Latest Research on Carboxylic Acid for Sustainable Lab Practices
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Research Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acids have been a cornerstone of organic chemistry for centuries, playing crucial roles in various industrial and biological processes. In recent years, the focus on sustainable laboratory practices has brought renewed attention to these versatile compounds. The evolution of carboxylic acid research has been marked by significant milestones, from their initial discovery to their current applications in green chemistry.
The primary objective of current research on carboxylic acids for sustainable lab practices is to develop environmentally friendly synthesis methods, explore novel applications, and optimize their use in various chemical processes. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing the environmental impact of laboratory operations and promoting sustainable science.
Historically, carboxylic acids were first identified in natural sources, such as acetic acid in vinegar. As analytical techniques advanced, scientists began to understand their molecular structure and chemical properties. The 20th century saw rapid progress in synthetic methods for carboxylic acids, leading to their widespread use in industry and research.
In the context of sustainable lab practices, carboxylic acids are being investigated for their potential to replace more harmful chemicals in various processes. Their relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and ability to form a wide range of derivatives make them attractive candidates for green chemistry applications.
Current research trends focus on several key areas. One is the development of bio-based production methods for carboxylic acids, utilizing renewable resources and enzymatic processes. Another area of interest is the use of carboxylic acids as green solvents, potentially replacing traditional organic solvents that pose environmental and health risks.
Researchers are also exploring the role of carboxylic acids in sustainable catalysis. Their ability to act as both Brønsted and Lewis acids makes them valuable in various catalytic processes, potentially reducing the need for metal-based catalysts.
The application of carboxylic acids in sustainable materials science is another growing field. They are being investigated for use in biodegradable polymers, environmentally friendly coatings, and advanced materials with reduced environmental impact.
As we look to the future, the research on carboxylic acids for sustainable lab practices is expected to expand further. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and high-throughput screening are likely to accelerate the discovery of new applications and optimization of existing processes. The integration of carboxylic acid chemistry with other sustainable technologies, such as flow chemistry and renewable energy, presents exciting opportunities for innovation in green chemistry.
The primary objective of current research on carboxylic acids for sustainable lab practices is to develop environmentally friendly synthesis methods, explore novel applications, and optimize their use in various chemical processes. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing the environmental impact of laboratory operations and promoting sustainable science.
Historically, carboxylic acids were first identified in natural sources, such as acetic acid in vinegar. As analytical techniques advanced, scientists began to understand their molecular structure and chemical properties. The 20th century saw rapid progress in synthetic methods for carboxylic acids, leading to their widespread use in industry and research.
In the context of sustainable lab practices, carboxylic acids are being investigated for their potential to replace more harmful chemicals in various processes. Their relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and ability to form a wide range of derivatives make them attractive candidates for green chemistry applications.
Current research trends focus on several key areas. One is the development of bio-based production methods for carboxylic acids, utilizing renewable resources and enzymatic processes. Another area of interest is the use of carboxylic acids as green solvents, potentially replacing traditional organic solvents that pose environmental and health risks.
Researchers are also exploring the role of carboxylic acids in sustainable catalysis. Their ability to act as both Brønsted and Lewis acids makes them valuable in various catalytic processes, potentially reducing the need for metal-based catalysts.
The application of carboxylic acids in sustainable materials science is another growing field. They are being investigated for use in biodegradable polymers, environmentally friendly coatings, and advanced materials with reduced environmental impact.
As we look to the future, the research on carboxylic acids for sustainable lab practices is expected to expand further. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and high-throughput screening are likely to accelerate the discovery of new applications and optimization of existing processes. The integration of carboxylic acid chemistry with other sustainable technologies, such as flow chemistry and renewable energy, presents exciting opportunities for innovation in green chemistry.
Sustainable Lab Practices Market Analysis
The sustainable lab practices market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for more eco-friendly research methodologies. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services designed to reduce the environmental impact of laboratory operations, including energy-efficient equipment, waste reduction solutions, and sustainable chemical alternatives.
The global market for sustainable lab practices is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including stringent environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and a growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility in the scientific community.
