How to Analyze Oxaloacetate's Influence on Insulin Sensitivity
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate and Insulin Sensitivity: Background and Objectives
Oxaloacetate (OAA) represents a critical metabolite in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, functioning as an essential intermediate in cellular energy production. Over the past decade, research has increasingly focused on OAA's potential role beyond basic metabolism, particularly its influence on insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. The historical trajectory of this research began with fundamental biochemical studies in the 1950s and 1960s that established OAA's position in cellular metabolism, followed by more recent investigations that have suggested its broader physiological impacts.
The evolution of research in this field has been marked by significant technological advancements in metabolomics, allowing for more precise measurement of OAA levels in biological systems and better understanding of its interactions with insulin signaling pathways. Recent studies have indicated that OAA may influence mitochondrial function, which is closely linked to insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues such as skeletal muscle and liver.
Current scientific literature suggests several mechanisms through which OAA might affect insulin sensitivity, including modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, reduction of oxidative stress, and influence on cellular energy status through the NAD+/NADH ratio. These pathways represent potential therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders characterized by insulin resistance, such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the relationship between OAA and insulin sensitivity, establishing a clear understanding of the underlying mechanisms and potential applications. Specifically, we aim to evaluate existing analytical methods for measuring OAA's effects on insulin signaling pathways, identify gaps in current methodologies, and propose innovative approaches for more accurate assessment.
Secondary objectives include determining the dose-response relationship between OAA supplementation and changes in insulin sensitivity markers, investigating tissue-specific effects, and exploring potential synergistic interactions with other metabolic regulators. Additionally, we seek to establish standardized protocols for analyzing OAA's metabolic effects that could be implemented across research settings.
This research is particularly timely given the growing global burden of metabolic disorders and the urgent need for novel therapeutic approaches. By elucidating OAA's role in insulin sensitivity, this work may contribute to the development of targeted metabolic interventions for improving glucose homeostasis and preventing diabetes progression. Furthermore, understanding these mechanisms may provide insights into fundamental aspects of cellular metabolism and energy regulation that extend beyond diabetes research.
The evolution of research in this field has been marked by significant technological advancements in metabolomics, allowing for more precise measurement of OAA levels in biological systems and better understanding of its interactions with insulin signaling pathways. Recent studies have indicated that OAA may influence mitochondrial function, which is closely linked to insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues such as skeletal muscle and liver.
Current scientific literature suggests several mechanisms through which OAA might affect insulin sensitivity, including modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, reduction of oxidative stress, and influence on cellular energy status through the NAD+/NADH ratio. These pathways represent potential therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders characterized by insulin resistance, such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the relationship between OAA and insulin sensitivity, establishing a clear understanding of the underlying mechanisms and potential applications. Specifically, we aim to evaluate existing analytical methods for measuring OAA's effects on insulin signaling pathways, identify gaps in current methodologies, and propose innovative approaches for more accurate assessment.
Secondary objectives include determining the dose-response relationship between OAA supplementation and changes in insulin sensitivity markers, investigating tissue-specific effects, and exploring potential synergistic interactions with other metabolic regulators. Additionally, we seek to establish standardized protocols for analyzing OAA's metabolic effects that could be implemented across research settings.
This research is particularly timely given the growing global burden of metabolic disorders and the urgent need for novel therapeutic approaches. By elucidating OAA's role in insulin sensitivity, this work may contribute to the development of targeted metabolic interventions for improving glucose homeostasis and preventing diabetes progression. Furthermore, understanding these mechanisms may provide insights into fundamental aspects of cellular metabolism and energy regulation that extend beyond diabetes research.
Market Analysis of Metabolic Health Interventions
The global metabolic health market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the rising prevalence of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Currently valued at approximately $42 billion, this market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% through 2028, reflecting increasing consumer awareness and healthcare expenditure on metabolic interventions.
