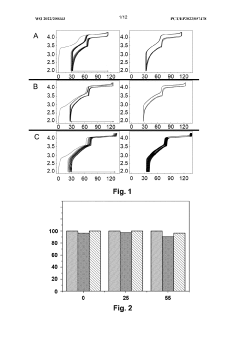
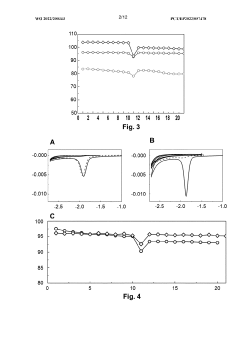
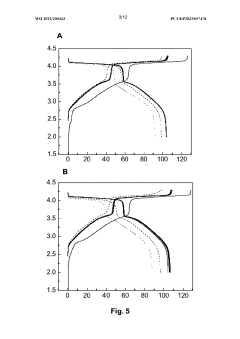
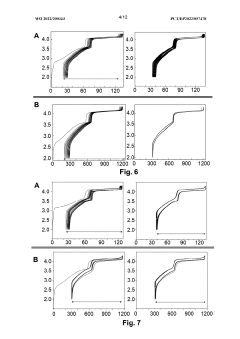
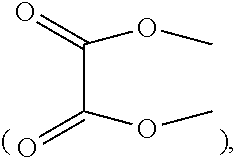
Impact of Salt Concentrations in Sodium Ion Battery Electrolytes
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Ion Battery Electrolyte Evolution
The evolution of sodium-ion battery electrolytes has been a critical aspect of advancing this promising energy storage technology. Initially, researchers focused on adapting electrolyte formulations from lithium-ion batteries, using organic carbonate-based solvents with sodium salts. However, this approach quickly revealed limitations due to the unique chemical properties of sodium ions.
Early electrolyte compositions typically consisted of sodium perchlorate (NaClO4) or sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF6) dissolved in a mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC) and propylene carbonate (PC). These formulations provided a foundation for initial sodium-ion battery research but suffered from issues such as poor ionic conductivity and unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing electrolytes specifically tailored for sodium-ion systems. One significant advancement was the introduction of fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) as an electrolyte additive. FEC was found to enhance the stability of the SEI layer, leading to improved cycling performance and battery longevity.
The exploration of alternative sodium salts marked another important milestone in electrolyte evolution. Sodium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (NaFSI) and sodium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (NaTFSI) emerged as promising candidates, offering better thermal stability and higher ionic conductivity compared to traditional salts.
Recent years have seen a surge in research on concentrated electrolytes, also known as "water-in-salt" electrolytes. These high-concentration formulations, typically containing 3-5 molal of sodium salt, have shown remarkable improvements in electrochemical stability windows and interfacial properties. This approach has opened new possibilities for developing aqueous sodium-ion batteries with enhanced safety and performance.
The latest frontier in sodium-ion battery electrolyte development involves the exploration of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. These novel electrolyte systems offer potential advantages such as non-flammability, wide electrochemical windows, and high thermal stability. While still in the early stages of research, they represent a promising direction for future electrolyte innovations.
Throughout this evolution, researchers have continuously refined electrolyte compositions, optimizing salt concentrations, solvent mixtures, and additives to address specific challenges in sodium-ion battery technology. The ongoing efforts aim to strike a balance between ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and compatibility with electrode materials, driving the development of more efficient and durable sodium-ion energy storage systems.
Early electrolyte compositions typically consisted of sodium perchlorate (NaClO4) or sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF6) dissolved in a mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC) and propylene carbonate (PC). These formulations provided a foundation for initial sodium-ion battery research but suffered from issues such as poor ionic conductivity and unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards developing electrolytes specifically tailored for sodium-ion systems. One significant advancement was the introduction of fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) as an electrolyte additive. FEC was found to enhance the stability of the SEI layer, leading to improved cycling performance and battery longevity.
The exploration of alternative sodium salts marked another important milestone in electrolyte evolution. Sodium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (NaFSI) and sodium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (NaTFSI) emerged as promising candidates, offering better thermal stability and higher ionic conductivity compared to traditional salts.
Recent years have seen a surge in research on concentrated electrolytes, also known as "water-in-salt" electrolytes. These high-concentration formulations, typically containing 3-5 molal of sodium salt, have shown remarkable improvements in electrochemical stability windows and interfacial properties. This approach has opened new possibilities for developing aqueous sodium-ion batteries with enhanced safety and performance.
