How to Utilize Sodium Acetate for Efficient Chemical Neutralization?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Acetate Neutralization Background and Objectives
Chemical neutralization is a fundamental process in various industries, from environmental remediation to pharmaceutical manufacturing. Sodium acetate, a versatile compound with the chemical formula CH3COONa, has emerged as a promising agent for efficient chemical neutralization. This report aims to explore the background and objectives of utilizing sodium acetate in neutralization processes.
The concept of chemical neutralization dates back to the early days of chemistry, with the understanding that acids and bases can react to form salts and water. Over time, this principle has been applied in numerous fields, including waste treatment, industrial processes, and laboratory practices. The evolution of neutralization techniques has led to the search for more efficient and environmentally friendly neutralizing agents, which is where sodium acetate comes into play.
Sodium acetate, also known as sodium ethanoate, is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid and sodium hydroxide. Its unique properties make it an attractive option for neutralization processes. The compound is highly soluble in water, non-toxic, and biodegradable, aligning well with the growing emphasis on sustainable chemical practices. Furthermore, its ability to act as a buffer in aqueous solutions provides additional benefits in maintaining stable pH levels during neutralization reactions.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium acetate for chemical neutralization is to achieve more efficient and controlled acid-base reactions. Traditional neutralization methods often involve strong bases like sodium hydroxide, which can lead to rapid pH changes and potential overshooting of the desired neutral point. Sodium acetate, with its buffering capacity, offers a more gradual and manageable neutralization process, reducing the risk of unintended pH fluctuations.
Another key objective is to enhance the safety and environmental profile of neutralization processes. Sodium acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive alternative to more hazardous neutralizing agents. This aligns with the increasing regulatory pressure and corporate responsibility initiatives aimed at reducing the environmental impact of chemical processes.
The use of sodium acetate also aims to improve the efficiency of neutralization in terms of reaction speed and completeness. Its high solubility allows for rapid dissolution and reaction, potentially reducing processing times in industrial applications. Additionally, the formation of acetate ions during the neutralization process can provide secondary benefits, such as enhanced metal ion complexation in certain environmental remediation scenarios.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for chemical management, the exploration of sodium acetate's potential in neutralization processes represents a convergence of scientific understanding and practical application. This research direction not only addresses immediate needs for more efficient neutralization methods but also paves the way for developing advanced, multi-functional neutralizing agents that can offer additional benefits beyond simple pH adjustment.
The concept of chemical neutralization dates back to the early days of chemistry, with the understanding that acids and bases can react to form salts and water. Over time, this principle has been applied in numerous fields, including waste treatment, industrial processes, and laboratory practices. The evolution of neutralization techniques has led to the search for more efficient and environmentally friendly neutralizing agents, which is where sodium acetate comes into play.
Sodium acetate, also known as sodium ethanoate, is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid and sodium hydroxide. Its unique properties make it an attractive option for neutralization processes. The compound is highly soluble in water, non-toxic, and biodegradable, aligning well with the growing emphasis on sustainable chemical practices. Furthermore, its ability to act as a buffer in aqueous solutions provides additional benefits in maintaining stable pH levels during neutralization reactions.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium acetate for chemical neutralization is to achieve more efficient and controlled acid-base reactions. Traditional neutralization methods often involve strong bases like sodium hydroxide, which can lead to rapid pH changes and potential overshooting of the desired neutral point. Sodium acetate, with its buffering capacity, offers a more gradual and manageable neutralization process, reducing the risk of unintended pH fluctuations.
Another key objective is to enhance the safety and environmental profile of neutralization processes. Sodium acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive alternative to more hazardous neutralizing agents. This aligns with the increasing regulatory pressure and corporate responsibility initiatives aimed at reducing the environmental impact of chemical processes.
The use of sodium acetate also aims to improve the efficiency of neutralization in terms of reaction speed and completeness. Its high solubility allows for rapid dissolution and reaction, potentially reducing processing times in industrial applications. Additionally, the formation of acetate ions during the neutralization process can provide secondary benefits, such as enhanced metal ion complexation in certain environmental remediation scenarios.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for chemical management, the exploration of sodium acetate's potential in neutralization processes represents a convergence of scientific understanding and practical application. This research direction not only addresses immediate needs for more efficient neutralization methods but also paves the way for developing advanced, multi-functional neutralizing agents that can offer additional benefits beyond simple pH adjustment.