Insulin sensitivity enhancers represent a particularly dynamic segment within this market, with pharmaceutical interventions dominating at 65% market share. However, nutraceutical approaches, including compounds like oxaloacetate, are gaining traction with an estimated 18% annual growth rate, outpacing traditional pharmaceutical solutions.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a notable shift toward preventative metabolic health solutions rather than solely treatment-focused approaches. This trend is especially pronounced among the 45-65 age demographic, where concerns about metabolic health and aging intersect. Market research indicates that 72% of consumers in this segment actively seek metabolic health optimization products, with 38% specifically interested in natural compounds that may influence insulin sensitivity.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the metabolic health market with 42% share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (22%). The latter region demonstrates the fastest growth trajectory at 10.5% annually, driven by increasing affluence, westernization of diets, and rising metabolic disorder prevalence in countries like China and India.
Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with direct-to-consumer models gaining prominence. E-commerce platforms now account for 34% of metabolic health product sales, compared to 22% five years ago. This shift has reduced barriers to market entry for innovative metabolic interventions like oxaloacetate-based supplements.
Pricing analysis reveals significant elasticity in this market, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay premium prices for products with substantiated efficacy claims. Products positioned as "metabolic optimizers" command an average 30% price premium over generic supplements, highlighting the value consumers place on metabolic health outcomes.
Competitive landscape assessment identifies three distinct market segments: pharmaceutical giants focusing on prescription metabolic medications, established nutraceutical companies expanding into metabolic health, and emerging biotechnology startups developing novel compounds like enhanced oxaloacetate formulations. This fragmentation presents both partnership opportunities and competitive challenges for new market entrants.
Insulin sensitivity enhancers represent a particularly dynamic segment within this market, with pharmaceutical interventions dominating at 65% market share. However, nutraceutical approaches, including compounds like oxaloacetate, are gaining traction with an estimated 18% annual growth rate, outpacing traditional pharmaceutical solutions.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a notable shift toward preventative metabolic health solutions rather than solely treatment-focused approaches. This trend is especially pronounced among the 45-65 age demographic, where concerns about metabolic health and aging intersect. Market research indicates that 72% of consumers in this segment actively seek metabolic health optimization products, with 38% specifically interested in natural compounds that may influence insulin sensitivity.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the metabolic health market with 42% share, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (22%). The latter region demonstrates the fastest growth trajectory at 10.5% annually, driven by increasing affluence, westernization of diets, and rising metabolic disorder prevalence in countries like China and India.
Distribution channels are evolving rapidly, with direct-to-consumer models gaining prominence. E-commerce platforms now account for 34% of metabolic health product sales, compared to 22% five years ago. This shift has reduced barriers to market entry for innovative metabolic interventions like oxaloacetate-based supplements.
Pricing analysis reveals significant elasticity in this market, with consumers demonstrating willingness to pay premium prices for products with substantiated efficacy claims. Products positioned as "metabolic optimizers" command an average 30% price premium over generic supplements, highlighting the value consumers place on metabolic health outcomes.
Competitive landscape assessment identifies three distinct market segments: pharmaceutical giants focusing on prescription metabolic medications, established nutraceutical companies expanding into metabolic health, and emerging biotechnology startups developing novel compounds like enhanced oxaloacetate formulations. This fragmentation presents both partnership opportunities and competitive challenges for new market entrants.
Current Research Status and Challenges in Oxaloacetate Studies
The field of oxaloacetate research in relation to insulin sensitivity has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, yet remains characterized by substantial knowledge gaps and methodological challenges. Current research has established oxaloacetate as a critical metabolic intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, with emerging evidence suggesting its potential role in glucose metabolism regulation and insulin signaling pathways.
Laboratory studies have demonstrated that oxaloacetate supplementation may enhance mitochondrial function, potentially improving cellular energy metabolism in insulin-responsive tissues. Several animal models have shown promising results, with oxaloacetate administration leading to improved glucose tolerance and enhanced insulin sensitivity in diabetic rodents. However, translation of these findings to human clinical applications remains limited, with only a handful of small-scale human trials completed to date.