The latest frontier in sodium-ion battery electrolyte development involves the exploration of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. These novel electrolyte systems offer potential advantages such as non-flammability, wide electrochemical windows, and high thermal stability. While still in the early stages of research, they represent a promising direction for future electrolyte innovations.
Throughout this evolution, researchers have continuously refined electrolyte compositions, optimizing salt concentrations, solvent mixtures, and additives to address specific challenges in sodium-ion battery technology. The ongoing efforts aim to strike a balance between ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and compatibility with electrode materials, driving the development of more efficient and durable sodium-ion energy storage systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for sodium-ion batteries has been steadily increasing, driven by the growing need for sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solutions. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources and electric vehicles, the demand for high-performance, affordable batteries continues to rise. Sodium-ion batteries have emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries, particularly in grid-scale energy storage applications and electric vehicles.
The impact of salt concentrations in sodium-ion battery electrolytes plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and market potential of these batteries. Optimizing salt concentrations can lead to improved energy density, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features, all of which are key factors in meeting market demands.
In the grid-scale energy storage sector, sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolyte salt concentrations are gaining traction due to their potential for lower costs and improved sustainability compared to lithium-ion batteries. The ability to fine-tune salt concentrations allows for better performance in large-scale applications, where long-term stability and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
The electric vehicle market is another significant driver for sodium-ion battery development. As automakers seek alternatives to lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion technology with optimized electrolytes offers a promising solution. The potential for improved safety, faster charging capabilities, and lower production costs make sodium-ion batteries increasingly attractive for mass-market electric vehicles.
Consumer electronics represent another potential market for sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolyte salt concentrations. As manufacturers look for ways to extend battery life and improve device performance, sodium-ion technology could offer a competitive edge. The ability to tailor electrolyte compositions for specific applications could lead to batteries that better meet the diverse needs of portable electronic devices.
The renewable energy sector is also driving demand for advanced sodium-ion battery technology. As solar and wind power generation continues to grow, the need for efficient and cost-effective energy storage solutions becomes more pressing. Sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolytes could provide a scalable and sustainable option for storing intermittent renewable energy.
Market analysis indicates that the global sodium-ion battery market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. The ongoing research and development efforts focused on electrolyte optimization are expected to further enhance the market potential of sodium-ion batteries across various industries. As the technology matures and production scales up, sodium-ion batteries with tailored electrolyte salt concentrations are likely to capture an increasing share of the energy storage market.
The impact of salt concentrations in sodium-ion battery electrolytes plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and market potential of these batteries. Optimizing salt concentrations can lead to improved energy density, longer cycle life, and enhanced safety features, all of which are key factors in meeting market demands.
In the grid-scale energy storage sector, sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolyte salt concentrations are gaining traction due to their potential for lower costs and improved sustainability compared to lithium-ion batteries. The ability to fine-tune salt concentrations allows for better performance in large-scale applications, where long-term stability and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
The electric vehicle market is another significant driver for sodium-ion battery development. As automakers seek alternatives to lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion technology with optimized electrolytes offers a promising solution. The potential for improved safety, faster charging capabilities, and lower production costs make sodium-ion batteries increasingly attractive for mass-market electric vehicles.
Consumer electronics represent another potential market for sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolyte salt concentrations. As manufacturers look for ways to extend battery life and improve device performance, sodium-ion technology could offer a competitive edge. The ability to tailor electrolyte compositions for specific applications could lead to batteries that better meet the diverse needs of portable electronic devices.
The renewable energy sector is also driving demand for advanced sodium-ion battery technology. As solar and wind power generation continues to grow, the need for efficient and cost-effective energy storage solutions becomes more pressing. Sodium-ion batteries with optimized electrolytes could provide a scalable and sustainable option for storing intermittent renewable energy.
Market analysis indicates that the global sodium-ion battery market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. The ongoing research and development efforts focused on electrolyte optimization are expected to further enhance the market potential of sodium-ion batteries across various industries. As the technology matures and production scales up, sodium-ion batteries with tailored electrolyte salt concentrations are likely to capture an increasing share of the energy storage market.
Current Challenges
The development of sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries has been hindered by several technical challenges, with the impact of salt concentrations in electrolytes being a critical area of concern. One of the primary challenges is the limited understanding of how different salt concentrations affect the overall performance and stability of SIBs.
