass and the development of green chemistry processes. Scientists are also investigating ways to minimize the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid production and use, aligning with global sustainability goals.
As we look to the future, the technological trajectory of fluoroantimonic acid points towards more precise control over its acidity and reactivity. This may involve the development of tunable superacid systems that can be tailored for specific applications. The integration of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis with other emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and artificial intelligence-driven reaction optimization, holds promise for further innovations in this field.
The primary objective of fluoroantimonic acid research is to harness its exceptional acidity for catalyzing reactions that were previously challenging or impossible with traditional acid catalysts. This superacid, formed by combining hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5), exhibits a Hammett acidity function (H0) of -28, making it over a billion times stronger than 100% sulfuric acid.
The evolution of fluoroantimonic acid technology has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and selective catalytic processes in the chemical industry. Its ability to protonate even extremely weak bases has opened up new possibilities in organic synthesis, isomerization reactions, and the cracking of hydrocarbons. The unique properties of fluoroantimonic acid have also sparked interest in its potential applications in materials science and nanotechnology.
One of the key technological goals in fluoroantimonic acid research is to develop more stable and manageable forms of the superacid. Due to its extreme reactivity and corrosive nature, handling and storage of fluoroantimonic acid pose significant challenges. Researchers are exploring ways to immobilize the acid on solid supports or develop ionic liquid analogues to mitigate these issues while retaining its catalytic prowess.
Another important objective is to expand the range of reactions that can be catalyzed by fluoroantimonic acid. This includes investigating its potential in asymmetric synthesis, C-H bond activation, and the formation of novel carbon-carbon bonds. The ability of fluoroantimonic acid to generate highly reactive carbocations has also led to studies on its use in polymerization reactions and the synthesis of advanced materials.
Environmental considerations have become increasingly important in recent years, prompting research into more sustainable and eco-friendly applications of fluoroantimonic acid. This includes exploring its role in the valorization of biomass and the development of green chemistry processes. Scientists are also investigating ways to minimize the environmental impact of fluoroantimonic acid production and use, aligning with global sustainability goals.
As we look to the future, the technological trajectory of fluoroantimonic acid points towards more precise control over its acidity and reactivity. This may involve the development of tunable superacid systems that can be tailored for specific applications. The integration of fluoroantimonic acid catalysis with other emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and artificial intelligence-driven reaction optimization, holds promise for further innovations in this field.
Market Analysis for Superacid Catalysts
The market for superacid catalysts, particularly fluoroantimonic acid, has been experiencing significant growth due to its exceptional catalytic properties and wide-ranging applications in various industries. The global superacid catalyst market is projected to expand at a steady rate over the next five years, driven by increasing demand in petrochemical processing, polymer production, and fine chemical synthesis.
Fluoroantimonic acid, being one of the strongest known superacids, has garnered substantial attention in the chemical industry. Its ability to catalyze reactions under milder conditions and with higher selectivity compared to traditional acid catalysts has led to its increased adoption in industrial processes. The petrochemical sector remains the largest consumer of superacid catalysts, utilizing them in alkylation processes for high-octane gasoline production and in the conversion of heavy hydrocarbons into more valuable lighter products.
The polymer industry has also emerged as a significant market for superacid catalysts, particularly in the production of specialty polymers and high-performance materials. Fluoroantimonic acid's unique properties enable the synthesis of novel polymer structures with enhanced properties, opening up new possibilities in materials science and engineering.
In the fine chemicals and pharmaceutical sectors, superacid catalysts are gaining traction due to their ability to facilitate complex organic transformations with high efficiency and selectivity. This has led to increased interest from pharmaceutical companies looking to optimize their synthetic processes and reduce production costs.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the superacid catalyst market, owing to their well-established chemical and petrochemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in chemical manufacturing infrastructure.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges such as the high cost of production and handling of superacid catalysts, as well as environmental concerns, may impact market growth. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these issues, focusing on developing more stable and environmentally friendly superacid catalysts.
The competitive landscape of the superacid catalyst market is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and specialized catalyst manufacturers. Key players are focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Fluoroantimonic acid, being one of the strongest known superacids, has garnered substantial attention in the chemical industry. Its ability to catalyze reactions under milder conditions and with higher selectivity compared to traditional acid catalysts has led to its increased adoption in industrial processes. The petrochemical sector remains the largest consumer of superacid catalysts, utilizing them in alkylation processes for high-octane gasoline production and in the conversion of heavy hydrocarbons into more valuable lighter products.