A significant challenge in this field is the inherent instability of oxaloacetate in aqueous solutions, which complicates both research methodologies and potential therapeutic applications. Researchers have attempted various stabilization techniques, including encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications, but optimal delivery systems remain elusive. This technical limitation has hindered progress in establishing consistent dosing protocols and reliable bioavailability data.
Analytical challenges also persist in accurately measuring oxaloacetate levels in biological samples. Current methods primarily rely on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) techniques, which require sophisticated equipment and expertise. The development of more accessible and cost-effective detection methods would significantly accelerate research progress in this area.
The mechanistic understanding of oxaloacetate's influence on insulin sensitivity remains incomplete. While some studies suggest direct effects on insulin signaling pathways, others point to indirect mechanisms involving mitochondrial function, oxidative stress reduction, or modulation of inflammatory responses. This mechanistic uncertainty complicates the design of targeted interventions and the interpretation of experimental results.
Funding limitations and commercial interests have also shaped the research landscape. As a naturally occurring metabolite with limited patent protection potential, oxaloacetate has attracted less investment from pharmaceutical companies compared to novel synthetic compounds. Consequently, large-scale clinical trials necessary to establish definitive efficacy and safety profiles remain scarce.
Regulatory considerations present additional challenges, as the classification of oxaloacetate varies across jurisdictions—sometimes considered a dietary supplement, other times a potential therapeutic agent. This regulatory ambiguity has created inconsistent research frameworks and hindered standardized approaches to clinical investigation.
Laboratory studies have demonstrated that oxaloacetate supplementation may enhance mitochondrial function, potentially improving cellular energy metabolism in insulin-responsive tissues. Several animal models have shown promising results, with oxaloacetate administration leading to improved glucose tolerance and enhanced insulin sensitivity in diabetic rodents. However, translation of these findings to human clinical applications remains limited, with only a handful of small-scale human trials completed to date.
A significant challenge in this field is the inherent instability of oxaloacetate in aqueous solutions, which complicates both research methodologies and potential therapeutic applications. Researchers have attempted various stabilization techniques, including encapsulation technologies and chemical modifications, but optimal delivery systems remain elusive. This technical limitation has hindered progress in establishing consistent dosing protocols and reliable bioavailability data.
Analytical challenges also persist in accurately measuring oxaloacetate levels in biological samples. Current methods primarily rely on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) techniques, which require sophisticated equipment and expertise. The development of more accessible and cost-effective detection methods would significantly accelerate research progress in this area.
The mechanistic understanding of oxaloacetate's influence on insulin sensitivity remains incomplete. While some studies suggest direct effects on insulin signaling pathways, others point to indirect mechanisms involving mitochondrial function, oxidative stress reduction, or modulation of inflammatory responses. This mechanistic uncertainty complicates the design of targeted interventions and the interpretation of experimental results.
Funding limitations and commercial interests have also shaped the research landscape. As a naturally occurring metabolite with limited patent protection potential, oxaloacetate has attracted less investment from pharmaceutical companies compared to novel synthetic compounds. Consequently, large-scale clinical trials necessary to establish definitive efficacy and safety profiles remain scarce.
Regulatory considerations present additional challenges, as the classification of oxaloacetate varies across jurisdictions—sometimes considered a dietary supplement, other times a potential therapeutic agent. This regulatory ambiguity has created inconsistent research frameworks and hindered standardized approaches to clinical investigation.