High salt concentrations in electrolytes have shown potential benefits, such as improved ionic conductivity and enhanced electrode-electrolyte interface stability. However, these advantages come with significant drawbacks. The increased viscosity of highly concentrated electrolytes can lead to reduced ion mobility, potentially limiting the battery's power output and charging capabilities. Additionally, the higher salt content may result in accelerated corrosion of battery components, particularly the current collectors, which can compromise the long-term durability of the battery.
Another challenge lies in the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer. The salt concentration directly influences the composition and properties of the SEI, which is crucial for battery performance and longevity. Researchers are still grappling with optimizing the salt concentration to achieve a stable and effective SEI layer that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation.
The cost implications of high salt concentrations pose a significant hurdle for large-scale commercialization of SIBs. As the electrolyte represents a substantial portion of the overall battery cost, increasing salt concentrations can lead to higher production expenses, potentially offsetting the cost advantages that SIBs hold over lithium-ion batteries.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of high salt concentrations in electrolytes is a growing concern. The production and disposal of these electrolytes may have unforeseen ecological consequences, necessitating comprehensive life cycle assessments to ensure the sustainability of SIB technology.
Researchers are also facing challenges in developing electrolyte formulations that maintain their performance across a wide temperature range. The behavior of salt concentrations in extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can significantly affect battery performance and safety. Finding the right balance that ensures consistent operation under various environmental conditions remains a complex task.
Lastly, the scalability of high-concentration electrolyte production presents a significant challenge. Ensuring uniform salt distribution and maintaining consistent quality in large-scale manufacturing processes is crucial for the commercial viability of SIBs. The industry must overcome these production hurdles to make high-performance SIBs a reality in the mass market.
High salt concentrations in electrolytes have shown potential benefits, such as improved ionic conductivity and enhanced electrode-electrolyte interface stability. However, these advantages come with significant drawbacks. The increased viscosity of highly concentrated electrolytes can lead to reduced ion mobility, potentially limiting the battery's power output and charging capabilities. Additionally, the higher salt content may result in accelerated corrosion of battery components, particularly the current collectors, which can compromise the long-term durability of the battery.
Another challenge lies in the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer. The salt concentration directly influences the composition and properties of the SEI, which is crucial for battery performance and longevity. Researchers are still grappling with optimizing the salt concentration to achieve a stable and effective SEI layer that can withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation.
The cost implications of high salt concentrations pose a significant hurdle for large-scale commercialization of SIBs. As the electrolyte represents a substantial portion of the overall battery cost, increasing salt concentrations can lead to higher production expenses, potentially offsetting the cost advantages that SIBs hold over lithium-ion batteries.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of high salt concentrations in electrolytes is a growing concern. The production and disposal of these electrolytes may have unforeseen ecological consequences, necessitating comprehensive life cycle assessments to ensure the sustainability of SIB technology.
Researchers are also facing challenges in developing electrolyte formulations that maintain their performance across a wide temperature range. The behavior of salt concentrations in extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can significantly affect battery performance and safety. Finding the right balance that ensures consistent operation under various environmental conditions remains a complex task.
Lastly, the scalability of high-concentration electrolyte production presents a significant challenge. Ensuring uniform salt distribution and maintaining consistent quality in large-scale manufacturing processes is crucial for the commercial viability of SIBs. The industry must overcome these production hurdles to make high-performance SIBs a reality in the mass market.
Existing Salt Concentration Solutions
01 Optimizing salt concentration in electrolytes
Researchers are focusing on optimizing the salt concentration in sodium ion battery electrolytes to improve performance. This involves finding the right balance of sodium salts to enhance ionic conductivity, stability, and electrochemical performance. Higher salt concentrations can lead to increased viscosity and reduced ion mobility, while lower concentrations may result in insufficient charge carriers.- Optimizing salt concentration in electrolytes: Researchers are focusing on optimizing the salt concentration in sodium ion battery electrolytes to improve performance. This involves finding the right balance of sodium salts to enhance ionic conductivity, stability, and overall battery efficiency. The concentration of salts can significantly impact the electrochemical properties and cycling stability of the battery.
- Novel electrolyte compositions: Development of new electrolyte compositions is a key area of research. This includes exploring various combinations of solvents and sodium salts, as well as additives to enhance the electrolyte's properties. Novel compositions aim to address issues such as dendrite formation, solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) stability, and improved sodium ion transport.