One of the key segments within this market is the development and adoption of sustainable chemical alternatives, such as carboxylic acids. These compounds are gaining traction due to their versatility, biodegradability, and potential to replace more harmful chemicals in various laboratory applications. The demand for carboxylic acids in sustainable lab practices is particularly notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and environmental testing.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has been a major driver of growth in the sustainable lab practices market. With increasing pressure to reduce the environmental footprint of drug discovery and development processes, pharmaceutical companies are actively seeking sustainable alternatives for their research and production activities. This trend has led to a surge in demand for eco-friendly solvents, reagents, and catalysts, including carboxylic acids.
In the biotechnology sector, the adoption of sustainable lab practices is being driven by the need for more efficient and environmentally friendly bioprocessing techniques. Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in this context, serving as building blocks for various biomolecules and as pH regulators in fermentation processes. The growing emphasis on bio-based products and green chemistry in this sector is expected to further boost the demand for sustainable chemical alternatives.
Environmental testing laboratories represent another significant market segment for sustainable lab practices. As these facilities are at the forefront of monitoring and assessing environmental quality, there is a growing imperative to adopt more sustainable methodologies. Carboxylic acids are increasingly being used in environmental analysis techniques, offering improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional chemical reagents.
The market for sustainable lab practices is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Large scientific equipment manufacturers are expanding their product lines to include more sustainable options, while specialized companies are emerging to address specific niches within the market. This competitive landscape is driving innovation and helping to accelerate the adoption of sustainable technologies in laboratories worldwide.
The global market for sustainable lab practices is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is fueled by several factors, including stringent environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and a growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility in the scientific community.
One of the key segments within this market is the development and adoption of sustainable chemical alternatives, such as carboxylic acids. These compounds are gaining traction due to their versatility, biodegradability, and potential to replace more harmful chemicals in various laboratory applications. The demand for carboxylic acids in sustainable lab practices is particularly notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and environmental testing.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has been a major driver of growth in the sustainable lab practices market. With increasing pressure to reduce the environmental footprint of drug discovery and development processes, pharmaceutical companies are actively seeking sustainable alternatives for their research and production activities. This trend has led to a surge in demand for eco-friendly solvents, reagents, and catalysts, including carboxylic acids.
In the biotechnology sector, the adoption of sustainable lab practices is being driven by the need for more efficient and environmentally friendly bioprocessing techniques. Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in this context, serving as building blocks for various biomolecules and as pH regulators in fermentation processes. The growing emphasis on bio-based products and green chemistry in this sector is expected to further boost the demand for sustainable chemical alternatives.
Environmental testing laboratories represent another significant market segment for sustainable lab practices. As these facilities are at the forefront of monitoring and assessing environmental quality, there is a growing imperative to adopt more sustainable methodologies. Carboxylic acids are increasingly being used in environmental analysis techniques, offering improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional chemical reagents.
The market for sustainable lab practices is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative start-ups. Large scientific equipment manufacturers are expanding their product lines to include more sustainable options, while specialized companies are emerging to address specific niches within the market. This competitive landscape is driving innovation and helping to accelerate the adoption of sustainable technologies in laboratories worldwide.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Utilization
Despite the widespread use of carboxylic acids in various industries, several challenges persist in their utilization, particularly in the context of sustainable lab practices. One of the primary concerns is the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of carboxylic acids. Traditional synthesis methods often involve the use of toxic reagents and generate significant amounts of waste, which contradicts the principles of green chemistry.
The volatility and corrosive nature of many carboxylic acids pose safety risks in laboratory settings. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are essential but can be complex and resource-intensive. This challenge is particularly acute in academic and small-scale research environments where advanced safety infrastructure may be limited.
Another significant hurdle is the energy-intensive nature of carboxylic acid production. Many industrial processes require high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy consumption and carbon footprint. Developing more energy-efficient synthesis routes remains a key challenge for researchers and industry professionals alike.
