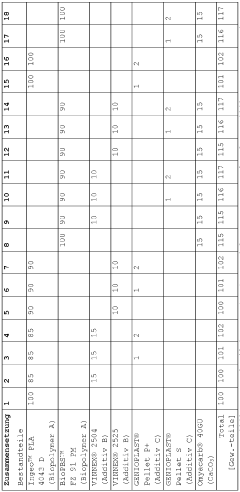
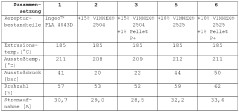
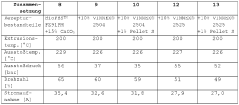
How Ethyl Propanoate Contributes to Biopolymer Blending Techniques
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate in Biopolymer Blending: Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a significant component in the field of biopolymer blending techniques. This ester compound, with its unique chemical properties, has garnered attention for its potential to enhance the performance and compatibility of biopolymer blends. The development of biopolymer blending techniques has been driven by the growing demand for sustainable and biodegradable materials across various industries.
The evolution of biopolymer blending techniques can be traced back to the early 1990s when researchers began exploring ways to improve the properties of biodegradable polymers. Initially, the focus was on blending different types of biopolymers to overcome individual limitations. However, as the field progressed, the incorporation of small molecules like ethyl propanoate gained traction due to their ability to modify interfacial properties and enhance miscibility between different polymer phases.
Ethyl propanoate's role in biopolymer blending has been increasingly recognized over the past decade. Its low molecular weight and ester functionality make it an excellent candidate for improving the compatibility between hydrophilic and hydrophobic biopolymers. This characteristic is particularly valuable in creating blends with enhanced mechanical properties and controlled degradation rates.
The primary objective of incorporating ethyl propanoate into biopolymer blending techniques is to develop materials with superior performance characteristics while maintaining their biodegradability. Researchers aim to exploit the plasticizing effect of ethyl propanoate to improve the flexibility and processability of biopolymer blends. Additionally, its potential to act as a reactive compatibilizer opens up new possibilities for creating novel biopolymer composites with tailored properties.
Current research trends in this field focus on optimizing the concentration and distribution of ethyl propanoate within biopolymer matrices. Scientists are exploring various blending methodologies, including melt blending, solution casting, and reactive extrusion, to achieve homogeneous dispersion of ethyl propanoate and maximize its impact on blend properties.
The integration of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending techniques aligns with the broader goals of sustainable materials development. As industries seek alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, the ability to create high-performance biopolymer blends using environmentally friendly additives like ethyl propanoate becomes increasingly crucial. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also opens up new avenues for material design in sectors such as packaging, agriculture, and biomedical applications.
The evolution of biopolymer blending techniques can be traced back to the early 1990s when researchers began exploring ways to improve the properties of biodegradable polymers. Initially, the focus was on blending different types of biopolymers to overcome individual limitations. However, as the field progressed, the incorporation of small molecules like ethyl propanoate gained traction due to their ability to modify interfacial properties and enhance miscibility between different polymer phases.
Ethyl propanoate's role in biopolymer blending has been increasingly recognized over the past decade. Its low molecular weight and ester functionality make it an excellent candidate for improving the compatibility between hydrophilic and hydrophobic biopolymers. This characteristic is particularly valuable in creating blends with enhanced mechanical properties and controlled degradation rates.
The primary objective of incorporating ethyl propanoate into biopolymer blending techniques is to develop materials with superior performance characteristics while maintaining their biodegradability. Researchers aim to exploit the plasticizing effect of ethyl propanoate to improve the flexibility and processability of biopolymer blends. Additionally, its potential to act as a reactive compatibilizer opens up new possibilities for creating novel biopolymer composites with tailored properties.
Current research trends in this field focus on optimizing the concentration and distribution of ethyl propanoate within biopolymer matrices. Scientists are exploring various blending methodologies, including melt blending, solution casting, and reactive extrusion, to achieve homogeneous dispersion of ethyl propanoate and maximize its impact on blend properties.
The integration of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending techniques aligns with the broader goals of sustainable materials development. As industries seek alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, the ability to create high-performance biopolymer blends using environmentally friendly additives like ethyl propanoate becomes increasingly crucial. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also opens up new avenues for material design in sectors such as packaging, agriculture, and biomedical applications.
Market Analysis for Biopolymer Blends
The market for biopolymer blends has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable materials across various industries. The global biopolymer market, which includes biopolymer blends, is projected to reach a substantial value by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% during the forecast period.
