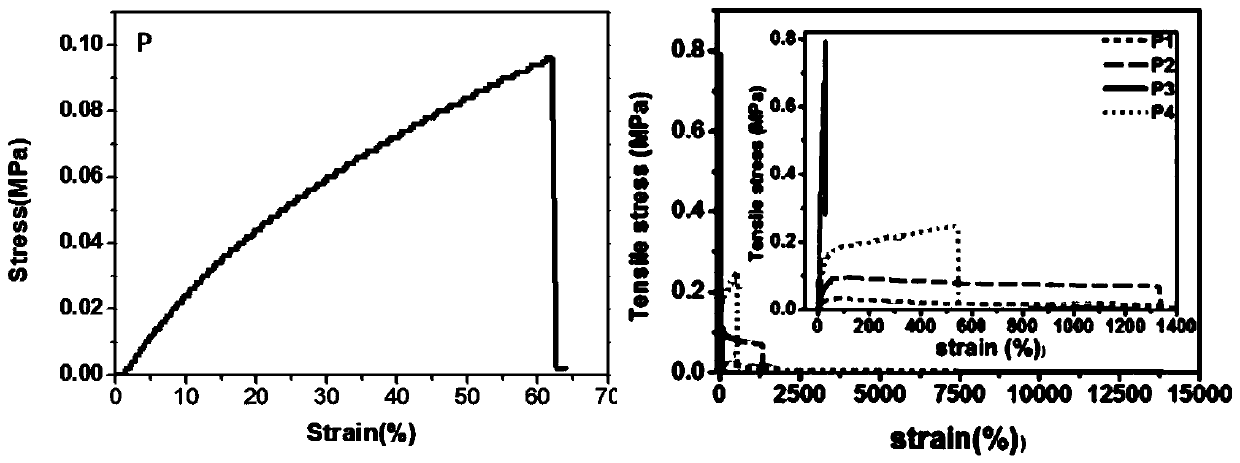
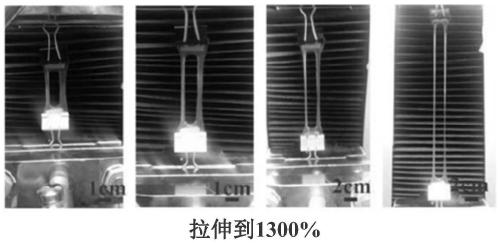
How Do Self-Healing Adhesives Rebuild Bond Strength Without External Pressure?
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Self-Healing Adhesives Background and Objectives
Self-healing adhesives represent a revolutionary advancement in materials science, emerging from the broader field of smart materials that can autonomously respond to environmental stimuli. The concept draws inspiration from biological systems, particularly the human body's ability to heal wounds without external intervention. Since the early 2000s, research in this domain has accelerated significantly, with pioneering work by researchers like White and Sottos at the University of Illinois establishing foundational principles for self-healing polymers.
The evolution of self-healing adhesives has progressed through several distinct phases: from early encapsulation-based systems to more sophisticated intrinsic healing mechanisms utilizing reversible chemical bonds. This technological progression aims to overcome the fundamental limitations of traditional adhesives, which typically fail permanently once their bond strength is compromised.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward biomimetic approaches and stimuli-responsive systems that can activate healing processes under specific environmental conditions. The integration of nanotechnology has further expanded possibilities, enabling more precise control over healing mechanisms at the molecular level.
The primary objective in self-healing adhesive development is to create bonding materials capable of autonomously restoring their structural integrity and adhesive strength after damage without requiring external pressure application—a significant challenge that distinguishes this technology from conventional repair methods. This capability would dramatically extend product lifecycles and reduce maintenance requirements across multiple industries.
Market projections suggest that successful implementation of pressure-independent self-healing adhesives could revolutionize sectors including aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronics, and medical devices, where adhesive failure often leads to costly system replacements rather than repairs.
Technical goals for next-generation self-healing adhesives include achieving rapid healing kinetics (minutes to hours rather than days), maintaining mechanical properties comparable to conventional adhesives, ensuring multiple healing cycles without performance degradation, and developing systems that function effectively across diverse environmental conditions including temperature extremes and high humidity.