The purification of carboxylic acids, especially on an industrial scale, presents its own set of difficulties. Conventional separation techniques often involve multiple steps and the use of organic solvents, which can be both environmentally harmful and economically inefficient. Improving separation and purification methodologies is crucial for enhancing the overall sustainability of carboxylic acid utilization.
In the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries, there is an ongoing challenge to develop stereoselective synthesis methods for complex carboxylic acid derivatives. Achieving high enantioselectivity while maintaining efficiency and sustainability is a delicate balance that researchers continue to pursue.
The limited solubility of some carboxylic acids in aqueous media poses challenges in certain applications, particularly in biological systems and green chemistry processes. Developing effective solubilization strategies or alternative reaction media is an area of active research.
Lastly, the scalability of sustainable carboxylic acid production methods remains a significant challenge. Many promising lab-scale techniques struggle to maintain their efficiency and environmental benefits when scaled up to industrial levels. Bridging this gap between laboratory innovation and practical implementation is crucial for advancing sustainable practices in carboxylic acid utilization.
The volatility and corrosive nature of many carboxylic acids pose safety risks in laboratory settings. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are essential but can be complex and resource-intensive. This challenge is particularly acute in academic and small-scale research environments where advanced safety infrastructure may be limited.
Another significant hurdle is the energy-intensive nature of carboxylic acid production. Many industrial processes require high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy consumption and carbon footprint. Developing more energy-efficient synthesis routes remains a key challenge for researchers and industry professionals alike.
The purification of carboxylic acids, especially on an industrial scale, presents its own set of difficulties. Conventional separation techniques often involve multiple steps and the use of organic solvents, which can be both environmentally harmful and economically inefficient. Improving separation and purification methodologies is crucial for enhancing the overall sustainability of carboxylic acid utilization.
In the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries, there is an ongoing challenge to develop stereoselective synthesis methods for complex carboxylic acid derivatives. Achieving high enantioselectivity while maintaining efficiency and sustainability is a delicate balance that researchers continue to pursue.
The limited solubility of some carboxylic acids in aqueous media poses challenges in certain applications, particularly in biological systems and green chemistry processes. Developing effective solubilization strategies or alternative reaction media is an area of active research.
Lastly, the scalability of sustainable carboxylic acid production methods remains a significant challenge. Many promising lab-scale techniques struggle to maintain their efficiency and environmental benefits when scaled up to industrial levels. Bridging this gap between laboratory innovation and practical implementation is crucial for advancing sustainable practices in carboxylic acid utilization.
Green Chemistry Solutions for Carboxylic Acids
01 Synthesis of carboxylic acids
Various methods for synthesizing carboxylic acids are described, including oxidation of primary alcohols or aldehydes, hydrolysis of nitriles, and carbonylation reactions. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high yields and selectivity.- Synthesis of carboxylic acids: Various methods for synthesizing carboxylic acids are described, including oxidation of primary alcohols or aldehydes, hydrolysis of nitriles, and carbonylation reactions. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve desired yields and selectivity.
- Carboxylic acid derivatives and applications: Carboxylic acids can be converted into various derivatives such as esters, amides, and anhydrides. These derivatives find applications in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other industrial processes. The synthesis and properties of these derivatives are explored in several patents.
- Purification and separation of carboxylic acids: Methods for purifying and separating carboxylic acids from reaction mixtures or natural sources are described. These include crystallization, distillation, extraction, and chromatographic techniques. The focus is on improving purity and yield while reducing energy consumption and waste generation.
- Carboxylic acids in polymer chemistry: Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, serving as monomers or modifiers in various polymerization processes. Patents describe the use of carboxylic acids in the production of polyesters, polyamides, and other functional polymers with specific properties.
- Industrial applications of carboxylic acids: Carboxylic acids find diverse applications in industries such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Patents describe their use as preservatives, flavoring agents, pH regulators, and intermediates in the synthesis of various compounds with commercial importance.
