K24 Engine Market Trends: Predicting Future Automotive Shifts
JUL 3, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
K24 Engine Evolution
The K24 engine, a prominent member of Honda's K-series engine family, has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the early 2000s. Initially designed as a 2.4-liter inline-four engine, the K24 has been continuously refined to meet changing market demands and regulatory requirements.
In its early iterations, the K24 engine focused primarily on delivering a balance of power and fuel efficiency for Honda's midsize vehicles. The first-generation K24A1 engine, introduced in 2002, produced around 160 horsepower and 161 lb-ft of torque. This engine quickly gained popularity for its smooth power delivery and reliability.
As environmental concerns grew and fuel economy standards became more stringent, Honda engineers worked to improve the K24's efficiency without sacrificing performance. The introduction of i-VTEC (intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) technology marked a significant milestone in the K24's evolution. This innovation allowed for better control over valve timing and lift, resulting in improved fuel economy and increased power output across a broader RPM range.
The mid-2000s saw the K24 engine receiving further enhancements, including the implementation of drive-by-wire throttle systems and more advanced engine management computers. These upgrades not only improved responsiveness but also allowed for better integration with emerging vehicle technologies such as traction control and stability systems.
As the automotive industry began shifting towards electrification, Honda adapted the K24 engine to serve in hybrid powertrains. The development of the Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) system, which paired the K24 with an electric motor, represented a significant step in the engine's evolution. This hybrid application demonstrated the K24's versatility and Honda's commitment to reducing emissions while maintaining performance.
In recent years, the K24 has seen further refinements to meet increasingly stringent emissions standards. The introduction of direct injection technology in some variants has improved fuel atomization, leading to more complete combustion and reduced emissions. Additionally, the integration of start-stop systems has helped to reduce fuel consumption in urban driving conditions.
Looking towards the future, the K24 engine is likely to continue evolving to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing automotive landscape. While pure electric vehicles are gaining market share, internal combustion engines like the K24 are expected to play a crucial role in the transition period. Potential future developments may include more advanced hybrid systems, further improvements in thermal efficiency, and possibly even adaptation for use with alternative fuels.
In its early iterations, the K24 engine focused primarily on delivering a balance of power and fuel efficiency for Honda's midsize vehicles. The first-generation K24A1 engine, introduced in 2002, produced around 160 horsepower and 161 lb-ft of torque. This engine quickly gained popularity for its smooth power delivery and reliability.
As environmental concerns grew and fuel economy standards became more stringent, Honda engineers worked to improve the K24's efficiency without sacrificing performance. The introduction of i-VTEC (intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) technology marked a significant milestone in the K24's evolution. This innovation allowed for better control over valve timing and lift, resulting in improved fuel economy and increased power output across a broader RPM range.
The mid-2000s saw the K24 engine receiving further enhancements, including the implementation of drive-by-wire throttle systems and more advanced engine management computers. These upgrades not only improved responsiveness but also allowed for better integration with emerging vehicle technologies such as traction control and stability systems.
As the automotive industry began shifting towards electrification, Honda adapted the K24 engine to serve in hybrid powertrains. The development of the Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) system, which paired the K24 with an electric motor, represented a significant step in the engine's evolution. This hybrid application demonstrated the K24's versatility and Honda's commitment to reducing emissions while maintaining performance.
In recent years, the K24 has seen further refinements to meet increasingly stringent emissions standards. The introduction of direct injection technology in some variants has improved fuel atomization, leading to more complete combustion and reduced emissions. Additionally, the integration of start-stop systems has helped to reduce fuel consumption in urban driving conditions.
Looking towards the future, the K24 engine is likely to continue evolving to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing automotive landscape. While pure electric vehicles are gaining market share, internal combustion engines like the K24 are expected to play a crucial role in the transition period. Potential future developments may include more advanced hybrid systems, further improvements in thermal efficiency, and possibly even adaptation for use with alternative fuels.
Market Demand Analysis
The K24 engine market is experiencing significant shifts driven by evolving consumer preferences, stringent environmental regulations, and technological advancements in the automotive industry. As global awareness of climate change intensifies, there is a growing demand for more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. This trend has led to increased interest in hybrid and electric powertrains, potentially impacting the traditional K24 engine market.
