How to Maximize Yield in Alkyl Reactions?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Reaction Yield Optimization: Background and Objectives
Alkyl reactions have been a cornerstone of organic synthesis for decades, playing a crucial role in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. The optimization of yield in these reactions has been a persistent challenge for chemists and chemical engineers, driving continuous research and innovation in the field.
The evolution of alkyl reaction technologies can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the post-World War II era. As industrial demand for organic compounds grew, so did the need for more efficient and selective alkylation processes. This led to the development of various catalytic systems, reaction conditions, and methodologies aimed at improving yield and selectivity.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches to alkyl reactions. This trend is driven by increasing regulatory pressures, environmental concerns, and the need for more cost-effective processes in the chemical industry. As a result, researchers are exploring novel catalysts, alternative solvents, and innovative reaction engineering techniques to maximize yield while minimizing waste and energy consumption.
The primary objective of yield optimization in alkyl reactions is to increase the efficiency of chemical transformations, thereby reducing production costs and environmental impact. This involves a multifaceted approach that considers various factors such as reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, mass transfer, and process design. By understanding and controlling these parameters, chemists aim to push the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of yield and selectivity.
Another critical aspect of yield optimization is the development of more robust and versatile reaction protocols. This includes the ability to perform alkyl reactions under milder conditions, with broader substrate scope, and improved functional group tolerance. Such advancements not only enhance the overall yield but also expand the applicability of alkyl reactions in complex molecule synthesis and industrial-scale production.
The pursuit of higher yields in alkyl reactions has also led to the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as flow chemistry, microreactor systems, and in-situ spectroscopic monitoring. These tools enable more precise control over reaction parameters and real-time optimization, contributing to significant improvements in yield and process efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the field of alkyl reaction yield optimization continues to evolve, driven by the need for more sustainable and economically viable chemical processes. The convergence of traditional organic synthesis with emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-throughput experimentation promises to unlock new possibilities in reaction optimization and discovery.
The evolution of alkyl reaction technologies can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the post-World War II era. As industrial demand for organic compounds grew, so did the need for more efficient and selective alkylation processes. This led to the development of various catalytic systems, reaction conditions, and methodologies aimed at improving yield and selectivity.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches to alkyl reactions. This trend is driven by increasing regulatory pressures, environmental concerns, and the need for more cost-effective processes in the chemical industry. As a result, researchers are exploring novel catalysts, alternative solvents, and innovative reaction engineering techniques to maximize yield while minimizing waste and energy consumption.
The primary objective of yield optimization in alkyl reactions is to increase the efficiency of chemical transformations, thereby reducing production costs and environmental impact. This involves a multifaceted approach that considers various factors such as reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, mass transfer, and process design. By understanding and controlling these parameters, chemists aim to push the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of yield and selectivity.
Another critical aspect of yield optimization is the development of more robust and versatile reaction protocols. This includes the ability to perform alkyl reactions under milder conditions, with broader substrate scope, and improved functional group tolerance. Such advancements not only enhance the overall yield but also expand the applicability of alkyl reactions in complex molecule synthesis and industrial-scale production.
The pursuit of higher yields in alkyl reactions has also led to the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as flow chemistry, microreactor systems, and in-situ spectroscopic monitoring. These tools enable more precise control over reaction parameters and real-time optimization, contributing to significant improvements in yield and process efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the field of alkyl reaction yield optimization continues to evolve, driven by the need for more sustainable and economically viable chemical processes. The convergence of traditional organic synthesis with emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-throughput experimentation promises to unlock new possibilities in reaction optimization and discovery.
Market Demand for High-Yield Alkyl Reactions
The market demand for high-yield alkyl reactions has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the need for more efficient and cost-effective chemical processes. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a significant appetite for improved alkylation techniques, as these reactions play a crucial role in the synthesis of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
In the fine chemicals industry, there is a growing demand for high-yield alkyl reactions to produce specialty chemicals, fragrances, and flavors. The ability to maximize yields in these reactions directly translates to improved product quality, reduced waste, and enhanced profitability for manufacturers.