The polymer industry has also emerged as a significant market for superacid catalysts, particularly in the production of specialty polymers and high-performance materials. Fluoroantimonic acid's unique properties enable the synthesis of novel polymer structures with enhanced properties, opening up new possibilities in materials science and engineering.
In the fine chemicals and pharmaceutical sectors, superacid catalysts are gaining traction due to their ability to facilitate complex organic transformations with high efficiency and selectivity. This has led to increased interest from pharmaceutical companies looking to optimize their synthetic processes and reduce production costs.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the superacid catalyst market, owing to their well-established chemical and petrochemical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in chemical manufacturing infrastructure.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges such as the high cost of production and handling of superacid catalysts, as well as environmental concerns, may impact market growth. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these issues, focusing on developing more stable and environmentally friendly superacid catalysts.
The competitive landscape of the superacid catalyst market is characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies and specialized catalyst manufacturers. Key players are focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Current Challenges in Fluoroantimonic Acid Production
Despite the remarkable potential of fluoroantimonic acid in catalysis, its production faces several significant challenges that hinder widespread industrial adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the extreme reactivity of the acid, which necessitates specialized handling and storage conditions. The corrosive nature of fluoroantimonic acid demands the use of highly resistant materials, such as Teflon or fluorinated polymers, for containment and processing equipment. This requirement significantly increases production costs and limits scalability.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis process itself. The production of fluoroantimonic acid involves the combination of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5), both of which are hazardous substances. The reaction must be carried out under strictly controlled conditions to ensure safety and product purity. The high reactivity of the components also poses risks of side reactions and impurities, which can affect the acid's catalytic performance.
Environmental and safety concerns present additional hurdles in fluoroantimonic acid production. The acid's extreme corrosiveness and toxicity raise significant environmental risks, necessitating robust containment and disposal protocols. Worker safety is a paramount concern, requiring extensive protective measures and specialized training for handling and production processes.
The instability of fluoroantimonic acid at room temperature further complicates its production and storage. The acid must be kept at low temperatures to maintain its integrity, which adds to the complexity and cost of production facilities. This instability also poses challenges for transportation and long-term storage, limiting its commercial viability for some applications.
Regulatory compliance represents another significant challenge in fluoroantimonic acid production. The hazardous nature of the acid and its precursors subjects manufacturers to stringent regulations and oversight. Compliance with these regulations often requires substantial investments in safety equipment, monitoring systems, and documentation processes, further increasing production costs.
The limited availability and high cost of raw materials, particularly high-purity antimony pentafluoride, also constrain production capabilities. The global supply chain for these materials can be volatile, affecting production consistency and scalability. Additionally, the specialized nature of fluoroantimonic acid production limits the number of facilities capable of manufacturing it, creating potential supply bottlenecks.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts. Innovations in materials science, process engineering, and safety protocols are essential to overcome the current limitations in fluoroantimonic acid production. As the demand for powerful acid catalysts grows in various industries, finding solutions to these production challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of fluoroantimonic acid in catalysis applications.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis process itself. The production of fluoroantimonic acid involves the combination of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5), both of which are hazardous substances. The reaction must be carried out under strictly controlled conditions to ensure safety and product purity. The high reactivity of the components also poses risks of side reactions and impurities, which can affect the acid's catalytic performance.
Environmental and safety concerns present additional hurdles in fluoroantimonic acid production. The acid's extreme corrosiveness and toxicity raise significant environmental risks, necessitating robust containment and disposal protocols. Worker safety is a paramount concern, requiring extensive protective measures and specialized training for handling and production processes.
The instability of fluoroantimonic acid at room temperature further complicates its production and storage. The acid must be kept at low temperatures to maintain its integrity, which adds to the complexity and cost of production facilities. This instability also poses challenges for transportation and long-term storage, limiting its commercial viability for some applications.
Regulatory compliance represents another significant challenge in fluoroantimonic acid production. The hazardous nature of the acid and its precursors subjects manufacturers to stringent regulations and oversight. Compliance with these regulations often requires substantial investments in safety equipment, monitoring systems, and documentation processes, further increasing production costs.