Despite the push towards electrification, the K24 engine still maintains a strong presence in certain market segments. Its reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness continue to appeal to a substantial consumer base, particularly in regions where electric vehicle infrastructure is still developing. The aftermarket and performance tuning sectors also contribute to sustained demand for K24 engines, as enthusiasts appreciate its modifiability and potential for power enhancement.
In emerging markets, where affordability remains a key factor, the K24 engine offers a balanced solution between performance and cost. These regions are expected to drive significant demand in the coming years as their automotive industries expand and mature. Additionally, the K24 engine's versatility allows it to be adapted for various vehicle types, from compact cars to SUVs, further broadening its market appeal.
The commercial vehicle sector presents another avenue for K24 engine demand. Light commercial vehicles and small trucks often prioritize reliability and longevity, attributes for which the K24 engine is well-known. As e-commerce and last-mile delivery services continue to grow, this segment could see increased demand for vehicles equipped with K24 engines.
However, the market is not without challenges. Tightening emissions standards in many countries are putting pressure on manufacturers to improve engine efficiency or transition to alternative powertrains. This regulatory landscape is likely to shape future demand patterns for the K24 engine, potentially leading to innovations in engine design or hybrid implementations to meet these standards.
The used car market also plays a role in shaping demand for K24 engines. As vehicles equipped with these engines enter the secondary market, they offer an affordable option for budget-conscious consumers, potentially extending the lifecycle and relevance of K24 technology.
Looking ahead, the K24 engine market is expected to undergo a gradual transformation. While immediate demand remains strong in certain sectors, long-term trends suggest a shift towards more efficient or alternative powertrain solutions. Manufacturers and suppliers in the K24 ecosystem will need to adapt to these changing market dynamics, potentially exploring hybrid technologies or focusing on niche applications where the K24 engine's strengths can be leveraged most effectively.
Despite the push towards electrification, the K24 engine still maintains a strong presence in certain market segments. Its reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness continue to appeal to a substantial consumer base, particularly in regions where electric vehicle infrastructure is still developing. The aftermarket and performance tuning sectors also contribute to sustained demand for K24 engines, as enthusiasts appreciate its modifiability and potential for power enhancement.
In emerging markets, where affordability remains a key factor, the K24 engine offers a balanced solution between performance and cost. These regions are expected to drive significant demand in the coming years as their automotive industries expand and mature. Additionally, the K24 engine's versatility allows it to be adapted for various vehicle types, from compact cars to SUVs, further broadening its market appeal.
The commercial vehicle sector presents another avenue for K24 engine demand. Light commercial vehicles and small trucks often prioritize reliability and longevity, attributes for which the K24 engine is well-known. As e-commerce and last-mile delivery services continue to grow, this segment could see increased demand for vehicles equipped with K24 engines.
However, the market is not without challenges. Tightening emissions standards in many countries are putting pressure on manufacturers to improve engine efficiency or transition to alternative powertrains. This regulatory landscape is likely to shape future demand patterns for the K24 engine, potentially leading to innovations in engine design or hybrid implementations to meet these standards.
The used car market also plays a role in shaping demand for K24 engines. As vehicles equipped with these engines enter the secondary market, they offer an affordable option for budget-conscious consumers, potentially extending the lifecycle and relevance of K24 technology.
Looking ahead, the K24 engine market is expected to undergo a gradual transformation. While immediate demand remains strong in certain sectors, long-term trends suggest a shift towards more efficient or alternative powertrain solutions. Manufacturers and suppliers in the K24 ecosystem will need to adapt to these changing market dynamics, potentially exploring hybrid technologies or focusing on niche applications where the K24 engine's strengths can be leveraged most effectively.
Technical Challenges
The K24 engine, while a popular choice in the automotive industry, faces several technical challenges that could impact its future market trends. One of the primary issues is meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide. As governments push for cleaner transportation, the K24 engine must adapt to reduce its carbon footprint and improve fuel efficiency without compromising performance.
