How Glacial Acetic Acid Affects Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glacial Acetic Acid in Organic Synthesis: Background and Objectives
Glacial acetic acid, a concentrated form of acetic acid with minimal water content, has been a cornerstone in organic synthesis for over a century. Its unique properties and versatile reactivity have made it an indispensable tool in the arsenal of organic chemists. The evolution of glacial acetic acid's use in organic chemistry can be traced back to the late 19th century, with its applications expanding significantly throughout the 20th century.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively examine how glacial acetic acid influences reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry. This investigation aims to elucidate the fundamental principles underlying its reactivity, explore its role as a solvent and reagent, and analyze its impact on various organic transformations.
Glacial acetic acid's importance in organic synthesis stems from its dual nature as both a protic solvent and a weak acid. Its ability to act as a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor, coupled with its moderate acidity, enables it to participate in a wide range of reactions. These include esterification, acetylation, and various acid-catalyzed processes.
The technological progression in the use of glacial acetic acid has been marked by several key developments. Early applications focused on its use as a simple solvent and acetylating agent. However, as understanding of reaction mechanisms deepened, more sophisticated applications emerged. These include its role in stereoselective syntheses, transition metal-catalyzed reactions, and as a crucial component in industrial processes.
Current trends in organic chemistry research are exploring novel applications of glacial acetic acid, particularly in green chemistry and sustainable synthesis. There is growing interest in utilizing glacial acetic acid as a bio-based solvent, aligning with the principles of environmental sustainability. Additionally, its potential in enabling new reaction pathways and improving existing processes continues to be a subject of intense study.
The technological goals for glacial acetic acid in organic synthesis are multifaceted. Researchers aim to develop more efficient and selective reactions, expand its use in asymmetric synthesis, and explore its potential in emerging fields such as flow chemistry and photocatalysis. There is also a focus on understanding the mechanistic details of reactions involving glacial acetic acid at a molecular level, leveraging advanced spectroscopic and computational techniques.
As we delve deeper into this technical research report, we will explore the intricate ways in which glacial acetic acid affects reaction mechanisms, its current applications, and the potential future directions in this field. This comprehensive analysis will provide valuable insights for both academic research and industrial applications in organic synthesis.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively examine how glacial acetic acid influences reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry. This investigation aims to elucidate the fundamental principles underlying its reactivity, explore its role as a solvent and reagent, and analyze its impact on various organic transformations.
Glacial acetic acid's importance in organic synthesis stems from its dual nature as both a protic solvent and a weak acid. Its ability to act as a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor, coupled with its moderate acidity, enables it to participate in a wide range of reactions. These include esterification, acetylation, and various acid-catalyzed processes.
The technological progression in the use of glacial acetic acid has been marked by several key developments. Early applications focused on its use as a simple solvent and acetylating agent. However, as understanding of reaction mechanisms deepened, more sophisticated applications emerged. These include its role in stereoselective syntheses, transition metal-catalyzed reactions, and as a crucial component in industrial processes.
Current trends in organic chemistry research are exploring novel applications of glacial acetic acid, particularly in green chemistry and sustainable synthesis. There is growing interest in utilizing glacial acetic acid as a bio-based solvent, aligning with the principles of environmental sustainability. Additionally, its potential in enabling new reaction pathways and improving existing processes continues to be a subject of intense study.
The technological goals for glacial acetic acid in organic synthesis are multifaceted. Researchers aim to develop more efficient and selective reactions, expand its use in asymmetric synthesis, and explore its potential in emerging fields such as flow chemistry and photocatalysis. There is also a focus on understanding the mechanistic details of reactions involving glacial acetic acid at a molecular level, leveraging advanced spectroscopic and computational techniques.
As we delve deeper into this technical research report, we will explore the intricate ways in which glacial acetic acid affects reaction mechanisms, its current applications, and the potential future directions in this field. This comprehensive analysis will provide valuable insights for both academic research and industrial applications in organic synthesis.
Market Demand for Glacial Acetic Acid in Chemical Industry
The market demand for glacial acetic acid in the chemical industry has been steadily growing due to its versatile applications and essential role in various manufacturing processes. As a key raw material in the production of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), purified terephthalic acid (PTA), and acetic anhydride, glacial acetic acid plays a crucial role in the polymer, textile, and pharmaceutical industries.