Market Analysis for Chemical Neutralization Solutions
The chemical neutralization solutions market has been experiencing steady growth due to increasing environmental regulations and industrial safety concerns. The global market for chemical neutralization products and services is projected to reach significant value in the coming years, driven by the expanding industrial sector and stringent waste management policies.
Sodium acetate, a versatile compound with neutralizing properties, is gaining traction in this market due to its effectiveness and relatively low environmental impact. The demand for sodium acetate in chemical neutralization applications is expected to grow, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
One of the key factors driving the market for sodium acetate-based neutralization solutions is the growing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional neutralizing agents. As industries seek more sustainable alternatives, sodium acetate offers a balance between effectiveness and eco-friendliness, making it an attractive option for many applications.
The pharmaceutical industry represents a significant segment of the chemical neutralization market, where sodium acetate is used in various processes, including drug formulation and waste treatment. The stringent regulatory requirements in this sector are expected to fuel the demand for efficient and safe neutralization solutions, benefiting sodium acetate suppliers.
In the wastewater treatment sector, sodium acetate is finding increased application due to its ability to neutralize acidic effluents effectively. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, the demand for efficient water treatment solutions is rising, creating opportunities for sodium acetate-based products.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to be a major growth driver for the chemical neutralization market, including sodium acetate solutions. Rapid industrialization, coupled with increasing environmental regulations in countries like China and India, is expected to boost the demand for effective neutralization products.
However, the market for sodium acetate in chemical neutralization faces competition from other neutralizing agents such as sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate. Manufacturers of sodium acetate-based solutions will need to focus on product innovation and cost-effectiveness to maintain and expand their market share.
The adoption of sodium acetate for chemical neutralization is also influenced by factors such as ease of handling, storage stability, and compatibility with existing industrial processes. As industries seek to optimize their operations, solutions that offer multiple benefits beyond neutralization are likely to gain preference.
Sodium acetate, a versatile compound with neutralizing properties, is gaining traction in this market due to its effectiveness and relatively low environmental impact. The demand for sodium acetate in chemical neutralization applications is expected to grow, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
One of the key factors driving the market for sodium acetate-based neutralization solutions is the growing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional neutralizing agents. As industries seek more sustainable alternatives, sodium acetate offers a balance between effectiveness and eco-friendliness, making it an attractive option for many applications.
The pharmaceutical industry represents a significant segment of the chemical neutralization market, where sodium acetate is used in various processes, including drug formulation and waste treatment. The stringent regulatory requirements in this sector are expected to fuel the demand for efficient and safe neutralization solutions, benefiting sodium acetate suppliers.
In the wastewater treatment sector, sodium acetate is finding increased application due to its ability to neutralize acidic effluents effectively. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, the demand for efficient water treatment solutions is rising, creating opportunities for sodium acetate-based products.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to be a major growth driver for the chemical neutralization market, including sodium acetate solutions. Rapid industrialization, coupled with increasing environmental regulations in countries like China and India, is expected to boost the demand for effective neutralization products.
However, the market for sodium acetate in chemical neutralization faces competition from other neutralizing agents such as sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate. Manufacturers of sodium acetate-based solutions will need to focus on product innovation and cost-effectiveness to maintain and expand their market share.
The adoption of sodium acetate for chemical neutralization is also influenced by factors such as ease of handling, storage stability, and compatibility with existing industrial processes. As industries seek to optimize their operations, solutions that offer multiple benefits beyond neutralization are likely to gain preference.
Current Challenges in Chemical Neutralization Techniques
Chemical neutralization is a critical process in various industries, including waste management, environmental remediation, and industrial manufacturing. However, current techniques face several significant challenges that hinder their efficiency and effectiveness.
One of the primary challenges is the limited selectivity of traditional neutralization agents. Many conventional methods struggle to target specific contaminants or pollutants without affecting other components in the mixture. This lack of precision often leads to over-treatment or under-treatment, resulting in inefficient use of resources and potential environmental risks.
The speed of neutralization reactions is another area of concern. In many industrial applications, rapid neutralization is crucial for maintaining production efficiency and safety. However, some current techniques are relatively slow, causing bottlenecks in processes and increasing the risk of chemical exposure.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in chemical neutralization. Many existing methods require expensive reagents or complex equipment, making them economically unfeasible for widespread adoption, particularly in smaller-scale operations or developing regions. This economic barrier limits the implementation of effective neutralization techniques where they are most needed.