Another significant challenge lies in the engine's compatibility with hybrid and electrification technologies. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, integrating the K24 engine into hybrid powertrains presents complex engineering hurdles. This includes optimizing the engine's performance when working in tandem with electric motors and ensuring seamless transitions between power sources.
The K24 engine also faces challenges in terms of weight reduction and compact design. As vehicle manufacturers strive for improved fuel economy and handling, there is a growing demand for lighter, more compact engines. Engineers must find innovative ways to reduce the K24's weight and size while maintaining its power output and reliability.
Durability and longevity present another set of technical challenges. With consumers expecting longer-lasting vehicles, the K24 engine must be designed to withstand increased mileage and more demanding operating conditions. This requires advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes to enhance engine durability without significantly increasing production costs.
The engine's adaptability to alternative fuels is another area of concern. As the market explores options like biofuels and synthetic fuels, the K24 engine needs to be flexible enough to accommodate these new fuel types without major modifications or performance losses.
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) reduction is an ongoing challenge for the K24 engine. As consumer expectations for quieter and smoother-running vehicles increase, engineers must continually refine the engine's design to minimize unwanted noise and vibrations.
Lastly, the K24 engine faces challenges in thermal management. As power outputs increase and engine bays become more compact, efficient cooling becomes crucial. Developing advanced cooling systems that can maintain optimal operating temperatures under various conditions is essential for the engine's performance and longevity.
These technical challenges collectively shape the future of the K24 engine in the automotive market. Overcoming them will be crucial for maintaining its relevance and competitiveness in an evolving industry landscape.
Another significant challenge lies in the engine's compatibility with hybrid and electrification technologies. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, integrating the K24 engine into hybrid powertrains presents complex engineering hurdles. This includes optimizing the engine's performance when working in tandem with electric motors and ensuring seamless transitions between power sources.
The K24 engine also faces challenges in terms of weight reduction and compact design. As vehicle manufacturers strive for improved fuel economy and handling, there is a growing demand for lighter, more compact engines. Engineers must find innovative ways to reduce the K24's weight and size while maintaining its power output and reliability.
Durability and longevity present another set of technical challenges. With consumers expecting longer-lasting vehicles, the K24 engine must be designed to withstand increased mileage and more demanding operating conditions. This requires advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes to enhance engine durability without significantly increasing production costs.
The engine's adaptability to alternative fuels is another area of concern. As the market explores options like biofuels and synthetic fuels, the K24 engine needs to be flexible enough to accommodate these new fuel types without major modifications or performance losses.
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) reduction is an ongoing challenge for the K24 engine. As consumer expectations for quieter and smoother-running vehicles increase, engineers must continually refine the engine's design to minimize unwanted noise and vibrations.
Lastly, the K24 engine faces challenges in thermal management. As power outputs increase and engine bays become more compact, efficient cooling becomes crucial. Developing advanced cooling systems that can maintain optimal operating temperatures under various conditions is essential for the engine's performance and longevity.
These technical challenges collectively shape the future of the K24 engine in the automotive market. Overcoming them will be crucial for maintaining its relevance and competitiveness in an evolving industry landscape.
Current K24 Solutions
01 Engine design and structure
The K24 engine is a 2.4-liter inline-four cylinder engine known for its compact design and efficient performance. It features a lightweight aluminum block and cylinder head, dual overhead camshafts, and i-VTEC technology for improved power and fuel efficiency. The engine's design allows for easy integration into various vehicle models and applications.- Engine design and components: The K24 engine is a 2.4-liter inline-four engine known for its design and components. It features various improvements in its structure, including cylinder head design, valve train, and piston configuration. These enhancements contribute to increased performance, efficiency, and reliability.
- Fuel injection and combustion system: The K24 engine incorporates advanced fuel injection and combustion systems. This includes direct injection technology, variable valve timing, and optimized combustion chamber design. These features help improve fuel efficiency, power output, and emissions control.
- Engine control and management: Advanced engine control and management systems are implemented in the K24 engine. This includes electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and actuators that monitor and adjust various engine parameters in real-time. These systems optimize performance, fuel economy, and emissions across different operating conditions.