In the polymer sector, the increasing demand for packaging materials, adhesives, and coatings has driven the consumption of glacial acetic acid. The growing popularity of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers in adhesives and packaging applications has further boosted the market demand. Additionally, the textile industry's reliance on PTA for polyester fiber production has contributed significantly to the overall consumption of glacial acetic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another major consumer of glacial acetic acid, utilizing it in the synthesis of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and as a solvent in drug formulations. The global expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, particularly in emerging markets, has led to increased demand for high-purity glacial acetic acid.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also influenced the market dynamics of glacial acetic acid. As industries seek more eco-friendly alternatives, there has been a growing interest in bio-based acetic acid production methods. This trend has opened up new opportunities for market players to develop and commercialize sustainable production processes.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as the largest consumer and producer of glacial acetic acid, driven by rapid industrialization and the growth of end-use industries. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-value applications in specialty chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global glacial acetic acid market in the coming years, reflecting the increasing demand across various industrial sectors. Factors such as urbanization, population growth, and rising disposable incomes in developing economies are expected to further drive the consumption of products that rely on glacial acetic acid as a key ingredient.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and stringent environmental regulations. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production efficiency and explore alternative feedstocks to mitigate these challenges and meet the growing market demand.
In the polymer sector, the increasing demand for packaging materials, adhesives, and coatings has driven the consumption of glacial acetic acid. The growing popularity of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers in adhesives and packaging applications has further boosted the market demand. Additionally, the textile industry's reliance on PTA for polyester fiber production has contributed significantly to the overall consumption of glacial acetic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another major consumer of glacial acetic acid, utilizing it in the synthesis of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and as a solvent in drug formulations. The global expansion of the pharmaceutical sector, particularly in emerging markets, has led to increased demand for high-purity glacial acetic acid.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also influenced the market dynamics of glacial acetic acid. As industries seek more eco-friendly alternatives, there has been a growing interest in bio-based acetic acid production methods. This trend has opened up new opportunities for market players to develop and commercialize sustainable production processes.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as the largest consumer and producer of glacial acetic acid, driven by rapid industrialization and the growth of end-use industries. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-value applications in specialty chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global glacial acetic acid market in the coming years, reflecting the increasing demand across various industrial sectors. Factors such as urbanization, population growth, and rising disposable incomes in developing economies are expected to further drive the consumption of products that rely on glacial acetic acid as a key ingredient.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and stringent environmental regulations. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production efficiency and explore alternative feedstocks to mitigate these challenges and meet the growing market demand.
Current Applications and Challenges in Organic Reactions
Glacial acetic acid plays a significant role in various organic reactions, serving as both a solvent and a reagent. Its unique properties, including high polarity and moderate acidity, make it a versatile component in numerous synthetic processes. Currently, it finds extensive applications in the production of vinyl acetate monomer, acetic anhydride, and cellulose acetate, which are crucial intermediates in the polymer and pharmaceutical industries.
In organic synthesis, glacial acetic acid is widely used as a reaction medium for acetylation reactions, particularly in the preparation of acetyl derivatives of alcohols and amines. Its ability to act as both a proton donor and acceptor facilitates nucleophilic substitution reactions, making it an excellent choice for various transformations. Moreover, its use in Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions has been well-established, enabling the introduction of acyl groups to aromatic compounds.
Despite its widespread use, the application of glacial acetic acid in organic reactions faces several challenges. One primary concern is its corrosive nature, which necessitates the use of specialized equipment and handling procedures. This aspect not only increases operational costs but also poses safety risks in large-scale industrial processes. Additionally, the high boiling point of acetic acid (118°C) can complicate product isolation and purification steps, often requiring energy-intensive distillation processes.
Another significant challenge lies in understanding and controlling the reaction mechanisms influenced by glacial acetic acid. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds and participate in proton transfer reactions can lead to complex reaction pathways, sometimes resulting in unexpected side products. This complexity often requires extensive optimization studies to achieve desired selectivity and yields, particularly in multi-step syntheses or when working with sensitive substrates.
The environmental impact of using glacial acetic acid in large quantities is also a growing concern. While it is biodegradable, its production and disposal can contribute to environmental pollution if not managed properly. This has led to increased research into greener alternatives and more sustainable reaction conditions, aligning with the principles of green chemistry.
Efforts to address these challenges have spurred innovation in reaction engineering and catalysis. Researchers are exploring the use of supported acid catalysts, ionic liquids, and flow chemistry techniques to mitigate some of the drawbacks associated with glacial acetic acid. These approaches aim to enhance reaction efficiency, reduce waste generation, and improve overall process sustainability.