Environmental impact is an increasingly important consideration in chemical neutralization. Some traditional methods generate secondary pollutants or require the use of environmentally harmful substances, contradicting the very purpose of the neutralization process. Finding eco-friendly alternatives that maintain efficacy while minimizing environmental footprint is a pressing challenge.
The disposal of neutralization by-products poses another significant issue. Many current techniques produce large volumes of waste that require further treatment or special disposal methods. This not only adds to the overall cost but also creates additional environmental concerns.
Scalability is a critical factor that many current neutralization techniques struggle with. Methods that work well in laboratory settings often face difficulties when scaled up to industrial levels. This gap between research and practical application hinders the adoption of potentially groundbreaking neutralization technologies.
Finally, the variability in chemical compositions of waste streams presents a substantial challenge. Industrial effluents and environmental contaminants can vary widely in composition, pH levels, and concentrations. Developing neutralization techniques that can adapt to this variability while maintaining effectiveness is a complex task that current methods often fail to address adequately.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for advancing the field of chemical neutralization. Innovative approaches, such as the potential use of sodium acetate, must be explored to overcome these limitations and develop more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly neutralization techniques.
One of the primary challenges is the limited selectivity of traditional neutralization agents. Many conventional methods struggle to target specific contaminants or pollutants without affecting other components in the mixture. This lack of precision often leads to over-treatment or under-treatment, resulting in inefficient use of resources and potential environmental risks.
The speed of neutralization reactions is another area of concern. In many industrial applications, rapid neutralization is crucial for maintaining production efficiency and safety. However, some current techniques are relatively slow, causing bottlenecks in processes and increasing the risk of chemical exposure.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in chemical neutralization. Many existing methods require expensive reagents or complex equipment, making them economically unfeasible for widespread adoption, particularly in smaller-scale operations or developing regions. This economic barrier limits the implementation of effective neutralization techniques where they are most needed.
Environmental impact is an increasingly important consideration in chemical neutralization. Some traditional methods generate secondary pollutants or require the use of environmentally harmful substances, contradicting the very purpose of the neutralization process. Finding eco-friendly alternatives that maintain efficacy while minimizing environmental footprint is a pressing challenge.
The disposal of neutralization by-products poses another significant issue. Many current techniques produce large volumes of waste that require further treatment or special disposal methods. This not only adds to the overall cost but also creates additional environmental concerns.
Scalability is a critical factor that many current neutralization techniques struggle with. Methods that work well in laboratory settings often face difficulties when scaled up to industrial levels. This gap between research and practical application hinders the adoption of potentially groundbreaking neutralization technologies.
Finally, the variability in chemical compositions of waste streams presents a substantial challenge. Industrial effluents and environmental contaminants can vary widely in composition, pH levels, and concentrations. Developing neutralization techniques that can adapt to this variability while maintaining effectiveness is a complex task that current methods often fail to address adequately.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for advancing the field of chemical neutralization. Innovative approaches, such as the potential use of sodium acetate, must be explored to overcome these limitations and develop more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly neutralization techniques.
Existing Sodium Acetate Neutralization Methodologies
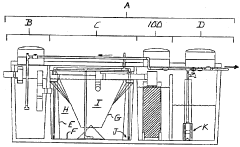
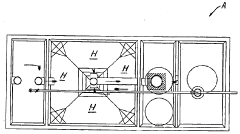
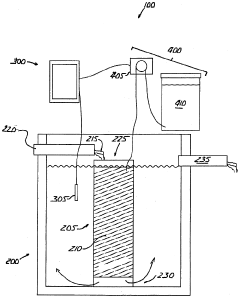
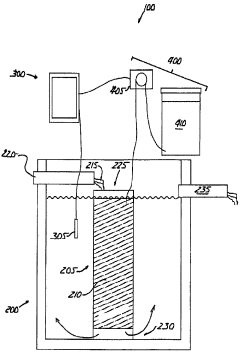
01 Neutralization efficiency in wastewater treatment
Sodium acetate is used in wastewater treatment processes to neutralize acidic effluents. The efficiency of neutralization depends on factors such as pH, temperature, and concentration of the solution. Proper dosing of sodium acetate can effectively raise the pH of acidic wastewater to a neutral level, making it suitable for discharge or further treatment.- Neutralization efficiency in industrial processes: Sodium acetate is used in various industrial processes for neutralization due to its efficiency. It can effectively neutralize acidic solutions in manufacturing, waste treatment, and chemical production. The neutralization efficiency of sodium acetate is particularly useful in applications requiring precise pH control.