- Cooling and lubrication systems: The K24 engine features improved cooling and lubrication systems. This includes optimized coolant flow, enhanced oil circulation, and temperature management. These systems help maintain optimal engine operating temperatures and reduce wear, contributing to increased durability and longevity.
- Performance enhancements and modifications: Various performance enhancements and modifications are available for the K24 engine. These may include aftermarket components, tuning options, and upgrades to improve power output, torque, and overall engine performance. Such modifications cater to enthusiasts seeking to maximize the engine's potential.
02 Fuel injection and combustion system
The K24 engine utilizes advanced fuel injection and combustion systems to optimize performance and emissions. It incorporates direct fuel injection technology, variable valve timing, and precise electronic control to enhance fuel atomization and combustion efficiency. These features contribute to improved power output, reduced fuel consumption, and lower emissions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Engine management and control systems
Advanced engine management and control systems are employed in the K24 engine to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. These systems include electronic throttle control, engine control units (ECU) with sophisticated algorithms, and various sensors to monitor and adjust engine parameters in real-time. The integration of these systems ensures optimal engine operation under various driving conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Engine cooling and lubrication
The K24 engine incorporates efficient cooling and lubrication systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and reduce wear. The cooling system may include advanced radiator designs, electric water pumps, and precise temperature control. The lubrication system ensures proper oil distribution throughout the engine, utilizing features such as variable displacement oil pumps and advanced filtration systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Engine accessories and integration
Various accessories and components are designed to integrate seamlessly with the K24 engine, enhancing its overall performance and functionality. These may include specialized intake and exhaust systems, turbochargers or superchargers for increased power output, and advanced alternators for improved electrical efficiency. The engine's design allows for easy integration of these components while maintaining compact dimensions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The K24 Engine Market is in a mature stage, characterized by established players and steady growth. The global market size is substantial, driven by increasing automotive production and demand for fuel-efficient engines. Technologically, the K24 engine has reached a high level of maturity, with ongoing refinements focused on performance and emissions. Key players like Honda Motor Co., Ford Global Technologies, and GM Global Technology Operations are leading innovation, while universities such as Tianjin University and Jilin University contribute to research and development. Emerging trends include the integration of hybrid technologies and advanced materials to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's K24 engine market strategy focuses on enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions while maintaining performance. They are developing advanced combustion technologies, including direct injection and variable valve timing, to optimize the K24 engine's efficiency[1]. Ford is also exploring hybrid integration with the K24 platform to meet stricter emissions regulations[2]. Their research includes lightweight materials and improved thermal management systems to further boost engine performance and fuel economy[3]. Ford is investing in predictive maintenance technologies for K24 engines, utilizing AI and IoT sensors to anticipate service needs and reduce downtime[4].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, extensive market presence, and established supply chain. Weaknesses: High development costs and potential challenges in rapidly adapting to full electrification trends.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's approach to the K24 engine market involves a dual strategy of improving internal combustion efficiency while transitioning to electrification. They are developing advanced K24 variants with cylinder deactivation technology and start-stop systems to enhance fuel economy[1]. GM is also investing in mild hybrid systems compatible with K24 engines to bridge the gap between traditional ICE and full electric vehicles[2]. Their research extends to alternative fuels, exploring the potential of hydrogen and synthetic fuels in K24 engines to reduce carbon footprint[3]. GM is leveraging big data analytics to optimize K24 engine performance across various driving conditions and usage patterns[4].
Strengths: Diverse powertrain portfolio, strong financial resources for R&D. Weaknesses: Balancing investment between ICE improvements and EV development.