In organic synthesis, glacial acetic acid is widely used as a reaction medium for acetylation reactions, particularly in the preparation of acetyl derivatives of alcohols and amines. Its ability to act as both a proton donor and acceptor facilitates nucleophilic substitution reactions, making it an excellent choice for various transformations. Moreover, its use in Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions has been well-established, enabling the introduction of acyl groups to aromatic compounds.
Despite its widespread use, the application of glacial acetic acid in organic reactions faces several challenges. One primary concern is its corrosive nature, which necessitates the use of specialized equipment and handling procedures. This aspect not only increases operational costs but also poses safety risks in large-scale industrial processes. Additionally, the high boiling point of acetic acid (118°C) can complicate product isolation and purification steps, often requiring energy-intensive distillation processes.
Another significant challenge lies in understanding and controlling the reaction mechanisms influenced by glacial acetic acid. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds and participate in proton transfer reactions can lead to complex reaction pathways, sometimes resulting in unexpected side products. This complexity often requires extensive optimization studies to achieve desired selectivity and yields, particularly in multi-step syntheses or when working with sensitive substrates.
The environmental impact of using glacial acetic acid in large quantities is also a growing concern. While it is biodegradable, its production and disposal can contribute to environmental pollution if not managed properly. This has led to increased research into greener alternatives and more sustainable reaction conditions, aligning with the principles of green chemistry.
Efforts to address these challenges have spurred innovation in reaction engineering and catalysis. Researchers are exploring the use of supported acid catalysts, ionic liquids, and flow chemistry techniques to mitigate some of the drawbacks associated with glacial acetic acid. These approaches aim to enhance reaction efficiency, reduce waste generation, and improve overall process sustainability.
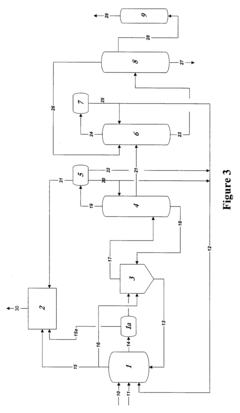
Existing Reaction Mechanisms Involving Glacial Acetic Acid
01 Esterification reactions
Glacial acetic acid is commonly used in esterification reactions, where it reacts with alcohols to form esters. This process typically requires an acid catalyst and often involves heating. The reaction mechanism includes protonation of the acetic acid, nucleophilic attack by the alcohol, and elimination of water to form the ester product.- Esterification reactions: Glacial acetic acid is commonly used in esterification reactions, where it reacts with alcohols to form esters. This process typically involves the nucleophilic addition of the alcohol to the carbonyl group of acetic acid, followed by the elimination of water. The reaction is often catalyzed by acids or enzymes to improve yield and reaction rate.
- Acetylation reactions: Glacial acetic acid serves as an acetylating agent in various organic syntheses. It can introduce acetyl groups into molecules through nucleophilic substitution reactions. This mechanism is widely used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other organic compounds, where the acetyl group acts as a protecting group or modifies the properties of the target molecule.
- Acid-catalyzed reactions: As a strong organic acid, glacial acetic acid can catalyze various reactions, including hydrolysis, dehydration, and rearrangements. It acts as a proton donor, initiating reaction mechanisms by protonating substrates or intermediates. This catalytic role is particularly important in organic synthesis and industrial processes.
- Solvent in organic reactions: Glacial acetic acid is widely used as a solvent in organic reactions due to its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar compounds. Its unique properties allow it to facilitate various reaction mechanisms by providing a suitable medium for reactants to interact. It can also participate in the reaction itself, acting as both solvent and reagent in some cases.
- Oxidation reactions: In the presence of oxidizing agents, glacial acetic acid can participate in oxidation reactions. It can act as a reducing agent, being oxidized to form various products depending on the reaction conditions. These oxidation mechanisms are important in organic synthesis and industrial processes for the production of various chemicals and intermediates.
