Investigating Magnesium Nitrate in Functional Composite Hydrogel Applications
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Mg(NO3)2 in Hydrogels: Background and Objectives
Magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2) has emerged as a promising component in the development of functional composite hydrogels, attracting significant attention in materials science and biomedical engineering. The integration of Mg(NO3)2 into hydrogel systems represents a convergence of inorganic chemistry and polymer science, offering unique properties and potential applications across various fields.
Historically, hydrogels have been extensively studied for their ability to absorb and retain large amounts of water while maintaining structural integrity. The incorporation of inorganic compounds, such as magnesium nitrate, into these polymer networks has opened new avenues for enhancing their functionality and expanding their application scope.
The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early investigations of ion-responsive hydrogels in the 1980s. However, the specific focus on magnesium nitrate in composite hydrogels has gained momentum in the past decade, driven by the growing demand for smart materials with tunable properties.
The primary objective of investigating Mg(NO3)2 in functional composite hydrogels is to develop advanced materials with enhanced mechanical, chemical, and biological properties. Researchers aim to exploit the unique characteristics of magnesium ions and nitrate anions to create hydrogels with improved strength, responsiveness to external stimuli, and biocompatibility.
Key technological goals include optimizing the incorporation methods of Mg(NO3)2 into various hydrogel matrices, understanding the interaction mechanisms between the inorganic component and polymer chains, and tailoring the resulting properties for specific applications. These applications range from drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds to environmental sensors and actuators.
The integration of Mg(NO3)2 in hydrogels also aligns with broader trends in materials science, such as the development of self-healing materials, stimuli-responsive systems, and biomimetic structures. This research direction holds promise for addressing challenges in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and advanced manufacturing.
As the field progresses, researchers are exploring the synergistic effects of combining Mg(NO3)2 with other inorganic compounds or nanoparticles to create multi-functional composite hydrogels. This approach aims to further expand the capabilities and potential applications of these advanced materials.
The investigation of Mg(NO3)2 in functional composite hydrogels represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving area of research, with significant potential for technological breakthroughs and innovative applications. As this field continues to advance, it is expected to contribute to the development of next-generation smart materials and enable novel solutions to complex challenges across various industries.
Historically, hydrogels have been extensively studied for their ability to absorb and retain large amounts of water while maintaining structural integrity. The incorporation of inorganic compounds, such as magnesium nitrate, into these polymer networks has opened new avenues for enhancing their functionality and expanding their application scope.
The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early investigations of ion-responsive hydrogels in the 1980s. However, the specific focus on magnesium nitrate in composite hydrogels has gained momentum in the past decade, driven by the growing demand for smart materials with tunable properties.
The primary objective of investigating Mg(NO3)2 in functional composite hydrogels is to develop advanced materials with enhanced mechanical, chemical, and biological properties. Researchers aim to exploit the unique characteristics of magnesium ions and nitrate anions to create hydrogels with improved strength, responsiveness to external stimuli, and biocompatibility.
Key technological goals include optimizing the incorporation methods of Mg(NO3)2 into various hydrogel matrices, understanding the interaction mechanisms between the inorganic component and polymer chains, and tailoring the resulting properties for specific applications. These applications range from drug delivery systems and tissue engineering scaffolds to environmental sensors and actuators.
The integration of Mg(NO3)2 in hydrogels also aligns with broader trends in materials science, such as the development of self-healing materials, stimuli-responsive systems, and biomimetic structures. This research direction holds promise for addressing challenges in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and advanced manufacturing.
As the field progresses, researchers are exploring the synergistic effects of combining Mg(NO3)2 with other inorganic compounds or nanoparticles to create multi-functional composite hydrogels. This approach aims to further expand the capabilities and potential applications of these advanced materials.
The investigation of Mg(NO3)2 in functional composite hydrogels represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving area of research, with significant potential for technological breakthroughs and innovative applications. As this field continues to advance, it is expected to contribute to the development of next-generation smart materials and enable novel solutions to complex challenges across various industries.
Market Analysis for Functional Composite Hydrogels
The functional composite hydrogel market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing applications in various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and environmental remediation. The global market for functional hydrogels is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for advanced wound care products, drug delivery systems, and smart materials in diverse industries.