K24 Innovations
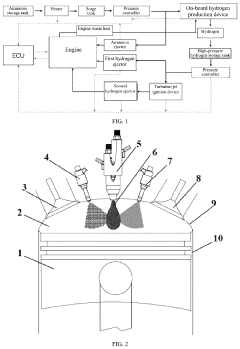
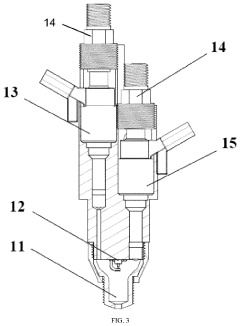
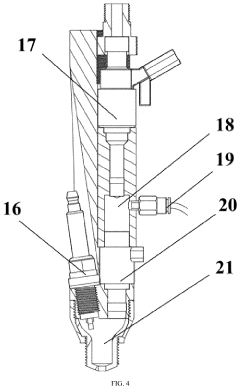
Ammonia-hydrogen fusion fuel diffusion combustion control system based on reactivity regulation
PatentInactiveUS20240018915A1
Innovation
- An ammonia-hydrogen fusion fuel diffusion combustion control system with a compact scavenging type precombustion chamber and ECU control, where hydrogen is injected to form a reactive environment, and ammonia is injected near top dead center, either before or synchronous with the precombustion chamber jet flame formation, to achieve diffusion combustion in the main combustion chamber.
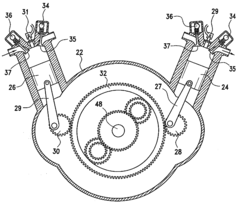
Power train for motor vehicles or the like
PatentInactiveUS20080188340A1
Innovation
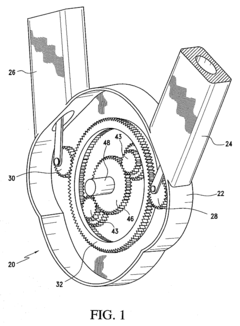
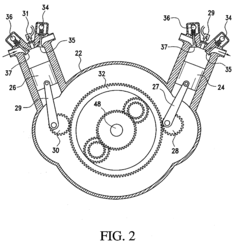
- A power train design that eliminates the crankshaft and flywheel by using a planetary gear system to convert linear piston motion into rotational motion, incorporating a single sump for lubrication, extending the engine cooling system to the gearbox, and employing roller bearings to reduce friction and heat, while allowing for removable cylinders and disengagement during braking.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of the K24 engine market and automotive industry as a whole. As governments worldwide intensify their efforts to combat climate change and reduce air pollution, stringent emission standards are being implemented across major automotive markets.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues to tighten regulations on vehicle emissions. The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which aim to improve fuel efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, are expected to become more stringent in the coming years. This regulatory pressure is driving automakers to invest heavily in cleaner engine technologies, including improvements to the K24 engine platform.
The European Union has also set ambitious targets for reducing CO2 emissions from new cars. The Euro 7 emission standards, set to be implemented in the near future, will further limit pollutant emissions from vehicles. These regulations are pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient K24 engines or consider alternative powertrains to meet the increasingly strict requirements.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has introduced its own set of emission standards modeled after European regulations. The China 6 standards, which are being phased in across the country, are among the most stringent in the world. This regulatory environment is forcing automakers to adapt their K24 engine designs to comply with these strict emission limits.
The global trend towards electrification is also influencing emission regulations. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines in favor of electric vehicles. This shift is putting pressure on manufacturers to improve the efficiency and cleanliness of K24 engines while also investing in hybrid and electric technologies.
As emission regulations continue to evolve, the K24 engine market is likely to see significant changes. Manufacturers may need to incorporate advanced technologies such as improved fuel injection systems, exhaust gas recirculation, and more efficient catalytic converters to meet these stringent standards. Additionally, the integration of mild hybrid systems with K24 engines could become more prevalent as a way to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy.
The impact of these regulations extends beyond just engine design. They are driving changes in vehicle architecture, materials used, and overall powertrain strategies. As a result, the future of the K24 engine market will be closely tied to how well manufacturers can adapt to these evolving regulatory landscapes while still meeting consumer demands for performance and affordability.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues to tighten regulations on vehicle emissions. The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which aim to improve fuel efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, are expected to become more stringent in the coming years. This regulatory pressure is driving automakers to invest heavily in cleaner engine technologies, including improvements to the K24 engine platform.
The European Union has also set ambitious targets for reducing CO2 emissions from new cars. The Euro 7 emission standards, set to be implemented in the near future, will further limit pollutant emissions from vehicles. These regulations are pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient K24 engines or consider alternative powertrains to meet the increasingly strict requirements.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has introduced its own set of emission standards modeled after European regulations. The China 6 standards, which are being phased in across the country, are among the most stringent in the world. This regulatory environment is forcing automakers to adapt their K24 engine designs to comply with these strict emission limits.