Research objectives also encompass improving sustainability profiles through bio-based formulations and reducing the environmental footprint of adhesive technologies. The field increasingly focuses on developing systems that eliminate toxic components while maintaining performance characteristics.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms by which self-healing adhesives rebuild bond strength without external pressure represents a critical research frontier, requiring interdisciplinary collaboration between polymer chemistry, materials science, and mechanical engineering to overcome current technological barriers and realize the full potential of these innovative materials.
The evolution of self-healing adhesives has progressed through several distinct phases: from early encapsulation-based systems to more sophisticated intrinsic healing mechanisms utilizing reversible chemical bonds. This technological progression aims to overcome the fundamental limitations of traditional adhesives, which typically fail permanently once their bond strength is compromised.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward biomimetic approaches and stimuli-responsive systems that can activate healing processes under specific environmental conditions. The integration of nanotechnology has further expanded possibilities, enabling more precise control over healing mechanisms at the molecular level.
The primary objective in self-healing adhesive development is to create bonding materials capable of autonomously restoring their structural integrity and adhesive strength after damage without requiring external pressure application—a significant challenge that distinguishes this technology from conventional repair methods. This capability would dramatically extend product lifecycles and reduce maintenance requirements across multiple industries.
Market projections suggest that successful implementation of pressure-independent self-healing adhesives could revolutionize sectors including aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronics, and medical devices, where adhesive failure often leads to costly system replacements rather than repairs.
Technical goals for next-generation self-healing adhesives include achieving rapid healing kinetics (minutes to hours rather than days), maintaining mechanical properties comparable to conventional adhesives, ensuring multiple healing cycles without performance degradation, and developing systems that function effectively across diverse environmental conditions including temperature extremes and high humidity.
Research objectives also encompass improving sustainability profiles through bio-based formulations and reducing the environmental footprint of adhesive technologies. The field increasingly focuses on developing systems that eliminate toxic components while maintaining performance characteristics.
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms by which self-healing adhesives rebuild bond strength without external pressure represents a critical research frontier, requiring interdisciplinary collaboration between polymer chemistry, materials science, and mechanical engineering to overcome current technological barriers and realize the full potential of these innovative materials.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis
The self-healing adhesives market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries seeking sustainable and durable bonding solutions. The global market for smart adhesives, including self-healing variants, was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.8% through 2030, according to industry reports.
Automotive manufacturing represents one of the largest application sectors, where self-healing adhesives that can rebuild bond strength without external pressure address critical challenges in vehicle assembly and maintenance. These adhesives extend component lifespan and reduce warranty claims by automatically repairing microcracks formed during thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Major automotive manufacturers have reported up to 40% reduction in joint failures when implementing these advanced adhesive systems.
The aerospace industry presents another high-value market segment, where bond reliability directly impacts safety and performance. Self-healing adhesives capable of autonomous strength restoration are particularly valuable for components subjected to extreme temperature variations and vibration. Market research indicates that aerospace applications account for approximately 18% of the total self-healing adhesives market, with growth accelerating as certification processes advance.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have emerged as early adopters, implementing self-healing adhesives in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The ability to maintain bond integrity without manual intervention addresses the industry's need for increasingly thin, lightweight designs while maintaining durability. This sector is expected to show the fastest growth rate at 12.3% annually through 2028.
Construction and infrastructure applications represent an expanding market opportunity, particularly for outdoor installations where environmental exposure creates bonding challenges. Self-healing adhesives that can maintain structural integrity despite temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, and UV radiation are gaining traction in building envelope systems and infrastructure maintenance.
Medical device manufacturing constitutes a premium niche market where the ability to maintain sterile, reliable bonds is paramount. Self-healing adhesives that can rebuild strength autonomously are being evaluated for implantable devices, wound closure systems, and diagnostic equipment. Though currently representing only 7% of the market, this segment commands premium pricing and is projected to grow substantially as regulatory approvals increase.
Market analysis reveals that end-users are willing to pay a premium of 30-45% for self-healing capabilities compared to conventional adhesives, primarily due to reduced maintenance costs and extended product lifecycles. This price tolerance is highest in aerospace and medical applications where failure consequences are most severe.
Automotive manufacturing represents one of the largest application sectors, where self-healing adhesives that can rebuild bond strength without external pressure address critical challenges in vehicle assembly and maintenance. These adhesives extend component lifespan and reduce warranty claims by automatically repairing microcracks formed during thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Major automotive manufacturers have reported up to 40% reduction in joint failures when implementing these advanced adhesive systems.
