How to Align V2G Development with ESG Goals?
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Technology Background and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology has emerged as a promising solution at the intersection of transportation and energy sectors. This innovative approach enables electric vehicles (EVs) to not only consume electricity but also feed it back into the grid when needed. The development of V2G technology dates back to the early 2000s, with the concept first proposed by Dr. Willett Kempton and his colleagues at the University of Delaware.
The evolution of V2G technology has been closely tied to the growth of the EV market and the increasing focus on renewable energy integration. As the global push for decarbonization intensifies, V2G has gained significant attention for its potential to enhance grid stability, reduce peak demand, and facilitate the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a symbiotic relationship between EVs and the power grid. By allowing bidirectional power flow, V2G aims to transform EVs from mere consumers of electricity into active participants in grid management. This transformation can potentially lead to more efficient use of energy resources, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved grid resilience.
In the context of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals, V2G technology presents a unique opportunity to align transportation electrification with broader sustainability objectives. The technology's ability to support renewable energy integration and reduce grid infrastructure costs aligns with environmental goals. Socially, V2G can contribute to energy equity by providing additional income streams for EV owners and potentially reducing electricity costs for all consumers.
The development trajectory of V2G technology is expected to focus on several key areas. These include improving bidirectional charging efficiency, enhancing battery management systems to minimize degradation from V2G operations, and developing sophisticated algorithms for optimal charging and discharging schedules. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on standardization and interoperability to ensure seamless integration of V2G-enabled vehicles across different manufacturers and grid systems.
As the technology matures, the integration of V2G with smart grid technologies and renewable energy systems is anticipated to play a crucial role in achieving a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem. This integration will require advancements in communication protocols, cybersecurity measures, and regulatory frameworks to ensure the safe and efficient operation of V2G systems at scale.
The alignment of V2G development with ESG goals necessitates a holistic approach that considers not only the technical aspects but also the broader environmental, social, and economic implications. This includes addressing challenges such as battery lifecycle management, equitable access to V2G benefits, and the development of sustainable business models that incentivize participation from both EV owners and utility companies.
The evolution of V2G technology has been closely tied to the growth of the EV market and the increasing focus on renewable energy integration. As the global push for decarbonization intensifies, V2G has gained significant attention for its potential to enhance grid stability, reduce peak demand, and facilitate the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
The primary objective of V2G technology is to create a symbiotic relationship between EVs and the power grid. By allowing bidirectional power flow, V2G aims to transform EVs from mere consumers of electricity into active participants in grid management. This transformation can potentially lead to more efficient use of energy resources, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved grid resilience.
In the context of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals, V2G technology presents a unique opportunity to align transportation electrification with broader sustainability objectives. The technology's ability to support renewable energy integration and reduce grid infrastructure costs aligns with environmental goals. Socially, V2G can contribute to energy equity by providing additional income streams for EV owners and potentially reducing electricity costs for all consumers.
The development trajectory of V2G technology is expected to focus on several key areas. These include improving bidirectional charging efficiency, enhancing battery management systems to minimize degradation from V2G operations, and developing sophisticated algorithms for optimal charging and discharging schedules. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on standardization and interoperability to ensure seamless integration of V2G-enabled vehicles across different manufacturers and grid systems.
As the technology matures, the integration of V2G with smart grid technologies and renewable energy systems is anticipated to play a crucial role in achieving a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem. This integration will require advancements in communication protocols, cybersecurity measures, and regulatory frameworks to ensure the safe and efficient operation of V2G systems at scale.
The alignment of V2G development with ESG goals necessitates a holistic approach that considers not only the technical aspects but also the broader environmental, social, and economic implications. This includes addressing challenges such as battery lifecycle management, equitable access to V2G benefits, and the development of sustainable business models that incentivize participation from both EV owners and utility companies.
