How to Strengthen Cellophane's Position in Green Markets?
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Evolution
Cellophane, a transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, has undergone significant evolution since its invention in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a moisture-proof coating for labels and packaging, cellophane quickly gained popularity due to its unique properties and versatility.
The evolution of cellophane can be traced through several key stages. In the 1920s and 1930s, cellophane saw widespread adoption in the food packaging industry, revolutionizing the way products were displayed and preserved. This period marked the beginning of cellophane's dominance in the packaging sector.
During the 1940s and 1950s, advancements in production techniques led to improved quality and reduced costs, further expanding cellophane's market reach. The material's ability to be heat-sealed and printed upon made it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from food packaging to industrial uses.
The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the emergence of synthetic plastics, which began to challenge cellophane's market position. However, cellophane maintained its relevance due to its unique combination of properties, including biodegradability and excellent barrier characteristics.
In recent decades, the evolution of cellophane has been driven by growing environmental concerns and the demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Manufacturers have focused on enhancing cellophane's eco-friendly attributes, such as improving its biodegradability and developing bio-based production methods.
The latest stage in cellophane's evolution involves addressing the challenges posed by the green market. This includes efforts to reduce the environmental impact of production processes, increase the use of renewable resources, and improve end-of-life recyclability or compostability.
As the market demands more sustainable packaging options, cellophane has the potential to regain prominence. Its inherent biodegradability gives it an advantage over many synthetic plastics. However, to strengthen its position in green markets, cellophane must continue to evolve in terms of production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall environmental performance.
The future evolution of cellophane is likely to focus on developing new formulations that enhance its green credentials while maintaining or improving its functional properties. This may involve incorporating advanced bio-based materials, optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and emissions, and exploring innovative applications that leverage cellophane's unique characteristics in environmentally conscious markets.
The evolution of cellophane can be traced through several key stages. In the 1920s and 1930s, cellophane saw widespread adoption in the food packaging industry, revolutionizing the way products were displayed and preserved. This period marked the beginning of cellophane's dominance in the packaging sector.
During the 1940s and 1950s, advancements in production techniques led to improved quality and reduced costs, further expanding cellophane's market reach. The material's ability to be heat-sealed and printed upon made it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from food packaging to industrial uses.
The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the emergence of synthetic plastics, which began to challenge cellophane's market position. However, cellophane maintained its relevance due to its unique combination of properties, including biodegradability and excellent barrier characteristics.
In recent decades, the evolution of cellophane has been driven by growing environmental concerns and the demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Manufacturers have focused on enhancing cellophane's eco-friendly attributes, such as improving its biodegradability and developing bio-based production methods.
The latest stage in cellophane's evolution involves addressing the challenges posed by the green market. This includes efforts to reduce the environmental impact of production processes, increase the use of renewable resources, and improve end-of-life recyclability or compostability.
As the market demands more sustainable packaging options, cellophane has the potential to regain prominence. Its inherent biodegradability gives it an advantage over many synthetic plastics. However, to strengthen its position in green markets, cellophane must continue to evolve in terms of production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall environmental performance.
The future evolution of cellophane is likely to focus on developing new formulations that enhance its green credentials while maintaining or improving its functional properties. This may involve incorporating advanced bio-based materials, optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and emissions, and exploring innovative applications that leverage cellophane's unique characteristics in environmentally conscious markets.
Green Market Demand
The green market for cellophane has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards sustainable packaging solutions. This trend is particularly evident in industries such as food and beverage, cosmetics, and consumer goods, where eco-friendly packaging options are becoming a key differentiator for brands.
Market research indicates that the global biodegradable packaging market, which includes cellophane, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by stringent regulations on single-use plastics, rising consumer demand for sustainable products, and corporate commitments to reduce environmental impact.
In the food packaging sector, cellophane's natural and biodegradable properties make it an attractive alternative to traditional plastic wraps. The transparency and barrier properties of cellophane align well with consumer preferences for visible, fresh products while providing adequate protection. This has led to increased adoption in bakery, produce, and confectionery packaging.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of green market demand for cellophane. As beauty brands increasingly focus on sustainability, cellophane's ability to create visually appealing, biodegradable packaging for items like face masks, soaps, and gift sets has gained traction. The material's versatility in terms of printing and customization further enhances its appeal in this sector.