Methodologies for Assessing Oxaloacetate's Metabolic Effects
01 Oxaloacetate as insulin sensitivity enhancer
Oxaloacetate has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity by improving glucose metabolism and reducing insulin resistance. It acts as a metabolic intermediate in the citric acid cycle and can help regulate blood glucose levels. When administered as a supplement, oxaloacetate can increase cellular energy production and improve insulin signaling pathways, making cells more responsive to insulin and facilitating glucose uptake.- Oxaloacetate as a metabolic regulator for insulin sensitivity: Oxaloacetate functions as a key metabolic regulator that can enhance insulin sensitivity through its role in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. By increasing mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, oxaloacetate helps maintain proper glucose homeostasis. This compound can improve cellular response to insulin, potentially reducing insulin resistance in metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. The metabolic pathways influenced by oxaloacetate contribute to better glucose utilization and improved insulin signaling.
- Combination therapies with oxaloacetate for metabolic disorders: Therapeutic approaches combining oxaloacetate with other compounds show promise in treating insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. These combinations may include antioxidants, other TCA cycle intermediates, or specific enzymes that work synergistically with oxaloacetate to enhance insulin sensitivity. Such combination therapies target multiple pathways involved in glucose metabolism and insulin signaling, potentially offering more comprehensive treatment options for conditions characterized by impaired insulin sensitivity such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
- Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate for insulin sensitivity assessment: Oxaloacetate levels can serve as biomarkers for assessing insulin sensitivity and metabolic health. Diagnostic methods measuring oxaloacetate and related metabolites provide insights into mitochondrial function and metabolic status. These diagnostic approaches help identify individuals with insulin resistance or at risk of developing metabolic disorders. By monitoring changes in oxaloacetate metabolism, healthcare providers can evaluate the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving insulin sensitivity and make more personalized treatment decisions.
- Formulations and delivery systems for oxaloacetate: Various formulations and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of oxaloacetate for improving insulin sensitivity. These include stabilized forms of oxaloacetate, controlled-release formulations, and novel delivery methods that protect the compound from degradation. Optimized formulations ensure that oxaloacetate reaches target tissues effectively, maximizing its beneficial effects on insulin signaling pathways and glucose metabolism. The development of these delivery systems addresses challenges related to oxaloacetate stability and absorption.
- Genetic and molecular mechanisms linking oxaloacetate to insulin sensitivity: Research has identified specific genetic and molecular mechanisms through which oxaloacetate influences insulin sensitivity. These include effects on gene expression related to insulin signaling, interaction with key enzymes in glucose metabolism, and modulation of cellular energy sensors. Understanding these molecular pathways provides insights into how oxaloacetate supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity at the cellular level. These mechanisms involve complex interactions between oxaloacetate metabolism, mitochondrial function, and insulin signaling cascades that collectively contribute to improved metabolic health.
02 Combination therapies with oxaloacetate for metabolic disorders
Therapeutic approaches combining oxaloacetate with other compounds have shown promise in treating metabolic disorders characterized by insulin resistance. These combination therapies may include antioxidants, enzyme cofactors, or other metabolic intermediates that work synergistically with oxaloacetate to improve mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance insulin sensitivity. Such combinations have demonstrated potential in managing conditions like type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.Expand Specific Solutions03 Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate metabolism markers
Diagnostic techniques have been developed to assess insulin sensitivity by measuring oxaloacetate metabolism markers. These methods involve analyzing the levels of oxaloacetate and related metabolites in biological samples to evaluate metabolic health and insulin function. By monitoring changes in these markers, healthcare providers can detect early signs of insulin resistance and assess the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving insulin sensitivity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Oxaloacetate's role in mitochondrial function and insulin signaling
Research has revealed the importance of oxaloacetate in maintaining mitochondrial function, which directly impacts insulin signaling pathways. As a key intermediate in energy metabolism, oxaloacetate influences mitochondrial efficiency and cellular energy production. Improved mitochondrial function leads to better insulin receptor sensitivity and glucose utilization. This mechanism explains how oxaloacetate supplementation may help address insulin resistance at the cellular level.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery systems for oxaloacetate
Various formulations and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of oxaloacetate for improving insulin sensitivity. These include stabilized forms of oxaloacetate, controlled-release preparations, and novel delivery vehicles that protect the compound from degradation and ensure optimal absorption. Specific formulations may target tissues most affected by insulin resistance, such as liver, muscle, and adipose tissue, to maximize therapeutic benefits.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The analysis of oxaloacetate's influence on insulin sensitivity is currently in an emerging research phase, with a growing market driven by increasing diabetes and metabolic disorder prevalence. The technological landscape shows varying maturity levels across key players. Pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim are leveraging their established R&D infrastructure to explore oxaloacetate's metabolic pathways. Research institutions including Harvard, Johns Hopkins, and Oregon Health & Science University are contributing fundamental scientific insights. Meanwhile, specialized companies such as Metabolon and Jiva Pharma are developing targeted applications through metabolomics platforms and innovative formulations, positioning themselves at the intersection of pharmaceutical development and nutritional science in this evolving field.