Market Analysis for V2G Solutions
The market for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) solutions is experiencing significant growth as the automotive industry shifts towards electrification and renewable energy integration becomes a priority. V2G technology enables electric vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back, creating a bidirectional flow that can support grid stability and optimize energy usage.
The global V2G market is driven by several factors, including the increasing adoption of EVs, growing concerns about climate change, and the need for grid modernization. As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, V2G solutions are becoming increasingly attractive to both consumers and utility companies.
In terms of market size, the V2G sector is projected to expand rapidly over the coming years. This growth is fueled by advancements in battery technology, smart grid infrastructure, and the proliferation of EV charging stations. The market is also benefiting from the rising interest in distributed energy resources and the concept of prosumers – consumers who both produce and consume energy.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the V2G market, with countries like Denmark, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom at the forefront of V2G pilot projects and commercial deployments. North America follows closely, with significant investments in V2G research and development, particularly in California and other progressive states. The Asia-Pacific region, led by Japan and South Korea, is also showing strong potential for V2G adoption, driven by their advanced automotive industries and commitment to sustainable energy practices.
The V2G market is segmented into various applications, including peak power sales, spinning reserves, and base load power. Among these, peak power sales represent the largest market share, as V2G technology can effectively address the challenge of managing peak demand periods by utilizing EV batteries as a distributed energy resource.
Key players in the V2G market include major automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and technology providers. These stakeholders are forming strategic partnerships to develop and deploy V2G solutions, recognizing the potential for new revenue streams and improved grid efficiency.
However, the V2G market also faces several challenges. These include the need for substantial infrastructure investments, concerns about battery degradation, and the complexity of integrating V2G systems with existing grid operations. Additionally, regulatory frameworks and market mechanisms need to evolve to fully support the widespread adoption of V2G technology.
Despite these challenges, the alignment of V2G development with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals presents significant opportunities. V2G solutions can contribute to reducing carbon emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation. This alignment is attracting investors and policymakers who are increasingly focused on ESG criteria, further driving market growth and innovation in the V2G sector.
The global V2G market is driven by several factors, including the increasing adoption of EVs, growing concerns about climate change, and the need for grid modernization. As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, V2G solutions are becoming increasingly attractive to both consumers and utility companies.
In terms of market size, the V2G sector is projected to expand rapidly over the coming years. This growth is fueled by advancements in battery technology, smart grid infrastructure, and the proliferation of EV charging stations. The market is also benefiting from the rising interest in distributed energy resources and the concept of prosumers – consumers who both produce and consume energy.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the V2G market, with countries like Denmark, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom at the forefront of V2G pilot projects and commercial deployments. North America follows closely, with significant investments in V2G research and development, particularly in California and other progressive states. The Asia-Pacific region, led by Japan and South Korea, is also showing strong potential for V2G adoption, driven by their advanced automotive industries and commitment to sustainable energy practices.
The V2G market is segmented into various applications, including peak power sales, spinning reserves, and base load power. Among these, peak power sales represent the largest market share, as V2G technology can effectively address the challenge of managing peak demand periods by utilizing EV batteries as a distributed energy resource.
Key players in the V2G market include major automotive manufacturers, energy companies, and technology providers. These stakeholders are forming strategic partnerships to develop and deploy V2G solutions, recognizing the potential for new revenue streams and improved grid efficiency.
However, the V2G market also faces several challenges. These include the need for substantial infrastructure investments, concerns about battery degradation, and the complexity of integrating V2G systems with existing grid operations. Additionally, regulatory frameworks and market mechanisms need to evolve to fully support the widespread adoption of V2G technology.
Despite these challenges, the alignment of V2G development with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals presents significant opportunities. V2G solutions can contribute to reducing carbon emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation. This alignment is attracting investors and policymakers who are increasingly focused on ESG criteria, further driving market growth and innovation in the V2G sector.