The limited availability and high cost of raw materials, particularly high-purity antimony pentafluoride, also constrain production capabilities. The global supply chain for these materials can be volatile, affecting production consistency and scalability. Additionally, the specialized nature of fluoroantimonic acid production limits the number of facilities capable of manufacturing it, creating potential supply bottlenecks.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts. Innovations in materials science, process engineering, and safety protocols are essential to overcome the current limitations in fluoroantimonic acid production. As the demand for powerful acid catalysts grows in various industries, finding solutions to these production challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of fluoroantimonic acid in catalysis applications.
Existing Applications of Fluoroantimonic Acid
01 Synthesis and properties of fluoroantimonic acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is a superacid formed by combining hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5). It is known for its extremely high acidity and is often used as a powerful catalyst in various chemical reactions. The synthesis and characterization of fluoroantimonic acid involve specialized techniques due to its highly corrosive nature.- Synthesis and properties of fluoroantimonic acid: Fluoroantimonic acid is a superacid composed of hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5). It is known for its extremely high acidity and is often used as a powerful catalyst in various chemical reactions. The synthesis typically involves the combination of HF and SbF5 under controlled conditions.
- Applications in organic synthesis: Fluoroantimonic acid is utilized in various organic synthesis reactions due to its strong acidic properties. It can catalyze reactions such as alkylations, acylations, and isomerizations. Its ability to protonate even weak bases makes it useful in generating highly reactive carbocations for synthetic purposes.
- Use in materials science and surface treatment: In materials science, fluoroantimonic acid is employed for surface treatments and modifications of various materials. It can be used to etch or activate surfaces, create specialized coatings, or modify the properties of polymers and other materials. Its strong acidic nature allows for unique surface interactions and modifications.
- Safety and handling considerations: Due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity, fluoroantimonic acid requires specialized handling and safety precautions. This includes the use of specific containment materials resistant to its corrosive effects, proper personal protective equipment, and controlled environmental conditions for storage and use.
- Analytical and characterization techniques: Various analytical and characterization techniques are employed to study fluoroantimonic acid and its reactions. These may include spectroscopic methods, electrochemical analyses, and specialized titration techniques adapted for superacids. Such methods are crucial for understanding the behavior and properties of this powerful acid in different chemical systems.
02 Applications in organic synthesis
Fluoroantimonic acid finds extensive use in organic synthesis as a catalyst for various reactions, including alkylations, acylations, and isomerizations. Its strong acidity enables it to activate less reactive substrates and promote challenging transformations that are difficult to achieve with conventional acids.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in materials science and surface treatments
In materials science, fluoroantimonic acid is employed for surface treatments of various materials, including metals and polymers. It can be used to etch surfaces, modify surface properties, or create specialized coatings with enhanced characteristics such as improved adhesion or corrosion resistance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety considerations and handling procedures
Due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity, handling fluoroantimonic acid requires stringent safety measures. Specialized equipment, containment systems, and personal protective gear are essential when working with this superacid. Proper disposal and neutralization procedures must be followed to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical applications and instrumentation
Fluoroantimonic acid is used in certain analytical techniques and instrumentation, particularly in mass spectrometry and spectroscopic methods. Its strong ionizing properties make it useful for analyzing complex organic compounds or materials that are difficult to ionize with conventional methods. Specialized instruments and sample preparation techniques are required for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Superacid Research and Development
The field of Fluoroantimonic Acid catalysis is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global acid catalysis market is expanding, driven by demand in petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and fine chemicals. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., BASF Corp., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. leading in innovation. Academic institutions such as Emory University and Zhejiang University contribute to fundamental research. Emerging players like Sinochem Lantian Co., Ltd. and Zhejiang Lantian Environmental Protection HI Tech Co. Ltd. are focusing on application-specific developments. The industry sees a blend of established chemical giants and specialized firms, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape in Fluoroantimonic Acid catalysis technology.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Technical Solution: Merck has developed a hybrid catalyst system combining fluoroantimonic acid with transition metal complexes for asymmetric synthesis. This innovative approach harnesses the strong acidity of fluoroantimonic acid while leveraging the selectivity of metal catalysts. The system is particularly effective in the synthesis of chiral pharmaceutical intermediates, offering high enantioselectivity and yield. Merck's technology also includes a novel recycling process for the catalyst, improving its economic viability and reducing environmental impact.