The aerospace industry presents another high-value market segment, where bond reliability directly impacts safety and performance. Self-healing adhesives capable of autonomous strength restoration are particularly valuable for components subjected to extreme temperature variations and vibration. Market research indicates that aerospace applications account for approximately 18% of the total self-healing adhesives market, with growth accelerating as certification processes advance.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have emerged as early adopters, implementing self-healing adhesives in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The ability to maintain bond integrity without manual intervention addresses the industry's need for increasingly thin, lightweight designs while maintaining durability. This sector is expected to show the fastest growth rate at 12.3% annually through 2028.
Construction and infrastructure applications represent an expanding market opportunity, particularly for outdoor installations where environmental exposure creates bonding challenges. Self-healing adhesives that can maintain structural integrity despite temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, and UV radiation are gaining traction in building envelope systems and infrastructure maintenance.
Medical device manufacturing constitutes a premium niche market where the ability to maintain sterile, reliable bonds is paramount. Self-healing adhesives that can rebuild strength autonomously are being evaluated for implantable devices, wound closure systems, and diagnostic equipment. Though currently representing only 7% of the market, this segment commands premium pricing and is projected to grow substantially as regulatory approvals increase.
Market analysis reveals that end-users are willing to pay a premium of 30-45% for self-healing capabilities compared to conventional adhesives, primarily due to reduced maintenance costs and extended product lifecycles. This price tolerance is highest in aerospace and medical applications where failure consequences are most severe.
Current Technology Status and Challenges
Self-healing adhesives represent a significant advancement in materials science, with global research efforts intensifying over the past decade. Currently, the technology exists in various stages of development across academic institutions and industrial research centers in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with particular concentration in the United States, Germany, Japan, and China.
The fundamental challenge in self-healing adhesive technology lies in achieving autonomous restoration of bond strength without external intervention such as pressure, heat, or additional catalysts. Current systems predominantly rely on one of three mechanisms: microencapsulation, reversible chemical bonds, or vascular networks. While each approach has demonstrated promising results in laboratory settings, their translation to commercial applications faces significant hurdles.
Microencapsulation-based systems, though relatively mature, struggle with limited healing cycles and potential weakening of the base adhesive matrix. The microcapsules, once ruptured and healing agents released, cannot be replenished naturally, resulting in diminishing self-healing capacity over time. Additionally, the incorporation of microcapsules often compromises the initial mechanical properties of the adhesive.
Reversible bond systems utilizing Diels-Alder reactions, hydrogen bonding, or dynamic covalent chemistry show excellent theoretical potential for multiple healing cycles. However, these systems frequently require external stimuli like temperature changes to initiate the healing process, contradicting the goal of truly autonomous repair. The kinetics of bond reformation also remains too slow for many practical applications.
Vascular network approaches, while promising for continuous healing capability, present significant manufacturing complexities that have limited their practical implementation beyond laboratory prototypes. The intricate network structures required are difficult to produce at scale using conventional manufacturing techniques.
A critical technical barrier across all approaches is the challenge of achieving sufficient mobility of healing agents within the solidified adhesive matrix to reach damaged areas without external pressure. This mobility issue becomes particularly pronounced in low-temperature environments or after aging of the adhesive.
Market adoption is further constrained by cost factors, with current self-healing adhesives typically commanding a 200-400% price premium over conventional alternatives. Stability and shelf-life concerns also persist, with many experimental formulations showing degradation of self-healing capabilities during storage.
Regulatory frameworks for these novel materials remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty for manufacturers regarding testing protocols and certification requirements, particularly in safety-critical applications like aerospace or medical devices.
The fundamental challenge in self-healing adhesive technology lies in achieving autonomous restoration of bond strength without external intervention such as pressure, heat, or additional catalysts. Current systems predominantly rely on one of three mechanisms: microencapsulation, reversible chemical bonds, or vascular networks. While each approach has demonstrated promising results in laboratory settings, their translation to commercial applications faces significant hurdles.
Microencapsulation-based systems, though relatively mature, struggle with limited healing cycles and potential weakening of the base adhesive matrix. The microcapsules, once ruptured and healing agents released, cannot be replenished naturally, resulting in diminishing self-healing capacity over time. Additionally, the incorporation of microcapsules often compromises the initial mechanical properties of the adhesive.