V2G Technical Challenges and Limitations
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, while promising, faces several technical challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for successful implementation and alignment with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. One of the primary challenges is the impact on battery life. Frequent charging and discharging cycles associated with V2G operations can accelerate battery degradation, potentially shortening the lifespan of electric vehicles (EVs). This raises concerns about sustainability and resource efficiency, key aspects of ESG objectives.
Another significant challenge is the complexity of bidirectional charging infrastructure. V2G systems require sophisticated hardware and software to manage the flow of electricity both to and from the grid. This includes advanced inverters, smart meters, and communication systems capable of real-time data exchange. The development and widespread deployment of such infrastructure present technical hurdles and substantial investment requirements, which may slow down V2G adoption and its potential ESG benefits.
Grid integration poses another set of challenges. The existing power grid infrastructure in many regions is not designed to handle large-scale bidirectional power flows. Integrating a significant number of V2G-enabled vehicles could lead to grid instability, voltage fluctuations, and power quality issues. Addressing these concerns requires advanced grid management systems and potentially costly upgrades to the existing infrastructure, which may conflict with short-term ESG goals related to resource efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Standardization and interoperability remain critical challenges in V2G development. The lack of universal standards for V2G communication protocols, charging interfaces, and grid integration methods hinders widespread adoption and creates barriers to entry for both vehicle manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers. This fragmentation can lead to inefficiencies and reduced overall impact of V2G on ESG objectives.
Energy management and optimization present another layer of complexity. Balancing the needs of vehicle owners (e.g., ensuring sufficient charge for daily use) with grid requirements demands sophisticated algorithms and predictive models. These systems must consider factors such as energy prices, grid demand, renewable energy availability, and individual driving patterns. Developing and implementing such systems at scale is a significant technical challenge that directly impacts the ESG potential of V2G technology.
Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns also pose limitations to V2G development. The interconnected nature of V2G systems creates potential vulnerabilities to cyber attacks, which could compromise grid stability or user data. Ensuring robust security measures while maintaining system efficiency and user privacy is a complex technical challenge that must be addressed to align with ESG principles of responsible governance and social responsibility.
Lastly, the limitation of current battery technologies in terms of capacity, charging speed, and longevity affects the overall effectiveness of V2G systems. Improvements in battery technology are crucial for maximizing the potential of V2G and its alignment with ESG goals, particularly in areas of environmental sustainability and resource efficiency.
Another significant challenge is the complexity of bidirectional charging infrastructure. V2G systems require sophisticated hardware and software to manage the flow of electricity both to and from the grid. This includes advanced inverters, smart meters, and communication systems capable of real-time data exchange. The development and widespread deployment of such infrastructure present technical hurdles and substantial investment requirements, which may slow down V2G adoption and its potential ESG benefits.
Grid integration poses another set of challenges. The existing power grid infrastructure in many regions is not designed to handle large-scale bidirectional power flows. Integrating a significant number of V2G-enabled vehicles could lead to grid instability, voltage fluctuations, and power quality issues. Addressing these concerns requires advanced grid management systems and potentially costly upgrades to the existing infrastructure, which may conflict with short-term ESG goals related to resource efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Standardization and interoperability remain critical challenges in V2G development. The lack of universal standards for V2G communication protocols, charging interfaces, and grid integration methods hinders widespread adoption and creates barriers to entry for both vehicle manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers. This fragmentation can lead to inefficiencies and reduced overall impact of V2G on ESG objectives.
Energy management and optimization present another layer of complexity. Balancing the needs of vehicle owners (e.g., ensuring sufficient charge for daily use) with grid requirements demands sophisticated algorithms and predictive models. These systems must consider factors such as energy prices, grid demand, renewable energy availability, and individual driving patterns. Developing and implementing such systems at scale is a significant technical challenge that directly impacts the ESG potential of V2G technology.
Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns also pose limitations to V2G development. The interconnected nature of V2G systems creates potential vulnerabilities to cyber attacks, which could compromise grid stability or user data. Ensuring robust security measures while maintaining system efficiency and user privacy is a complex technical challenge that must be addressed to align with ESG principles of responsible governance and social responsibility.