E-commerce packaging represents a growing opportunity for cellophane in the green market. With the rise of online shopping, there is a pressing need for sustainable packaging solutions that can protect products during shipping while minimizing environmental impact. Cellophane's lightweight nature and potential for composting or recycling make it a viable option for e-commerce businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Consumer surveys reveal that a significant portion of shoppers are willing to pay a premium for products with environmentally friendly packaging. This willingness to pay more for sustainable options creates a favorable market condition for cellophane, as it allows manufacturers to offset potentially higher production costs associated with the material.
However, the green market demand for cellophane is not without challenges. Competition from other biodegradable materials, such as PLA (polylactic acid) and bio-based plastics, is intensifying. To strengthen its position, cellophane manufacturers must focus on highlighting the material's unique benefits, such as its natural origin, established biodegradability, and versatile applications.
Additionally, there is a growing demand for packaging solutions that not only biodegrade but also contribute to circular economy principles. This presents an opportunity for cellophane to innovate in areas such as recyclability and the development of closed-loop systems for material recovery and reuse.
Market research indicates that the global biodegradable packaging market, which includes cellophane, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by stringent regulations on single-use plastics, rising consumer demand for sustainable products, and corporate commitments to reduce environmental impact.
In the food packaging sector, cellophane's natural and biodegradable properties make it an attractive alternative to traditional plastic wraps. The transparency and barrier properties of cellophane align well with consumer preferences for visible, fresh products while providing adequate protection. This has led to increased adoption in bakery, produce, and confectionery packaging.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of green market demand for cellophane. As beauty brands increasingly focus on sustainability, cellophane's ability to create visually appealing, biodegradable packaging for items like face masks, soaps, and gift sets has gained traction. The material's versatility in terms of printing and customization further enhances its appeal in this sector.
E-commerce packaging represents a growing opportunity for cellophane in the green market. With the rise of online shopping, there is a pressing need for sustainable packaging solutions that can protect products during shipping while minimizing environmental impact. Cellophane's lightweight nature and potential for composting or recycling make it a viable option for e-commerce businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Consumer surveys reveal that a significant portion of shoppers are willing to pay a premium for products with environmentally friendly packaging. This willingness to pay more for sustainable options creates a favorable market condition for cellophane, as it allows manufacturers to offset potentially higher production costs associated with the material.
However, the green market demand for cellophane is not without challenges. Competition from other biodegradable materials, such as PLA (polylactic acid) and bio-based plastics, is intensifying. To strengthen its position, cellophane manufacturers must focus on highlighting the material's unique benefits, such as its natural origin, established biodegradability, and versatile applications.
Additionally, there is a growing demand for packaging solutions that not only biodegrade but also contribute to circular economy principles. This presents an opportunity for cellophane to innovate in areas such as recyclability and the development of closed-loop systems for material recovery and reuse.
Eco-Challenges
As cellophane seeks to strengthen its position in green markets, it faces several significant eco-challenges that must be addressed. These challenges stem from both the material's inherent properties and the evolving demands of environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory bodies.
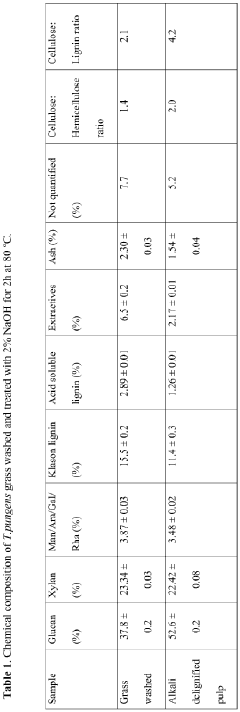
One of the primary eco-challenges for cellophane is its biodegradability. While cellophane is derived from renewable resources, typically wood pulp or cotton linter, its degradation process in natural environments can be slow. This poses a challenge in markets where rapid biodegradability is increasingly valued as a key sustainability feature. Improving the biodegradation rate of cellophane without compromising its desirable properties is a critical area for innovation.