The packaging industry remains the largest consumer of biopolymer blends, accounting for over 40% of the market share. This sector's demand is fueled by the need for eco-friendly packaging solutions in response to stringent regulations and changing consumer preferences. The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown a strong inclination towards biopolymer blends for packaging applications.
Automotive and transportation sectors are emerging as promising markets for biopolymer blends. These industries are increasingly adopting biopolymer-based composites to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. The market share of biopolymer blends in this sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% in the coming years.
The medical and healthcare industry presents another lucrative opportunity for biopolymer blends. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of these materials make them ideal for applications such as drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and medical implants. This sector is anticipated to witness rapid growth, with a projected CAGR of around 18% through 2025.
Geographically, Europe leads the biopolymer blends market, followed closely by North America. These regions benefit from stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness regarding sustainable products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing environmental consciousness.
The market for biopolymer blends faces certain challenges, including higher production costs compared to conventional polymers and limitations in performance characteristics. However, ongoing research and development efforts, including the exploration of ethyl propanoate's role in biopolymer blending techniques, are addressing these issues and expanding the potential applications of these materials.
Key market players in the biopolymer blends industry include NatureWorks LLC, Novamont S.p.A., BASF SE, and Total Corbion PLA. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the properties and reduce the costs of biopolymer blends, thereby driving market growth and innovation.
The packaging industry remains the largest consumer of biopolymer blends, accounting for over 40% of the market share. This sector's demand is fueled by the need for eco-friendly packaging solutions in response to stringent regulations and changing consumer preferences. The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown a strong inclination towards biopolymer blends for packaging applications.
Automotive and transportation sectors are emerging as promising markets for biopolymer blends. These industries are increasingly adopting biopolymer-based composites to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. The market share of biopolymer blends in this sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% in the coming years.
The medical and healthcare industry presents another lucrative opportunity for biopolymer blends. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of these materials make them ideal for applications such as drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and medical implants. This sector is anticipated to witness rapid growth, with a projected CAGR of around 18% through 2025.
Geographically, Europe leads the biopolymer blends market, followed closely by North America. These regions benefit from stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness regarding sustainable products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing environmental consciousness.
The market for biopolymer blends faces certain challenges, including higher production costs compared to conventional polymers and limitations in performance characteristics. However, ongoing research and development efforts, including the exploration of ethyl propanoate's role in biopolymer blending techniques, are addressing these issues and expanding the potential applications of these materials.
Key market players in the biopolymer blends industry include NatureWorks LLC, Novamont S.p.A., BASF SE, and Total Corbion PLA. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the properties and reduce the costs of biopolymer blends, thereby driving market growth and innovation.
Current Challenges in Biopolymer Blending Techniques
Biopolymer blending techniques have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to create sustainable and biodegradable materials. However, several challenges persist in this field, hindering the widespread adoption and optimization of these techniques.
One of the primary challenges is achieving consistent and uniform blending of different biopolymers. The inherent incompatibility between various biopolymers often results in phase separation, leading to poor mechanical properties and inconsistent material performance. This issue is particularly pronounced when attempting to blend hydrophilic and hydrophobic biopolymers, as their contrasting chemical nature makes it difficult to achieve a homogeneous mixture.
Another significant challenge is maintaining the desired properties of individual biopolymers in the final blend. Often, the blending process can compromise the unique characteristics that make each biopolymer valuable. For instance, the high strength of one polymer may be diminished when blended with a more flexible counterpart, resulting in a material that fails to meet the required specifications for specific applications.
The processing conditions for biopolymer blends also present a considerable challenge. Different biopolymers often have varying optimal processing temperatures and shear rates, making it difficult to establish a single set of processing parameters that work effectively for all components in the blend. This can lead to thermal degradation of heat-sensitive biopolymers or insufficient melting of others, resulting in suboptimal blend properties.
Stability and long-term performance of biopolymer blends remain ongoing concerns. Many biopolymers are susceptible to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and microbial attack. When blended, these vulnerabilities can be exacerbated, leading to accelerated degradation or loss of desired properties over time. Developing effective stabilization strategies that protect the blend without compromising its biodegradability is a complex task.
The scalability of biopolymer blending techniques also poses a significant challenge. While many promising blends have been developed at the laboratory scale, translating these successes to industrial-scale production often proves difficult. Issues such as maintaining blend consistency, controlling reaction kinetics, and managing heat transfer in larger batches can significantly impact the final product quality and economic viability of the process.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding biopolymer blends, especially those intended for food contact or medical applications, presents additional hurdles. Ensuring compliance with various regional and international standards while maintaining the desired blend properties adds another layer of complexity to the development and commercialization of biopolymer blends.
