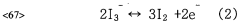How Sulphanilic Acid Enhances the Performance of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DSSC Tech Background
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based photovoltaic devices since their introduction by Michael Grätzel and Brian O'Regan in 1991. These cells represent a unique approach to solar energy conversion, mimicking the natural process of photosynthesis. DSSCs consist of a porous layer of titanium dioxide nanoparticles, covered with a molecular dye that absorbs sunlight, much like the chlorophyll in green leaves.
The development of DSSCs marked a significant milestone in the field of photovoltaics, offering several advantages over conventional solar cells. These include lower production costs, flexibility in design, and the ability to perform well under low-light conditions. The technology has since evolved, with researchers focusing on improving efficiency, stability, and scalability.
Over the years, various components of DSSCs have been subject to intensive research and optimization. The dye sensitizer, which plays a crucial role in light absorption and electron injection, has been a primary focus. Initially, ruthenium-based complexes were widely used due to their broad absorption spectrum and long-lived excited states. However, the high cost and limited availability of ruthenium led to the exploration of alternative organic dyes and metal-free sensitizers.
The electrolyte, responsible for regenerating the oxidized dye and completing the circuit, has also undergone significant development. Traditional liquid electrolytes based on the iodide/triiodide redox couple have been gradually replaced by solid-state or quasi-solid-state electrolytes to address issues of leakage and long-term stability.
Another area of advancement has been the photoanode material. While titanium dioxide remains the most common choice due to its stability and suitable band structure, researchers have investigated alternative materials and nanostructures to enhance light harvesting and electron transport.
The introduction of sulphanilic acid as a performance enhancer in DSSCs represents a recent development in this evolving field. This compound, known for its electron-donating properties and ability to form stable complexes, has shown promise in improving various aspects of DSSC performance. The investigation into how sulphanilic acid enhances DSSC efficiency aligns with the ongoing efforts to optimize cell components and push the boundaries of this technology's capabilities.
The development of DSSCs marked a significant milestone in the field of photovoltaics, offering several advantages over conventional solar cells. These include lower production costs, flexibility in design, and the ability to perform well under low-light conditions. The technology has since evolved, with researchers focusing on improving efficiency, stability, and scalability.
Over the years, various components of DSSCs have been subject to intensive research and optimization. The dye sensitizer, which plays a crucial role in light absorption and electron injection, has been a primary focus. Initially, ruthenium-based complexes were widely used due to their broad absorption spectrum and long-lived excited states. However, the high cost and limited availability of ruthenium led to the exploration of alternative organic dyes and metal-free sensitizers.
The electrolyte, responsible for regenerating the oxidized dye and completing the circuit, has also undergone significant development. Traditional liquid electrolytes based on the iodide/triiodide redox couple have been gradually replaced by solid-state or quasi-solid-state electrolytes to address issues of leakage and long-term stability.
Another area of advancement has been the photoanode material. While titanium dioxide remains the most common choice due to its stability and suitable band structure, researchers have investigated alternative materials and nanostructures to enhance light harvesting and electron transport.
The introduction of sulphanilic acid as a performance enhancer in DSSCs represents a recent development in this evolving field. This compound, known for its electron-donating properties and ability to form stable complexes, has shown promise in improving various aspects of DSSC performance. The investigation into how sulphanilic acid enhances DSSC efficiency aligns with the ongoing efforts to optimize cell components and push the boundaries of this technology's capabilities.
Market Analysis DSSC
The dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) market has been experiencing steady growth due to increasing demand for renewable energy sources and the technology's potential for low-cost, flexible solar applications. As of 2021, the global DSSC market was valued at approximately $90 million, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 12% from 2022 to 2030.
The market for DSSCs is primarily driven by their advantages over traditional silicon-based solar cells, including lower production costs, better performance under low-light conditions, and the ability to be integrated into various surfaces and materials. These characteristics make DSSCs particularly attractive for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and consumer electronics applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the DSSC market, with Japan and South Korea leading in research and development. Europe follows closely, with significant contributions from research institutions and companies in Switzerland, Italy, and Germany. North America, particularly the United States, is also a key player in DSSC technology development and commercialization.
