How Ethyl Acetate Drives Innovation in Eco-Conscious Design?
Ethyl Acetate Background and Objectives
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has emerged as a key player in the realm of eco-conscious design. This colorless liquid, with its fruity odor and low toxicity, has been utilized in various industries for decades. However, its potential to drive innovation in sustainable product development has only recently gained significant attention.
The evolution of ethyl acetate's role in eco-friendly design can be traced back to the growing awareness of environmental issues in the late 20th century. As concerns about climate change and resource depletion intensified, industries began seeking alternatives to traditional, harmful chemicals. Ethyl acetate, with its biodegradable nature and relatively low environmental impact, presented itself as a promising candidate for sustainable applications.
In recent years, the push for greener technologies has accelerated the exploration of ethyl acetate's capabilities. Its unique properties, including low toxicity, high solvency power, and rapid evaporation rate, have made it an attractive option for replacing more hazardous solvents in various manufacturing processes. This shift aligns with the global trend towards adopting cleaner production methods and reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations.
The technical objectives surrounding ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers and industry professionals aim to expand its application in green chemistry, focusing on developing new synthesis routes that are more energy-efficient and produce fewer by-products. Additionally, there is a growing interest in enhancing ethyl acetate's performance in specific applications, such as improving its efficacy as a cleaning agent or increasing its stability in certain formulations.
Another key objective is to optimize the production of ethyl acetate from renewable resources. While traditionally synthesized from petrochemical feedstocks, recent efforts have been directed towards developing bio-based production methods. This aligns with the broader goal of transitioning towards a circular economy, where materials are sustainably sourced and can be easily recycled or biodegraded at the end of their lifecycle.
The integration of ethyl acetate into eco-conscious design also aims to address regulatory challenges. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, industries are under pressure to adopt safer and more sustainable practices. Ethyl acetate's favorable environmental profile positions it as a compliant alternative in many applications, driving research into its expanded use across diverse sectors.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design is expected to focus on innovation in material science. This includes exploring its potential in developing new biodegradable plastics, enhancing the performance of eco-friendly coatings, and creating novel composite materials with reduced environmental impact. The ultimate goal is to leverage ethyl acetate's properties to create products that are not only functional but also align with the principles of sustainability and circular economy.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Solvents
The market demand for eco-friendly solvents has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Ethyl acetate, a biodegradable and low-toxicity solvent, has emerged as a key player in this shift towards more sustainable chemical solutions.
In the paints and coatings industry, there is a significant push for water-based and low-VOC formulations. Ethyl acetate's ability to dissolve a wide range of resins and its quick evaporation rate make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining product performance. This has led to a surge in demand from both industrial and consumer segments.
The personal care and cosmetics sector has also shown a strong interest in ethyl acetate as a replacement for more harmful solvents. Its mild odor and low skin irritation potential make it suitable for use in nail polish removers, fragrances, and other beauty products. Consumers are increasingly seeking out products with "clean" and "natural" labels, driving brands to reformulate with eco-friendly ingredients like ethyl acetate.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl acetate's low toxicity profile has made it a preferred solvent for drug synthesis and extraction processes. As the industry faces pressure to adopt greener practices, the demand for ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical manufacturing is expected to grow substantially.
The electronics sector, particularly in the production of printed circuit boards and semiconductor cleaning, has been exploring ethyl acetate as an alternative to traditional chlorinated solvents. Its effectiveness in removing flux residues without damaging sensitive components has led to increased adoption in high-tech manufacturing processes.
The packaging industry, especially flexible packaging, has seen a rise in the use of ethyl acetate-based adhesives. These adhesives offer improved sustainability profiles compared to solvent-based alternatives, meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions in the food and beverage sector.
Agricultural applications have also contributed to the growing market for ethyl acetate. Its use in pesticide formulations as a more environmentally friendly carrier solvent aligns with the trend towards sustainable farming practices and reduced chemical impact on ecosystems.
As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, industries are proactively seeking alternatives to traditional solvents. This regulatory pressure, combined with corporate sustainability initiatives and consumer preferences, is expected to further boost the demand for eco-friendly solvents like ethyl acetate in the coming years.
Current State and Challenges in Green Chemistry
The field of green chemistry has made significant strides in recent years, with ethyl acetate emerging as a key player in driving eco-conscious design innovations. Currently, the global chemical industry is undergoing a paradigm shift towards more sustainable practices, with a focus on reducing environmental impact and improving resource efficiency. Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has gained prominence due to its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability compared to traditional solvents.