One of the primary challenges is achieving consistent and uniform blending of different biopolymers. The inherent incompatibility between various biopolymers often results in phase separation, leading to poor mechanical properties and inconsistent material performance. This issue is particularly pronounced when attempting to blend hydrophilic and hydrophobic biopolymers, as their contrasting chemical nature makes it difficult to achieve a homogeneous mixture.
Another significant challenge is maintaining the desired properties of individual biopolymers in the final blend. Often, the blending process can compromise the unique characteristics that make each biopolymer valuable. For instance, the high strength of one polymer may be diminished when blended with a more flexible counterpart, resulting in a material that fails to meet the required specifications for specific applications.
The processing conditions for biopolymer blends also present a considerable challenge. Different biopolymers often have varying optimal processing temperatures and shear rates, making it difficult to establish a single set of processing parameters that work effectively for all components in the blend. This can lead to thermal degradation of heat-sensitive biopolymers or insufficient melting of others, resulting in suboptimal blend properties.
Stability and long-term performance of biopolymer blends remain ongoing concerns. Many biopolymers are susceptible to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and microbial attack. When blended, these vulnerabilities can be exacerbated, leading to accelerated degradation or loss of desired properties over time. Developing effective stabilization strategies that protect the blend without compromising its biodegradability is a complex task.
The scalability of biopolymer blending techniques also poses a significant challenge. While many promising blends have been developed at the laboratory scale, translating these successes to industrial-scale production often proves difficult. Issues such as maintaining blend consistency, controlling reaction kinetics, and managing heat transfer in larger batches can significantly impact the final product quality and economic viability of the process.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding biopolymer blends, especially those intended for food contact or medical applications, presents additional hurdles. Ensuring compliance with various regional and international standards while maintaining the desired blend properties adds another layer of complexity to the development and commercialization of biopolymer blends.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate-Based Blending Solutions
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. This process typically involves catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high yields and purity. The synthesis can be optimized for industrial-scale production, considering factors such as reaction kinetics and thermodynamics.- Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.
- Applications of ethyl propanoate in fragrances and flavors: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, air fresheners, and food flavorings to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.
- Use of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as a versatile solvent and intermediate in various chemical processes. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds, offering advantages such as low toxicity and good solvency properties.
- Purification and separation techniques for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for purifying and separating ethyl propanoate from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These techniques include distillation, extraction, and chromatography, aimed at obtaining high-purity ethyl propanoate for industrial and research applications.
- Environmental and safety considerations in ethyl propanoate production: Innovations in the production and handling of ethyl propanoate focus on improving environmental sustainability and safety. This includes developing green synthesis methods, reducing waste, and implementing safety measures to minimize risks associated with its flammability and potential health hazards.
02 Applications in flavor and fragrance industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is commonly employed as a flavoring agent in food products and beverages, as well as in perfumes and cosmetics. The compound's low toxicity and pleasant aroma make it a versatile ingredient in various consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial processes, particularly in the production of paints, inks, and coatings. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its properties make it suitable for dissolving a wide range of organic substances.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production methods and process optimization
Various production methods for ethyl propanoate have been developed, focusing on improving yield, reducing costs, and enhancing sustainability. These include continuous flow processes, biocatalytic approaches, and the use of novel catalysts. Process optimization techniques aim to increase efficiency and reduce environmental impact in large-scale manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
As with many chemical compounds, the production and use of ethyl propanoate require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes developing methods for proper handling, storage, and disposal, as well as assessing potential environmental impacts. Research in this area focuses on reducing emissions, improving worker safety, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biopolymer and Ethyl Propanoate Industries
The ethyl propanoate biopolymer blending market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable materials across industries. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Novozymes, LG Chem, and DuPont leading innovation in biopolymer formulations and blending techniques. ExxonMobil and Dow are leveraging their petrochemical expertise to develop novel bio-based solutions. Academic institutions such as MIT and the University of California are contributing fundamental research, while companies like Sinopec and Mitsui Chemicals are focusing on scalable production methods. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical giants and specialized biotech firms vying for market share.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed a novel biopolymer blending technique incorporating ethyl propanoate as a key component. Their approach involves using ethyl propanoate as a compatibilizer to improve the miscibility of different biopolymers, such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). The process includes a reactive extrusion step where ethyl propanoate acts as both a plasticizer and a coupling agent, facilitating the formation of covalent bonds between the polymer chains[1][3]. This results in enhanced mechanical properties and improved thermal stability of the final blended material. Dow's method also incorporates a controlled release mechanism of ethyl propanoate during processing, which helps in fine-tuning the blend morphology and interfacial adhesion[2].