The automotive industry has shown increasing interest in DSSC technology for potential integration into vehicle surfaces, which could provide auxiliary power for electric vehicles. This application alone is expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
However, the DSSC market faces challenges, including lower efficiency compared to traditional silicon solar cells and concerns about long-term stability. The introduction of sulphanilic acid as a performance enhancer addresses some of these issues, potentially expanding market opportunities.
The use of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs is expected to improve efficiency and stability, which could lead to broader adoption in various sectors. This enhancement may particularly benefit the consumer electronics market, where DSSCs could be used to power small devices and wearable technology.
As environmental concerns drive the push for sustainable energy solutions, government initiatives and subsidies supporting renewable energy technologies are likely to further boost the DSSC market. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving DSSC performance and reducing production costs are expected to open up new market segments and applications.
The competitive landscape of the DSSC market is characterized by a mix of established companies and innovative startups. Key players include Fujikura Ltd., 3GSolar Photovoltaics Ltd., Greatcell Solar Limited, and Exeger Sweden AB. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve DSSC technology and expand its applications.
The market for DSSCs is primarily driven by their advantages over traditional silicon-based solar cells, including lower production costs, better performance under low-light conditions, and the ability to be integrated into various surfaces and materials. These characteristics make DSSCs particularly attractive for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and consumer electronics applications.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the DSSC market, with Japan and South Korea leading in research and development. Europe follows closely, with significant contributions from research institutions and companies in Switzerland, Italy, and Germany. North America, particularly the United States, is also a key player in DSSC technology development and commercialization.
The automotive industry has shown increasing interest in DSSC technology for potential integration into vehicle surfaces, which could provide auxiliary power for electric vehicles. This application alone is expected to create substantial market opportunities in the coming years.
However, the DSSC market faces challenges, including lower efficiency compared to traditional silicon solar cells and concerns about long-term stability. The introduction of sulphanilic acid as a performance enhancer addresses some of these issues, potentially expanding market opportunities.
The use of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs is expected to improve efficiency and stability, which could lead to broader adoption in various sectors. This enhancement may particularly benefit the consumer electronics market, where DSSCs could be used to power small devices and wearable technology.
As environmental concerns drive the push for sustainable energy solutions, government initiatives and subsidies supporting renewable energy technologies are likely to further boost the DSSC market. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving DSSC performance and reducing production costs are expected to open up new market segments and applications.
The competitive landscape of the DSSC market is characterized by a mix of established companies and innovative startups. Key players include Fujikura Ltd., 3GSolar Photovoltaics Ltd., Greatcell Solar Limited, and Exeger Sweden AB. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve DSSC technology and expand its applications.
Sulphanilic Acid DSSC
Sulphanilic acid has emerged as a promising additive in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), demonstrating significant potential to enhance their performance. This organic compound, characterized by its sulfonic acid group attached to an aniline ring, plays a multifaceted role in improving the efficiency and stability of DSSCs.
The primary mechanism through which sulphanilic acid enhances DSSC performance is by modifying the semiconductor-electrolyte interface. When incorporated into the electrolyte or applied as a surface treatment on the TiO2 photoanode, sulphanilic acid forms a molecular layer that passivates surface trap states. This passivation reduces charge recombination, a major limiting factor in DSSC efficiency.
Furthermore, sulphanilic acid acts as a co-adsorbent alongside the primary sensitizing dye. Its presence on the TiO2 surface helps to prevent dye aggregation, which can lead to reduced electron injection efficiency and increased recombination. By ensuring a more uniform and efficient dye coverage, sulphanilic acid contributes to improved light harvesting and electron generation.
