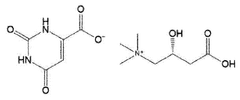
Investigating lithium orotate's role in antioxidative defense mechanisms
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Research Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its potential role in antioxidative defense mechanisms. The exploration of this compound's properties and effects represents a convergence of psychiatric pharmacology and oxidative stress research, two fields that have increasingly recognized their interconnectedness.
The historical context of lithium in medicine dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the specific form of lithium orotate has emerged as a subject of interest due to its purported enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. This has led to a renewed focus on understanding the broader physiological impacts of lithium, particularly in the realm of cellular protection and oxidative stress mitigation.
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to counteract their harmful effects, has been implicated in a wide range of pathological conditions. These include neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and even mood disorders. The potential of lithium orotate to modulate antioxidative defense mechanisms presents an intriguing avenue for therapeutic intervention across multiple medical domains.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate's role in antioxidative defense mechanisms is to elucidate the molecular pathways through which this compound exerts its protective effects. This includes examining its impact on key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, as well as its influence on the expression of genes involved in the cellular stress response.
Furthermore, this research aims to compare the efficacy of lithium orotate with other forms of lithium and established antioxidants, to determine its unique advantages and potential applications. The investigation also seeks to identify optimal dosages and administration methods that maximize antioxidative benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate when combined with other antioxidants or neuroprotective agents. This could lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for conditions characterized by oxidative stress and cellular damage.
By comprehensively examining lithium orotate's antioxidative properties, this research endeavors to bridge the gap between psychiatric treatments and broader cellular health interventions. The findings could potentially revolutionize our approach to managing oxidative stress-related disorders and open new avenues for preventive medicine and healthy aging strategies.
The historical context of lithium in medicine dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the specific form of lithium orotate has emerged as a subject of interest due to its purported enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. This has led to a renewed focus on understanding the broader physiological impacts of lithium, particularly in the realm of cellular protection and oxidative stress mitigation.
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to counteract their harmful effects, has been implicated in a wide range of pathological conditions. These include neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and even mood disorders. The potential of lithium orotate to modulate antioxidative defense mechanisms presents an intriguing avenue for therapeutic intervention across multiple medical domains.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate's role in antioxidative defense mechanisms is to elucidate the molecular pathways through which this compound exerts its protective effects. This includes examining its impact on key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, as well as its influence on the expression of genes involved in the cellular stress response.
Furthermore, this research aims to compare the efficacy of lithium orotate with other forms of lithium and established antioxidants, to determine its unique advantages and potential applications. The investigation also seeks to identify optimal dosages and administration methods that maximize antioxidative benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate when combined with other antioxidants or neuroprotective agents. This could lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for conditions characterized by oxidative stress and cellular damage.
By comprehensively examining lithium orotate's antioxidative properties, this research endeavors to bridge the gap between psychiatric treatments and broader cellular health interventions. The findings could potentially revolutionize our approach to managing oxidative stress-related disorders and open new avenues for preventive medicine and healthy aging strategies.
Market Analysis for Antioxidative Supplements
The global market for antioxidative supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness. This trend is particularly evident in developed countries where aging populations and rising healthcare costs have led to a greater focus on preventive health measures. The antioxidative supplement market, which includes a wide range of products from vitamins to specialized compounds like lithium orotate, is expected to continue its upward trajectory.
Market research indicates that the antioxidative supplement sector is highly fragmented, with numerous players competing for market share. Key segments within this market include vitamins (such as Vitamin C and E), minerals, herbal extracts, and specialty antioxidants. Lithium orotate, while less known than traditional antioxidants, is gaining attention due to its potential neuroprotective properties and role in antioxidative defense mechanisms.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping market demand. The primary target audience for antioxidative supplements includes health-conscious individuals, athletes, and the elderly population. There is a growing interest among younger consumers as well, particularly those seeking to improve cognitive function and manage stress-related oxidative damage.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the antioxidative supplement market, owing to high disposable incomes and well-established health and wellness industries. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing health awareness and rising middle-class populations in countries like China and India.