In the healthcare sector, functional composite hydrogels are gaining traction due to their biocompatibility, controlled release properties, and ability to mimic natural tissue environments. The aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic wounds are key factors driving the demand for hydrogel-based wound dressings and tissue engineering scaffolds. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry is leveraging these materials for targeted drug delivery systems, contributing to market expansion.
The agriculture sector presents another significant market opportunity for functional composite hydrogels. With growing concerns over water scarcity and the need for sustainable farming practices, hydrogels are being increasingly adopted for soil moisture retention and controlled release of fertilizers. This application is particularly relevant in arid and semi-arid regions, where water management is crucial for crop productivity.
Environmental applications of functional composite hydrogels are also on the rise. These materials show promise in water purification, heavy metal removal, and oil spill cleanup, addressing critical environmental challenges. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental protection is expected to drive further growth in this segment.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the functional composite hydrogel market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and significant research and development activities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of advanced materials in countries like China and India.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition and continuous innovation. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to enhance product performance and expand application areas. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are accelerating the development of novel hydrogel formulations, including those incorporating magnesium nitrate for specific functional properties.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and regulatory hurdles in certain applications may impact market growth. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing cross-industry applications are expected to mitigate these challenges, paving the way for sustained market expansion in the functional composite hydrogel sector.
In the healthcare sector, functional composite hydrogels are gaining traction due to their biocompatibility, controlled release properties, and ability to mimic natural tissue environments. The aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic wounds are key factors driving the demand for hydrogel-based wound dressings and tissue engineering scaffolds. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry is leveraging these materials for targeted drug delivery systems, contributing to market expansion.
The agriculture sector presents another significant market opportunity for functional composite hydrogels. With growing concerns over water scarcity and the need for sustainable farming practices, hydrogels are being increasingly adopted for soil moisture retention and controlled release of fertilizers. This application is particularly relevant in arid and semi-arid regions, where water management is crucial for crop productivity.
Environmental applications of functional composite hydrogels are also on the rise. These materials show promise in water purification, heavy metal removal, and oil spill cleanup, addressing critical environmental challenges. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental protection is expected to drive further growth in this segment.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the functional composite hydrogel market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and significant research and development activities. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of advanced materials in countries like China and India.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition and continuous innovation. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to enhance product performance and expand application areas. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are accelerating the development of novel hydrogel formulations, including those incorporating magnesium nitrate for specific functional properties.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high production costs and regulatory hurdles in certain applications may impact market growth. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing cross-industry applications are expected to mitigate these challenges, paving the way for sustained market expansion in the functional composite hydrogel sector.
Current Challenges in Mg(NO3)2-Hydrogel Integration
The integration of magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2) into functional composite hydrogels presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must address. One of the primary obstacles is achieving uniform distribution of Mg(NO3)2 within the hydrogel matrix. The ionic nature of magnesium nitrate can lead to aggregation and uneven dispersion, potentially compromising the mechanical and functional properties of the composite hydrogel.
Another critical challenge lies in maintaining the stability of the hydrogel structure in the presence of Mg(NO3)2. The introduction of ionic compounds can disrupt the crosslinking network of the hydrogel, potentially leading to decreased mechanical strength or altered swelling behavior. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring long-term stability or specific mechanical properties.
The release kinetics of Mg(NO3)2 from the hydrogel matrix pose another significant hurdle. Controlling the rate at which magnesium and nitrate ions are released is crucial for many applications, such as controlled drug delivery or nutrient release in agricultural settings. Achieving a sustained and predictable release profile while maintaining the structural integrity of the hydrogel remains a complex task.
Biocompatibility and potential toxicity concerns also present challenges, especially in biomedical applications. While magnesium is an essential element for biological processes, high concentrations of nitrate ions can be harmful. Balancing the beneficial effects of magnesium with the potential risks associated with nitrate requires careful consideration and extensive testing.
The interaction between Mg(NO3)2 and other components within the hydrogel system adds another layer of complexity. These interactions can affect the overall performance of the composite, including its mechanical properties, responsiveness to stimuli, and functionality. Understanding and controlling these interactions is essential for optimizing the composite hydrogel's performance.