Reversible bond systems utilizing Diels-Alder reactions, hydrogen bonding, or dynamic covalent chemistry show excellent theoretical potential for multiple healing cycles. However, these systems frequently require external stimuli like temperature changes to initiate the healing process, contradicting the goal of truly autonomous repair. The kinetics of bond reformation also remains too slow for many practical applications.
Vascular network approaches, while promising for continuous healing capability, present significant manufacturing complexities that have limited their practical implementation beyond laboratory prototypes. The intricate network structures required are difficult to produce at scale using conventional manufacturing techniques.
A critical technical barrier across all approaches is the challenge of achieving sufficient mobility of healing agents within the solidified adhesive matrix to reach damaged areas without external pressure. This mobility issue becomes particularly pronounced in low-temperature environments or after aging of the adhesive.
Market adoption is further constrained by cost factors, with current self-healing adhesives typically commanding a 200-400% price premium over conventional alternatives. Stability and shelf-life concerns also persist, with many experimental formulations showing degradation of self-healing capabilities during storage.
Regulatory frameworks for these novel materials remain underdeveloped, creating uncertainty for manufacturers regarding testing protocols and certification requirements, particularly in safety-critical applications like aerospace or medical devices.
Autonomous Healing Mechanisms and Solutions
01 Self-healing mechanisms in adhesives
Self-healing adhesives incorporate mechanisms that allow them to repair damage and restore bond strength after failure. These mechanisms can include microencapsulated healing agents that release when damage occurs, reversible chemical bonds that can reform after breaking, or materials that flow to fill gaps when heated or activated. These self-healing properties significantly extend the lifespan of adhesive bonds by preventing catastrophic failure from minor damage.- Self-healing mechanisms in adhesives: Self-healing adhesives incorporate mechanisms that allow them to repair damage and restore bond strength after being compromised. These mechanisms can include microencapsulated healing agents that release when damage occurs, reversible chemical bonds that can reform after breaking, or materials that flow into damaged areas when stimulated by heat or pressure. These self-healing properties help maintain bond integrity over time and extend the service life of adhesive joints.
- Polymer-based self-healing adhesives: Polymer-based self-healing adhesives utilize specific polymer chemistries to achieve both strong initial bonding and self-healing capabilities. These formulations often incorporate dynamic covalent bonds, supramolecular interactions, or thermally reversible cross-linking systems. The polymer matrices can be designed to respond to environmental triggers such as temperature changes, allowing them to flow and repair damage while maintaining overall structural integrity and bond strength.
- Composite and reinforced self-healing adhesives: Composite self-healing adhesives incorporate reinforcing materials such as fibers, nanoparticles, or specialized fillers to enhance both mechanical properties and healing capabilities. These additives can improve initial bond strength while also participating in or facilitating the healing process. The reinforcing components may create multiple healing pathways, improve crack resistance, or enhance the distribution of healing agents throughout the adhesive matrix.
- Testing and measurement of self-healing bond strength: Specialized testing methods have been developed to evaluate both the initial bond strength and self-healing efficiency of adhesives. These include cyclic loading tests, controlled damage protocols, and comparative strength measurements before and after healing events. Advanced analytical techniques such as microscopy, spectroscopy, and mechanical testing are employed to quantify healing efficiency and understand the mechanisms involved in strength recovery after damage.
- Environmental factors affecting self-healing and bond strength: The performance of self-healing adhesives is significantly influenced by environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals. Formulations can be tailored to optimize healing efficiency and bond strength under specific environmental conditions. Some self-healing adhesives are designed to activate their healing mechanisms in response to environmental triggers, while others maintain consistent performance across a range of conditions through specialized additives or protective components.