The market for specialized antioxidants, including lithium orotate, represents a niche but growing segment. As research into the role of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense mechanisms progresses, there is potential for increased market penetration. However, this growth is contingent upon factors such as regulatory approval, clinical evidence, and consumer education.
Distribution channels for antioxidative supplements are diverse, encompassing pharmacies, health food stores, online retailers, and direct-to-consumer sales. The e-commerce sector, in particular, has seen substantial growth, offering consumers easy access to a wide range of products and information.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles, particularly for novel compounds like lithium orotate, and the need for robust scientific evidence to support product claims. Additionally, the market faces competition from functional foods and beverages that offer antioxidative benefits, potentially cannibalizing supplement sales.
Looking ahead, the antioxidative supplement market is poised for continued growth, driven by aging populations, increasing health consciousness, and ongoing research into the benefits of antioxidants. The potential role of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense mechanisms represents an exciting area for market expansion, provided that research continues to support its efficacy and safety profile.
Market research indicates that the antioxidative supplement sector is highly fragmented, with numerous players competing for market share. Key segments within this market include vitamins (such as Vitamin C and E), minerals, herbal extracts, and specialty antioxidants. Lithium orotate, while less known than traditional antioxidants, is gaining attention due to its potential neuroprotective properties and role in antioxidative defense mechanisms.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping market demand. The primary target audience for antioxidative supplements includes health-conscious individuals, athletes, and the elderly population. There is a growing interest among younger consumers as well, particularly those seeking to improve cognitive function and manage stress-related oxidative damage.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the antioxidative supplement market, owing to high disposable incomes and well-established health and wellness industries. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing health awareness and rising middle-class populations in countries like China and India.
The market for specialized antioxidants, including lithium orotate, represents a niche but growing segment. As research into the role of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense mechanisms progresses, there is potential for increased market penetration. However, this growth is contingent upon factors such as regulatory approval, clinical evidence, and consumer education.
Distribution channels for antioxidative supplements are diverse, encompassing pharmacies, health food stores, online retailers, and direct-to-consumer sales. The e-commerce sector, in particular, has seen substantial growth, offering consumers easy access to a wide range of products and information.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles, particularly for novel compounds like lithium orotate, and the need for robust scientific evidence to support product claims. Additionally, the market faces competition from functional foods and beverages that offer antioxidative benefits, potentially cannibalizing supplement sales.
Looking ahead, the antioxidative supplement market is poised for continued growth, driven by aging populations, increasing health consciousness, and ongoing research into the benefits of antioxidants. The potential role of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense mechanisms represents an exciting area for market expansion, provided that research continues to support its efficacy and safety profile.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
The current status of lithium orotate research in antioxidative defense mechanisms is characterized by a growing body of evidence supporting its potential therapeutic benefits, yet significant challenges remain in fully understanding its mechanisms of action and optimizing its clinical applications.
Recent studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate exhibits potent antioxidant properties, effectively reducing oxidative stress in various cellular and animal models. Researchers have observed its ability to enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, while also decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species. These findings suggest a promising role for lithium orotate in combating oxidative damage associated with numerous pathological conditions.
However, the precise molecular pathways through which lithium orotate exerts its antioxidative effects are not fully elucidated. While some studies have implicated the modulation of signaling cascades such as the Nrf2/ARE pathway, others have suggested direct scavenging of free radicals. This lack of comprehensive understanding presents a significant challenge in optimizing the therapeutic potential of lithium orotate.
Another major hurdle in lithium orotate research is the limited number of large-scale clinical trials. Most studies to date have been conducted in vitro or in animal models, with only a handful of small human trials. This paucity of clinical data hinders the translation of promising laboratory findings into practical therapeutic applications.
The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate also present challenges. While some researchers claim that lithium orotate has superior bioavailability compared to other lithium salts, there is a lack of robust pharmacokinetic studies to support these assertions. Understanding the absorption, distribution, and elimination of lithium orotate is crucial for determining optimal dosing regimens and assessing its long-term safety profile.
Furthermore, the regulatory status of lithium orotate varies across different countries, with some classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug. This classification discrepancy complicates the research landscape, affecting funding opportunities and the design of clinical trials.