Lastly, the limitation of current battery technologies in terms of capacity, charging speed, and longevity affects the overall effectiveness of V2G systems. Improvements in battery technology are crucial for maximizing the potential of V2G and its alignment with ESG goals, particularly in areas of environmental sustainability and resource efficiency.
Current V2G Implementation Strategies
01 V2G integration with renewable energy sources
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology can be aligned with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals by integrating electric vehicles with renewable energy sources. This integration allows for better management of intermittent renewable energy, reduces carbon emissions, and supports the transition to a cleaner energy grid. V2G systems can store excess renewable energy in vehicle batteries during off-peak hours and feed it back to the grid during peak demand, enhancing grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.- V2G integration with renewable energy sources: Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology can be aligned with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals by integrating electric vehicles with renewable energy sources. This integration allows for better management of intermittent renewable energy, reduces carbon emissions, and supports the transition to a cleaner energy grid. V2G systems can store excess renewable energy in vehicle batteries during off-peak hours and feed it back to the grid during peak demand, enhancing grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Smart charging and load balancing for grid stability: V2G systems can contribute to ESG objectives by implementing smart charging and load balancing strategies. These technologies optimize the charging and discharging of electric vehicles based on grid demand, energy prices, and renewable energy availability. By intelligently managing the flow of electricity between vehicles and the grid, V2G systems can help reduce peak loads, improve grid reliability, and minimize the need for additional power generation infrastructure.
- V2G for emergency power supply and resilience: V2G technology can enhance community resilience and support ESG goals by providing emergency power supply during grid outages or natural disasters. Electric vehicles equipped with V2G capabilities can serve as mobile power sources, supplying electricity to critical infrastructure, homes, or businesses during emergencies. This application of V2G technology improves energy security, reduces vulnerability to power disruptions, and supports social responsibility initiatives.
- V2G-enabled microgrids and community energy systems: V2G technology can be integrated into microgrids and community energy systems to support ESG objectives. These localized energy networks can leverage V2G-enabled electric vehicles to balance supply and demand, increase energy independence, and reduce reliance on centralized power generation. By enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and local energy management, V2G-enabled microgrids can foster community engagement, promote energy equity, and support sustainable urban development.
- V2G data analytics for improved grid management: V2G systems can generate valuable data on energy consumption patterns, charging behaviors, and grid performance. By leveraging advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms, grid operators can optimize energy distribution, predict demand fluctuations, and identify opportunities for improving grid efficiency. This data-driven approach aligns with ESG principles by enabling more sustainable and efficient energy management practices, reducing waste, and supporting evidence-based decision-making in the energy sector.
02 Smart charging and load balancing for grid stability
V2G systems can contribute to ESG goals by implementing smart charging and load balancing strategies. These technologies optimize the charging and discharging of electric vehicles based on grid demand, energy prices, and renewable energy availability. By intelligently managing the flow of electricity between vehicles and the grid, V2G systems can reduce strain on the power infrastructure, improve grid reliability, and maximize the use of clean energy sources.Expand Specific Solutions03 V2G for community resilience and energy equity
V2G technology can be leveraged to enhance community resilience and promote energy equity, aligning with social and governance aspects of ESG. By enabling electric vehicles to serve as mobile power sources during emergencies or power outages, V2G systems can provide backup power to critical infrastructure and vulnerable communities. This application of V2G technology supports social responsibility goals and improves the overall resilience of energy systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 V2G data management and privacy protection
To align with ESG governance principles, V2G systems must incorporate robust data management and privacy protection measures. This includes secure communication protocols, encryption of sensitive information, and transparent data handling practices. By ensuring the privacy and security of user data, V2G implementations can build trust among stakeholders and comply with data protection regulations, supporting good governance practices in the transition to smart grid technologies.Expand Specific Solutions05 V2G incentive mechanisms and market integration
Developing fair and transparent incentive mechanisms for V2G participation is crucial for ESG alignment. This includes creating market structures that compensate electric vehicle owners for grid services, designing time-of-use pricing schemes, and integrating V2G services into existing energy markets. By establishing equitable financial incentives and clear market rules, V2G systems can encourage widespread adoption and ensure that the benefits of the technology are shared among all stakeholders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in V2G Industry
The development of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology and its alignment with ESG goals is in an early growth stage, with increasing market potential as electric vehicle adoption rises. The global V2G market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by the push for sustainable energy solutions. Technologically, V2G is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different companies. State Grid Corporation of China and Honda Motor Co. are among the leaders, investing heavily in V2G research and pilot projects. Other key players like Hyundai, Kia, and various research institutes are also making strides, though at different stages of development and implementation.