02 Polymer-based self-healing adhesives
Polymer-based self-healing adhesives utilize specific polymer structures to achieve both strong initial bonding and self-healing capabilities. These formulations often incorporate dynamic covalent bonds, supramolecular interactions, or thermally reversible cross-linking systems. The polymer matrices can be designed to respond to various stimuli such as temperature, pH, or mechanical stress, allowing them to recover bond strength after damage while maintaining structural integrity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanoparticle reinforcement for enhanced bond strength
Incorporating nanoparticles into self-healing adhesive formulations can significantly enhance bond strength while maintaining self-healing properties. Nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, silica, or metal oxides create additional bonding sites within the adhesive matrix. This reinforcement improves mechanical properties including tensile strength, shear resistance, and durability, resulting in stronger bonds that can still undergo self-healing when damaged.Expand Specific Solutions04 Testing methods for self-healing adhesive bond strength
Specialized testing methods have been developed to evaluate both the initial bond strength and self-healing efficiency of adhesives. These include cyclic loading tests, lap shear strength measurements before and after healing, and advanced imaging techniques to visualize the healing process. Testing protocols often involve controlled damage application followed by healing periods under specific conditions to quantify the percentage of bond strength recovery after multiple healing cycles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of self-healing adhesives
Self-healing adhesives with high bond strength have found applications across various industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. These adhesives are particularly valuable in applications where maintenance is difficult or impossible, or where bond failure could lead to catastrophic consequences. Formulations have been developed to meet specific industry requirements such as temperature resistance, chemical stability, electrical conductivity, and compatibility with different substrate materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions
Self-healing adhesives represent an emerging technology at the intersection of materials science and chemistry, currently in the early growth phase. The market is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant scale as industries recognize the potential for maintenance-free bonding solutions. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different approaches. Academic institutions like Jiangnan University, Nanjing University, and Peking University are advancing fundamental research in autonomous healing mechanisms, while companies such as Fundación CIDETEC, Mitsui Chemicals, and Sony Group Corp. are developing commercial applications. The most promising technologies involve intrinsic self-healing through reversible chemical bonds and microencapsulated healing agents that activate upon fracture. The competition is intensifying as research institutions partner with industrial players to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and market-ready products.
Jiangnan University
Technical Solution: Jiangnan University has developed innovative self-healing adhesives based on dynamic imine bond chemistry. Their approach utilizes Schiff base reactions between amine and aldehyde functional groups incorporated into polymer backbones, creating reversible crosslinks that can break and reform without external pressure application. When damage occurs, these dynamic bonds undergo exchange reactions at the interface, allowing polymer chains to reconnect across the damaged area. The healing mechanism is facilitated by slight molecular mobility at the damage interface, where free amine and aldehyde groups from broken bonds can find new reaction partners. This process is enhanced by incorporating phase-separated domains with different glass transition temperatures, creating regions of higher chain mobility that facilitate healing while maintaining overall structural integrity. Jiangnan researchers have demonstrated healing efficiencies of 75-85% within 24-48 hours at ambient conditions, with healing rates accelerated by mild heating (40-60°C) or exposure to specific pH environments. Their latest formulations incorporate catalytic nanoparticles that lower the energy barrier for imine exchange reactions, enabling faster healing kinetics without compromising adhesive performance.
Strengths: Multiple healing cycles possible due to the reversible nature of imine bonds; environmentally responsive healing can be triggered by pH changes; good compatibility with various substrate materials; maintains reasonable shelf stability. Weaknesses: Slower healing kinetics compared to pressure-assisted systems; moisture sensitivity can affect long-term stability in humid environments; mechanical properties may be compromised after multiple healing cycles; healing efficiency decreases at lower temperatures.
Fundación CIDETEC
Technical Solution: CIDETEC has developed advanced self-healing adhesives based on dynamic covalent chemistry, specifically utilizing Diels-Alder reactions that enable reversible bond formation. Their technology incorporates furan and maleimide functional groups within polymer networks that can undergo thermally-activated healing. When damage occurs, these adhesives rebuild bond strength through temperature-triggered rearrangement of covalent bonds without requiring external pressure application. The healing mechanism relies on the thermoreversible nature of the Diels-Alder adducts, which dissociate at elevated temperatures (typically 120-150°C) and reform upon cooling, effectively "zipping" the damaged interfaces back together. CIDETEC has demonstrated healing efficiencies of up to 95% of original bond strength in their epoxy-based systems, with complete restoration occurring within 1-2 heating/cooling cycles.
Strengths: Achieves near-complete restoration of mechanical properties without pressure application; healing can be repeated multiple times without significant property degradation; compatible with existing manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Requires thermal activation which limits applications in heat-sensitive environments; healing process is relatively slow compared to pressure-assisted systems; may have reduced initial bond strength compared to conventional adhesives.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs
Self-healing elastomer material based on reversible noncovalent interaction and preparation method of self-healing elastomer material
PatentActiveCN107955161A
Innovation
- By introducing high bond energy ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds to build a dual interaction network of reversible hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds between molecules, a new self-healing polyamide material is prepared, using polybasic organic acids, polyamines and alkaline metal compounds. Reacts under specific conditions to form a self-healing elastomer with high mechanical strength and room temperature self-healing properties.