Lastly, there is a need for standardization in lithium orotate research methodologies. Variations in experimental protocols, dosages, and outcome measures make it challenging to compare results across different studies and draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy in antioxidative defense mechanisms.
Recent studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate exhibits potent antioxidant properties, effectively reducing oxidative stress in various cellular and animal models. Researchers have observed its ability to enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, while also decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species. These findings suggest a promising role for lithium orotate in combating oxidative damage associated with numerous pathological conditions.
However, the precise molecular pathways through which lithium orotate exerts its antioxidative effects are not fully elucidated. While some studies have implicated the modulation of signaling cascades such as the Nrf2/ARE pathway, others have suggested direct scavenging of free radicals. This lack of comprehensive understanding presents a significant challenge in optimizing the therapeutic potential of lithium orotate.
Another major hurdle in lithium orotate research is the limited number of large-scale clinical trials. Most studies to date have been conducted in vitro or in animal models, with only a handful of small human trials. This paucity of clinical data hinders the translation of promising laboratory findings into practical therapeutic applications.
The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate also present challenges. While some researchers claim that lithium orotate has superior bioavailability compared to other lithium salts, there is a lack of robust pharmacokinetic studies to support these assertions. Understanding the absorption, distribution, and elimination of lithium orotate is crucial for determining optimal dosing regimens and assessing its long-term safety profile.
Furthermore, the regulatory status of lithium orotate varies across different countries, with some classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug. This classification discrepancy complicates the research landscape, affecting funding opportunities and the design of clinical trials.
Lastly, there is a need for standardization in lithium orotate research methodologies. Variations in experimental protocols, dosages, and outcome measures make it challenging to compare results across different studies and draw definitive conclusions about its efficacy in antioxidative defense mechanisms.
Existing Methodologies for Studying Antioxidative Effects
01 Lithium orotate as an antioxidant
Lithium orotate has been found to possess antioxidant properties, contributing to the body's antioxidative defense mechanisms. It can help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, potentially protecting cells from damage. This compound may enhance the body's natural antioxidant systems, supporting overall cellular health and function.- Lithium orotate as an antioxidant: Lithium orotate has been found to possess antioxidant properties, contributing to the body's antioxidative defense mechanisms. It can help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, potentially protecting cells from damage. This compound may enhance the body's natural antioxidant systems, supporting overall cellular health and function.
- Combination with other antioxidants: Lithium orotate can be combined with other antioxidants to create a synergistic effect in enhancing antioxidative defense mechanisms. These combinations may include vitamins, minerals, and plant-based compounds known for their antioxidant properties. Such formulations can provide a more comprehensive approach to combating oxidative stress and supporting cellular health.
- Neuroprotective effects: Lithium orotate has shown potential neuroprotective effects through its antioxidative properties. It may help protect neurons from oxidative damage and support brain health. This compound could be beneficial in addressing neurodegenerative conditions and maintaining cognitive function by enhancing the brain's antioxidative defense mechanisms.
- Cellular stress response modulation: Lithium orotate may play a role in modulating cellular stress responses, particularly in relation to oxidative stress. It could influence signaling pathways involved in the activation of antioxidant defense mechanisms, helping cells adapt to and overcome oxidative challenges. This modulation may contribute to improved cellular resilience and longevity.
- Mitochondrial function support: The antioxidative properties of lithium orotate may extend to supporting mitochondrial function. By reducing oxidative stress within mitochondria, it could help maintain energy production and cellular metabolism. This support of mitochondrial health is crucial for overall cellular function and may contribute to the compound's broader antioxidative defense mechanisms.