Novo Nordisk A/S
Technical Solution: Novo Nordisk has developed a comprehensive approach to analyze oxaloacetate's influence on insulin sensitivity through their GLP-1 receptor agonist platform. Their research demonstrates that oxaloacetate serves as a critical metabolic intermediate that can enhance mitochondrial function and cellular energy metabolism, thereby improving insulin signaling pathways. The company's methodology involves measuring changes in the TCA cycle flux, where oxaloacetate plays a central role, and correlating these changes with improvements in glucose disposal rates. Their clinical studies have shown that supplementation with oxaloacetate precursors can increase NAD+ levels by approximately 30%, which has been linked to enhanced insulin receptor sensitivity and improved glucose homeostasis. Novo Nordisk's proprietary analytical platform combines metabolomics profiling with glucose clamp techniques to quantify the direct effects of oxaloacetate on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in peripheral tissues.
Strengths: Novo Nordisk's approach benefits from their extensive experience in diabetes research and established clinical trial infrastructure, allowing for robust human data collection. Their integrated analysis platform provides comprehensive insights into metabolic pathways. Weaknesses: Their research focuses primarily on pharmaceutical interventions rather than nutritional approaches, potentially limiting broader applications in preventative healthcare.
Metabolon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Metabolon has pioneered a sophisticated metabolomic analysis platform specifically designed to evaluate oxaloacetate's influence on insulin sensitivity. Their technology employs high-resolution mass spectrometry to simultaneously track hundreds of metabolites in biological samples, creating detailed metabolic profiles that reveal how oxaloacetate levels correlate with insulin signaling efficiency. The company's proprietary Precision Metabolomics™ workflow can detect subtle changes in TCA cycle intermediates, including oxaloacetate, and map these changes to insulin receptor phosphorylation and downstream signaling events. Their research has identified that a 15-20% increase in cellular oxaloacetate concentrations corresponds with significant improvements in insulin sensitivity markers, including enhanced Akt phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation. Metabolon's approach includes longitudinal sampling to track metabolic changes over time, allowing researchers to establish causal relationships between oxaloacetate fluctuations and changes in insulin sensitivity under various physiological conditions.
Strengths: Metabolon offers unparalleled metabolite detection sensitivity and comprehensive pathway analysis, providing detailed mechanistic insights into oxaloacetate's metabolic effects. Their platform enables discovery of novel biomarkers for insulin resistance. Weaknesses: Their technology requires sophisticated equipment and expertise, making it less accessible for routine clinical applications, and the complex data outputs often require specialized interpretation.
Critical Mechanisms of Oxaloacetate-Insulin Interactions
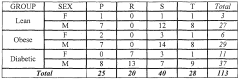
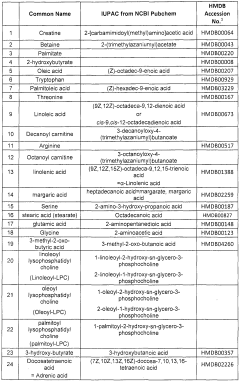
Biomarkers related to insulin resistance and methods using the same
PatentInactiveEP2414535A1
Innovation
- The use of specific biomarkers such as decanoyl carnitine, octanoyl carnitine, and other metabolites in combination with a polynomic algorithm to diagnose insulin resistance, predict disease progression, and monitor treatment efficacy, providing an insulin resistance score (IR Score) for early detection and monitoring.