02 Carboxylic acid derivatives and applications
Carboxylic acids can be converted into various derivatives such as esters, amides, and anhydrides. These derivatives have wide-ranging applications in industries including pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals. The synthesis and properties of these derivatives are explored in several patents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation of carboxylic acids
Methods for purifying and separating carboxylic acids from reaction mixtures or natural sources are described. These include techniques such as crystallization, distillation, extraction, and chromatography. The focus is on achieving high purity and efficient separation of target compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Carboxylic acids in polymer chemistry
Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, serving as monomers or modifiers in various polymerization processes. Patents describe the use of carboxylic acids in the production of polyesters, polyamides, and other functional polymers with specific properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids find diverse applications in industries such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Patents describe their use as preservatives, flavoring agents, pH regulators, and intermediates in the synthesis of various compounds with specific functionalities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Chemistry
The research on carboxylic acid for sustainable lab practices is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring both established chemical companies and research institutions. Major players like DuPont de Nemours, Evonik Operations, and Clariant Finance are driving innovation in this field. Universities such as Korea University and Jiangnan University are contributing to academic research. The market is seeing a shift towards eco-friendly solutions, with companies like Ecolab USA focusing on sustainable practices. As the technology matures, collaborations between industry and academia are becoming more prevalent, fostering rapid development and application of carboxylic acid in sustainable lab environments.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a novel approach to sustainable carboxylic acid production using renewable feedstocks and bio-based processes. Their research focuses on the fermentation of biomass-derived sugars to produce short-chain carboxylic acids, such as acetic and propionic acid[1]. The company has also invested in developing catalytic processes for the conversion of these bio-based acids into longer-chain carboxylic acids, which have applications in various industries, including polymers and lubricants[2]. DuPont's technology incorporates advanced separation techniques, such as reactive distillation and membrane processes, to improve the efficiency and sustainability of carboxylic acid production[3]. Additionally, they are exploring the use of genetically engineered microorganisms to enhance the yield and selectivity of carboxylic acid biosynthesis[4].
Strengths: Utilizes renewable feedstocks, reducing reliance on fossil fuels; Integrates advanced separation techniques for improved efficiency. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up bio-based processes; Potential higher production costs compared to traditional petrochemical routes.
Cargill, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cargill has made significant strides in sustainable carboxylic acid production through its bio-based platform. The company focuses on producing carboxylic acids from renewable resources, particularly corn-based feedstocks[1]. Their process involves the fermentation of corn-derived sugars to produce lactic acid, which can be further converted into various carboxylic acids[2]. Cargill has developed proprietary fermentation technology that allows for high-yield production of lactic acid with minimal byproducts[3]. Additionally, they have invested in downstream processing technologies, including advanced purification methods and catalytic conversion processes, to produce a range of carboxylic acids and their derivatives[4]. The company is also exploring the use of agricultural waste and other non-food biomass sources to further enhance the sustainability of their carboxylic acid production[5].
Strengths: Utilizes renewable corn-based feedstocks; Proprietary high-yield fermentation technology. Weaknesses: Potential competition for agricultural resources; May be affected by fluctuations in corn prices and availability.
Innovative Carboxylic Acid Applications
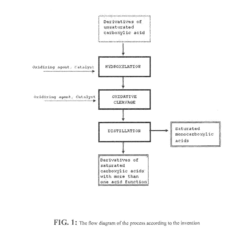
Continuous process for the production of derivatives of saturated carboxylic acids
PatentActiveUS20160237015A1
Innovation
- A continuous process involving two continuous reactors where unsaturated carboxylic acid derivatives are oxidized to vicinal diols, followed by oxidation to carboxylic groups using a controlled flow of oxidizing agents and catalysts, maintaining constant reaction conditions and low radical concentrations to prevent uncontrolled reactions and by-product formation.