02 Acetylation reactions
Glacial acetic acid serves as an acetylating agent in various organic syntheses. It can introduce acetyl groups into molecules through nucleophilic substitution reactions. The mechanism often involves the formation of an acetyl cation intermediate, which then reacts with nucleophiles to form acetylated products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Acid-catalyzed reactions
As a strong acid, glacial acetic acid can catalyze various organic reactions. It acts as a proton donor in acid-catalyzed processes such as hydrolysis, dehydration, and rearrangements. The reaction mechanism typically involves protonation of the substrate, followed by subsequent steps specific to each reaction type.Expand Specific Solutions04 Solvent in organic reactions
Glacial acetic acid is widely used as a solvent in organic synthesis due to its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar compounds. It can participate in reaction mechanisms by stabilizing intermediates, facilitating proton transfer, or influencing the equilibrium of reactions through solvation effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Oxidation reactions
In the presence of oxidizing agents, glacial acetic acid can participate in oxidation reactions. It can act as both a solvent and a reactant in these processes. The reaction mechanisms may involve the formation of peracetic acid intermediates or direct oxidation of substrates in acidic conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Glacial Acetic Acid Production and Research
The field of glacial acetic acid's impact on organic chemistry reaction mechanisms is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and significant research contributions. The global market for acetic acid, including its glacial form, is substantial, driven by diverse industrial applications. Technologically, this area is well-developed, with leading institutions and companies contributing to its advancement. Key players include BASF Plant Science LLC, Daicel Corp., and Celanese International Corp., who have made significant strides in understanding and applying glacial acetic acid in various chemical processes. Academic institutions like the University of Geneva and Cornell University continue to push the boundaries of research in this field, ensuring ongoing innovation and refinement of reaction mechanisms.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed innovative applications of glacial acetic acid in organic synthesis, focusing on its role as a proton donor and nucleophile. Their research has led to the development of a novel acylation process using glacial acetic acid under mild conditions, which is particularly useful for sensitive substrates [2]. Evonik has also explored the use of glacial acetic acid in combination with heterogeneous catalysts to promote selective C-H functionalization reactions [4]. The company has invested in understanding the solvent effects of glacial acetic acid on reaction rates and equilibria, leading to improved predictive models for reaction outcomes [6].
Strengths: Mild reaction conditions, selective functionalization, improved predictive models. Weaknesses: Potential equipment corrosion, limited substrate scope for some reactions, environmental concerns related to acetic acid disposal.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed advanced processes for the production and application of glacial acetic acid in organic chemistry reactions. Their approach involves using high-purity glacial acetic acid (>99.8%) as both a solvent and reagent in various organic syntheses. The company has optimized reaction conditions to enhance the electrophilic nature of glacial acetic acid, allowing for more efficient acetylation reactions [1]. They have also implemented a novel catalytic system that improves the selectivity and yield of esterification reactions using glacial acetic acid [3]. Celanese's research has shown that controlling the water content in glacial acetic acid is crucial for maintaining its reactivity and influencing reaction mechanisms [5].
Strengths: High-purity product, optimized reaction conditions, improved selectivity in esterification. Weaknesses: Potential corrosion issues, safety concerns due to acidity, limited application in some sensitive organic reactions.
Innovative Applications in Organic Synthesis
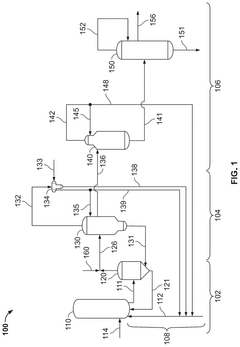
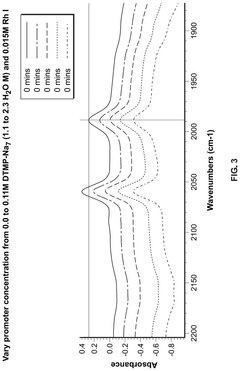
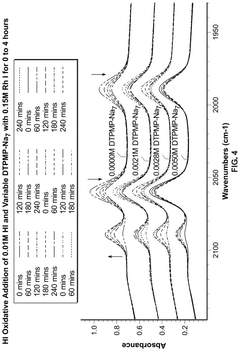
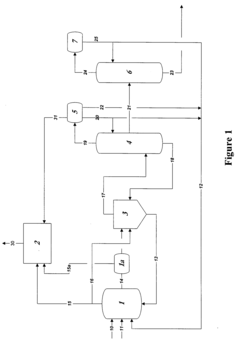
Polyphoshates and polyphosphonates as rate promoters for the glacial acetic acid process
PatentPendingUS20250074856A1
Innovation
- The process involves using a reaction mixture comprising a carbonylation catalyst, water, and specific rate-promoting compounds such as Group I and Group II polyphosphate and polyphosphonate salts, which are added at an iodide to promoter molar ratio greater than 2, to enhance the rate of acetic acid formation while reducing the amount of water required.