The global trend towards electrification is also influencing emission regulations. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines in favor of electric vehicles. This shift is putting pressure on manufacturers to improve the efficiency and cleanliness of K24 engines while also investing in hybrid and electric technologies.
As emission regulations continue to evolve, the K24 engine market is likely to see significant changes. Manufacturers may need to incorporate advanced technologies such as improved fuel injection systems, exhaust gas recirculation, and more efficient catalytic converters to meet these stringent standards. Additionally, the integration of mild hybrid systems with K24 engines could become more prevalent as a way to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy.
The impact of these regulations extends beyond just engine design. They are driving changes in vehicle architecture, materials used, and overall powertrain strategies. As a result, the future of the K24 engine market will be closely tied to how well manufacturers can adapt to these evolving regulatory landscapes while still meeting consumer demands for performance and affordability.
Alternative Powertrains
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with alternative powertrains emerging as a key driver of change. As traditional internal combustion engines face increasing scrutiny due to environmental concerns, manufacturers are exploring various alternative powertrain technologies to meet stringent emissions regulations and consumer demands for more sustainable transportation options.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained substantial traction in recent years, with major automakers investing heavily in battery technology and charging infrastructure. The rapid advancement in battery energy density and decreasing costs are making EVs more accessible to a broader market. However, challenges such as limited range and long charging times still persist, prompting ongoing research and development efforts.
Hybrid powertrains, combining internal combustion engines with electric motors, continue to serve as a transitional technology. They offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions while alleviating range anxiety associated with pure electric vehicles. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are gaining popularity, providing the flexibility of short all-electric trips and extended range using conventional fuel.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent another promising alternative powertrain technology. While still in the early stages of commercialization, fuel cell vehicles offer quick refueling times and long-range capabilities. However, the lack of widespread hydrogen infrastructure and high production costs remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) powertrains continue to find applications in certain markets, particularly for commercial vehicles and fleet operations. These alternative fuels offer reduced emissions compared to traditional gasoline and diesel engines, though their adoption is often limited by the availability of refueling stations.
The development of synthetic fuels and biofuels is also progressing, with the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of existing internal combustion engines. These alternative fuels could play a crucial role in the transition period, allowing for the continued use of conventional engine technology while reducing overall emissions.
As the automotive industry shifts towards alternative powertrains, the K24 engine market is likely to face challenges. Manufacturers may need to adapt their production strategies and invest in new technologies to remain competitive in an evolving landscape. The transition to alternative powertrains will likely be gradual, with different technologies coexisting in the market for the foreseeable future.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained substantial traction in recent years, with major automakers investing heavily in battery technology and charging infrastructure. The rapid advancement in battery energy density and decreasing costs are making EVs more accessible to a broader market. However, challenges such as limited range and long charging times still persist, prompting ongoing research and development efforts.
Hybrid powertrains, combining internal combustion engines with electric motors, continue to serve as a transitional technology. They offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions while alleviating range anxiety associated with pure electric vehicles. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are gaining popularity, providing the flexibility of short all-electric trips and extended range using conventional fuel.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent another promising alternative powertrain technology. While still in the early stages of commercialization, fuel cell vehicles offer quick refueling times and long-range capabilities. However, the lack of widespread hydrogen infrastructure and high production costs remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) powertrains continue to find applications in certain markets, particularly for commercial vehicles and fleet operations. These alternative fuels offer reduced emissions compared to traditional gasoline and diesel engines, though their adoption is often limited by the availability of refueling stations.
The development of synthetic fuels and biofuels is also progressing, with the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of existing internal combustion engines. These alternative fuels could play a crucial role in the transition period, allowing for the continued use of conventional engine technology while reducing overall emissions.
As the automotive industry shifts towards alternative powertrains, the K24 engine market is likely to face challenges. Manufacturers may need to adapt their production strategies and invest in new technologies to remain competitive in an evolving landscape. The transition to alternative powertrains will likely be gradual, with different technologies coexisting in the market for the foreseeable future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!