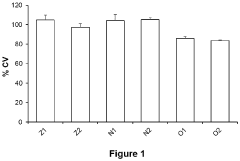
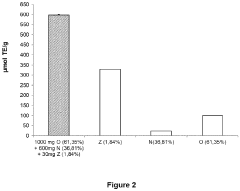
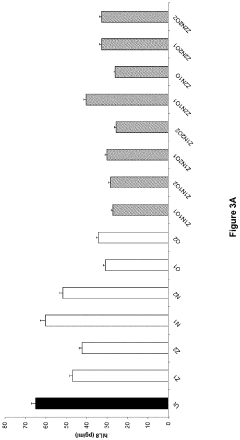
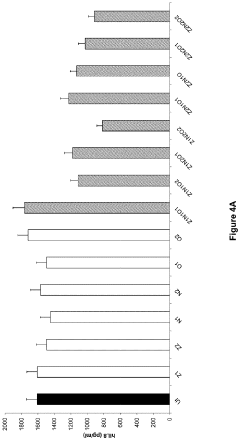
Lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential neuroprotective properties. This organic salt of lithium has been the subject of numerous studies investigating its effects on brain health and function, particularly in relation to mitochondrial activity in neuronal cells.
The history of lithium as a therapeutic agent dates back to the mid-19th century when it was first used to treat various mental health disorders. However, the specific form of lithium orotate emerged as a subject of interest in the 1970s when Dr. Hans Nieper proposed its use as a more bioavailable and potentially safer alternative to conventional lithium carbonate.
Lithium orotate's unique chemical structure allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium compounds. This enhanced bioavailability has led researchers to explore its potential benefits in neurological health, with a particular focus on its impact on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, play a crucial role in neuronal health and function. These organelles are responsible for energy production, calcium homeostasis, and regulation of cell death pathways. Dysfunction of mitochondria has been implicated in various neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and bipolar disorder.
The intersection of lithium orotate and mitochondrial function in neuronal cells represents a promising area of research in neuroscience. Studies have suggested that lithium orotate may exert its neuroprotective effects through multiple mechanisms, including the modulation of mitochondrial dynamics, enhancement of energy metabolism, and regulation of oxidative stress.
Recent investigations have focused on elucidating the specific pathways through which lithium orotate influences mitochondrial function. These studies have explored its effects on mitochondrial biogenesis, fusion and fission processes, and the regulation of key enzymes involved in energy production and cellular respiration.
As research in this field progresses, there is growing interest in understanding how lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function may translate into therapeutic applications for various neurological disorders. The potential for lithium orotate to enhance mitochondrial health and function in neuronal cells could have far-reaching implications for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
The history of lithium as a therapeutic agent dates back to the mid-19th century when it was first used to treat various mental health disorders. However, the specific form of lithium orotate emerged as a subject of interest in the 1970s when Dr. Hans Nieper proposed its use as a more bioavailable and potentially safer alternative to conventional lithium carbonate.
Lithium orotate's unique chemical structure allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium compounds. This enhanced bioavailability has led researchers to explore its potential benefits in neurological health, with a particular focus on its impact on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, play a crucial role in neuronal health and function. These organelles are responsible for energy production, calcium homeostasis, and regulation of cell death pathways. Dysfunction of mitochondria has been implicated in various neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and bipolar disorder.
The intersection of lithium orotate and mitochondrial function in neuronal cells represents a promising area of research in neuroscience. Studies have suggested that lithium orotate may exert its neuroprotective effects through multiple mechanisms, including the modulation of mitochondrial dynamics, enhancement of energy metabolism, and regulation of oxidative stress.
Recent investigations have focused on elucidating the specific pathways through which lithium orotate influences mitochondrial function. These studies have explored its effects on mitochondrial biogenesis, fusion and fission processes, and the regulation of key enzymes involved in energy production and cellular respiration.
As research in this field progresses, there is growing interest in understanding how lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function may translate into therapeutic applications for various neurological disorders. The potential for lithium orotate to enhance mitochondrial health and function in neuronal cells could have far-reaching implications for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Neuronal Health Market
The neuronal health market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by an increasing awareness of neurological disorders and a growing aging population. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services aimed at maintaining and improving brain health, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, medical devices, and diagnostic tools.
The global neuronal health market size was valued at approximately $28.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $41.6 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis, as well as the increasing demand for innovative treatments and preventive measures.
One of the key drivers of market growth is the aging population worldwide. As people age, they become more susceptible to neurological disorders, leading to a higher demand for neuronal health products and services. Additionally, the growing awareness of mental health issues and the importance of cognitive function has led to increased consumer interest in brain health supplements and preventive measures.
The market is segmented into various categories, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, medical devices, and diagnostic tools. Among these, pharmaceuticals hold the largest market share, accounting for over 60% of the total market revenue. However, the nutraceuticals segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by the increasing consumer preference for natural and preventive approaches to brain health.
Geographically, North America dominates the neuronal health market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and strong presence of key market players. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare infrastructure and rising disposable incomes.
The competitive landscape of the neuronal health market is characterized by the presence of several large pharmaceutical companies, as well as numerous smaller biotech firms and nutraceutical manufacturers. Key players in the market include Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Merck, and Biogen, among others. These companies are actively engaged in research and development activities to develop novel therapies and diagnostic tools for neurological disorders.