One of the primary challenges in green chemistry is the development of environmentally friendly solvents that can effectively replace harmful alternatives. Ethyl acetate has shown promise in this regard, particularly in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances while maintaining a lower environmental footprint has made it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to align with sustainability goals.
However, the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate and other green solvents faces several obstacles. Cost remains a significant barrier, as the production of eco-friendly alternatives often involves more expensive processes compared to conventional methods. This economic challenge has slowed the transition in some sectors, particularly where profit margins are tight.
Another hurdle is the need for process optimization and equipment modifications to accommodate the different properties of green solvents. Many existing manufacturing systems are designed for traditional solvents, and retrofitting or replacing these systems requires substantial investment and technical expertise. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and may temporarily disrupt production, deterring some companies from making the switch.
Regulatory frameworks also play a crucial role in the current state of green chemistry. While there is growing support for sustainable practices, the lack of uniform global standards and incentives for adopting green technologies can hinder progress. Some regions have implemented stricter regulations on chemical use and emissions, driving innovation in eco-friendly solutions, but disparities in international policies create challenges for companies operating in multiple markets.
Research and development in the field of green chemistry continue to push boundaries, with efforts focused on improving the efficiency and scalability of ethyl acetate production. Biotechnological approaches, such as the use of engineered microorganisms for ethyl acetate synthesis, show promise in reducing energy consumption and increasing yield. However, these methods are still in the early stages of development and face challenges in scaling up to industrial levels.
The integration of ethyl acetate into eco-conscious design also requires a holistic approach to product lifecycle assessment. While the compound itself may be more environmentally friendly, its production and end-of-life disposal must also be considered to ensure a truly sustainable solution. This comprehensive evaluation adds complexity to the adoption process but is essential for long-term environmental benefits.
Existing Eco-Conscious Applications of Ethyl Acetate
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of catalysts. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate, which is an important industrial solvent and chemical intermediate.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent for extractions, reactions, and formulations. It is particularly useful in the production of pharmaceuticals, coatings, and other industrial products due to its favorable properties and relatively low toxicity.
- Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science: Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer and material science applications, such as in the preparation of polymer solutions, as a component in adhesives, and in the production of various materials. Its use can affect the properties and performance of the resulting products.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing more sustainable production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices to minimize risks associated with its flammability and volatility.
- Novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate: Researchers are exploring novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate to enhance its properties or create new compounds with desirable characteristics. This includes the development of functionalized versions of ethyl acetate for specific applications in various industries.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in chemical synthesis is highlighted.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
The use of ethyl acetate as an extraction solvent or in separation processes is described. Its properties make it suitable for extracting various compounds from mixtures or for use in chromatographic techniques. Applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries are mentioned.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Processes and systems for handling, storing, and disposing of ethyl acetate safely are discussed. This includes methods for reducing emissions, recovering ethyl acetate from waste streams, and ensuring worker safety when dealing with this volatile organic compound.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulations and compositions containing ethyl acetate
Innovative formulations and compositions incorporating ethyl acetate are presented. These may include adhesives, coatings, cleaning solutions, or specialty chemical blends where ethyl acetate serves as a key component or solvent, enhancing the performance or properties of the final product.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Acetate Production
The market for ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable materials across industries. The technology is in a mature stage, with established players like Eastman Chemical Co. and LG Chem Ltd. leading innovation. However, emerging companies such as Viridis Chemical LLC are disrupting the market with 100% bio-based ethyl acetate production. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring chemical giants, specialized manufacturers, and research institutions collaborating to develop greener solutions. As environmental regulations tighten globally, companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve production efficiency and reduce carbon footprint, indicating a shift towards more sustainable practices in the ethyl acetate industry.
Celanese International Corp.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Acetate Synthesis
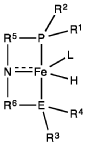
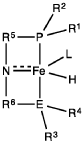
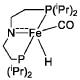
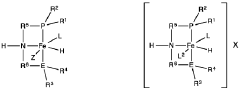
- A process utilizing a homogeneous iron catalyst with a tridentate pincer ligand for dehydrogenative coupling of ethanol at moderate temperatures, producing ethyl acetate efficiently and selectively, with iron loadings as low as 0.001 mol%, allowing for continuous operation and easy separation of ethyl acetate from the catalyst.