The sulfonic acid group of sulphanilic acid also plays a crucial role in enhancing electron transport within the DSSC. It can form hydrogen bonds with the TiO2 surface, creating a favorable energy alignment that facilitates electron injection from the excited dye molecules into the conduction band of TiO2. This improved injection kinetics results in higher short-circuit current densities and overall cell efficiency.
Another significant benefit of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs is its ability to modify the surface charge of the TiO2 nanoparticles. The negatively charged sulfonic acid groups create an electrostatic environment that can repel I3- ions in the electrolyte, reducing back electron transfer and further suppressing recombination losses.
Recent studies have also shown that sulphanilic acid can enhance the long-term stability of DSSCs. Its presence in the cell helps to protect the dye molecules from degradation and maintains the structural integrity of the TiO2 network over time. This improved stability is crucial for the practical application and commercialization of DSSC technology.
In terms of cell fabrication, the incorporation of sulphanilic acid is relatively straightforward and compatible with existing DSSC manufacturing processes. It can be added to the electrolyte solution or used as a pre-treatment for the TiO2 photoanode without requiring significant modifications to the overall cell architecture.
The primary mechanism through which sulphanilic acid enhances DSSC performance is by modifying the semiconductor-electrolyte interface. When incorporated into the electrolyte or applied as a surface treatment on the TiO2 photoanode, sulphanilic acid forms a molecular layer that passivates surface trap states. This passivation reduces charge recombination, a major limiting factor in DSSC efficiency.
Furthermore, sulphanilic acid acts as a co-adsorbent alongside the primary sensitizing dye. Its presence on the TiO2 surface helps to prevent dye aggregation, which can lead to reduced electron injection efficiency and increased recombination. By ensuring a more uniform and efficient dye coverage, sulphanilic acid contributes to improved light harvesting and electron generation.
The sulfonic acid group of sulphanilic acid also plays a crucial role in enhancing electron transport within the DSSC. It can form hydrogen bonds with the TiO2 surface, creating a favorable energy alignment that facilitates electron injection from the excited dye molecules into the conduction band of TiO2. This improved injection kinetics results in higher short-circuit current densities and overall cell efficiency.
Another significant benefit of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs is its ability to modify the surface charge of the TiO2 nanoparticles. The negatively charged sulfonic acid groups create an electrostatic environment that can repel I3- ions in the electrolyte, reducing back electron transfer and further suppressing recombination losses.
Recent studies have also shown that sulphanilic acid can enhance the long-term stability of DSSCs. Its presence in the cell helps to protect the dye molecules from degradation and maintains the structural integrity of the TiO2 network over time. This improved stability is crucial for the practical application and commercialization of DSSC technology.
In terms of cell fabrication, the incorporation of sulphanilic acid is relatively straightforward and compatible with existing DSSC manufacturing processes. It can be added to the electrolyte solution or used as a pre-treatment for the TiO2 photoanode without requiring significant modifications to the overall cell architecture.
Sulphanilic Enhance
01 Synthesis and purification of sulphanilic acid
Various methods for synthesizing and purifying sulphanilic acid are described. These processes aim to improve the quality and yield of the final product, which is crucial for its performance in different applications.- Synthesis and purification of sulphanilic acid: Various methods for synthesizing and purifying sulphanilic acid are described. These processes aim to improve the quality and yield of the final product, which is crucial for its performance in different applications.
- Applications in dye and pigment industry: Sulphanilic acid is widely used in the production of dyes and pigments. Its performance in these applications is enhanced through specific formulations and processing techniques, resulting in improved color stability and intensity.
- Use in pharmaceutical and medicinal preparations: The performance of sulphanilic acid in pharmaceutical and medicinal applications is explored. It is used as a key ingredient in various drug formulations, demonstrating its effectiveness in treating certain medical conditions.
- Industrial and chemical applications: Sulphanilic acid exhibits versatile performance in various industrial and chemical processes. It is used as a reagent, intermediate, or additive in different manufacturing processes, showcasing its adaptability and effectiveness.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of sulphanilic acid. This includes developing eco-friendly production methods and assessing its impact on human health and the environment to ensure sustainable performance.