02 Combination with other antioxidants
Lithium orotate can be combined with other antioxidants to create a synergistic effect in enhancing antioxidative defense mechanisms. These combinations may include vitamins, minerals, and plant-based compounds known for their antioxidant properties. Such formulations can provide a more comprehensive approach to combating oxidative stress and supporting cellular health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neuroprotective effects
Lithium orotate has shown potential neuroprotective effects through its antioxidative properties. It may help protect neurons from oxidative damage and support brain health. This compound could be beneficial in addressing neurodegenerative conditions and supporting cognitive function by enhancing the brain's antioxidative defense mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cellular stress response modulation
Lithium orotate may play a role in modulating cellular stress responses, particularly in relation to oxidative stress. It could influence cellular pathways involved in antioxidant production and stress adaptation, potentially enhancing the body's ability to cope with various forms of cellular stress and maintain homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Mitochondrial function support
Research suggests that lithium orotate may support mitochondrial function, which is crucial for cellular energy production and antioxidative defense. By enhancing mitochondrial health and efficiency, this compound could contribute to improved cellular resilience against oxidative stress and support overall metabolic function.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate and Antioxidant Research
The investigation into lithium orotate's role in antioxidative defense mechanisms is in an early stage of development, with a relatively small market size but growing interest. The technology is still emerging, with limited commercial applications and ongoing research to establish its efficacy. Companies like PolyPlus Battery Co., Inc. and BYD Co., Ltd. are exploring lithium-based technologies, but primarily in battery applications rather than antioxidative defense. Research institutions such as Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and Shandong University are likely at the forefront of investigating lithium orotate's potential in this specific area. The competitive landscape is currently characterized by academic and early-stage research, with few established industry players directly focused on this niche application of lithium orotate.
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Technical Solution: Cedars-Sinai Medical Center has been investigating the role of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense mechanisms. Their research focuses on the potential neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate, particularly in relation to oxidative stress. The center has conducted studies examining how lithium orotate may enhance the body's natural antioxidant defenses, potentially offering protection against neurodegenerative diseases[1]. Their approach involves analyzing the impact of lithium orotate on key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, as well as its effect on glutathione levels, a crucial cellular antioxidant[2]. Additionally, they are exploring the potential of lithium orotate to modulate inflammatory responses and mitochondrial function, both of which play significant roles in oxidative stress and cellular damage[3].
Strengths: Access to advanced medical research facilities and expertise in neuroscience. Weaknesses: Limited focus on commercial applications, primarily academic research-oriented.
Biojiva LLC
Technical Solution: Biojiva LLC has developed a proprietary formulation incorporating lithium orotate for enhancing antioxidative defense mechanisms. Their approach focuses on the synergistic effects of lithium orotate combined with other natural antioxidants. The company's research suggests that their formulation may increase the expression of Nrf2, a key transcription factor involved in the regulation of antioxidant genes[4]. Biojiva's studies have shown potential benefits in reducing oxidative stress markers and improving cellular resilience against free radical damage[5]. Their technology also explores the potential of lithium orotate in modulating inflammatory pathways, which are closely linked to oxidative stress in various health conditions[6].
Strengths: Focused research on practical applications of lithium orotate in antioxidative defense. Weaknesses: Limited resources compared to larger research institutions.
Core Innovations in Lithium Orotate Antioxidative Research
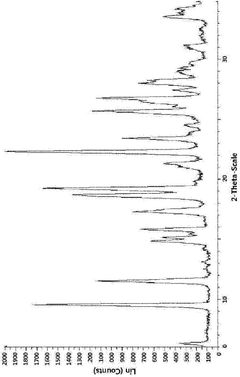
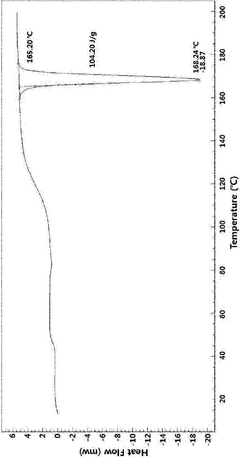
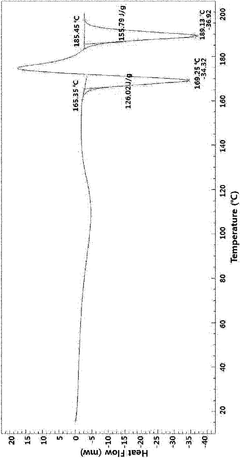
Crystalline polymorph of l-carnitine orotate, production method therefor, or use thereof
PatentWO2017105090A1
Innovation
- A novel crystalline polymorph of L-carnitine orotate is developed, characterized by specific X-ray diffraction angles and thermodynamic stability, produced through a method involving the reaction of L-carnitine and orotic acid in a controlled solvent system, followed by filtration and vacuum drying, enhancing wettability and stability without the drawbacks of D,L-carnitine.