- Sodium acetate in wastewater treatment: Sodium acetate plays a crucial role in wastewater treatment processes. It is used to neutralize acidic effluents and adjust pH levels in treatment plants. The compound's neutralization efficiency helps in removing contaminants and improving the overall quality of treated water.
- Neutralization in pharmaceutical applications: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, sodium acetate is utilized for its neutralization efficiency. It helps in adjusting the pH of drug formulations, ensuring stability and effectiveness of active ingredients. The compound's ability to neutralize acids makes it valuable in various stages of pharmaceutical production.
- Sodium acetate in food processing: The food industry benefits from sodium acetate's neutralization efficiency. It is used as a pH regulator and preservative in various food products. The compound helps in maintaining the desired acidity levels, enhancing flavor, and extending shelf life of processed foods.
- Neutralization in chemical synthesis: Sodium acetate's neutralization efficiency is valuable in chemical synthesis processes. It serves as a buffering agent and pH adjuster in various reactions. The compound's ability to neutralize acids efficiently makes it useful in producing a wide range of chemical products and intermediates.
02 Sodium acetate as a buffering agent
Sodium acetate acts as an effective buffering agent in various chemical processes. Its ability to maintain a stable pH in solutions makes it valuable in applications where pH control is critical. The buffering capacity of sodium acetate contributes to its neutralization efficiency by resisting rapid changes in pH when acids or bases are added to the system.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neutralization in industrial processes
Sodium acetate is utilized in various industrial processes for neutralization purposes. Its efficiency in neutralizing acidic compounds makes it suitable for applications in textile manufacturing, metal processing, and chemical production. The neutralization process helps in maintaining optimal pH conditions for specific reactions or treatments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium acetate in pharmaceutical formulations
In pharmaceutical applications, sodium acetate is used to adjust the pH of drug formulations and as a buffering agent. Its neutralization efficiency helps in maintaining the stability and effectiveness of various medications. The controlled release of sodium acetate in certain formulations can provide sustained neutralization effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Neutralization efficiency in food processing
Sodium acetate finds applications in food processing for pH adjustment and preservation. Its neutralization efficiency helps in controlling acidity in food products, extending shelf life, and enhancing flavor profiles. The use of sodium acetate as a food additive is regulated to ensure safe consumption levels.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chemical Neutralization Industry
The market for sodium acetate in chemical neutralization is in a growth phase, driven by increasing industrial applications and environmental regulations. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with steady annual growth projected. Technologically, the process is mature but innovations continue in efficiency and sustainability. Key players like Ecolab, Bayer, and Henkel are advancing applications in water treatment and industrial processes. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University of Technology and Beijing University of Technology are contributing to research and development. Emerging companies like Zhejiang Yishu Environmental Protection Technology are also entering the market with specialized solutions, indicating a competitive and evolving landscape.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab USA, Inc. has developed an advanced chemical neutralization system utilizing sodium acetate for efficient pH control in industrial processes. Their approach involves a precise dosing mechanism that introduces sodium acetate into waste streams or chemical reactions to neutralize acids effectively. The system incorporates real-time pH monitoring and automated feed control, ensuring optimal neutralization while minimizing chemical usage[1]. Ecolab's technology also includes a proprietary buffering formulation that enhances the stability of the neutralized solution, preventing pH rebounds and reducing the need for additional treatments[3].
Strengths: Precise pH control, reduced chemical consumption, and improved process efficiency. Weaknesses: May require initial investment in specialized equipment and ongoing maintenance of monitoring systems.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has patented a novel approach to chemical neutralization using sodium acetate in conjunction with their proprietary catalytic systems. Their method involves integrating sodium acetate into refinery and petrochemical processes to neutralize acidic byproducts efficiently. The technology utilizes a specially designed reactor system that optimizes the contact between sodium acetate and acidic compounds, achieving rapid neutralization with minimal energy input[2]. ExxonMobil's process also incorporates a recovery system that allows for the regeneration and reuse of excess sodium acetate, improving overall process economics[5].