- High-concentration electrolytes: High-concentration or 'super-concentrated' electrolytes are being investigated for their potential benefits in sodium ion batteries. These electrolytes, with significantly higher salt concentrations than conventional systems, can offer improved thermal stability, wider electrochemical windows, and enhanced safety properties.
- Electrolyte additives for performance enhancement: Various additives are being explored to enhance the performance of sodium ion battery electrolytes. These additives can help in forming stable SEI layers, improving the wettability of electrodes, mitigating unwanted side reactions, and extending the cycle life of the battery. The type and concentration of additives are crucial factors in optimizing battery performance.
- Temperature-resistant electrolyte formulations: Developing electrolyte formulations that maintain stability and performance across a wide temperature range is a significant focus. This includes creating electrolytes that resist freezing at low temperatures and remain stable at high temperatures, ensuring consistent battery performance in diverse environmental conditions.
02 Novel electrolyte compositions
Development of new electrolyte compositions is a key area of research. This includes exploring various combinations of solvents, salts, and additives to create electrolytes with improved properties. Novel compositions aim to enhance the overall battery performance, including capacity, cycling stability, and safety.Expand Specific Solutions03 High-concentration electrolytes
High-concentration electrolytes, also known as 'solvent-in-salt' electrolytes, are being investigated for their potential benefits. These electrolytes typically contain a higher ratio of salt to solvent, which can lead to improved thermal stability, reduced flammability, and enhanced electrochemical performance. However, challenges such as increased viscosity and cost need to be addressed.Expand Specific Solutions04 Additives for electrolyte enhancement
Researchers are exploring various additives to enhance the properties of sodium ion battery electrolytes. These additives can help form stable solid electrolyte interphases (SEI), improve ionic conductivity, or enhance the electrolyte's stability at high voltages. The right combination of additives can significantly impact the battery's performance and lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature-dependent electrolyte formulations
Developing electrolyte formulations that perform well across a wide temperature range is crucial for sodium ion batteries. This involves adjusting salt concentrations and solvent compositions to maintain good ionic conductivity and stability at both low and high temperatures. Such formulations can expand the operating range of sodium ion batteries, making them suitable for diverse applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The impact of salt concentrations in sodium ion battery electrolytes is a rapidly evolving field within the broader context of energy storage technology. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest from both established players and innovative startups. Companies like LG Energy Solution, Contemporary Amperex Technology, and Sumitomo Chemical are investing heavily in research and development. The market size is expanding, driven by the demand for sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solutions. While the technology is still maturing, significant progress has been made in understanding the role of salt concentrations in improving battery performance, with academic institutions like Nankai University and Arizona State University contributing valuable research insights.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has focused on developing advanced electrolyte formulations for sodium-ion batteries with optimized salt concentrations. Their approach involves using a dual-salt strategy, combining sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF6) with sodium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (NaFSI) in carefully controlled ratios. This dual-salt system aims to leverage the benefits of both salts while mitigating their individual drawbacks. LG's research has demonstrated that a total salt concentration of 1.0-1.5 M, with a NaPF6:NaFSI ratio of 3:7, can significantly enhance the electrochemical performance of sodium-ion batteries[4][5]. The optimized salt concentration and composition help improve the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte while also promoting the formation of a stable and protective SEI layer on the electrode surfaces.
Strengths: Improved ionic conductivity, enhanced SEI stability, and balanced electrochemical performance. Weaknesses: Complexity in electrolyte preparation and potential increased cost due to the use of multiple salts.
Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Physics
Technical Solution: The Institute of Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has conducted extensive research on the impact of salt concentrations in sodium-ion battery electrolytes. Their approach focuses on understanding the fundamental mechanisms of ion transport and interfacial reactions at varying salt concentrations. Using advanced characterization techniques such as in-situ NMR spectroscopy and synchrotron-based X-ray absorption spectroscopy, researchers have elucidated the solvation structure and dynamics of sodium ions in electrolytes with different salt concentrations[10][11]. Their studies have revealed that moderate to high salt concentrations (1.5-3 M) can significantly alter the solvation shell of sodium ions, leading to enhanced ion mobility and improved interfacial stability. The institute has also investigated the use of sodium-based ionic liquids as electrolyte solvents, demonstrating that these systems can maintain high ionic conductivity even at elevated salt concentrations, potentially offering a path to safer and more stable sodium-ion batteries.