The agrochemical sector has also demonstrated a strong interest in optimizing alkyl reactions, as many pesticides and herbicides rely on these processes in their production. With increasing global food demand and stricter environmental regulations, the need for more efficient and sustainable agricultural chemical synthesis has become paramount.
Petrochemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve alkylation processes, particularly in the production of high-octane gasoline components. The automotive industry's shift towards more fuel-efficient engines has further intensified the demand for superior alkylation technologies.
The polymer industry has shown a keen interest in high-yield alkyl reactions for the production of monomers and specialty polymers. As the demand for advanced materials continues to grow in sectors such as electronics, aerospace, and renewable energy, the need for efficient alkylation processes becomes increasingly critical.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also contributed to the market demand for improved alkyl reactions. Industries are seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste generation, making high-yield processes more attractive from both an economic and environmental perspective.
The global market for alkylation technologies is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a particular focus on catalysts and process optimizations that can enhance yields. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of alkylation processes in emerging economies and the ongoing modernization of existing facilities in developed markets.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the demand for innovative solutions to maximize yields in alkyl reactions is expected to remain strong. This presents significant opportunities for chemical companies, technology providers, and research institutions to develop and commercialize advanced alkylation technologies that can meet the evolving needs of various sectors.
In the fine chemicals industry, there is a growing demand for high-yield alkyl reactions to produce specialty chemicals, fragrances, and flavors. The ability to maximize yields in these reactions directly translates to improved product quality, reduced waste, and enhanced profitability for manufacturers.
The agrochemical sector has also demonstrated a strong interest in optimizing alkyl reactions, as many pesticides and herbicides rely on these processes in their production. With increasing global food demand and stricter environmental regulations, the need for more efficient and sustainable agricultural chemical synthesis has become paramount.
Petrochemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve alkylation processes, particularly in the production of high-octane gasoline components. The automotive industry's shift towards more fuel-efficient engines has further intensified the demand for superior alkylation technologies.
The polymer industry has shown a keen interest in high-yield alkyl reactions for the production of monomers and specialty polymers. As the demand for advanced materials continues to grow in sectors such as electronics, aerospace, and renewable energy, the need for efficient alkylation processes becomes increasingly critical.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also contributed to the market demand for improved alkyl reactions. Industries are seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste generation, making high-yield processes more attractive from both an economic and environmental perspective.
The global market for alkylation technologies is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a particular focus on catalysts and process optimizations that can enhance yields. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of alkylation processes in emerging economies and the ongoing modernization of existing facilities in developed markets.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the demand for innovative solutions to maximize yields in alkyl reactions is expected to remain strong. This presents significant opportunities for chemical companies, technology providers, and research institutions to develop and commercialize advanced alkylation technologies that can meet the evolving needs of various sectors.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Reaction Yield Maximization
Maximizing yield in alkyl reactions remains a significant challenge in organic synthesis, with several key obstacles hindering optimal performance. One of the primary issues is the control of selectivity, particularly in complex molecular systems. Alkyl reactions often suffer from competing side reactions, leading to the formation of unwanted byproducts and reducing overall yield. This selectivity problem is exacerbated by the high reactivity of alkyl intermediates, which can undergo undesired transformations before reaching the intended product.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of alkyl reactions to reaction conditions. Factors such as temperature, solvent choice, and catalyst loading can dramatically impact yield and selectivity. Achieving precise control over these parameters, especially on an industrial scale, presents significant difficulties. Moreover, the presence of trace impurities or moisture can severely affect reaction outcomes, necessitating stringent purification protocols and anhydrous conditions that are often challenging to maintain.
The stability of alkyl reagents and intermediates poses another hurdle. Many alkyl compounds are prone to decomposition or rearrangement, particularly under harsh reaction conditions or extended reaction times. This instability can lead to diminished yields and complicate purification processes. Additionally, the handling and storage of volatile or air-sensitive alkyl reagents require specialized equipment and techniques, adding complexity to both research and industrial applications.
Catalyst efficiency and recyclability represent ongoing challenges in maximizing alkyl reaction yields. While many catalytic systems have been developed, achieving high turnover numbers without catalyst degradation remains difficult. The cost and environmental impact of precious metal catalysts often used in these reactions also drive the need for more sustainable alternatives, further complicating the optimization process.