Strengths: Improved miscibility of biopolymers, enhanced mechanical properties, and better thermal stability. Weaknesses: Potential for residual ethyl propanoate affecting material purity, complexity in controlling the release mechanism during processing.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has pioneered a biopolymer blending technique utilizing ethyl propanoate as a reactive compatibilizer. Their method involves a two-step process: first, ethyl propanoate is used to modify the surface of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), enhancing their dispersion in hydrophobic biopolymer matrices[4]. Second, the modified CNCs are blended with biopolymers like polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) using a specialized twin-screw extruder. The ethyl propanoate-modified CNCs act as nucleating agents and reinforcing fillers, significantly improving the mechanical and barrier properties of the resulting biocomposites[5]. ExxonMobil's technique also incorporates a proprietary in-situ polymerization step, where ethyl propanoate initiates graft polymerization at the biopolymer-CNC interface, further enhancing compatibility[6].
Strengths: Improved dispersion of CNCs in hydrophobic matrices, enhanced mechanical and barrier properties. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs due to the two-step process, possible limitations in scalability.
Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate for Biopolymer Compatibility
Compatibilizing surfactants for polyurethane polyols and resins
PatentInactiveUS20090312447A1
Innovation
- A phase-stable resin blend composition comprising a polyol, a compatibilizing agent such as an ethoxylate propoxylate surfactant, and a hydrocarbon blowing agent, where the compatibilizing agent is produced by reacting propylene oxide and ethylene oxide with a short-chain initiator, enhancing the compatibility and solubility of hydrocarbon blowing agents within the polyol and resin blends.
Additive-containing biopolymer compositions
PatentWO2022174894A1
Innovation
- A composition combining biopolymers with specific organopolysiloxane granules, vinyl acetate-based homopolymers or copolymers, and boric acid-containing additives, which are mixed with reinforcing or non-reinforcing fillers to create fully free-flowing granules that enhance mechanical and surface properties.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Propanoate in Biopolymer Processing
The environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing is a critical consideration as the use of biopolymers continues to grow in various industries. Ethyl propanoate, a naturally occurring ester, plays a significant role in enhancing the properties of biopolymer blends, but its production and application also have environmental implications that must be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing is its potential to reduce the overall carbon footprint of the manufacturing process. As a bio-based solvent, ethyl propanoate can be derived from renewable resources, such as agricultural waste or fermentation processes. This renewable origin contributes to a more sustainable production cycle compared to traditional petroleum-based solvents.
However, the production of ethyl propanoate itself requires energy and resources, which must be factored into the overall environmental assessment. The fermentation and distillation processes used to produce ethyl propanoate can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental gains achieved through its use in biopolymer blending.
In terms of air quality, ethyl propanoate has a relatively low volatility compared to many other organic solvents. This characteristic reduces the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during biopolymer processing, contributing to improved air quality in manufacturing environments and surrounding areas. The lower VOC emissions also align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations in many regions.
Water pollution is another aspect to consider when evaluating the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing. While ethyl propanoate is biodegradable and less toxic than many synthetic solvents, proper waste management practices are still essential to prevent contamination of water sources. Efficient recovery and recycling systems can significantly mitigate the risk of water pollution and reduce the overall environmental footprint of the process.
The use of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending techniques can also contribute to the development of more environmentally friendly end products. By improving the compatibility and processability of different biopolymers, ethyl propanoate enables the creation of materials with enhanced properties, potentially reducing the need for less sustainable alternatives. This indirect environmental benefit extends throughout the lifecycle of the final products.
As the demand for sustainable materials grows, the role of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing is likely to expand. To maximize its positive environmental impact, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing production methods, improving recovery and recycling techniques, and exploring novel applications that leverage its unique properties in biopolymer blending.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing is its potential to reduce the overall carbon footprint of the manufacturing process. As a bio-based solvent, ethyl propanoate can be derived from renewable resources, such as agricultural waste or fermentation processes. This renewable origin contributes to a more sustainable production cycle compared to traditional petroleum-based solvents.