Strengths: Deep fundamental understanding of ion transport mechanisms, potential for developing novel electrolyte systems based on ionic liquids. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on basic research, which may require additional development for practical applications.
Innovative Electrolyte Formulations
Electrolyte composition for sodium-ion battery
PatentWO2022200343A1
Innovation
- A non-aqueous liquid electrolyte composition for sodium-ion batteries comprising a mixture of ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, and succinonitrile with tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite and vinylene carbonate as additives, which enhances the stability of the cathode electrolyte interphase, reduces oxidation of the electrolyte solvent, and improves wettability, thereby addressing the pressure and performance issues.
Electrolyte solution for sodium-ion battery, secondary battery, battery module, battery pack, and electrical apparatus
PatentPendingUS20250079520A1
Innovation
- An electrolyte solution comprising a sodium salt of formula NaBOaFxRy−z, a fluoroalkyl ether, and other ethers, which improves the solvability of sodium ions and enhances the stability and oxidation resistance of the electrolyte solution, thereby broadening the electrochemical window, enhancing coulombic efficiency, and improving cycling and safety performance.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of sodium-ion battery electrolytes, particularly concerning salt concentrations, is a critical aspect of sustainable energy storage development. As sodium-ion batteries emerge as a potential alternative to lithium-ion batteries, understanding their environmental footprint becomes increasingly important.
Salt concentrations in electrolytes play a crucial role in battery performance and longevity. However, they also have significant implications for the environment throughout the battery lifecycle. During the production phase, the extraction and processing of salts for electrolytes can lead to habitat disruption, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions. The type and concentration of salts used can influence the energy requirements and chemical processes involved in manufacturing, potentially affecting the overall carbon footprint of battery production.
In the operational phase, the environmental impact of salt concentrations is primarily related to battery efficiency and lifespan. Higher salt concentrations can improve ionic conductivity and battery performance but may also lead to increased corrosion and degradation of battery components. This trade-off has implications for the frequency of battery replacement and the associated environmental costs of disposal and new battery production.
The end-of-life phase presents both challenges and opportunities. The presence of high salt concentrations in spent batteries can complicate recycling processes, potentially leading to increased energy consumption and chemical waste during material recovery. However, advancements in recycling technologies specifically tailored to sodium-ion batteries could mitigate these issues and improve the overall sustainability of the technology.
Water usage and contamination are significant concerns related to electrolyte salt concentrations. The production and disposal of high-concentration electrolytes may require substantial water resources and pose risks of saline contamination to local water bodies if not properly managed. This aspect is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions where battery production or recycling facilities may be located.
Biodiversity impacts must also be considered, especially in areas where salt extraction for electrolytes occurs. Changes in soil salinity due to mining activities or improper disposal can affect local flora and fauna, potentially leading to ecosystem disruptions. The extent of these impacts depends on the specific salts used and the scale of production.
In conclusion, while sodium-ion batteries with optimized salt concentrations in electrolytes offer promising environmental benefits compared to some existing technologies, careful consideration of their full lifecycle environmental impact is essential. Balancing performance requirements with environmental sustainability will be key to realizing the potential of this technology in the transition to cleaner energy storage solutions.
Salt concentrations in electrolytes play a crucial role in battery performance and longevity. However, they also have significant implications for the environment throughout the battery lifecycle. During the production phase, the extraction and processing of salts for electrolytes can lead to habitat disruption, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions. The type and concentration of salts used can influence the energy requirements and chemical processes involved in manufacturing, potentially affecting the overall carbon footprint of battery production.
In the operational phase, the environmental impact of salt concentrations is primarily related to battery efficiency and lifespan. Higher salt concentrations can improve ionic conductivity and battery performance but may also lead to increased corrosion and degradation of battery components. This trade-off has implications for the frequency of battery replacement and the associated environmental costs of disposal and new battery production.
The end-of-life phase presents both challenges and opportunities. The presence of high salt concentrations in spent batteries can complicate recycling processes, potentially leading to increased energy consumption and chemical waste during material recovery. However, advancements in recycling technologies specifically tailored to sodium-ion batteries could mitigate these issues and improve the overall sustainability of the technology.
Water usage and contamination are significant concerns related to electrolyte salt concentrations. The production and disposal of high-concentration electrolytes may require substantial water resources and pose risks of saline contamination to local water bodies if not properly managed. This aspect is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions where battery production or recycling facilities may be located.