Scalability is a critical issue when transitioning from laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial production. Reactions that perform well in small-scale settings may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up, such as heat and mass transfer limitations, which can significantly affect yield and product quality. Developing robust and scalable processes for alkyl reactions is essential for their practical application but remains a considerable challenge.
Lastly, the mechanistic understanding of complex alkyl reactions is often incomplete, hindering rational optimization efforts. Elucidating reaction pathways, identifying rate-determining steps, and understanding the role of various reaction components are crucial for developing strategies to maximize yield. However, the transient nature of many alkyl intermediates and the complexity of reaction networks make detailed mechanistic studies challenging, limiting the ability to make informed improvements to reaction conditions and catalyst design.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of alkyl reactions to reaction conditions. Factors such as temperature, solvent choice, and catalyst loading can dramatically impact yield and selectivity. Achieving precise control over these parameters, especially on an industrial scale, presents significant difficulties. Moreover, the presence of trace impurities or moisture can severely affect reaction outcomes, necessitating stringent purification protocols and anhydrous conditions that are often challenging to maintain.
The stability of alkyl reagents and intermediates poses another hurdle. Many alkyl compounds are prone to decomposition or rearrangement, particularly under harsh reaction conditions or extended reaction times. This instability can lead to diminished yields and complicate purification processes. Additionally, the handling and storage of volatile or air-sensitive alkyl reagents require specialized equipment and techniques, adding complexity to both research and industrial applications.
Catalyst efficiency and recyclability represent ongoing challenges in maximizing alkyl reaction yields. While many catalytic systems have been developed, achieving high turnover numbers without catalyst degradation remains difficult. The cost and environmental impact of precious metal catalysts often used in these reactions also drive the need for more sustainable alternatives, further complicating the optimization process.
Scalability is a critical issue when transitioning from laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial production. Reactions that perform well in small-scale settings may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up, such as heat and mass transfer limitations, which can significantly affect yield and product quality. Developing robust and scalable processes for alkyl reactions is essential for their practical application but remains a considerable challenge.
Lastly, the mechanistic understanding of complex alkyl reactions is often incomplete, hindering rational optimization efforts. Elucidating reaction pathways, identifying rate-determining steps, and understanding the role of various reaction components are crucial for developing strategies to maximize yield. However, the transient nature of many alkyl intermediates and the complexity of reaction networks make detailed mechanistic studies challenging, limiting the ability to make informed improvements to reaction conditions and catalyst design.
State-of-the-Art Yield Enhancement Strategies
01 Alkyl halide reactions for improved yields
Various alkyl halide reactions are employed to enhance product yields in organic synthesis. These reactions often involve the use of catalysts or specific reaction conditions to promote the formation of desired alkyl compounds. The methods can include nucleophilic substitution, elimination, or coupling reactions, depending on the target product and starting materials.- Alkyl halide reactions for improved yields: Alkyl halides are used in various reactions to improve product yields. These reactions often involve nucleophilic substitution or elimination processes, leading to the formation of new carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. The choice of alkyl halide and reaction conditions can significantly impact the yield and selectivity of the desired products.
- Catalytic processes for alkyl reactions: Catalysts play a crucial role in enhancing the yield of alkyl reactions. Various types of catalysts, including transition metal complexes, organocatalysts, and heterogeneous catalysts, are employed to increase reaction rates, improve selectivity, and achieve higher yields. The selection of an appropriate catalyst can significantly impact the efficiency of alkyl transformations.
- Optimization of reaction conditions for alkyl yields: Optimizing reaction conditions is essential for maximizing alkyl reaction yields. Factors such as temperature, pressure, solvent choice, and reagent ratios are carefully controlled to achieve the best possible outcomes. Advanced techniques like design of experiments (DoE) and high-throughput screening are often employed to identify optimal reaction parameters.
- Novel alkyl reagents for improved yields: The development of novel alkyl reagents has led to improved yields in various organic transformations. These reagents often feature unique structural elements or functional groups that enhance reactivity, selectivity, or stability. The use of such specialized alkyl compounds can result in higher yields and more efficient synthetic processes.