Autonomous self-repairing elastomer with high tensile property as well as preparation method and application thereof
PatentActiveCN111285988A
Innovation
- Silicone resin, disulfide bond monomers, weak hydrogen bonding compounds, and strong hydrogen bonding compounds are chemically cross-linked to form a dynamic supramolecular polymer network to achieve autonomous self-healing, and can be used at room temperature, low temperature, underwater, and low-temperature water. Has high tensile properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Self-healing adhesives represent a significant advancement in sustainable materials science, offering substantial environmental benefits compared to traditional adhesive systems. The elimination of the need for external pressure during the healing process further enhances their sustainability profile by reducing energy requirements and operational complexity.
The environmental impact of self-healing adhesives begins with their extended service life. By autonomously repairing damage and restoring bond strength, these materials significantly reduce the frequency of replacement and maintenance. This longevity directly translates to decreased raw material consumption, lower manufacturing energy expenditure, and reduced waste generation throughout the product lifecycle.
Particularly noteworthy is the contribution of self-healing adhesives to the circular economy model. Many contemporary self-healing systems incorporate biodegradable components or bio-based materials, such as those derived from plant oils, cellulose, or chitosan. These renewable resources minimize dependence on petroleum-based feedstocks, substantially reducing the carbon footprint associated with adhesive production.
The waste reduction potential of these materials extends beyond their primary application. When self-healing adhesives are used in composite materials or bonded assemblies, they can prevent premature failure of the entire structure. This cascading effect prevents the disposal of otherwise functional components, addressing a significant waste stream in industries such as electronics, automotive manufacturing, and construction.
From a lifecycle assessment perspective, self-healing adhesives demonstrate favorable environmental metrics. The energy invested in developing more sophisticated adhesive chemistry is offset by savings in maintenance operations, replacement manufacturing, and waste management. Studies indicate that the embodied energy of self-healing systems becomes advantageous after just a few healing cycles in most applications.
Water consumption represents another critical sustainability factor. Traditional adhesive manufacturing often involves water-intensive processes and generates contaminated wastewater. Many self-healing mechanisms, particularly those based on supramolecular chemistry or dynamic covalent bonds, can be formulated with reduced water requirements and fewer harmful effluents.
The end-of-life considerations for self-healing adhesives also present opportunities for environmental improvement. Research is advancing toward systems that not only self-heal but can also be triggered to debond on demand, facilitating the separation of materials for recycling. This property addresses one of the most persistent challenges in adhesive sustainability: enabling the recovery of bonded components without contamination or degradation.
The environmental impact of self-healing adhesives begins with their extended service life. By autonomously repairing damage and restoring bond strength, these materials significantly reduce the frequency of replacement and maintenance. This longevity directly translates to decreased raw material consumption, lower manufacturing energy expenditure, and reduced waste generation throughout the product lifecycle.
Particularly noteworthy is the contribution of self-healing adhesives to the circular economy model. Many contemporary self-healing systems incorporate biodegradable components or bio-based materials, such as those derived from plant oils, cellulose, or chitosan. These renewable resources minimize dependence on petroleum-based feedstocks, substantially reducing the carbon footprint associated with adhesive production.
The waste reduction potential of these materials extends beyond their primary application. When self-healing adhesives are used in composite materials or bonded assemblies, they can prevent premature failure of the entire structure. This cascading effect prevents the disposal of otherwise functional components, addressing a significant waste stream in industries such as electronics, automotive manufacturing, and construction.
From a lifecycle assessment perspective, self-healing adhesives demonstrate favorable environmental metrics. The energy invested in developing more sophisticated adhesive chemistry is offset by savings in maintenance operations, replacement manufacturing, and waste management. Studies indicate that the embodied energy of self-healing systems becomes advantageous after just a few healing cycles in most applications.
Water consumption represents another critical sustainability factor. Traditional adhesive manufacturing often involves water-intensive processes and generates contaminated wastewater. Many self-healing mechanisms, particularly those based on supramolecular chemistry or dynamic covalent bonds, can be formulated with reduced water requirements and fewer harmful effluents.