However, the production of ethyl propanoate itself requires energy and resources, which must be factored into the overall environmental assessment. The fermentation and distillation processes used to produce ethyl propanoate can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental gains achieved through its use in biopolymer blending.
In terms of air quality, ethyl propanoate has a relatively low volatility compared to many other organic solvents. This characteristic reduces the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during biopolymer processing, contributing to improved air quality in manufacturing environments and surrounding areas. The lower VOC emissions also align with increasingly stringent environmental regulations in many regions.
Water pollution is another aspect to consider when evaluating the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing. While ethyl propanoate is biodegradable and less toxic than many synthetic solvents, proper waste management practices are still essential to prevent contamination of water sources. Efficient recovery and recycling systems can significantly mitigate the risk of water pollution and reduce the overall environmental footprint of the process.
The use of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending techniques can also contribute to the development of more environmentally friendly end products. By improving the compatibility and processability of different biopolymers, ethyl propanoate enables the creation of materials with enhanced properties, potentially reducing the need for less sustainable alternatives. This indirect environmental benefit extends throughout the lifecycle of the final products.
As the demand for sustainable materials grows, the role of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer processing is likely to expand. To maximize its positive environmental impact, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing production methods, improving recovery and recycling techniques, and exploring novel applications that leverage its unique properties in biopolymer blending.
Regulatory Framework for Biopolymer Additives
The regulatory framework for biopolymer additives plays a crucial role in the development and application of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending techniques. As the use of biopolymers and their additives continues to grow, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines to ensure safety, environmental protection, and product quality.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of biopolymer additives used in food packaging and medical devices. The FDA's Food Contact Substance Notification Program requires manufacturers to submit detailed information about the chemical composition, intended use, and safety data of additives like ethyl propanoate before they can be approved for use in food-contact applications.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to all chemical substances, including biopolymer additives. Under REACH, manufacturers must register their substances and provide comprehensive safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This regulation ensures that potential risks associated with the use of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending are thoroughly assessed and mitigated.
In addition to these overarching regulations, specific standards have been developed for biopolymer additives. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established the ASTM D6400 standard for compostable plastics, which includes guidelines for additives used in biodegradable polymers. This standard ensures that additives like ethyl propanoate do not hinder the biodegradability of the final product.
Environmental considerations are also a significant aspect of the regulatory framework. Many countries have implemented regulations to promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable materials. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive encourages the development of biodegradable alternatives, which may involve the use of biopolymer blends containing ethyl propanoate.
The regulatory landscape for biopolymer additives is continually evolving as new research emerges and environmental concerns grow. Manufacturers and researchers working with ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending must stay informed about these regulatory changes and ensure compliance with the latest standards. This may involve conducting additional safety studies, modifying formulations, or seeking new certifications as regulations are updated.
As the field of biopolymer blending advances, it is likely that more specific regulations will be developed to address the unique properties and applications of additives like ethyl propanoate. Industry stakeholders should actively participate in the development of these regulations to ensure that they are both scientifically sound and practically implementable.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of biopolymer additives used in food packaging and medical devices. The FDA's Food Contact Substance Notification Program requires manufacturers to submit detailed information about the chemical composition, intended use, and safety data of additives like ethyl propanoate before they can be approved for use in food-contact applications.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to all chemical substances, including biopolymer additives. Under REACH, manufacturers must register their substances and provide comprehensive safety data to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This regulation ensures that potential risks associated with the use of ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending are thoroughly assessed and mitigated.
In addition to these overarching regulations, specific standards have been developed for biopolymer additives. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established the ASTM D6400 standard for compostable plastics, which includes guidelines for additives used in biodegradable polymers. This standard ensures that additives like ethyl propanoate do not hinder the biodegradability of the final product.
Environmental considerations are also a significant aspect of the regulatory framework. Many countries have implemented regulations to promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable materials. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive encourages the development of biodegradable alternatives, which may involve the use of biopolymer blends containing ethyl propanoate.
The regulatory landscape for biopolymer additives is continually evolving as new research emerges and environmental concerns grow. Manufacturers and researchers working with ethyl propanoate in biopolymer blending must stay informed about these regulatory changes and ensure compliance with the latest standards. This may involve conducting additional safety studies, modifying formulations, or seeking new certifications as regulations are updated.
As the field of biopolymer blending advances, it is likely that more specific regulations will be developed to address the unique properties and applications of additives like ethyl propanoate. Industry stakeholders should actively participate in the development of these regulations to ensure that they are both scientifically sound and practically implementable.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!