Environmental factors, such as pH and temperature, can significantly impact the behavior of Mg(NO3)2-loaded hydrogels. Changes in these conditions may alter the solubility and release characteristics of the magnesium nitrate, affecting the overall performance and stability of the composite. Developing hydrogel systems that maintain consistent properties across a range of environmental conditions remains a significant challenge.
Scalability and manufacturing considerations also present obstacles in the practical application of Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites. Translating laboratory-scale successes to large-scale production while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a complex process that requires careful optimization of synthesis and processing parameters.
Another critical challenge lies in maintaining the stability of the hydrogel structure in the presence of Mg(NO3)2. The introduction of ionic compounds can disrupt the crosslinking network of the hydrogel, potentially leading to decreased mechanical strength or altered swelling behavior. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring long-term stability or specific mechanical properties.
The release kinetics of Mg(NO3)2 from the hydrogel matrix pose another significant hurdle. Controlling the rate at which magnesium and nitrate ions are released is crucial for many applications, such as controlled drug delivery or nutrient release in agricultural settings. Achieving a sustained and predictable release profile while maintaining the structural integrity of the hydrogel remains a complex task.
Biocompatibility and potential toxicity concerns also present challenges, especially in biomedical applications. While magnesium is an essential element for biological processes, high concentrations of nitrate ions can be harmful. Balancing the beneficial effects of magnesium with the potential risks associated with nitrate requires careful consideration and extensive testing.
The interaction between Mg(NO3)2 and other components within the hydrogel system adds another layer of complexity. These interactions can affect the overall performance of the composite, including its mechanical properties, responsiveness to stimuli, and functionality. Understanding and controlling these interactions is essential for optimizing the composite hydrogel's performance.
Environmental factors, such as pH and temperature, can significantly impact the behavior of Mg(NO3)2-loaded hydrogels. Changes in these conditions may alter the solubility and release characteristics of the magnesium nitrate, affecting the overall performance and stability of the composite. Developing hydrogel systems that maintain consistent properties across a range of environmental conditions remains a significant challenge.
Scalability and manufacturing considerations also present obstacles in the practical application of Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites. Translating laboratory-scale successes to large-scale production while maintaining consistent quality and performance is a complex process that requires careful optimization of synthesis and processing parameters.
Existing Mg(NO3)2-Hydrogel Composite Solutions
01 Incorporation of magnesium nitrate in hydrogel composites
Magnesium nitrate is incorporated into functional composite hydrogels to enhance their properties. This addition can improve the mechanical strength, water retention capacity, and overall performance of the hydrogel. The presence of magnesium ions can also contribute to the crosslinking of the polymer network, resulting in a more stable and durable hydrogel structure.- Incorporation of magnesium nitrate in hydrogel composites: Magnesium nitrate is incorporated into functional composite hydrogels to enhance their properties. This addition can improve the mechanical strength, water retention capacity, and overall performance of the hydrogel. The presence of magnesium ions can also contribute to the crosslinking of the polymer network, resulting in a more stable and durable hydrogel structure.
- Magnesium nitrate as a source of nutrients in agricultural hydrogels: Functional composite hydrogels containing magnesium nitrate are used in agricultural applications. The magnesium and nitrate ions serve as essential nutrients for plant growth, while the hydrogel matrix provides controlled release and improved water retention in soil. This combination enhances crop yield and reduces the frequency of fertilizer application.
- Use of magnesium nitrate in hydrogels for biomedical applications: Magnesium nitrate is incorporated into functional composite hydrogels for various biomedical applications. These hydrogels can be used for wound healing, drug delivery, and tissue engineering. The presence of magnesium ions can promote cell adhesion and proliferation, while the hydrogel matrix provides a suitable environment for tissue regeneration.
- Magnesium nitrate in hydrogels for environmental remediation: Functional composite hydrogels containing magnesium nitrate are utilized in environmental remediation processes. These hydrogels can effectively remove heavy metals and other pollutants from water and soil. The magnesium nitrate component enhances the adsorption capacity and selectivity of the hydrogel for specific contaminants.