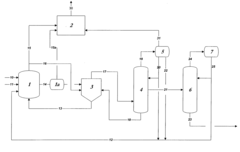
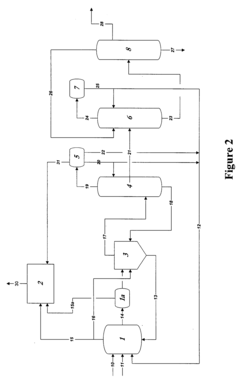
Control of impurities in product glacial acetic acid of rhodium-catalyzed methanol carbonylation
PatentInactiveUS20090187043A1
Innovation
- A method involving a rhodium-catalyzed carbonylation process with controlled water and iodide concentrations, combined with the use of a macroreticular strong-acid cation exchange resin and silver or mercury exchanged cation exchange substrates to manage impurities, ensuring high purity glacial acetic acid production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The use of glacial acetic acid in organic chemistry reactions raises significant environmental and sustainability concerns. As a strong organic acid, its production, handling, and disposal require careful consideration to minimize ecological impact and ensure sustainable practices.
Glacial acetic acid is primarily produced through petrochemical processes, which rely on non-renewable fossil fuel resources. This dependency contributes to carbon emissions and the depletion of finite resources. However, alternative production methods using renewable feedstocks, such as biomass fermentation, are being developed to address these sustainability issues.
The manufacturing process of glacial acetic acid can generate harmful byproducts and waste streams. Proper treatment and disposal of these waste materials are essential to prevent environmental contamination. Advanced waste management techniques, including recycling and recovery systems, are being implemented to reduce the environmental footprint of acetic acid production.
In laboratory settings, the use of glacial acetic acid poses potential risks to air and water quality if not handled properly. Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from acetic acid can contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Implementing proper ventilation systems and containment measures is crucial to mitigate these risks.
Water contamination is another concern, as improper disposal of acetic acid-containing waste can lead to acidification of water bodies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Neutralization and treatment of acetic acid waste before disposal are necessary to minimize environmental impact.
From a sustainability perspective, efforts are being made to develop greener alternatives to glacial acetic acid in organic synthesis. These include the use of less hazardous organic acids, ionic liquids, or water-based reaction systems. Such alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact while maintaining or improving reaction efficiency.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are being conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of glacial acetic acid use in organic chemistry. These assessments consider factors such as resource consumption, energy use, and emissions throughout the entire life cycle of the chemical, from production to disposal.
Implementing green chemistry principles in reaction design can help minimize the use of glacial acetic acid and reduce its environmental impact. This includes exploring catalytic processes, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing more atom-efficient synthetic routes that require less acetic acid or eliminate its use altogether.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the chemical industry, there is a growing focus on developing circular economy approaches for acetic acid. This involves exploring ways to recycle and reuse acetic acid within chemical processes, reducing waste and minimizing the need for continuous production of fresh material.
Glacial acetic acid is primarily produced through petrochemical processes, which rely on non-renewable fossil fuel resources. This dependency contributes to carbon emissions and the depletion of finite resources. However, alternative production methods using renewable feedstocks, such as biomass fermentation, are being developed to address these sustainability issues.
The manufacturing process of glacial acetic acid can generate harmful byproducts and waste streams. Proper treatment and disposal of these waste materials are essential to prevent environmental contamination. Advanced waste management techniques, including recycling and recovery systems, are being implemented to reduce the environmental footprint of acetic acid production.
In laboratory settings, the use of glacial acetic acid poses potential risks to air and water quality if not handled properly. Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from acetic acid can contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Implementing proper ventilation systems and containment measures is crucial to mitigate these risks.
Water contamination is another concern, as improper disposal of acetic acid-containing waste can lead to acidification of water bodies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Neutralization and treatment of acetic acid waste before disposal are necessary to minimize environmental impact.
From a sustainability perspective, efforts are being made to develop greener alternatives to glacial acetic acid in organic synthesis. These include the use of less hazardous organic acids, ionic liquids, or water-based reaction systems. Such alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact while maintaining or improving reaction efficiency.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are being conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of glacial acetic acid use in organic chemistry. These assessments consider factors such as resource consumption, energy use, and emissions throughout the entire life cycle of the chemical, from production to disposal.