Strengths: High selectivity in asymmetric synthesis, improved catalyst recyclability, and potential for green chemistry applications. Weaknesses: Complexity of the catalyst system and potential metal contamination in products.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a supported fluoroantimonic acid catalyst using their proprietary fluoropolymer technology. The catalyst is immobilized on a highly fluorinated porous support, allowing for heterogeneous catalysis while maintaining the superacid's extreme acidity. This innovation enables the use of fluoroantimonic acid in fixed-bed reactors and other continuous processing systems, significantly enhancing its applicability in large-scale industrial processes. The supported catalyst also shows improved thermal stability and easier separation from reaction mixtures.
Strengths: Heterogeneous catalysis capabilities, improved thermal stability, and easier product separation. Weaknesses: Potential diffusion limitations and reduced activity compared to homogeneous systems.
Core Innovations in Fluoroantimonic Acid Synthesis
Mixed metal double salt ionic liquids with tunable acidity
PatentInactiveUS20170209858A1
Innovation
- Development of mixed metal double salt ionic liquids with tunable acidity, comprising at least one organic cation and two metal halide anions, which can be used as catalysts for acid-catalyzed reactions, including Friedel Crafts alkylation and biodiesel production, with a melting point below 150°C, allowing for recyclability and improved safety.
Foamed acidizing fluids
PatentInactiveEP1342881B1
Innovation
- A foamed acidizing fluid comprising an aqueous acid solution, gas to form a foam, and an additive of hydrolyzed keratin, which is environmentally degradable and effective for foaming and stabilizing the fluid, is used for acidizing or fracture-acidizing subterranean zones.
Safety and Handling Protocols for Fluoroantimonic Acid
Fluoroantimonic acid, recognized as the world's strongest superacid, demands rigorous safety measures and handling protocols due to its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity. The primary concern when working with this compound is its violent reaction with water, which can lead to explosive situations. Therefore, all handling must occur in a completely anhydrous environment, typically using specialized glassware or containers made of materials resistant to hydrofluoric acid, such as PTFE (Teflon).
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling fluoroantimonic acid. This includes chemical-resistant suits, gloves, and face shields. Respiratory protection is also essential, as the acid can release highly toxic fumes. All personnel working with the acid must undergo thorough training on its properties, hazards, and emergency procedures.
Storage of fluoroantimonic acid requires specially designed facilities with controlled temperature and humidity. The acid must be kept in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers, away from any potential sources of water or moisture. Proper labeling and segregation from incompatible materials are vital to prevent accidental mixing.
In case of spills, specialized neutralization and containment procedures must be followed. This typically involves the use of dry, inert absorbents and careful neutralization with appropriate bases. Emergency showers and eyewash stations must be readily available in all areas where the acid is handled or stored.
Disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related waste materials requires strict adherence to hazardous waste regulations. Neutralization and dilution processes must be carried out by trained professionals in designated facilities equipped to handle such dangerous substances.
Regular safety audits and equipment inspections are essential to maintain the integrity of containment systems and ensure compliance with safety protocols. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, leaks, or degradation in storage and handling equipment.
Given the extreme hazards associated with fluoroantimonic acid, many research institutions and industries opt for alternatives when possible. When its use is unavoidable, remote handling systems or robotic manipulators may be employed to minimize direct human contact with the substance.
Comprehensive emergency response plans must be in place, including procedures for evacuation, containment, and medical treatment in case of exposure. Coordination with local emergency services is crucial to ensure they are prepared to respond to incidents involving this highly dangerous compound.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling fluoroantimonic acid. This includes chemical-resistant suits, gloves, and face shields. Respiratory protection is also essential, as the acid can release highly toxic fumes. All personnel working with the acid must undergo thorough training on its properties, hazards, and emergency procedures.
Storage of fluoroantimonic acid requires specially designed facilities with controlled temperature and humidity. The acid must be kept in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers, away from any potential sources of water or moisture. Proper labeling and segregation from incompatible materials are vital to prevent accidental mixing.
In case of spills, specialized neutralization and containment procedures must be followed. This typically involves the use of dry, inert absorbents and careful neutralization with appropriate bases. Emergency showers and eyewash stations must be readily available in all areas where the acid is handled or stored.
Disposal of fluoroantimonic acid and related waste materials requires strict adherence to hazardous waste regulations. Neutralization and dilution processes must be carried out by trained professionals in designated facilities equipped to handle such dangerous substances.