Another significant challenge lies in the production process of cellophane. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve the use of chemicals such as carbon disulfide, which can have negative environmental impacts. The industry faces pressure to develop greener production techniques that minimize the use of harmful substances and reduce overall environmental footprint. This includes addressing issues related to water consumption, energy use, and emissions throughout the production cycle.
The recyclability of cellophane presents another eco-challenge. While theoretically recyclable, the practical aspects of collecting, sorting, and processing used cellophane products can be complex and economically challenging. Developing efficient recycling systems and improving the material's compatibility with existing recycling streams is crucial for enhancing its green credentials.
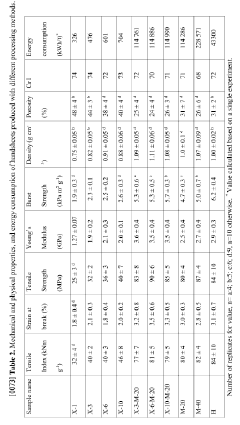
Cellophane's barrier properties, while beneficial for many applications, can be a double-edged sword from an environmental perspective. Improving these properties to extend product shelf life and reduce food waste must be balanced against the need for easier biodegradability or recyclability. Finding this balance is essential for maintaining cellophane's relevance in green markets.
The perception of cellophane as a plastic-like material, despite its bio-based origins, poses a marketing and education challenge. Overcoming misconceptions and clearly communicating cellophane's environmental benefits compared to petroleum-based plastics is crucial for strengthening its position in eco-conscious markets.
Lastly, the competition from newer, potentially more environmentally friendly materials presents an ongoing challenge. Cellophane must continuously innovate to keep pace with or surpass the environmental performance of alternative materials, such as PLA (polylactic acid) or other bioplastics that are gaining traction in green markets.
One of the primary eco-challenges for cellophane is its biodegradability. While cellophane is derived from renewable resources, typically wood pulp or cotton linter, its degradation process in natural environments can be slow. This poses a challenge in markets where rapid biodegradability is increasingly valued as a key sustainability feature. Improving the biodegradation rate of cellophane without compromising its desirable properties is a critical area for innovation.
Another significant challenge lies in the production process of cellophane. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve the use of chemicals such as carbon disulfide, which can have negative environmental impacts. The industry faces pressure to develop greener production techniques that minimize the use of harmful substances and reduce overall environmental footprint. This includes addressing issues related to water consumption, energy use, and emissions throughout the production cycle.
The recyclability of cellophane presents another eco-challenge. While theoretically recyclable, the practical aspects of collecting, sorting, and processing used cellophane products can be complex and economically challenging. Developing efficient recycling systems and improving the material's compatibility with existing recycling streams is crucial for enhancing its green credentials.
Cellophane's barrier properties, while beneficial for many applications, can be a double-edged sword from an environmental perspective. Improving these properties to extend product shelf life and reduce food waste must be balanced against the need for easier biodegradability or recyclability. Finding this balance is essential for maintaining cellophane's relevance in green markets.
The perception of cellophane as a plastic-like material, despite its bio-based origins, poses a marketing and education challenge. Overcoming misconceptions and clearly communicating cellophane's environmental benefits compared to petroleum-based plastics is crucial for strengthening its position in eco-conscious markets.
Lastly, the competition from newer, potentially more environmentally friendly materials presents an ongoing challenge. Cellophane must continuously innovate to keep pace with or surpass the environmental performance of alternative materials, such as PLA (polylactic acid) or other bioplastics that are gaining traction in green markets.
Green Cellophane Tech
01 Cellophane positioning in packaging systems
Various packaging systems utilize cellophane in specific positions to enhance product protection and presentation. These systems may include mechanisms for precise placement of cellophane sheets or rolls in packaging machinery, ensuring optimal coverage and sealing of products.- Cellophane positioning in packaging systems: Cellophane is used in various packaging systems where its position is crucial for proper functionality. This includes positioning cellophane in wrapping machines, packaging lines, and sealing systems. The precise placement of cellophane sheets or rolls ensures efficient packaging processes and product protection.
- Cellophane positioning in optical and display applications: Cellophane's optical properties make it useful in display technologies and optical systems. The positioning of cellophane layers is critical in creating desired visual effects, color filters, or polarization. This includes applications in LCD screens, optical filters, and decorative displays.