- Synthesis methods for magnesium nitrate-containing hydrogels: Various synthesis methods are employed to incorporate magnesium nitrate into functional composite hydrogels. These methods include in-situ polymerization, solution mixing, and interpenetrating network formation. The choice of synthesis method affects the distribution of magnesium nitrate within the hydrogel matrix and influences the final properties of the composite.
02 Magnesium nitrate as a source of magnesium ions for biomedical applications
Functional composite hydrogels containing magnesium nitrate are utilized in biomedical applications. The controlled release of magnesium ions from the hydrogel matrix can promote tissue regeneration, enhance bone formation, and support various physiological processes. These hydrogels can be used in wound healing, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Magnesium nitrate in hydrogels for environmental remediation
Composite hydrogels incorporating magnesium nitrate are developed for environmental applications. These hydrogels can be used for water purification, removal of heavy metals, and soil remediation. The presence of magnesium nitrate enhances the adsorption capacity and ion exchange properties of the hydrogel, making it effective in removing contaminants from various environmental matrices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Magnesium nitrate-based hydrogels for energy storage applications
Functional composite hydrogels containing magnesium nitrate are explored for energy storage applications. These hydrogels can be used as electrolytes in batteries or supercapacitors, providing improved ionic conductivity and electrochemical performance. The presence of magnesium ions contributes to the overall energy storage capacity and cycling stability of the devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synthesis and characterization of magnesium nitrate-containing hydrogels
Various methods are developed for synthesizing and characterizing functional composite hydrogels containing magnesium nitrate. These techniques include in-situ polymerization, sol-gel processes, and freeze-drying methods. Advanced characterization techniques such as spectroscopy, microscopy, and rheology are employed to analyze the structure, morphology, and properties of these hydrogels, providing insights into their behavior and potential applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Functional Composite Hydrogel Industry
The research into magnesium nitrate in functional composite hydrogel applications is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as the technology matures. The global hydrogel market is expanding, driven by increasing applications in healthcare, agriculture, and consumer products. Key players in this field include academic institutions like Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, as well as companies such as Shanxi Jiaocheng Hongxing Chemicals Co. Ltd. and Hydro-Québec. These organizations are at various stages of research and development, with some focusing on fundamental science while others are moving towards commercialization. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing efforts to optimize performance and scalability.
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
Technical Solution: CNRS has developed innovative functional composite hydrogels incorporating magnesium nitrate for advanced applications. Their approach involves creating a network of cross-linked polymers with magnesium nitrate dispersed throughout the matrix. This results in hydrogels with enhanced mechanical properties and stimuli-responsive behavior[1]. The incorporation of magnesium nitrate allows for controlled ion release, making these hydrogels suitable for biomedical applications such as drug delivery and tissue engineering[2]. CNRS researchers have also explored the use of these composite hydrogels in environmental remediation, leveraging the ion exchange properties of magnesium nitrate for water purification[3].
Strengths: Excellent control over ion release kinetics, biocompatibility, and versatility in applications. Weaknesses: Potential issues with long-term stability and scalability of production processes.
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Technical Solution: EPFL has pioneered the development of smart composite hydrogels utilizing magnesium nitrate for energy storage and conversion applications. Their innovative approach involves the synthesis of nanostructured hydrogels with magnesium nitrate integrated into the polymer network at the molecular level[4]. This results in hydrogels with exceptional ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability. EPFL's research has demonstrated the potential of these materials in next-generation batteries and supercapacitors, offering high energy density and rapid charge-discharge capabilities[5]. Additionally, they have explored the use of these composite hydrogels in thermoelectric devices, leveraging the Seebeck effect enhanced by the presence of magnesium ions[6].
Strengths: High ionic conductivity, excellent electrochemical performance, and potential for energy harvesting applications. Weaknesses: Challenges in maintaining long-term stability under extreme conditions and potential high production costs.