Regular safety audits and equipment inspections are essential to maintain the integrity of containment systems and ensure compliance with safety protocols. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, leaks, or degradation in storage and handling equipment.
Given the extreme hazards associated with fluoroantimonic acid, many research institutions and industries opt for alternatives when possible. When its use is unavoidable, remote handling systems or robotic manipulators may be employed to minimize direct human contact with the substance.
Comprehensive emergency response plans must be in place, including procedures for evacuation, containment, and medical treatment in case of exposure. Coordination with local emergency services is crucial to ensure they are prepared to respond to incidents involving this highly dangerous compound.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Fluoroantimonic acid, as a superacid catalyst, presents significant environmental concerns that require careful assessment and management. The production, use, and disposal of this powerful acid can have far-reaching impacts on ecosystems, human health, and the overall environment. One of the primary environmental risks associated with fluoroantimonic acid is its extreme corrosiveness and reactivity. Any accidental release or improper handling could lead to severe contamination of soil, water bodies, and air, potentially causing long-term ecological damage.
The acid's ability to react violently with water and many organic compounds poses a particular threat to aquatic ecosystems. Even small quantities released into water sources could drastically alter pH levels, leading to the death of aquatic organisms and disruption of entire food chains. Furthermore, the fluorine and antimony components of the acid can persist in the environment, potentially bioaccumulating in various organisms and moving up the food chain.
Air pollution is another significant concern, as the volatile nature of fluoroantimonic acid can result in the release of toxic fumes. These emissions may contribute to the formation of acid rain, further exacerbating environmental degradation over a wider area. The potential for long-range transport of these pollutants means that the environmental impact could extend far beyond the immediate vicinity of production or use sites.
From a human health perspective, exposure to fluoroantimonic acid or its byproducts can cause severe respiratory issues, skin burns, and other health problems. This necessitates stringent safety measures and protective equipment for workers involved in its production and handling. The potential for accidental exposure in surrounding communities also requires comprehensive emergency response plans and public safety protocols.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment for fluoroantimonic acid. The disposal of spent acid and contaminated materials must be carefully controlled to prevent environmental contamination. Specialized treatment facilities and neutralization processes are essential to render the waste safe for disposal, adding complexity and cost to the overall environmental management strategy.
Given these significant environmental risks, the use of fluoroantimonic acid in catalysis applications must be weighed against potential alternatives. Research into greener catalysts and more environmentally friendly processes is crucial for reducing the reliance on such hazardous substances. Additionally, comprehensive life cycle assessments should be conducted to fully understand and mitigate the environmental footprint of fluoroantimonic acid throughout its production, use, and disposal phases.
The acid's ability to react violently with water and many organic compounds poses a particular threat to aquatic ecosystems. Even small quantities released into water sources could drastically alter pH levels, leading to the death of aquatic organisms and disruption of entire food chains. Furthermore, the fluorine and antimony components of the acid can persist in the environment, potentially bioaccumulating in various organisms and moving up the food chain.
Air pollution is another significant concern, as the volatile nature of fluoroantimonic acid can result in the release of toxic fumes. These emissions may contribute to the formation of acid rain, further exacerbating environmental degradation over a wider area. The potential for long-range transport of these pollutants means that the environmental impact could extend far beyond the immediate vicinity of production or use sites.
From a human health perspective, exposure to fluoroantimonic acid or its byproducts can cause severe respiratory issues, skin burns, and other health problems. This necessitates stringent safety measures and protective equipment for workers involved in its production and handling. The potential for accidental exposure in surrounding communities also requires comprehensive emergency response plans and public safety protocols.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment for fluoroantimonic acid. The disposal of spent acid and contaminated materials must be carefully controlled to prevent environmental contamination. Specialized treatment facilities and neutralization processes are essential to render the waste safe for disposal, adding complexity and cost to the overall environmental management strategy.
Given these significant environmental risks, the use of fluoroantimonic acid in catalysis applications must be weighed against potential alternatives. Research into greener catalysts and more environmentally friendly processes is crucial for reducing the reliance on such hazardous substances. Additionally, comprehensive life cycle assessments should be conducted to fully understand and mitigate the environmental footprint of fluoroantimonic acid throughout its production, use, and disposal phases.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!