- Cellophane positioning in biotechnology and medical devices: In biotechnology and medical applications, cellophane positioning is important for creating controlled environments for cell culture, drug delivery systems, or diagnostic devices. The precise placement of cellophane membranes or films can affect the performance of these systems.
- Cellophane positioning in manufacturing processes: The positioning of cellophane is crucial in various manufacturing processes, including textile production, paper making, and composite material fabrication. Proper alignment and placement of cellophane sheets or films can affect the quality and properties of the final product.
- Cellophane positioning in food packaging and preservation: In food packaging applications, the position of cellophane layers is important for maintaining food freshness, controlling moisture, and providing barrier properties. This includes the use of cellophane in multi-layer packaging structures and modified atmosphere packaging systems.
02 Cellophane positioning in manufacturing processes
Manufacturing processes often require precise positioning of cellophane for product assembly or wrapping. This may involve automated systems for aligning and feeding cellophane sheets or continuous rolls into production lines, ensuring consistent placement and integration with other materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cellophane positioning in display and retail applications
Retail and display applications often utilize cellophane in specific positions to enhance product visibility and protection. This may include specialized fixtures or holders designed to maintain cellophane in optimal positions for wrapping or showcasing merchandise.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cellophane positioning in food packaging
Food packaging often requires precise positioning of cellophane to ensure proper sealing, freshness, and presentation. This may involve specialized equipment for aligning and applying cellophane to food containers or wrapping food products in specific orientations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cellophane positioning in medical and laboratory applications
Medical and laboratory settings may require specific positioning of cellophane for various applications, such as sample preparation or sterile packaging. This can involve specialized tools or devices designed to manipulate and position cellophane sheets with high precision in controlled environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for green cellophane is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental awareness and sustainability demands. The global market size for biodegradable packaging, including green cellophane, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. While the technology is maturing, there is still room for innovation and improvement. Key players like Suzano SA, Danisco US, Inc., and SixRing, Inc. are actively developing and refining eco-friendly cellophane alternatives. Universities such as the University of São Paulo and South China University of Technology are contributing to research and development in this field, indicating a collaborative effort between industry and academia to advance green cellophane technology.
Danisco US, Inc.
Technical Solution: Danisco US, Inc., a subsidiary of IFF (International Flavors & Fragrances), has focused on developing bio-based alternatives to traditional cellophane additives. Their research has led to the creation of plant-based plasticizers that can replace phthalates, improving cellophane's environmental profile without sacrificing flexibility or durability[7]. The company has also introduced natural antimicrobial agents derived from plant extracts, which extend the shelf life of products wrapped in cellophane while maintaining its biodegradability[8]. Additionally, Danisco has developed a range of bio-based adhesives specifically designed for cellophane packaging, further enhancing its appeal in green markets[9].
Strengths: Improved safety profile, extended product shelf life, and enhanced overall sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs of bio-based additives and the need for extensive testing to ensure long-term stability.
Suzano SA
Technical Solution: Suzano SA, a leading Brazilian pulp and paper company, has developed innovative approaches to strengthen cellophane's position in green markets. They have implemented a bio-based production process that uses eucalyptus pulp as the primary raw material, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of cellophane production[1]. The company has also invested in advanced water treatment technologies, allowing for up to 80% water reuse in their manufacturing processes[2]. Additionally, Suzano has developed biodegradable additives that enhance cellophane's compostability without compromising its barrier properties, making it more attractive for eco-conscious consumers and businesses[3].
Strengths: Sustainable raw material sourcing, reduced carbon footprint, improved water efficiency, and enhanced biodegradability. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs and limited scalability of some technologies.
Eco-Innovation Patents
Materials containing cellulose nanofibers
PatentWO2019237149A1
Innovation
- A method involving a mild alkali treatment followed by mechanical processing, such as twin-screw extrusion and high-energy ball milling, is used to produce cellulose nanofibers with a high hemicellulose content, which maintains fiber integrity and enhances adhesion properties, allowing for the creation of a gel material suitable for adhesives and composites.