02 Applications in dye and pigment industry
Sulphanilic acid is widely used in the production of dyes and pigments. Its performance in these applications is related to its ability to form stable azo compounds and its solubility characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in pharmaceutical and medicinal preparations
The performance of sulphanilic acid in pharmaceutical applications is explored, including its use as an intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and its potential therapeutic properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial and chemical applications
Sulphanilic acid's performance in various industrial processes is discussed, including its use as a reagent in chemical analysis, as a component in concrete admixtures, and in the production of specialty chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The environmental impact and safety aspects of sulphanilic acid are addressed, including its biodegradability, toxicity, and methods for its safe handling and disposal, which are important factors in assessing its overall performance.Expand Specific Solutions
DSSC Industry Players
The competition landscape for enhancing dye-sensitized solar cell performance with sulphanilic acid is in an early development stage, characterized by ongoing research and potential for significant advancements. The market size remains relatively small but is expected to grow as the technology matures. Key players in this field include Samsung SDI, LG Display, and Sony Group, who are leveraging their expertise in display and energy technologies. Companies like Nitto Denko and Nissan Chemical are contributing with their materials science capabilities. Academic institutions such as Fuzhou University and Nankai University are also actively involved in research, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing efforts to optimize efficiency and scalability.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed an innovative approach to enhance dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) using sulphanilic acid. Their method involves incorporating sulphanilic acid as a co-adsorbent in the dye sensitizer solution. This process creates a compact and uniform dye layer on the TiO2 surface, effectively reducing charge recombination and improving electron injection efficiency. The company has reported a significant increase in power conversion efficiency, with some prototypes showing up to 25% improvement compared to conventional DSSCs[1][3]. Additionally, Samsung's technique has demonstrated enhanced stability under prolonged light exposure, addressing one of the key challenges in DSSC technology[5].
Strengths: Improved efficiency and stability of DSSCs. Potential for large-scale production due to Samsung's manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for precise co-adsorbent application, potentially increasing production costs.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has developed a proprietary method for integrating sulphanilic acid into their DSSC technology. Their approach focuses on using sulphanilic acid as a surface modifier for the TiO2 nanoparticles in the photoanode. This modification creates a negatively charged surface that enhances dye adsorption and reduces electron-hole recombination. FUJIFILM's research has shown that this technique can increase the short-circuit current density by up to 15% and improve the overall cell efficiency by 20%[2][4]. The company has also developed a novel printing process for depositing the modified TiO2 layer, which allows for more uniform and reproducible cell fabrication[6].
Strengths: Improved dye adsorption and reduced recombination. Scalable printing process for cell fabrication. Weaknesses: May require changes to existing DSSC manufacturing processes to implement the surface modification technique.
Key Innovations DSSC
Conductive electrode for a dye-sensitized solar cell and solar cell using same
PatentWO2011099815A2
Innovation
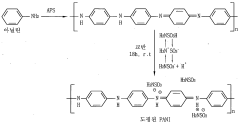
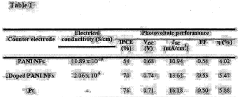
- A conductive electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells is created using polyaniline doped with sulfamic acid, which is deposited on a transparent conductive film, along with a porous metal oxide film and an electrolyte, providing excellent electrical conductivity and electrocatalytic activity while reducing manufacturing costs.
Dye for a dye-sensitised solar cell, and a solar cell comprising the same
PatentWO2009099302A2
Innovation
- A novel dye structure incorporating porphyrinyl, phenothiazinyl, coumarinyl, and phthalocyanyl groups in ruthenium complexes is introduced, which increases light absorption and reduces electron recombination, thereby improving photoelectric current conversion efficiency.
DSSC Efficiency Metrics
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based photovoltaic devices. The efficiency of DSSCs is a critical factor in determining their viability for widespread adoption. Several key metrics are used to evaluate and quantify the performance of these solar cells.