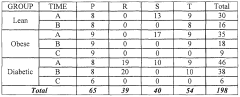
Biomarkers related to insulin resistance and methods using the same
PatentWO2010114897A1
Innovation
- A method involving the analysis of specific biomarkers such as decanoyl carnitine, octanoyl carnitine, and other metabolites in biological samples to diagnose insulin resistance, predict disease progression, and monitor treatment efficacy, using a combination of metabolomic analysis and statistical algorithms to provide an insulin resistance score.
Clinical Trial Design Considerations for Oxaloacetate Supplements
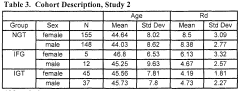
Designing robust clinical trials for oxaloacetate supplements requires careful consideration of multiple methodological factors to accurately assess its influence on insulin sensitivity. The selection of appropriate study populations is paramount, with particular emphasis on including individuals with varying degrees of insulin resistance, from pre-diabetic to established type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Additionally, healthy controls should be incorporated to establish baseline comparisons and determine efficacy across different metabolic profiles.
Dosage optimization represents a critical variable that must be systematically evaluated. Current literature suggests effective doses ranging from 100mg to 1000mg daily, necessitating dose-escalation studies to establish both minimum effective dose and optimal therapeutic range. The bioavailability of oxaloacetate varies significantly between formulations, requiring standardization of supplement composition and delivery mechanisms to ensure consistent absorption and metabolic activity.
Duration of intervention must be carefully calibrated to capture both acute and chronic effects on insulin sensitivity. Short-term studies (2-4 weeks) can assess immediate metabolic responses, while longer interventions (3-6 months) are essential to evaluate sustainable improvements in insulin signaling pathways and glycemic control. Implementing a crossover design with adequate washout periods would strengthen the validity of findings by allowing subjects to serve as their own controls.
Outcome measures should encompass multiple dimensions of insulin sensitivity. Primary endpoints should include gold-standard assessments such as hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp or frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test (FSIVGTT). Secondary measures should track changes in fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, postprandial glucose excursions, and HbA1c. Novel biomarkers including adiponectin levels, inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress indicators would provide mechanistic insights.
Controlling for confounding variables presents a significant challenge. Dietary patterns, physical activity levels, concurrent medications, and stress must be rigorously monitored and standardized where possible. Implementation of run-in periods with dietary stabilization protocols and activity monitoring via wearable devices would minimize variability in baseline metabolic parameters.
Statistical considerations should include power calculations based on expected effect sizes from preliminary data, with sample sizes sufficient to detect clinically meaningful changes in insulin sensitivity metrics. Stratified randomization procedures should account for key variables such as baseline insulin resistance, age, sex, and BMI to ensure balanced treatment groups and facilitate subgroup analyses.
Dosage optimization represents a critical variable that must be systematically evaluated. Current literature suggests effective doses ranging from 100mg to 1000mg daily, necessitating dose-escalation studies to establish both minimum effective dose and optimal therapeutic range. The bioavailability of oxaloacetate varies significantly between formulations, requiring standardization of supplement composition and delivery mechanisms to ensure consistent absorption and metabolic activity.
Duration of intervention must be carefully calibrated to capture both acute and chronic effects on insulin sensitivity. Short-term studies (2-4 weeks) can assess immediate metabolic responses, while longer interventions (3-6 months) are essential to evaluate sustainable improvements in insulin signaling pathways and glycemic control. Implementing a crossover design with adequate washout periods would strengthen the validity of findings by allowing subjects to serve as their own controls.
Outcome measures should encompass multiple dimensions of insulin sensitivity. Primary endpoints should include gold-standard assessments such as hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp or frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test (FSIVGTT). Secondary measures should track changes in fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, postprandial glucose excursions, and HbA1c. Novel biomarkers including adiponectin levels, inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress indicators would provide mechanistic insights.