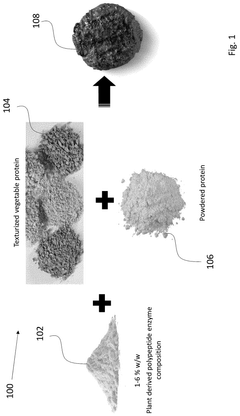
Edible plant-based protein composition
PatentPendingUS20240349755A1
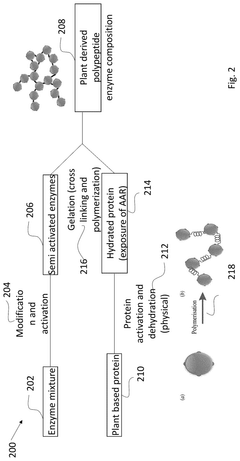
Innovation
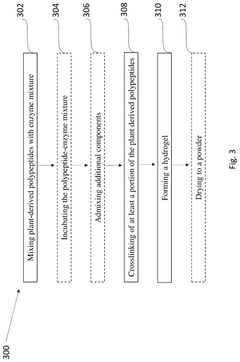
- A composition comprising crosslinked plant-derived polypeptides and specific enzymes capable of catalyzing amino acid oxidation or forming peptide bonds, creating a hydrogel that mimics the texture of animal-based products without synthetic gelling agents.
Biodegradability Regs
Biodegradability regulations play a crucial role in shaping the green market landscape for packaging materials like cellophane. These regulations are designed to promote the use of environmentally friendly materials and reduce the impact of waste on ecosystems. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the stringency and scope of biodegradability regulations worldwide, driven by growing environmental concerns and consumer demand for sustainable products.
The European Union has been at the forefront of implementing comprehensive biodegradability regulations. The EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials, including biodegradable options. This directive has been regularly updated, with the most recent amendment in 2018 (Directive (EU) 2018/852) setting more ambitious targets for recycling and recovery of packaging waste.
In the United States, biodegradability regulations are primarily governed by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and state-level legislation. The FTC's Green Guides provide guidelines for environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability. Several states, such as California, have enacted stricter regulations on biodegradable plastics and packaging materials.
Many countries in Asia have also implemented biodegradability regulations in response to growing environmental concerns. Japan's Containers and Packaging Recycling Law mandates the use of recyclable or biodegradable materials in packaging. China has introduced restrictions on non-biodegradable single-use plastics, creating opportunities for alternative materials like cellophane.
To strengthen cellophane's position in green markets, it is essential to align its properties with these evolving regulations. Manufacturers must ensure that cellophane meets or exceeds the biodegradability standards set by various regulatory bodies. This may involve improving the material's decomposition rate in different environmental conditions and ensuring that it leaves no harmful residues.
Certification and labeling play a crucial role in demonstrating compliance with biodegradability regulations. Obtaining recognized certifications, such as the European EN 13432 standard for compostable packaging, can enhance cellophane's credibility in green markets. Clear and accurate labeling of cellophane products, including information on proper disposal methods, is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and gaining consumer trust.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying ahead of regulatory changes and actively participating in policy discussions can help position cellophane as a proactive and environmentally responsible choice in the packaging industry. This approach can create opportunities for cellophane to gain market share as stricter regulations phase out less sustainable alternatives.
The European Union has been at the forefront of implementing comprehensive biodegradability regulations. The EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials, including biodegradable options. This directive has been regularly updated, with the most recent amendment in 2018 (Directive (EU) 2018/852) setting more ambitious targets for recycling and recovery of packaging waste.
In the United States, biodegradability regulations are primarily governed by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and state-level legislation. The FTC's Green Guides provide guidelines for environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability. Several states, such as California, have enacted stricter regulations on biodegradable plastics and packaging materials.
Many countries in Asia have also implemented biodegradability regulations in response to growing environmental concerns. Japan's Containers and Packaging Recycling Law mandates the use of recyclable or biodegradable materials in packaging. China has introduced restrictions on non-biodegradable single-use plastics, creating opportunities for alternative materials like cellophane.
To strengthen cellophane's position in green markets, it is essential to align its properties with these evolving regulations. Manufacturers must ensure that cellophane meets or exceeds the biodegradability standards set by various regulatory bodies. This may involve improving the material's decomposition rate in different environmental conditions and ensuring that it leaves no harmful residues.