Core Innovations in Mg(NO3)2-Hydrogel Technology
A process of synthesis and charecterization of NANO metal matrix composites
PatentActiveIN202041038828A
Innovation
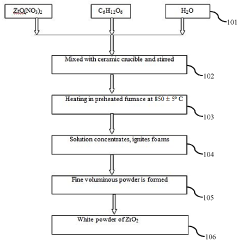
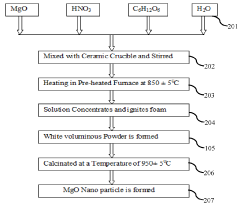
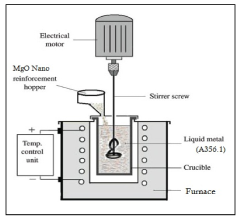
- A method involving the dissolution of zirconyle nitrate and crystalline sugar in double-distilled water, followed by preheating and boiling to form a transparent gel, which reacts to produce amorphous white powders with extremely porous structures, and subsequent calcination to create ZrO2 and MgO nano powders, which are then reinforced into an A356.1 aluminum alloy using the stir casting technique.
Environmental Impact of Mg(NO3)2-Hydrogel Composites
The environmental impact of Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites is a critical consideration in their development and application. These composites, which combine magnesium nitrate with hydrogel matrices, have shown promising potential in various fields, including agriculture, water treatment, and biomedical applications. However, their widespread use necessitates a thorough assessment of their environmental implications.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites is the potential release of nitrate ions into soil and water systems. Nitrate pollution is a well-documented environmental issue, contributing to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems and posing health risks to humans and animals when present in drinking water. The controlled release properties of these composites may mitigate this risk to some extent, but long-term studies are needed to fully understand the leaching behavior of nitrates from these materials under various environmental conditions.
The biodegradability of the hydrogel component is another crucial factor in evaluating the environmental impact. While many hydrogels are designed to be biodegradable, the rate and products of degradation can vary significantly depending on the specific polymer composition. The interaction between the degrading hydrogel and the released magnesium nitrate must be carefully studied to ensure that no harmful byproducts are formed during the breakdown process.
The production and disposal of Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites also warrant consideration from an environmental perspective. The synthesis of these materials often involves chemical processes that may generate waste or require significant energy inputs. Implementing green chemistry principles in the manufacturing process could help minimize the environmental footprint of production. Additionally, the end-of-life management of these composites, including recycling or disposal options, needs to be addressed to prevent accumulation in landfills or environmental contamination.
On the positive side, Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites have the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. In agriculture, their use as controlled-release fertilizers could reduce overall fertilizer application rates, thereby decreasing nutrient runoff and associated environmental problems. In water treatment applications, these composites could aid in the removal of contaminants, potentially improving water quality in both natural and engineered systems.
The environmental impact of these composites is also closely tied to their performance efficiency. If they can significantly enhance crop yields or improve water treatment processes, the net environmental benefit could outweigh the potential risks associated with their use. However, this balance must be carefully evaluated through comprehensive life cycle assessments that consider all stages from production to disposal.
In conclusion, while Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites offer promising applications with potential environmental benefits, their widespread adoption must be preceded by thorough environmental impact assessments. Future research should focus on optimizing the composition and design of these materials to maximize their beneficial properties while minimizing any negative environmental consequences.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites is the potential release of nitrate ions into soil and water systems. Nitrate pollution is a well-documented environmental issue, contributing to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems and posing health risks to humans and animals when present in drinking water. The controlled release properties of these composites may mitigate this risk to some extent, but long-term studies are needed to fully understand the leaching behavior of nitrates from these materials under various environmental conditions.
The biodegradability of the hydrogel component is another crucial factor in evaluating the environmental impact. While many hydrogels are designed to be biodegradable, the rate and products of degradation can vary significantly depending on the specific polymer composition. The interaction between the degrading hydrogel and the released magnesium nitrate must be carefully studied to ensure that no harmful byproducts are formed during the breakdown process.
The production and disposal of Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites also warrant consideration from an environmental perspective. The synthesis of these materials often involves chemical processes that may generate waste or require significant energy inputs. Implementing green chemistry principles in the manufacturing process could help minimize the environmental footprint of production. Additionally, the end-of-life management of these composites, including recycling or disposal options, needs to be addressed to prevent accumulation in landfills or environmental contamination.