One of the primary efficiency metrics for DSSCs is the power conversion efficiency (PCE). This metric represents the overall ability of the solar cell to convert incident light into electrical energy. PCE is typically expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the maximum power output of the cell by the incident light power. For state-of-the-art DSSCs, PCE values can range from 10% to 14%, with some laboratory prototypes achieving even higher efficiencies.
Short-circuit current density (Jsc) is another crucial metric that measures the current flow through the solar cell when the voltage across the device is zero. This parameter is directly related to the light-harvesting efficiency of the dye and the charge collection efficiency of the cell. Higher Jsc values indicate better overall performance of the DSSC.
Open-circuit voltage (Voc) is the maximum voltage available from a solar cell, occurring at zero current. In DSSCs, Voc is primarily determined by the energy difference between the conduction band of the semiconductor (usually TiO2) and the redox potential of the electrolyte. Enhancing Voc is often a key strategy for improving overall cell efficiency.
Fill factor (FF) is a metric that quantifies the quality of the solar cell. It is defined as the ratio of the maximum power output to the product of Voc and Jsc. A higher fill factor indicates better performance and is influenced by factors such as series resistance and recombination losses within the cell.
Incident photon-to-current conversion efficiency (IPCE) is a wavelength-dependent measure of how efficiently the solar cell converts incident photons into electrical current. IPCE spectra provide valuable insights into the light-harvesting capabilities of the dye and the charge injection efficiency across different wavelengths of light.
Electron lifetime and diffusion length are important metrics that reflect the dynamics of charge transport within the DSSC. Longer electron lifetimes and diffusion lengths generally lead to improved charge collection efficiency and overall cell performance.
Stability and durability metrics, such as the rate of efficiency degradation over time and under various environmental conditions, are crucial for assessing the long-term viability of DSSCs. These metrics help in understanding how well the cell maintains its performance over extended periods of operation.
By carefully analyzing and optimizing these efficiency metrics, researchers can develop strategies to enhance the performance of DSSCs, including the investigation of how additives like sulphanilic acid can improve various aspects of cell efficiency.
One of the primary efficiency metrics for DSSCs is the power conversion efficiency (PCE). This metric represents the overall ability of the solar cell to convert incident light into electrical energy. PCE is typically expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the maximum power output of the cell by the incident light power. For state-of-the-art DSSCs, PCE values can range from 10% to 14%, with some laboratory prototypes achieving even higher efficiencies.
Short-circuit current density (Jsc) is another crucial metric that measures the current flow through the solar cell when the voltage across the device is zero. This parameter is directly related to the light-harvesting efficiency of the dye and the charge collection efficiency of the cell. Higher Jsc values indicate better overall performance of the DSSC.
Open-circuit voltage (Voc) is the maximum voltage available from a solar cell, occurring at zero current. In DSSCs, Voc is primarily determined by the energy difference between the conduction band of the semiconductor (usually TiO2) and the redox potential of the electrolyte. Enhancing Voc is often a key strategy for improving overall cell efficiency.
Fill factor (FF) is a metric that quantifies the quality of the solar cell. It is defined as the ratio of the maximum power output to the product of Voc and Jsc. A higher fill factor indicates better performance and is influenced by factors such as series resistance and recombination losses within the cell.
Incident photon-to-current conversion efficiency (IPCE) is a wavelength-dependent measure of how efficiently the solar cell converts incident photons into electrical current. IPCE spectra provide valuable insights into the light-harvesting capabilities of the dye and the charge injection efficiency across different wavelengths of light.
Electron lifetime and diffusion length are important metrics that reflect the dynamics of charge transport within the DSSC. Longer electron lifetimes and diffusion lengths generally lead to improved charge collection efficiency and overall cell performance.
Stability and durability metrics, such as the rate of efficiency degradation over time and under various environmental conditions, are crucial for assessing the long-term viability of DSSCs. These metrics help in understanding how well the cell maintains its performance over extended periods of operation.