Certification and labeling play a crucial role in demonstrating compliance with biodegradability regulations. Obtaining recognized certifications, such as the European EN 13432 standard for compostable packaging, can enhance cellophane's credibility in green markets. Clear and accurate labeling of cellophane products, including information on proper disposal methods, is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and gaining consumer trust.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying ahead of regulatory changes and actively participating in policy discussions can help position cellophane as a proactive and environmentally responsible choice in the packaging industry. This approach can create opportunities for cellophane to gain market share as stricter regulations phase out less sustainable alternatives.
Circular Economy Impact
The circular economy concept has a significant impact on cellophane's position in green markets. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, cellophane's biodegradability and potential for recycling align well with circular economy principles. This alignment creates opportunities for cellophane to strengthen its market position by emphasizing its eco-friendly characteristics and adaptability to circular systems.
In a circular economy, materials are designed to be reused, recycled, or composted, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact. Cellophane, being biodegradable and compostable, fits naturally into this model. Its ability to break down in natural environments without leaving harmful residues makes it an attractive option for businesses and consumers seeking to reduce their ecological footprint.
The circular economy also emphasizes the importance of renewable resources, which further benefits cellophane's market position. As a product derived from renewable plant-based materials, cellophane can be positioned as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This aspect is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, the circular economy promotes the development of closed-loop systems, where materials are continuously cycled through the economy. Cellophane's potential for recycling and composting aligns with this principle, offering opportunities for innovative collection and processing systems. By participating in or initiating such systems, cellophane manufacturers can strengthen their position in green markets and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
The circular economy's focus on product longevity and durability also presents opportunities for cellophane. While traditionally seen as a single-use material, innovations in cellophane production could lead to more durable versions suitable for multiple uses. This would enhance cellophane's appeal in markets prioritizing reusable packaging solutions.
Furthermore, the circular economy encourages collaboration between different sectors and stakeholders. Cellophane producers can leverage this principle by forming partnerships with recycling facilities, composting plants, and other businesses in the circular value chain. Such collaborations can lead to improved collection and processing of used cellophane, enhancing its overall sustainability profile and market appeal.
In conclusion, the circular economy's principles of sustainability, resource efficiency, and waste reduction provide a favorable context for cellophane to strengthen its position in green markets. By aligning its production, use, and end-of-life management with circular economy concepts, cellophane can differentiate itself from less sustainable alternatives and capture a larger share of the growing market for eco-friendly materials.
In a circular economy, materials are designed to be reused, recycled, or composted, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact. Cellophane, being biodegradable and compostable, fits naturally into this model. Its ability to break down in natural environments without leaving harmful residues makes it an attractive option for businesses and consumers seeking to reduce their ecological footprint.
The circular economy also emphasizes the importance of renewable resources, which further benefits cellophane's market position. As a product derived from renewable plant-based materials, cellophane can be positioned as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This aspect is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, the circular economy promotes the development of closed-loop systems, where materials are continuously cycled through the economy. Cellophane's potential for recycling and composting aligns with this principle, offering opportunities for innovative collection and processing systems. By participating in or initiating such systems, cellophane manufacturers can strengthen their position in green markets and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
The circular economy's focus on product longevity and durability also presents opportunities for cellophane. While traditionally seen as a single-use material, innovations in cellophane production could lead to more durable versions suitable for multiple uses. This would enhance cellophane's appeal in markets prioritizing reusable packaging solutions.
Furthermore, the circular economy encourages collaboration between different sectors and stakeholders. Cellophane producers can leverage this principle by forming partnerships with recycling facilities, composting plants, and other businesses in the circular value chain. Such collaborations can lead to improved collection and processing of used cellophane, enhancing its overall sustainability profile and market appeal.
In conclusion, the circular economy's principles of sustainability, resource efficiency, and waste reduction provide a favorable context for cellophane to strengthen its position in green markets. By aligning its production, use, and end-of-life management with circular economy concepts, cellophane can differentiate itself from less sustainable alternatives and capture a larger share of the growing market for eco-friendly materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!