Method for producing carboxylic acid
PatentInactiveUS7193110B2
Innovation
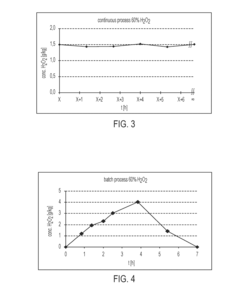
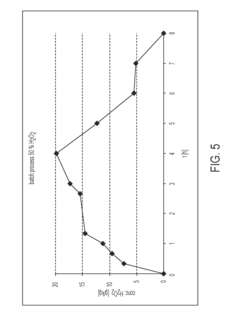
- A heterogeneous solution system using an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution and a water-insoluble aldehyde-containing oily solution in the presence of a polymer sulfonic acid catalyst, such as styrene polymers or fluorocarbon polymers, facilitates the production of carboxylic acid under mild conditions without the need for solvent removal, reducing environmental and health impacts.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of carboxylic acid usage in sustainable lab practices reveals both positive and negative effects on the ecosystem and human health. On the positive side, the adoption of carboxylic acids in green chemistry applications has led to a reduction in the use of more harmful solvents and reagents. This shift has resulted in decreased emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other toxic substances, contributing to improved air quality in laboratory settings and surrounding areas.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of many carboxylic acids has reduced the environmental burden associated with waste disposal. Unlike persistent organic pollutants, these compounds can be more readily broken down by natural processes, minimizing long-term accumulation in soil and water systems. This characteristic has also facilitated the development of more environmentally friendly cleaning and decontamination procedures in laboratories.
However, the increased production and use of carboxylic acids are not without environmental concerns. The synthesis of these compounds often requires energy-intensive processes, potentially contributing to greenhouse gas emissions if not managed properly. Additionally, the release of concentrated carboxylic acids into aquatic environments can lead to localized pH changes, potentially disrupting ecosystems and aquatic life.
Recent studies have focused on the potential for carboxylic acids to act as precursors in the formation of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) in the atmosphere. While the direct impact of laboratory-scale use may be limited, the cumulative effect of industrial-scale applications could contribute to air quality issues and climate change effects.
The assessment also considers the lifecycle impact of carboxylic acid production and use. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials for carboxylic acid synthesis, such as biomass-derived feedstocks, has shown promise in reducing the overall carbon footprint. However, the environmental benefits must be weighed against potential land-use changes and competition with food production.
In terms of human health, the transition to carboxylic acid-based practices has generally led to improved safety profiles in laboratory environments. Reduced exposure to more toxic alternatives has decreased the risk of acute and chronic health effects among researchers and lab personnel. Nevertheless, proper handling and disposal protocols remain crucial, as some carboxylic acids can still pose health risks through skin contact or inhalation of vapors.
Overall, the environmental impact assessment suggests that the integration of carboxylic acids in sustainable lab practices offers significant benefits when compared to traditional methods. However, ongoing research and vigilance are necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential long-term environmental consequences associated with their increased use.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of many carboxylic acids has reduced the environmental burden associated with waste disposal. Unlike persistent organic pollutants, these compounds can be more readily broken down by natural processes, minimizing long-term accumulation in soil and water systems. This characteristic has also facilitated the development of more environmentally friendly cleaning and decontamination procedures in laboratories.
However, the increased production and use of carboxylic acids are not without environmental concerns. The synthesis of these compounds often requires energy-intensive processes, potentially contributing to greenhouse gas emissions if not managed properly. Additionally, the release of concentrated carboxylic acids into aquatic environments can lead to localized pH changes, potentially disrupting ecosystems and aquatic life.
Recent studies have focused on the potential for carboxylic acids to act as precursors in the formation of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) in the atmosphere. While the direct impact of laboratory-scale use may be limited, the cumulative effect of industrial-scale applications could contribute to air quality issues and climate change effects.
The assessment also considers the lifecycle impact of carboxylic acid production and use. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials for carboxylic acid synthesis, such as biomass-derived feedstocks, has shown promise in reducing the overall carbon footprint. However, the environmental benefits must be weighed against potential land-use changes and competition with food production.
In terms of human health, the transition to carboxylic acid-based practices has generally led to improved safety profiles in laboratory environments. Reduced exposure to more toxic alternatives has decreased the risk of acute and chronic health effects among researchers and lab personnel. Nevertheless, proper handling and disposal protocols remain crucial, as some carboxylic acids can still pose health risks through skin contact or inhalation of vapors.