Positive electrode material for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
PatentWO2017047639A1
Innovation
- A positive electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary batteries comprising a positive electrode active material, a binder, and a water-soluble antioxidant, such as ascorbic acid or its salts, erythorbic acid, green tea polyphenols, glutathione, lipoic acid, or rosemary extracts, which reduces internal resistance and improves charge/discharge cycle characteristics by suppressing oxidative decomposition.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Lithium Orotate
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention in the field of mental health and neurological disorders, requires careful consideration regarding its safety profile and efficacy. The safety of lithium orotate is a primary concern, as it is not FDA-approved and lacks extensive clinical trials compared to its carbonate counterpart. While some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have a lower risk of side effects due to its potentially enhanced bioavailability, this claim requires further investigation and validation through rigorous scientific research.
One of the key safety considerations is the potential for lithium toxicity, which can occur if blood levels become too high. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is closely monitored in clinical settings, lithium orotate is often used as an over-the-counter supplement, potentially leading to inadequate monitoring and increased risk of adverse effects. Additionally, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on kidney function and thyroid health remain unclear, necessitating careful observation and further study.
Regarding efficacy, preliminary research suggests that lithium orotate may have potential benefits in mood stabilization, neuroprotection, and cognitive enhancement. Some studies indicate that it may be effective in managing bipolar disorder and depression, albeit at lower doses than traditional lithium carbonate. However, the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials limits the strength of these findings, and more robust evidence is needed to establish its efficacy conclusively.
The antioxidative properties of lithium orotate are of particular interest in the context of its potential neuroprotective effects. Research indicates that lithium may enhance antioxidative defense mechanisms in the brain, potentially offering protection against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. This aspect of lithium orotate's action could have implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and age-related cognitive decline.
However, the optimal dosage and duration of lithium orotate treatment for various conditions remain uncertain. The variability in product quality and concentration across different over-the-counter formulations further complicates the assessment of its safety and efficacy. Standardization of lithium orotate products and dosing protocols is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable outcomes in both research and clinical applications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in several areas of mental health and neuroprotection, its safety and efficacy profile requires further elucidation through comprehensive clinical trials and long-term studies. Healthcare providers and researchers must approach its use with caution, balancing potential benefits against the risks associated with inadequate regulation and monitoring. Future research should focus on establishing clear guidelines for its use, optimizing dosing regimens, and investigating its long-term effects on various physiological systems.
One of the key safety considerations is the potential for lithium toxicity, which can occur if blood levels become too high. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is closely monitored in clinical settings, lithium orotate is often used as an over-the-counter supplement, potentially leading to inadequate monitoring and increased risk of adverse effects. Additionally, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on kidney function and thyroid health remain unclear, necessitating careful observation and further study.
Regarding efficacy, preliminary research suggests that lithium orotate may have potential benefits in mood stabilization, neuroprotection, and cognitive enhancement. Some studies indicate that it may be effective in managing bipolar disorder and depression, albeit at lower doses than traditional lithium carbonate. However, the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials limits the strength of these findings, and more robust evidence is needed to establish its efficacy conclusively.
The antioxidative properties of lithium orotate are of particular interest in the context of its potential neuroprotective effects. Research indicates that lithium may enhance antioxidative defense mechanisms in the brain, potentially offering protection against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. This aspect of lithium orotate's action could have implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and age-related cognitive decline.
However, the optimal dosage and duration of lithium orotate treatment for various conditions remain uncertain. The variability in product quality and concentration across different over-the-counter formulations further complicates the assessment of its safety and efficacy. Standardization of lithium orotate products and dosing protocols is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable outcomes in both research and clinical applications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in several areas of mental health and neuroprotection, its safety and efficacy profile requires further elucidation through comprehensive clinical trials and long-term studies. Healthcare providers and researchers must approach its use with caution, balancing potential benefits against the risks associated with inadequate regulation and monitoring. Future research should focus on establishing clear guidelines for its use, optimizing dosing regimens, and investigating its long-term effects on various physiological systems.