Strengths: Highly efficient for large-scale industrial applications, potential for chemical recycling. Weaknesses: May be less adaptable to smaller-scale or diverse pH neutralization needs.
Innovative Approaches in Sodium Acetate Utilization
Apparatus for and method of denitrifying a solution
PatentActiveCA2602062A1
Innovation
- The use of diacetin, a non-toxic, unregulated carbon source derived from glycerol acetates, which is easily miscible with water, non-flammable, and provides a readily available form of acetate for denitrifying bacteria, promoting efficient nitrate reduction in anoxic conditions by controlling the introduction of carbon sources through a sensor and controller system.
Method for producing endotoxin-free nucleic acids and the use thereof
PatentInactiveEP1165579A1
Innovation
- A method using potassium acetate and a silica gel-like carrier material, such as silicon dioxide, to isolate and purify nucleic acids, where the biological sample is digested, and then treated with an alcohol solution containing a detergent, allowing for efficient binding and washing of nucleic acids without chaotropic substances, significantly reducing endotoxin content.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Acetate Neutralization
The environmental impact of sodium acetate neutralization is a critical consideration in its application for chemical neutralization processes. When used as a neutralizing agent, sodium acetate interacts with acidic substances, resulting in the formation of water and sodium salts. This reaction generally produces minimal harmful byproducts, making it an environmentally friendly option compared to some other neutralization methods.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium acetate for neutralization is its low toxicity. Unlike some other neutralizing agents, sodium acetate is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment for extended periods. This characteristic reduces the risk of long-term ecological damage and minimizes the potential for bioaccumulation in living organisms.
However, the release of sodium ions into aquatic ecosystems can have some ecological implications. Increased sodium levels in freshwater bodies may affect the osmotic balance of aquatic organisms, potentially impacting their physiology and behavior. Therefore, proper management and monitoring of sodium acetate usage in areas near sensitive water bodies is essential to mitigate any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
The production of sodium acetate itself has environmental considerations. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of acetic acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. While these processes are generally well-controlled in industrial settings, they do require energy inputs and may generate some emissions. Efforts to optimize production methods and utilize renewable energy sources can help reduce the overall environmental footprint of sodium acetate production.
In terms of waste management, the byproducts of sodium acetate neutralization are typically easier to handle and dispose of compared to those from other neutralization processes. The resulting sodium salts are often less hazardous and can be managed through conventional wastewater treatment systems. This aspect contributes to reduced environmental risks associated with waste disposal and treatment.
It is worth noting that the environmental impact of sodium acetate neutralization can vary depending on the specific application and scale of use. Large-scale industrial applications may require careful monitoring and management to ensure that local ecosystems are not adversely affected by increased sodium levels or other potential impacts. Implementing best practices for handling, storage, and disposal of sodium acetate and its byproducts is crucial for minimizing environmental risks.
In conclusion, while sodium acetate offers several environmental advantages as a neutralizing agent, its use should be accompanied by appropriate environmental management strategies. Ongoing research and development in this area continue to focus on further improving the environmental profile of sodium acetate neutralization processes, aiming to enhance its sustainability and minimize any potential ecological impacts.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium acetate for neutralization is its low toxicity. Unlike some other neutralizing agents, sodium acetate is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment for extended periods. This characteristic reduces the risk of long-term ecological damage and minimizes the potential for bioaccumulation in living organisms.
However, the release of sodium ions into aquatic ecosystems can have some ecological implications. Increased sodium levels in freshwater bodies may affect the osmotic balance of aquatic organisms, potentially impacting their physiology and behavior. Therefore, proper management and monitoring of sodium acetate usage in areas near sensitive water bodies is essential to mitigate any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
The production of sodium acetate itself has environmental considerations. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of acetic acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. While these processes are generally well-controlled in industrial settings, they do require energy inputs and may generate some emissions. Efforts to optimize production methods and utilize renewable energy sources can help reduce the overall environmental footprint of sodium acetate production.
In terms of waste management, the byproducts of sodium acetate neutralization are typically easier to handle and dispose of compared to those from other neutralization processes. The resulting sodium salts are often less hazardous and can be managed through conventional wastewater treatment systems. This aspect contributes to reduced environmental risks associated with waste disposal and treatment.