Overall, the environmental impact assessment suggests that the integration of carboxylic acids in sustainable lab practices offers significant benefits when compared to traditional methods. However, ongoing research and vigilance are necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential long-term environmental consequences associated with their increased use.
Safety Protocols for Carboxylic Acid Handling
Safety protocols for handling carboxylic acids are crucial in sustainable lab practices. These protocols encompass a range of measures designed to protect researchers, equipment, and the environment from potential hazards associated with carboxylic acids. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a fundamental aspect of these protocols. Researchers must wear appropriate gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles when handling carboxylic acids. The selection of gloves is particularly important, as different carboxylic acids may require specific materials for adequate protection.
Proper ventilation is another key component of safety protocols. Carboxylic acids can produce irritating and potentially harmful vapors, necessitating the use of fume hoods or well-ventilated areas during handling and storage. This not only protects researchers from inhalation risks but also helps maintain air quality in the laboratory environment.
Storage considerations are equally important in carboxylic acid safety protocols. These compounds should be stored in cool, dry areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Compatibility with other chemicals must be taken into account to prevent dangerous reactions. Proper labeling of containers is essential, including clear identification of the acid, concentration, and any specific hazard warnings.
Spill response procedures form a critical part of safety protocols. Laboratories should have readily available spill kits specifically designed for acid neutralization and containment. These kits typically include absorbent materials, neutralizing agents, and personal protective equipment for safe cleanup. Training in spill response techniques is vital for all laboratory personnel working with carboxylic acids.
Waste disposal is another crucial aspect of safety protocols for carboxylic acids. Proper neutralization and disposal methods must be followed to comply with environmental regulations and minimize ecological impact. This often involves dilution, neutralization, and disposal through approved waste management systems.
Emergency response planning is an integral part of carboxylic acid safety protocols. This includes having easily accessible safety showers and eyewash stations in the laboratory, as well as clear procedures for seeking medical attention in case of exposure. Regular safety drills and training sessions help ensure that all laboratory personnel are prepared to respond effectively in emergency situations.
Lastly, ongoing education and training are essential components of carboxylic acid safety protocols. Regular updates on best practices, new safety equipment, and emerging hazards help maintain a culture of safety in the laboratory. This continuous learning approach is crucial for adapting to new research techniques and ensuring that sustainable lab practices remain at the forefront of carboxylic acid handling procedures.
Proper ventilation is another key component of safety protocols. Carboxylic acids can produce irritating and potentially harmful vapors, necessitating the use of fume hoods or well-ventilated areas during handling and storage. This not only protects researchers from inhalation risks but also helps maintain air quality in the laboratory environment.
Storage considerations are equally important in carboxylic acid safety protocols. These compounds should be stored in cool, dry areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Compatibility with other chemicals must be taken into account to prevent dangerous reactions. Proper labeling of containers is essential, including clear identification of the acid, concentration, and any specific hazard warnings.
Spill response procedures form a critical part of safety protocols. Laboratories should have readily available spill kits specifically designed for acid neutralization and containment. These kits typically include absorbent materials, neutralizing agents, and personal protective equipment for safe cleanup. Training in spill response techniques is vital for all laboratory personnel working with carboxylic acids.
Waste disposal is another crucial aspect of safety protocols for carboxylic acids. Proper neutralization and disposal methods must be followed to comply with environmental regulations and minimize ecological impact. This often involves dilution, neutralization, and disposal through approved waste management systems.
Emergency response planning is an integral part of carboxylic acid safety protocols. This includes having easily accessible safety showers and eyewash stations in the laboratory, as well as clear procedures for seeking medical attention in case of exposure. Regular safety drills and training sessions help ensure that all laboratory personnel are prepared to respond effectively in emergency situations.
Lastly, ongoing education and training are essential components of carboxylic acid safety protocols. Regular updates on best practices, new safety equipment, and emerging hazards help maintain a culture of safety in the laboratory. This continuous learning approach is crucial for adapting to new research techniques and ensuring that sustainable lab practices remain at the forefront of carboxylic acid handling procedures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!