Biodiversity impacts must also be considered, especially in areas where salt extraction for electrolytes occurs. Changes in soil salinity due to mining activities or improper disposal can affect local flora and fauna, potentially leading to ecosystem disruptions. The extent of these impacts depends on the specific salts used and the scale of production.
In conclusion, while sodium-ion batteries with optimized salt concentrations in electrolytes offer promising environmental benefits compared to some existing technologies, careful consideration of their full lifecycle environmental impact is essential. Balancing performance requirements with environmental sustainability will be key to realizing the potential of this technology in the transition to cleaner energy storage solutions.
Safety and Stability Considerations
The safety and stability of sodium-ion battery electrolytes are critical factors in determining the overall performance and commercial viability of these energy storage systems. The concentration of salt in the electrolyte plays a significant role in influencing these aspects, necessitating careful consideration and optimization.
High salt concentrations in sodium-ion battery electrolytes can lead to increased viscosity, potentially impacting ion mobility and overall battery performance. This heightened viscosity may also contribute to the formation of dendrites, which are needle-like structures that can grow from the anode and potentially cause short circuits, posing serious safety risks.
Conversely, low salt concentrations may result in insufficient ionic conductivity, limiting the battery's power output and efficiency. Additionally, inadequate salt concentrations can lead to increased electrode degradation due to insufficient protection of the electrode surface, potentially compromising the long-term stability of the battery.
The choice of salt and its concentration also affects the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer. This protective layer on the electrode surface is crucial for preventing continuous electrolyte decomposition and ensuring the longevity of the battery. Optimal salt concentrations can promote the formation of a stable and effective SEI layer, enhancing the overall stability and cycle life of the battery.
Temperature sensitivity is another critical consideration when evaluating the impact of salt concentrations on safety and stability. Electrolytes with high salt concentrations may be more prone to crystallization at low temperatures, potentially leading to capacity loss and increased internal resistance. Conversely, at elevated temperatures, high salt concentrations can exacerbate electrolyte decomposition, accelerating capacity fade and potentially leading to thermal runaway events.
The corrosive nature of certain salts at high concentrations must also be taken into account. Excessive salt concentrations can lead to increased corrosion of battery components, including current collectors and separators, potentially compromising the structural integrity of the battery and introducing additional safety risks.
Balancing these various factors to achieve optimal safety and stability requires careful consideration of the specific battery chemistry, operating conditions, and intended applications. Researchers and engineers must conduct thorough testing and analysis to determine the ideal salt concentration range that maximizes performance while maintaining robust safety and stability profiles for sodium-ion battery electrolytes.
High salt concentrations in sodium-ion battery electrolytes can lead to increased viscosity, potentially impacting ion mobility and overall battery performance. This heightened viscosity may also contribute to the formation of dendrites, which are needle-like structures that can grow from the anode and potentially cause short circuits, posing serious safety risks.
Conversely, low salt concentrations may result in insufficient ionic conductivity, limiting the battery's power output and efficiency. Additionally, inadequate salt concentrations can lead to increased electrode degradation due to insufficient protection of the electrode surface, potentially compromising the long-term stability of the battery.
The choice of salt and its concentration also affects the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer. This protective layer on the electrode surface is crucial for preventing continuous electrolyte decomposition and ensuring the longevity of the battery. Optimal salt concentrations can promote the formation of a stable and effective SEI layer, enhancing the overall stability and cycle life of the battery.
Temperature sensitivity is another critical consideration when evaluating the impact of salt concentrations on safety and stability. Electrolytes with high salt concentrations may be more prone to crystallization at low temperatures, potentially leading to capacity loss and increased internal resistance. Conversely, at elevated temperatures, high salt concentrations can exacerbate electrolyte decomposition, accelerating capacity fade and potentially leading to thermal runaway events.
The corrosive nature of certain salts at high concentrations must also be taken into account. Excessive salt concentrations can lead to increased corrosion of battery components, including current collectors and separators, potentially compromising the structural integrity of the battery and introducing additional safety risks.
Balancing these various factors to achieve optimal safety and stability requires careful consideration of the specific battery chemistry, operating conditions, and intended applications. Researchers and engineers must conduct thorough testing and analysis to determine the ideal salt concentration range that maximizes performance while maintaining robust safety and stability profiles for sodium-ion battery electrolytes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!