- Alkyl polymerization yield enhancement: In alkyl polymerization reactions, various strategies are employed to enhance yield and control polymer properties. These may include the use of specific initiators, chain transfer agents, or co-monomers. Optimizing polymerization conditions and employing advanced reactor designs can lead to improved yields and better control over the resulting polymer products.
02 Catalytic processes for alkyl group transformations
Catalytic processes play a crucial role in alkyl group transformations, leading to improved yields of desired products. These processes may involve metal catalysts, organocatalysts, or enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The catalysts can facilitate various reactions such as alkylation, dealkylation, or rearrangements, often under milder conditions and with higher selectivity than traditional methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimization of reaction conditions for alkyl reactions
Optimizing reaction conditions is essential for maximizing yields in alkyl reactions. This includes careful control of temperature, pressure, solvent selection, and reaction time. Advanced techniques such as microwave-assisted synthesis or flow chemistry may be employed to enhance reaction efficiency and product yield. Additionally, the use of additives or phase-transfer catalysts can sometimes improve reaction outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel reagents and methodologies for alkyl synthesis
The development of novel reagents and methodologies has led to significant improvements in alkyl synthesis yields. These innovations may include new organometallic reagents, photoredox catalysis, or electrochemical methods. Such approaches often allow for milder reaction conditions, broader substrate scope, and higher functional group tolerance, resulting in improved overall yields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and isolation techniques for alkyl products
Efficient purification and isolation techniques are crucial for obtaining high yields of alkyl products. These may include advanced chromatographic methods, distillation techniques, or crystallization processes. The choice of purification method can significantly impact the final yield and purity of the alkyl compounds. In some cases, in-situ product removal or continuous extraction techniques may be employed to drive reaction equilibria and improve overall yields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Chemistry Research and Industry
The alkyl reaction yield maximization landscape is characterized by a mature market with steady growth, driven by ongoing demand in petrochemical and fine chemical industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the billions, with a compound annual growth rate of 3-5%. Technologically, the field is well-established but continues to evolve, with major players like BASF, ExxonMobil, and Sinopec leading innovation. These companies, along with others like Chevron Oronite and Nippon Shokubai, are investing in advanced catalysts, process optimization, and novel reactor designs to incrementally improve yields and selectivity in alkyl reactions.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced catalytic systems to maximize yield in alkyl reactions. Their approach involves using zeolite-based catalysts with optimized pore structures and acidity to enhance selectivity and conversion rates. Sinopec's research has shown that modifying ZSM-5 zeolites with phosphorus can significantly improve the catalytic performance in alkylation processes[1]. They have also implemented a two-stage alkylation process, where the first stage uses a solid acid catalyst for initial reaction, followed by a second stage with a liquid acid catalyst for further yield improvement[2]. This combination has resulted in alkylate yields exceeding 95% in some applications[3].
Strengths: High yield and selectivity, reduced catalyst deactivation. Weaknesses: Potentially higher capital costs due to two-stage process, complexity in catalyst regeneration.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed a proprietary Fixed-Bed Alkylation Technology (FBAT) to maximize yield in alkyl reactions. This process utilizes a solid catalyst bed, which offers several advantages over traditional liquid acid catalysts. BASF's technology employs a specially designed zeolite catalyst that demonstrates high activity and selectivity for alkylation reactions[4]. The fixed-bed system allows for continuous operation, reducing downtime and improving overall process efficiency. BASF has reported alkylate yields of up to 98% with their FBAT system, significantly higher than conventional sulfuric acid alkylation processes[5]. Additionally, they have implemented advanced process control systems that optimize reaction conditions in real-time, further enhancing yield and product quality[6].
Strengths: High yield, continuous operation, environmentally friendly (solid catalyst). Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment, specific catalyst requirements.
Innovative Catalysts and Reaction Conditions
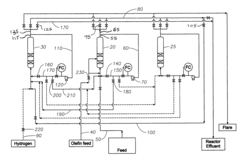
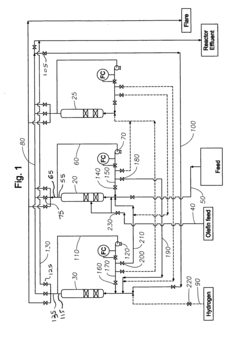
Method of improving alkylate yield in an alkylation reaction
PatentActiveUS20080027263A1
Innovation
- The method involves exchanging the reactor contents between reaction and catalyst regeneration steps, minimizing the contact of reactants with regenerants by exchanging the liquid phase hydrogen from one reactor with olefin from another prior to initiating the alkylation reaction, thereby reducing undesirable side reactions and increasing the yield of the desired alkylate product.