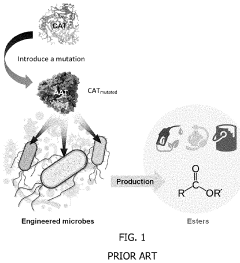
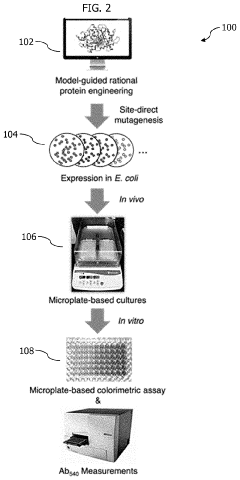
- A high-throughput microbial screening platform using preselected plasmids and a colorimetric assay is developed to identify AATs for ester biosynthesis, involving in situ fermentation with a solvent overlay and subsequent measurement of ester concentration through an iron-hydroxamic acid complex, allowing for rapid and efficient selection of AATs and synthesis of butyryl-CoA derived esters by modularly designing ester biosynthesis pathways.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design reveals a complex interplay of benefits and challenges. As a solvent widely used in various industries, ethyl acetate's role in driving innovation towards more sustainable practices is significant.
Ethyl acetate's biodegradability and low toxicity make it an attractive alternative to more harmful solvents. Its rapid evaporation rate and minimal residue contribute to reduced environmental persistence. These properties align well with the principles of green chemistry and sustainable product design, supporting the development of eco-friendly coatings, adhesives, and cleaning solutions.
In the realm of waste reduction, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances enables more efficient recycling processes, particularly in the recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste. This application not only conserves resources but also minimizes the environmental burden of e-waste disposal.
However, the production of ethyl acetate itself presents environmental considerations. Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions. Innovative approaches using bio-based feedstocks are emerging, offering a more sustainable production pathway. These bio-based alternatives have the potential to significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with ethyl acetate production.
The use of ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design also impacts air quality. While its low toxicity is advantageous, its volatile nature can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This necessitates careful handling and emission control strategies in industrial applications to mitigate potential air quality impacts.
Water pollution risks associated with ethyl acetate are generally low due to its high volatility and biodegradability. However, proper disposal and handling practices remain crucial to prevent contamination of water bodies, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
In the context of life cycle assessment, products utilizing ethyl acetate often demonstrate improved environmental performance compared to those using more persistent or toxic solvents. This advantage extends throughout the product lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal, supporting the circular economy principles.
The adoption of ethyl acetate in eco-conscious design also drives innovation in related fields. It encourages the development of more efficient application technologies, improved recycling methods, and novel formulations that maximize its benefits while minimizing environmental impact. This ripple effect of innovation contributes to broader advancements in sustainable chemistry and manufacturing practices.
Regulatory Framework for Green Solvents
The regulatory framework for green solvents, including ethyl acetate, plays a crucial role in driving innovation in eco-conscious design. As environmental concerns continue to grow, governments and international organizations have implemented stringent regulations to promote the use of sustainable and environmentally friendly solvents in various industries.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation sets the standard for chemical safety and environmental protection. Under REACH, ethyl acetate is classified as a low-risk substance, making it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to comply with EU regulations. The regulation encourages the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, further promoting the use of green solvents like ethyl acetate.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of solvents through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Clean Air Act. The EPA has designated ethyl acetate as a low-toxicity solvent, exempt from volatile organic compound (VOC) regulations in many applications. This regulatory status has incentivized industries to adopt ethyl acetate as a replacement for more harmful solvents, driving innovation in product formulations and manufacturing processes.
The global push towards circular economy principles has also influenced the regulatory landscape for green solvents. Many countries have introduced extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including the solvents used in production. This has led to increased research and development in solvent recovery and recycling technologies, with ethyl acetate's relatively low boiling point making it an ideal candidate for efficient recovery processes.
International standards and certification schemes have emerged to support the regulatory framework for green solvents. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standards for environmental management (ISO 14000 series) and life cycle assessment (ISO 14040 series), which provide guidelines for evaluating the environmental impact of solvents throughout their lifecycle. These standards have become important benchmarks for companies seeking to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and comply with regulatory requirements.
In developing countries, regulatory frameworks for green solvents are evolving rapidly. Many nations are adopting or adapting regulations from more established markets, recognizing the importance of aligning with global environmental standards. This harmonization of regulations across different regions is creating new opportunities for innovation in eco-conscious design, as companies develop products that can meet diverse regulatory requirements while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with increasing focus on the circular economy, resource efficiency, and reduction of carbon footprint. As a result, the regulatory framework for green solvents is expected to become more comprehensive and stringent in the coming years, further driving innovation in eco-conscious design and solidifying the position of ethyl acetate as a key player in sustainable industrial practices.