On the positive side, Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites have the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability in several ways. In agriculture, their use as controlled-release fertilizers could reduce overall fertilizer application rates, thereby decreasing nutrient runoff and associated environmental problems. In water treatment applications, these composites could aid in the removal of contaminants, potentially improving water quality in both natural and engineered systems.
The environmental impact of these composites is also closely tied to their performance efficiency. If they can significantly enhance crop yields or improve water treatment processes, the net environmental benefit could outweigh the potential risks associated with their use. However, this balance must be carefully evaluated through comprehensive life cycle assessments that consider all stages from production to disposal.
In conclusion, while Mg(NO3)2-hydrogel composites offer promising applications with potential environmental benefits, their widespread adoption must be preceded by thorough environmental impact assessments. Future research should focus on optimizing the composition and design of these materials to maximize their beneficial properties while minimizing any negative environmental consequences.
Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
The scalability and manufacturing considerations for functional composite hydrogels incorporating magnesium nitrate are crucial aspects that determine the feasibility of large-scale production and commercial viability. One of the primary challenges in scaling up the production of these hydrogels is maintaining consistent quality and performance across batches. The incorporation of magnesium nitrate into the hydrogel matrix requires precise control over the mixing and crosslinking processes to ensure uniform distribution and optimal functionality.
To address these challenges, advanced manufacturing techniques such as continuous flow reactors and microfluidic systems can be employed. These methods offer better control over reaction conditions and can produce hydrogels with more consistent properties. Additionally, the use of automated systems for material handling and quality control can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of the manufacturing process.
The choice of raw materials and their sourcing also play a critical role in scalability. Ensuring a stable supply chain for high-quality magnesium nitrate and other hydrogel components is essential for consistent production. Manufacturers may need to establish partnerships with reliable suppliers or consider vertical integration to secure their material needs.
Another important consideration is the development of cost-effective production methods. As the scale of production increases, opportunities for process optimization and cost reduction emerge. This may involve exploring alternative crosslinking methods, optimizing the use of reagents, or developing more efficient purification and drying techniques for the final product.
Environmental and safety considerations must also be addressed in the scaling process. The handling of magnesium nitrate and other chemicals used in hydrogel production requires strict safety protocols and waste management procedures. Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes can help minimize environmental impact and improve overall sustainability.
Packaging and storage of the final product present additional challenges. The hydrogels must maintain their properties during transportation and storage, which may require specialized packaging solutions or the development of dehydrated forms that can be rehydrated before use.
Regulatory compliance is another critical factor in scaling up production. Manufacturers must ensure that their processes and products meet all relevant safety and quality standards, particularly for applications in biomedical or food-related fields. This may involve extensive documentation, validation studies, and potentially clinical trials for certain applications.
To address these challenges, advanced manufacturing techniques such as continuous flow reactors and microfluidic systems can be employed. These methods offer better control over reaction conditions and can produce hydrogels with more consistent properties. Additionally, the use of automated systems for material handling and quality control can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of the manufacturing process.
The choice of raw materials and their sourcing also play a critical role in scalability. Ensuring a stable supply chain for high-quality magnesium nitrate and other hydrogel components is essential for consistent production. Manufacturers may need to establish partnerships with reliable suppliers or consider vertical integration to secure their material needs.
Another important consideration is the development of cost-effective production methods. As the scale of production increases, opportunities for process optimization and cost reduction emerge. This may involve exploring alternative crosslinking methods, optimizing the use of reagents, or developing more efficient purification and drying techniques for the final product.
Environmental and safety considerations must also be addressed in the scaling process. The handling of magnesium nitrate and other chemicals used in hydrogel production requires strict safety protocols and waste management procedures. Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes can help minimize environmental impact and improve overall sustainability.
Packaging and storage of the final product present additional challenges. The hydrogels must maintain their properties during transportation and storage, which may require specialized packaging solutions or the development of dehydrated forms that can be rehydrated before use.
Regulatory compliance is another critical factor in scaling up production. Manufacturers must ensure that their processes and products meet all relevant safety and quality standards, particularly for applications in biomedical or food-related fields. This may involve extensive documentation, validation studies, and potentially clinical trials for certain applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!