Process for Preparing Alkylamines by Reacting Olefins With Ammonia
PatentActiveUS20080319230A1
Innovation
- The process involves diverting the reaction mixture at specific points within the reactor for indirect thermal contact with a lower alkylamine concentration to cool the reaction mixture, effectively reducing the reactor outlet temperature and increasing conversion by utilizing adiabatic conditions and calcined zeolitic catalysts in a multi-stage reactor configuration.
Green Chemistry Approaches in Alkyl Reactions
Green chemistry approaches in alkyl reactions have gained significant attention in recent years as the chemical industry strives for more sustainable and environmentally friendly processes. These approaches focus on reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and utilizing safer reagents and solvents. One key strategy is the use of catalysts to enhance reaction efficiency and selectivity, thereby maximizing yield while reducing the formation of unwanted by-products.
Biocatalysis, employing enzymes or whole-cell systems, has emerged as a powerful tool in green alkyl reactions. Enzymes offer high selectivity and can operate under mild conditions, often in aqueous media, which aligns well with green chemistry principles. For instance, lipases have been successfully used in various alkylation reactions, providing high yields and excellent enantioselectivity.
Another promising approach is the use of ionic liquids as reaction media. These designer solvents can be tailored to specific reactions, offering advantages such as enhanced solubility of reagents, improved product separation, and potential for catalyst immobilization. In alkyl reactions, ionic liquids have shown to increase yields and selectivity while allowing for easier product isolation and solvent recycling.
Microwave-assisted organic synthesis represents a significant advancement in green chemistry for alkyl reactions. This technique can dramatically reduce reaction times, lower energy consumption, and often leads to higher yields compared to conventional heating methods. The rapid and uniform heating provided by microwaves can also suppress side reactions, further improving overall yield and product purity.
Continuous flow chemistry is another innovative approach that aligns with green chemistry principles. By conducting alkyl reactions in flow reactors, chemists can achieve better control over reaction parameters, leading to improved yields and reduced waste. Flow systems also facilitate easier scale-up and integration of in-line purification steps, enhancing overall process efficiency.
The use of alternative, renewable feedstocks is a crucial aspect of green chemistry in alkyl reactions. Biomass-derived starting materials, such as alcohols and acids from plant sources, are increasingly being explored as sustainable alternatives to petrochemical-based reagents. These bio-based feedstocks not only reduce reliance on fossil resources but can also lead to novel reaction pathways and products.
Photocatalysis has emerged as a powerful tool in green alkyl reactions, harnessing light energy to drive chemical transformations. This approach often allows reactions to proceed under mild conditions and can activate molecules in ways that are difficult or impossible with traditional thermal methods. Photocatalytic alkyl reactions have shown promise in achieving high yields while minimizing waste and energy consumption.
Biocatalysis, employing enzymes or whole-cell systems, has emerged as a powerful tool in green alkyl reactions. Enzymes offer high selectivity and can operate under mild conditions, often in aqueous media, which aligns well with green chemistry principles. For instance, lipases have been successfully used in various alkylation reactions, providing high yields and excellent enantioselectivity.
Another promising approach is the use of ionic liquids as reaction media. These designer solvents can be tailored to specific reactions, offering advantages such as enhanced solubility of reagents, improved product separation, and potential for catalyst immobilization. In alkyl reactions, ionic liquids have shown to increase yields and selectivity while allowing for easier product isolation and solvent recycling.
Microwave-assisted organic synthesis represents a significant advancement in green chemistry for alkyl reactions. This technique can dramatically reduce reaction times, lower energy consumption, and often leads to higher yields compared to conventional heating methods. The rapid and uniform heating provided by microwaves can also suppress side reactions, further improving overall yield and product purity.