State Grid Corp. of China
Technical Solution: State Grid Corp. of China has developed a comprehensive V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) strategy aligned with ESG goals. Their approach includes implementing smart charging infrastructure, integrating renewable energy sources, and developing advanced energy management systems. The company has deployed over 1 million charging piles across China[1], with plans to increase this number significantly. They are also focusing on bi-directional charging technology, allowing electric vehicles to feed energy back into the grid during peak demand periods[2]. State Grid's V2G initiatives aim to reduce carbon emissions by optimizing grid efficiency and promoting the use of clean energy sources. They have implemented pilot projects in several cities, demonstrating the potential of V2G technology to balance grid loads and reduce overall energy consumption[3].
Strengths: Extensive infrastructure network, strong government support, and significant R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in standardization across diverse regions and the need for large-scale consumer adoption of V2G-enabled vehicles.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda Motor Co., Ltd. has been actively developing V2G technology as part of its commitment to ESG goals. Their approach focuses on creating a sustainable mobility ecosystem that integrates electric vehicles with smart grid systems. Honda's V2G strategy includes the development of bi-directional charging systems and smart energy management platforms. They have partnered with various energy companies to conduct V2G pilot projects, demonstrating the potential of their technology to support grid stability and reduce carbon emissions[1]. Honda's V2G-enabled vehicles can provide power back to the grid during peak demand periods, helping to balance energy supply and demand. The company is also investing in AI and IoT technologies to optimize V2G operations, ensuring efficient energy transfer between vehicles and the grid[2]. Honda's commitment to V2G aligns with their goal of achieving carbon neutrality for all products and corporate activities by 2050[3].
Strengths: Strong brand reputation, extensive automotive expertise, and global market presence. Weaknesses: Relatively late entry into the EV market compared to some competitors, which may impact V2G adoption rates.
Core V2G Innovations and Patents
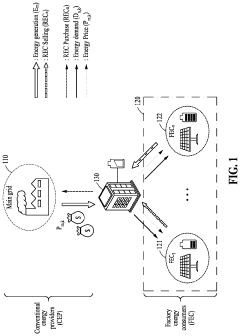
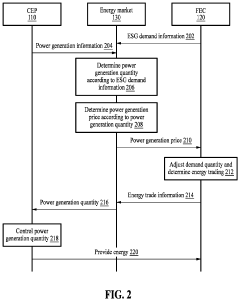
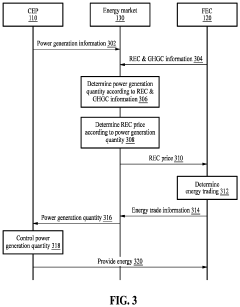
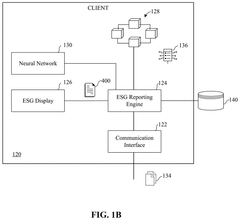
Energy trading method and system for supporting environmental, social, and governance management
PatentPendingUS20240161190A1
Innovation
- An energy trading method and system that evaluates utility by receiving ESG demand information and power generation data to determine optimal energy distribution quantities, enabling factories with surplus energy to sell back to the grid and those with high demand to purchase energy based on calculated prices, thereby maximizing total utility and enhancing ESG scores.