Potential Clinical Applications of Lithium Orotate
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention in the field of mental health and neurological disorders, shows promising potential for various clinical applications. Its unique properties and mechanisms of action open up possibilities for treating a range of conditions beyond traditional lithium carbonate applications.
One of the most significant potential clinical applications of lithium orotate is in the treatment of bipolar disorder. The compound's ability to stabilize mood and reduce manic episodes could provide an alternative to conventional lithium treatments, potentially offering fewer side effects and improved patient compliance.
In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases, lithium orotate shows promise in neuroprotection. Studies suggest it may help slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease by reducing the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein tangles. This could lead to new therapeutic approaches for managing and potentially preventing cognitive decline in aging populations.
Lithium orotate's antioxidative properties make it a candidate for treating oxidative stress-related conditions. Its potential to enhance the body's natural antioxidant defense mechanisms could be beneficial in managing conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and chronic inflammatory disorders.
The compound's neuroprotective effects extend to potential applications in traumatic brain injury and stroke recovery. By promoting neurogenesis and reducing inflammation, lithium orotate could aid in post-injury brain healing and functional recovery, offering new hope for patients with these challenging conditions.
In the field of mental health, lithium orotate shows promise for treating depression, especially in cases resistant to conventional antidepressants. Its unique mechanism of action, which includes modulating neurotransmitter systems and promoting neuroplasticity, could provide an alternative treatment option for patients who do not respond well to current therapies.
Additionally, lithium orotate's potential in managing anxiety disorders is being explored. Its calming effects on the central nervous system could offer a new approach to treating generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety, potentially with fewer side effects than traditional anxiolytic medications.
The compound's role in bone health is another area of interest. Lithium orotate may stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone resorption, suggesting potential applications in treating osteoporosis and other bone-related disorders, particularly in aging populations.
As research continues, the potential clinical applications of lithium orotate continue to expand, offering hope for improved treatments across a wide spectrum of neurological, psychiatric, and metabolic disorders. However, further clinical trials and long-term safety studies are necessary to fully establish its efficacy and safety profile in these various applications.
One of the most significant potential clinical applications of lithium orotate is in the treatment of bipolar disorder. The compound's ability to stabilize mood and reduce manic episodes could provide an alternative to conventional lithium treatments, potentially offering fewer side effects and improved patient compliance.
In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases, lithium orotate shows promise in neuroprotection. Studies suggest it may help slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease by reducing the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein tangles. This could lead to new therapeutic approaches for managing and potentially preventing cognitive decline in aging populations.
Lithium orotate's antioxidative properties make it a candidate for treating oxidative stress-related conditions. Its potential to enhance the body's natural antioxidant defense mechanisms could be beneficial in managing conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and chronic inflammatory disorders.
The compound's neuroprotective effects extend to potential applications in traumatic brain injury and stroke recovery. By promoting neurogenesis and reducing inflammation, lithium orotate could aid in post-injury brain healing and functional recovery, offering new hope for patients with these challenging conditions.
In the field of mental health, lithium orotate shows promise for treating depression, especially in cases resistant to conventional antidepressants. Its unique mechanism of action, which includes modulating neurotransmitter systems and promoting neuroplasticity, could provide an alternative treatment option for patients who do not respond well to current therapies.
Additionally, lithium orotate's potential in managing anxiety disorders is being explored. Its calming effects on the central nervous system could offer a new approach to treating generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety, potentially with fewer side effects than traditional anxiolytic medications.
The compound's role in bone health is another area of interest. Lithium orotate may stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone resorption, suggesting potential applications in treating osteoporosis and other bone-related disorders, particularly in aging populations.
As research continues, the potential clinical applications of lithium orotate continue to expand, offering hope for improved treatments across a wide spectrum of neurological, psychiatric, and metabolic disorders. However, further clinical trials and long-term safety studies are necessary to fully establish its efficacy and safety profile in these various applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!