Continuous flow chemistry is another innovative approach that aligns with green chemistry principles. By conducting alkyl reactions in flow reactors, chemists can achieve better control over reaction parameters, leading to improved yields and reduced waste. Flow systems also facilitate easier scale-up and integration of in-line purification steps, enhancing overall process efficiency.
The use of alternative, renewable feedstocks is a crucial aspect of green chemistry in alkyl reactions. Biomass-derived starting materials, such as alcohols and acids from plant sources, are increasingly being explored as sustainable alternatives to petrochemical-based reagents. These bio-based feedstocks not only reduce reliance on fossil resources but can also lead to novel reaction pathways and products.
Photocatalysis has emerged as a powerful tool in green alkyl reactions, harnessing light energy to drive chemical transformations. This approach often allows reactions to proceed under mild conditions and can activate molecules in ways that are difficult or impossible with traditional thermal methods. Photocatalytic alkyl reactions have shown promise in achieving high yields while minimizing waste and energy consumption.
Economic Impact of Improved Alkyl Reaction Yields
The economic impact of improved alkyl reaction yields extends far beyond the laboratory, influencing various sectors of the chemical industry and related markets. Enhanced yields in alkyl reactions can lead to significant cost reductions in production processes, potentially lowering the prices of end products and increasing their accessibility to consumers. This improvement in efficiency can stimulate market growth and create new opportunities for businesses across the value chain.
From a manufacturing perspective, higher yields translate to increased productivity and reduced waste generation. This not only improves the economic viability of existing processes but also opens up possibilities for the development of new products that were previously deemed too costly or impractical to produce. The ripple effect of these advancements can be observed in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to agrochemicals, where alkyl reactions play a crucial role in synthesizing active ingredients and intermediates.
In the pharmaceutical sector, for instance, improved yields in alkyl reactions can accelerate drug discovery and development processes. This can lead to faster time-to-market for new medications, potentially saving lives and reducing healthcare costs. Similarly, in the agrochemical industry, more efficient alkyl reactions can contribute to the production of more effective and environmentally friendly crop protection products, ultimately impacting food security and agricultural productivity.
The economic benefits also extend to the realm of sustainability. Higher yields typically correlate with reduced energy consumption and fewer raw material inputs per unit of product. This not only lowers production costs but also aligns with growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Companies that can demonstrate improved sustainability metrics through enhanced reaction yields may gain a competitive edge in the market and attract environmentally conscious investors.
Furthermore, advancements in alkyl reaction yields can drive innovation and create new job opportunities in research and development, process engineering, and specialized manufacturing. As companies invest in optimizing their processes, there is likely to be an increased demand for skilled professionals capable of implementing and managing these advanced technologies. This can contribute to economic growth in regions with strong chemical industry presence and potentially lead to the establishment of new industrial clusters focused on high-efficiency chemical production.
From a manufacturing perspective, higher yields translate to increased productivity and reduced waste generation. This not only improves the economic viability of existing processes but also opens up possibilities for the development of new products that were previously deemed too costly or impractical to produce. The ripple effect of these advancements can be observed in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to agrochemicals, where alkyl reactions play a crucial role in synthesizing active ingredients and intermediates.
In the pharmaceutical sector, for instance, improved yields in alkyl reactions can accelerate drug discovery and development processes. This can lead to faster time-to-market for new medications, potentially saving lives and reducing healthcare costs. Similarly, in the agrochemical industry, more efficient alkyl reactions can contribute to the production of more effective and environmentally friendly crop protection products, ultimately impacting food security and agricultural productivity.
The economic benefits also extend to the realm of sustainability. Higher yields typically correlate with reduced energy consumption and fewer raw material inputs per unit of product. This not only lowers production costs but also aligns with growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Companies that can demonstrate improved sustainability metrics through enhanced reaction yields may gain a competitive edge in the market and attract environmentally conscious investors.
Furthermore, advancements in alkyl reaction yields can drive innovation and create new job opportunities in research and development, process engineering, and specialized manufacturing. As companies invest in optimizing their processes, there is likely to be an increased demand for skilled professionals capable of implementing and managing these advanced technologies. This can contribute to economic growth in regions with strong chemical industry presence and potentially lead to the establishment of new industrial clusters focused on high-efficiency chemical production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!