It is worth noting that the environmental impact of sodium acetate neutralization can vary depending on the specific application and scale of use. Large-scale industrial applications may require careful monitoring and management to ensure that local ecosystems are not adversely affected by increased sodium levels or other potential impacts. Implementing best practices for handling, storage, and disposal of sodium acetate and its byproducts is crucial for minimizing environmental risks.
In conclusion, while sodium acetate offers several environmental advantages as a neutralizing agent, its use should be accompanied by appropriate environmental management strategies. Ongoing research and development in this area continue to focus on further improving the environmental profile of sodium acetate neutralization processes, aiming to enhance its sustainability and minimize any potential ecological impacts.
Safety Protocols for Handling Sodium Acetate
Handling sodium acetate requires adherence to strict safety protocols to ensure the well-being of laboratory personnel and the integrity of experimental procedures. When working with this chemical compound, it is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, chemical-resistant gloves, and a laboratory coat. These protective measures help prevent skin contact and potential eye irritation that may occur during handling.
Proper ventilation is crucial when working with sodium acetate. Laboratories should be equipped with fume hoods or local exhaust ventilation systems to minimize exposure to dust or vapors. This is particularly important when handling large quantities or during processes that may generate airborne particles.
Storage of sodium acetate demands careful consideration. The compound should be kept in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry area away from direct sunlight and sources of heat. It is important to separate sodium acetate from incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizing agents, to prevent potentially hazardous reactions.
Spill management protocols are vital for safe handling. In the event of a spill, the affected area should be immediately cordoned off, and only trained personnel equipped with proper PPE should handle the cleanup. For small spills, absorbent materials can be used, followed by proper disposal according to local regulations. Larger spills may require more extensive decontamination procedures and professional assistance.
Training and education play a crucial role in maintaining safety standards. All personnel working with sodium acetate should receive comprehensive training on its properties, potential hazards, and proper handling techniques. Regular refresher courses and safety briefings can help reinforce best practices and keep staff updated on any changes in safety protocols.
Emergency response procedures should be clearly defined and communicated to all laboratory staff. This includes the location of safety showers, eyewash stations, and fire extinguishers. A well-stocked first aid kit should be readily accessible, and staff should be trained in basic first aid procedures specific to chemical exposure.
Proper labeling and documentation are essential components of safety protocols. All containers holding sodium acetate should be clearly labeled with the chemical name, concentration, potential hazards, and date of preparation or expiration. Maintaining up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) and ensuring they are easily accessible to all staff members is crucial for quick reference in case of emergencies.
Waste disposal procedures for sodium acetate must comply with local, state, and federal regulations. Proper segregation of chemical waste and use of designated disposal containers are necessary to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety during the disposal process.
Proper ventilation is crucial when working with sodium acetate. Laboratories should be equipped with fume hoods or local exhaust ventilation systems to minimize exposure to dust or vapors. This is particularly important when handling large quantities or during processes that may generate airborne particles.
Storage of sodium acetate demands careful consideration. The compound should be kept in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry area away from direct sunlight and sources of heat. It is important to separate sodium acetate from incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizing agents, to prevent potentially hazardous reactions.
Spill management protocols are vital for safe handling. In the event of a spill, the affected area should be immediately cordoned off, and only trained personnel equipped with proper PPE should handle the cleanup. For small spills, absorbent materials can be used, followed by proper disposal according to local regulations. Larger spills may require more extensive decontamination procedures and professional assistance.
Training and education play a crucial role in maintaining safety standards. All personnel working with sodium acetate should receive comprehensive training on its properties, potential hazards, and proper handling techniques. Regular refresher courses and safety briefings can help reinforce best practices and keep staff updated on any changes in safety protocols.
Emergency response procedures should be clearly defined and communicated to all laboratory staff. This includes the location of safety showers, eyewash stations, and fire extinguishers. A well-stocked first aid kit should be readily accessible, and staff should be trained in basic first aid procedures specific to chemical exposure.
Proper labeling and documentation are essential components of safety protocols. All containers holding sodium acetate should be clearly labeled with the chemical name, concentration, potential hazards, and date of preparation or expiration. Maintaining up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) and ensuring they are easily accessible to all staff members is crucial for quick reference in case of emergencies.
Waste disposal procedures for sodium acetate must comply with local, state, and federal regulations. Proper segregation of chemical waste and use of designated disposal containers are necessary to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety during the disposal process.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!