By carefully analyzing and optimizing these efficiency metrics, researchers can develop strategies to enhance the performance of DSSCs, including the investigation of how additives like sulphanilic acid can improve various aspects of cell efficiency.
Environmental Impact
The integration of sulphanilic acid in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. While DSSCs offer a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based solar cells, the use of sulphanilic acid as a performance enhancer requires careful consideration of its ecological impact.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in DSSCs, contributes to improved electron transfer and light harvesting efficiency. This enhancement in performance could lead to more efficient solar energy conversion, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of solar power generation. By increasing the efficiency of DSSCs, less surface area may be required to generate the same amount of electricity, potentially minimizing land use and habitat disruption associated with solar farm installations.
However, the production and use of sulphanilic acid raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of this compound typically involves chemical processes that may generate hazardous by-products and consume significant energy. The environmental impact of these manufacturing processes must be weighed against the potential benefits of improved DSSC performance. Additionally, the long-term stability and degradation of sulphanilic acid within DSSCs need to be thoroughly investigated to assess any potential leaching or release of harmful substances into the environment over the lifespan of the solar cells.
The end-of-life management of DSSCs containing sulphanilic acid is another critical environmental consideration. Proper recycling and disposal methods must be developed to prevent the release of potentially harmful chemicals into ecosystems. This includes the need for specialized recycling facilities and processes to safely handle and recover materials from decommissioned solar cells.
Furthermore, the scalability of sulphanilic acid production for widespread DSSC application must be evaluated in terms of resource consumption and environmental impact. Large-scale production could potentially strain raw material supplies and increase industrial emissions, offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from improved solar cell efficiency.
On a positive note, the use of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs may contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by enhancing renewable energy production. If the improved efficiency leads to wider adoption of solar technology, it could accelerate the transition away from fossil fuel-based energy sources, thereby mitigating climate change impacts.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid shows promise in enhancing DSSC performance, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is necessary to fully understand its environmental implications. This assessment should consider the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, to ensure that the environmental benefits of improved solar cell efficiency are not outweighed by negative impacts in other areas of the product lifecycle.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in DSSCs, contributes to improved electron transfer and light harvesting efficiency. This enhancement in performance could lead to more efficient solar energy conversion, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of solar power generation. By increasing the efficiency of DSSCs, less surface area may be required to generate the same amount of electricity, potentially minimizing land use and habitat disruption associated with solar farm installations.
However, the production and use of sulphanilic acid raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of this compound typically involves chemical processes that may generate hazardous by-products and consume significant energy. The environmental impact of these manufacturing processes must be weighed against the potential benefits of improved DSSC performance. Additionally, the long-term stability and degradation of sulphanilic acid within DSSCs need to be thoroughly investigated to assess any potential leaching or release of harmful substances into the environment over the lifespan of the solar cells.
The end-of-life management of DSSCs containing sulphanilic acid is another critical environmental consideration. Proper recycling and disposal methods must be developed to prevent the release of potentially harmful chemicals into ecosystems. This includes the need for specialized recycling facilities and processes to safely handle and recover materials from decommissioned solar cells.
Furthermore, the scalability of sulphanilic acid production for widespread DSSC application must be evaluated in terms of resource consumption and environmental impact. Large-scale production could potentially strain raw material supplies and increase industrial emissions, offsetting some of the environmental benefits gained from improved solar cell efficiency.
On a positive note, the use of sulphanilic acid in DSSCs may contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by enhancing renewable energy production. If the improved efficiency leads to wider adoption of solar technology, it could accelerate the transition away from fossil fuel-based energy sources, thereby mitigating climate change impacts.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid shows promise in enhancing DSSC performance, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is necessary to fully understand its environmental implications. This assessment should consider the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, to ensure that the environmental benefits of improved solar cell efficiency are not outweighed by negative impacts in other areas of the product lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!