Implementing green chemistry principles in reaction design can help minimize the use of glacial acetic acid and reduce its environmental impact. This includes exploring catalytic processes, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing more atom-efficient synthetic routes that require less acetic acid or eliminate its use altogether.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the chemical industry, there is a growing focus on developing circular economy approaches for acetic acid. This involves exploring ways to recycle and reuse acetic acid within chemical processes, reducing waste and minimizing the need for continuous production of fresh material.
Safety Protocols and Handling Guidelines
Glacial acetic acid is a potent and corrosive organic compound widely used in organic chemistry reactions. Due to its hazardous nature, strict safety protocols and handling guidelines are essential to ensure the well-being of laboratory personnel and the integrity of experimental procedures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with glacial acetic acid. Laboratory workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, preferably made of butyl rubber or neoprene, to prevent skin contact. Safety goggles or a face shield are mandatory to protect the eyes from splashes or vapors. A lab coat and closed-toe shoes are also required to minimize exposure risks.
Proper ventilation is crucial when handling glacial acetic acid. All operations involving this compound should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent the accumulation of vapors in the laboratory atmosphere. The fume hood should be inspected regularly to ensure optimal performance and containment of hazardous fumes.
Storage of glacial acetic acid requires special considerations. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as glass or high-density polyethylene. Storage areas must be well-ventilated, cool, and dry, away from sources of heat or ignition. Segregation from incompatible materials, such as oxidizing agents and strong bases, is essential to prevent dangerous reactions.
Spill response procedures must be established and communicated to all laboratory personnel. In case of a small spill, absorbent materials like vermiculite or activated charcoal should be used to contain and neutralize the acid. For larger spills, immediate evacuation of the area and notification of emergency response teams are necessary.
Proper waste disposal is critical when working with glacial acetic acid. Waste solutions containing the acid should never be disposed of down the drain. Instead, they must be collected in designated waste containers and handled according to institutional and local regulations for hazardous waste disposal.
Training and education are fundamental components of safety protocols. All personnel working with glacial acetic acid should receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness.
Emergency response plans must be in place and readily accessible. This includes the location of eyewash stations, safety showers, and first aid kits. Personnel should be trained in emergency procedures, including evacuation routes and the use of fire extinguishers suitable for acid fires.
Documentation and record-keeping are essential aspects of safety management. Detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for glacial acetic acid must be readily available in the laboratory. Incident reports, exposure records, and equipment maintenance logs should be meticulously maintained to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to facilitate continuous improvement of safety protocols.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with glacial acetic acid. Laboratory workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, preferably made of butyl rubber or neoprene, to prevent skin contact. Safety goggles or a face shield are mandatory to protect the eyes from splashes or vapors. A lab coat and closed-toe shoes are also required to minimize exposure risks.
Proper ventilation is crucial when handling glacial acetic acid. All operations involving this compound should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent the accumulation of vapors in the laboratory atmosphere. The fume hood should be inspected regularly to ensure optimal performance and containment of hazardous fumes.
Storage of glacial acetic acid requires special considerations. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as glass or high-density polyethylene. Storage areas must be well-ventilated, cool, and dry, away from sources of heat or ignition. Segregation from incompatible materials, such as oxidizing agents and strong bases, is essential to prevent dangerous reactions.
Spill response procedures must be established and communicated to all laboratory personnel. In case of a small spill, absorbent materials like vermiculite or activated charcoal should be used to contain and neutralize the acid. For larger spills, immediate evacuation of the area and notification of emergency response teams are necessary.
Proper waste disposal is critical when working with glacial acetic acid. Waste solutions containing the acid should never be disposed of down the drain. Instead, they must be collected in designated waste containers and handled according to institutional and local regulations for hazardous waste disposal.
Training and education are fundamental components of safety protocols. All personnel working with glacial acetic acid should receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, and proper handling techniques. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain awareness and preparedness.
Emergency response plans must be in place and readily accessible. This includes the location of eyewash stations, safety showers, and first aid kits. Personnel should be trained in emergency procedures, including evacuation routes and the use of fire extinguishers suitable for acid fires.
Documentation and record-keeping are essential aspects of safety management. Detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for glacial acetic acid must be readily available in the laboratory. Incident reports, exposure records, and equipment maintenance logs should be meticulously maintained to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to facilitate continuous improvement of safety protocols.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!