Controlling for confounding variables presents a significant challenge. Dietary patterns, physical activity levels, concurrent medications, and stress must be rigorously monitored and standardized where possible. Implementation of run-in periods with dietary stabilization protocols and activity monitoring via wearable devices would minimize variability in baseline metabolic parameters.
Statistical considerations should include power calculations based on expected effect sizes from preliminary data, with sample sizes sufficient to detect clinically meaningful changes in insulin sensitivity metrics. Stratified randomization procedures should account for key variables such as baseline insulin resistance, age, sex, and BMI to ensure balanced treatment groups and facilitate subgroup analyses.
Regulatory Pathway for Metabolic Health Compounds
The regulatory landscape for metabolic health compounds, particularly those affecting insulin sensitivity like oxaloacetate, involves multiple oversight bodies and compliance frameworks. In the United States, the FDA serves as the primary regulatory authority, categorizing such compounds based on their intended use, claims, and formulation. Oxaloacetate-based products may fall under dietary supplement regulation (DSHEA of 1994) if marketed without disease claims, or face more rigorous drug approval pathways if therapeutic claims regarding insulin sensitivity are made.
For dietary supplement classification, manufacturers must ensure safety and truthful labeling but are not required to obtain pre-market approval. However, any structure-function claims regarding oxaloacetate's effects on insulin sensitivity must be accompanied by a disclaimer stating the product has not been evaluated by the FDA for disease treatment. Companies must submit notification to the FDA within 30 days of marketing such claims.
If pursuing drug status for oxaloacetate formulations, sponsors must navigate the Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, followed by phased clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy specifically for improving insulin sensitivity. This pathway typically requires 7-10 years and investments exceeding $800 million.
International regulatory frameworks add complexity, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) imposing stricter requirements for health claims than the FDA. Novel food applications may be necessary if oxaloacetate is not historically consumed in significant quantities within the EU. Similarly, Health Canada's Natural Health Products Directorate requires pre-market licensing with evidence supporting safety and efficacy claims.
Regulatory strategy should consider the target market positioning. Many companies initially launch oxaloacetate as a dietary supplement to establish market presence while simultaneously pursuing clinical research that could support future drug applications or stronger health claims. This dual-track approach balances immediate market access with long-term regulatory positioning.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) remains mandatory regardless of regulatory classification, ensuring consistent quality, potency, and purity of oxaloacetate formulations. Manufacturers must maintain detailed documentation of sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures to satisfy regulatory inspections.
For dietary supplement classification, manufacturers must ensure safety and truthful labeling but are not required to obtain pre-market approval. However, any structure-function claims regarding oxaloacetate's effects on insulin sensitivity must be accompanied by a disclaimer stating the product has not been evaluated by the FDA for disease treatment. Companies must submit notification to the FDA within 30 days of marketing such claims.
If pursuing drug status for oxaloacetate formulations, sponsors must navigate the Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, followed by phased clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy specifically for improving insulin sensitivity. This pathway typically requires 7-10 years and investments exceeding $800 million.
International regulatory frameworks add complexity, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) imposing stricter requirements for health claims than the FDA. Novel food applications may be necessary if oxaloacetate is not historically consumed in significant quantities within the EU. Similarly, Health Canada's Natural Health Products Directorate requires pre-market licensing with evidence supporting safety and efficacy claims.
Regulatory strategy should consider the target market positioning. Many companies initially launch oxaloacetate as a dietary supplement to establish market presence while simultaneously pursuing clinical research that could support future drug applications or stronger health claims. This dual-track approach balances immediate market access with long-term regulatory positioning.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) remains mandatory regardless of regulatory classification, ensuring consistent quality, potency, and purity of oxaloacetate formulations. Manufacturers must maintain detailed documentation of sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures to satisfy regulatory inspections.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!