Blockchain-enabled ESG management
PatentPendingUS20250005567A1
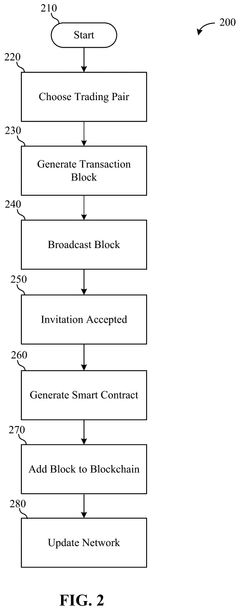
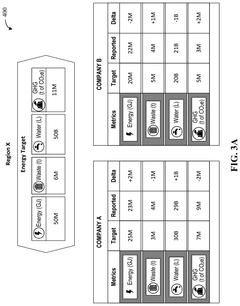
Innovation
- A blockchain-based ESG management platform that identifies trading pairs between sustainability factors like energy, water, and emissions, generates transaction blocks, and uses smart contracts to facilitate trades based on regional demand, enabling automatic determination of trade thresholds and conditions between regions or units within an enterprise.
ESG Impact Assessment of V2G
The ESG Impact Assessment of V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) technology is crucial for understanding its potential to contribute to sustainable development goals. V2G systems enable bidirectional energy flow between electric vehicles and the power grid, offering significant opportunities for grid stabilization and renewable energy integration. From an environmental perspective, V2G can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by facilitating the increased use of renewable energy sources. By allowing excess renewable energy to be stored in vehicle batteries and fed back to the grid during peak demand, V2G helps balance supply and demand, reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants.
Socially, V2G technology can contribute to energy equity by providing additional income streams for EV owners through grid services. This democratization of energy production and distribution can empower communities and individuals to participate actively in the energy transition. Moreover, V2G can enhance grid resilience, potentially reducing power outages and improving energy security for vulnerable populations.
Governance aspects of V2G implementation involve developing robust regulatory frameworks to ensure fair compensation for EV owners, data privacy protection, and cybersecurity measures. Transparent policies and standards for V2G participation are essential to build trust and encourage widespread adoption. Additionally, the technology can support smart city initiatives by enabling more efficient urban energy management.
The economic implications of V2G are substantial. By optimizing grid operations and reducing the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades, V2G can lead to overall cost savings in the energy sector. This could potentially result in lower electricity prices for consumers and businesses. Furthermore, the development of V2G technology creates new business opportunities and jobs in areas such as software development, energy management, and EV charging infrastructure.
However, the ESG assessment must also consider potential challenges. These include the need for significant initial investments in infrastructure, potential battery degradation concerns for EV owners, and the complexity of integrating V2G systems with existing grid infrastructure. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts between policymakers, utilities, automakers, and technology providers to ensure that V2G development aligns with broader ESG goals while maximizing its benefits for all stakeholders.
Socially, V2G technology can contribute to energy equity by providing additional income streams for EV owners through grid services. This democratization of energy production and distribution can empower communities and individuals to participate actively in the energy transition. Moreover, V2G can enhance grid resilience, potentially reducing power outages and improving energy security for vulnerable populations.
Governance aspects of V2G implementation involve developing robust regulatory frameworks to ensure fair compensation for EV owners, data privacy protection, and cybersecurity measures. Transparent policies and standards for V2G participation are essential to build trust and encourage widespread adoption. Additionally, the technology can support smart city initiatives by enabling more efficient urban energy management.
The economic implications of V2G are substantial. By optimizing grid operations and reducing the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades, V2G can lead to overall cost savings in the energy sector. This could potentially result in lower electricity prices for consumers and businesses. Furthermore, the development of V2G technology creates new business opportunities and jobs in areas such as software development, energy management, and EV charging infrastructure.