The end-of-life considerations for self-healing adhesives also present opportunities for environmental improvement. Research is advancing toward systems that not only self-heal but can also be triggered to debond on demand, facilitating the separation of materials for recycling. This property addresses one of the most persistent challenges in adhesive sustainability: enabling the recovery of bonded components without contamination or degradation.
Performance Metrics and Testing Standards
Evaluating the performance of self-healing adhesives requires standardized metrics and testing protocols that differ significantly from conventional adhesives. The primary challenge lies in quantifying not only initial bond strength but also recovery efficiency after damage events. Standard tests such as lap shear strength, peel resistance, and tensile strength must be adapted to include measurements before damage, immediately after damage, and following the healing period.
The healing efficiency ratio has emerged as a critical performance indicator, calculated as the percentage of original bond strength recovered after the healing process. High-performing self-healing adhesives typically achieve 70-95% recovery without external pressure application, though this varies significantly based on chemistry and environmental conditions. Time-dependent recovery curves are essential for characterizing healing kinetics, with measurements taken at multiple intervals to determine both immediate and long-term recovery profiles.
Environmental testing standards have been developed to assess healing performance across temperature ranges (-20°C to 80°C), humidity levels, and exposure to chemicals or UV radiation. These parameters significantly impact the autonomous healing mechanisms, particularly for systems relying on molecular diffusion or dynamic covalent chemistry. Accelerated aging protocols have been adapted specifically for self-healing materials to predict long-term performance and durability.
Cyclic damage-heal testing represents another crucial evaluation method, where adhesives undergo multiple damage-healing cycles to assess cumulative recovery capacity. Leading self-healing systems maintain over 60% of their original strength even after five consecutive healing cycles, though performance typically degrades with each iteration. This metric is particularly relevant for applications in vibration-prone environments where repeated microcracking occurs.
Microscopic evaluation techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and Raman spectroscopy have been standardized to visualize and quantify the physical healing process at the molecular level. These techniques allow researchers to correlate macroscopic strength recovery with microscopic structural reorganization, providing insights into healing mechanisms.
Industry-specific standards are emerging through organizations like ASTM International and ISO, which are developing dedicated testing protocols for self-healing materials. The ASTM D7234-21 standard has been modified to include healing efficiency measurements, while ISO 10365 now incorporates guidelines for evaluating autonomous recovery in adhesive bonds. These evolving standards are crucial for enabling meaningful comparisons between different self-healing technologies and accelerating their commercial adoption.
The healing efficiency ratio has emerged as a critical performance indicator, calculated as the percentage of original bond strength recovered after the healing process. High-performing self-healing adhesives typically achieve 70-95% recovery without external pressure application, though this varies significantly based on chemistry and environmental conditions. Time-dependent recovery curves are essential for characterizing healing kinetics, with measurements taken at multiple intervals to determine both immediate and long-term recovery profiles.
Environmental testing standards have been developed to assess healing performance across temperature ranges (-20°C to 80°C), humidity levels, and exposure to chemicals or UV radiation. These parameters significantly impact the autonomous healing mechanisms, particularly for systems relying on molecular diffusion or dynamic covalent chemistry. Accelerated aging protocols have been adapted specifically for self-healing materials to predict long-term performance and durability.
Cyclic damage-heal testing represents another crucial evaluation method, where adhesives undergo multiple damage-healing cycles to assess cumulative recovery capacity. Leading self-healing systems maintain over 60% of their original strength even after five consecutive healing cycles, though performance typically degrades with each iteration. This metric is particularly relevant for applications in vibration-prone environments where repeated microcracking occurs.
Microscopic evaluation techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and Raman spectroscopy have been standardized to visualize and quantify the physical healing process at the molecular level. These techniques allow researchers to correlate macroscopic strength recovery with microscopic structural reorganization, providing insights into healing mechanisms.
Industry-specific standards are emerging through organizations like ASTM International and ISO, which are developing dedicated testing protocols for self-healing materials. The ASTM D7234-21 standard has been modified to include healing efficiency measurements, while ISO 10365 now incorporates guidelines for evaluating autonomous recovery in adhesive bonds. These evolving standards are crucial for enabling meaningful comparisons between different self-healing technologies and accelerating their commercial adoption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!