However, the ESG assessment must also consider potential challenges. These include the need for significant initial investments in infrastructure, potential battery degradation concerns for EV owners, and the complexity of integrating V2G systems with existing grid infrastructure. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts between policymakers, utilities, automakers, and technology providers to ensure that V2G development aligns with broader ESG goals while maximizing its benefits for all stakeholders.
V2G Policy and Regulatory Framework
The development of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology requires a robust policy and regulatory framework to ensure its alignment with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. This framework must address various aspects of V2G implementation, including energy market regulations, grid integration standards, and environmental policies.
At the core of V2G policy development is the need for clear regulations governing the participation of electric vehicles in energy markets. These regulations should define how V2G services are valued, compensated, and integrated into existing electricity market structures. Policymakers must establish mechanisms for fair pricing of grid services provided by electric vehicles, considering both the benefits to the grid and the costs to vehicle owners.
Grid integration standards play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless operation of V2G systems. Regulatory bodies need to develop and enforce technical standards for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure. These standards should address issues such as communication protocols, data security, and interoperability between different vehicle models and charging systems.
Environmental policies are essential for maximizing the positive impact of V2G on sustainability goals. Regulations should incentivize the use of renewable energy sources in V2G operations, potentially through preferential tariffs or carbon credits. Additionally, policies should be implemented to manage the lifecycle of electric vehicle batteries, including their second-life applications and recycling processes.
Consumer protection and privacy regulations are vital components of the V2G policy framework. These should outline the rights and responsibilities of V2G participants, ensuring transparency in pricing, data usage, and service agreements. Policymakers must also address concerns related to battery degradation and vehicle warranty implications resulting from V2G participation.
To promote widespread adoption of V2G technology, supportive policies and incentives are necessary. These may include tax credits for V2G-enabled vehicles, grants for infrastructure development, and regulatory sandboxes to facilitate pilot projects. Governments should also consider mandates for V2G readiness in new buildings and public charging stations.
Cross-sector collaboration is crucial for developing an effective V2G policy framework. Regulators must engage with automakers, utilities, technology providers, and consumer groups to create policies that balance the interests of all stakeholders. This collaborative approach will help ensure that V2G regulations are practical, equitable, and aligned with broader ESG objectives.
At the core of V2G policy development is the need for clear regulations governing the participation of electric vehicles in energy markets. These regulations should define how V2G services are valued, compensated, and integrated into existing electricity market structures. Policymakers must establish mechanisms for fair pricing of grid services provided by electric vehicles, considering both the benefits to the grid and the costs to vehicle owners.
Grid integration standards play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless operation of V2G systems. Regulatory bodies need to develop and enforce technical standards for V2G-enabled vehicles and charging infrastructure. These standards should address issues such as communication protocols, data security, and interoperability between different vehicle models and charging systems.
Environmental policies are essential for maximizing the positive impact of V2G on sustainability goals. Regulations should incentivize the use of renewable energy sources in V2G operations, potentially through preferential tariffs or carbon credits. Additionally, policies should be implemented to manage the lifecycle of electric vehicle batteries, including their second-life applications and recycling processes.
Consumer protection and privacy regulations are vital components of the V2G policy framework. These should outline the rights and responsibilities of V2G participants, ensuring transparency in pricing, data usage, and service agreements. Policymakers must also address concerns related to battery degradation and vehicle warranty implications resulting from V2G participation.
To promote widespread adoption of V2G technology, supportive policies and incentives are necessary. These may include tax credits for V2G-enabled vehicles, grants for infrastructure development, and regulatory sandboxes to facilitate pilot projects. Governments should also consider mandates for V2G readiness in new buildings and public charging stations.
Cross-sector collaboration is crucial for developing an effective V2G policy framework. Regulators must engage with automakers, utilities, technology providers, and consumer groups to create policies that balance the interests of all stakeholders. This collaborative approach will help ensure that V2G regulations are practical, equitable, and aligned with broader ESG objectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!