In the context of lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, this research area represents a potential growth opportunity within the neuronal health market. As mitochondrial dysfunction is increasingly recognized as a key factor in various neurological disorders, therapies targeting mitochondrial function could gain significant traction in the market. The development of novel compounds or formulations that enhance mitochondrial function in neuronal cells could lead to new treatment options for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
The global neuronal health market size was valued at approximately $28.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $41.6 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis, as well as the increasing demand for innovative treatments and preventive measures.
One of the key drivers of market growth is the aging population worldwide. As people age, they become more susceptible to neurological disorders, leading to a higher demand for neuronal health products and services. Additionally, the growing awareness of mental health issues and the importance of cognitive function has led to increased consumer interest in brain health supplements and preventive measures.
The market is segmented into various categories, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, medical devices, and diagnostic tools. Among these, pharmaceuticals hold the largest market share, accounting for over 60% of the total market revenue. However, the nutraceuticals segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by the increasing consumer preference for natural and preventive approaches to brain health.
Geographically, North America dominates the neuronal health market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and strong presence of key market players. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years due to improving healthcare infrastructure and rising disposable incomes.
The competitive landscape of the neuronal health market is characterized by the presence of several large pharmaceutical companies, as well as numerous smaller biotech firms and nutraceutical manufacturers. Key players in the market include Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Merck, and Biogen, among others. These companies are actively engaged in research and development activities to develop novel therapies and diagnostic tools for neurological disorders.
In the context of lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, this research area represents a potential growth opportunity within the neuronal health market. As mitochondrial dysfunction is increasingly recognized as a key factor in various neurological disorders, therapies targeting mitochondrial function could gain significant traction in the market. The development of novel compounds or formulations that enhance mitochondrial function in neuronal cells could lead to new treatment options for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Mitochondrial Function State
Mitochondria play a crucial role in neuronal cells, serving as the powerhouses that generate the energy required for various cellular processes. The current state of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells is characterized by a delicate balance between energy production and cellular homeostasis. Mitochondria in neurons are responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through oxidative phosphorylation, which is essential for maintaining synaptic transmission, ion homeostasis, and overall cellular health.
Recent research has highlighted the importance of mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal function. These dynamics include processes such as fusion, fission, and mitophagy, which are critical for maintaining a healthy mitochondrial population. In neuronal cells, mitochondria are distributed throughout the cell body, axons, and dendrites, with their localization being tightly regulated to meet the specific energy demands of different cellular compartments.
The current state of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells also involves complex interactions with other cellular organelles, particularly the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The mitochondria-ER contact sites play a vital role in calcium signaling, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial division. These interactions are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and proper neuronal function.
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in various neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease. In these conditions, impaired mitochondrial function leads to reduced ATP production, increased oxidative stress, and disrupted calcium homeostasis, ultimately contributing to neuronal death.
The relationship between mitochondrial function and synaptic plasticity is another critical aspect of the current state of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. Mitochondria play a crucial role in regulating synaptic strength and plasticity by modulating local ATP levels and calcium signaling at synapses. This function is particularly important for learning and memory processes.
Recent advancements in imaging techniques and molecular biology have provided new insights into the real-time dynamics of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. These techniques have revealed the heterogeneity of mitochondrial populations within neurons and the importance of mitochondrial trafficking in maintaining cellular health.
In the context of lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, current research suggests that lithium may have neuroprotective properties by modulating mitochondrial function. Lithium has been shown to enhance mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, increase ATP production, and improve mitochondrial membrane potential in neuronal cells. These effects may contribute to its therapeutic potential in various neurological disorders.
Recent research has highlighted the importance of mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal function. These dynamics include processes such as fusion, fission, and mitophagy, which are critical for maintaining a healthy mitochondrial population. In neuronal cells, mitochondria are distributed throughout the cell body, axons, and dendrites, with their localization being tightly regulated to meet the specific energy demands of different cellular compartments.
The current state of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells also involves complex interactions with other cellular organelles, particularly the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The mitochondria-ER contact sites play a vital role in calcium signaling, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial division. These interactions are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and proper neuronal function.
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in various neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease. In these conditions, impaired mitochondrial function leads to reduced ATP production, increased oxidative stress, and disrupted calcium homeostasis, ultimately contributing to neuronal death.
The relationship between mitochondrial function and synaptic plasticity is another critical aspect of the current state of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. Mitochondria play a crucial role in regulating synaptic strength and plasticity by modulating local ATP levels and calcium signaling at synapses. This function is particularly important for learning and memory processes.
Recent advancements in imaging techniques and molecular biology have provided new insights into the real-time dynamics of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. These techniques have revealed the heterogeneity of mitochondrial populations within neurons and the importance of mitochondrial trafficking in maintaining cellular health.
In the context of lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, current research suggests that lithium may have neuroprotective properties by modulating mitochondrial function. Lithium has been shown to enhance mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, increase ATP production, and improve mitochondrial membrane potential in neuronal cells. These effects may contribute to its therapeutic potential in various neurological disorders.
Current Lithium Treatments
01 Lithium orotate's effect on mitochondrial function
Lithium orotate has been found to positively influence mitochondrial function. It may help regulate energy production, reduce oxidative stress, and improve overall cellular health by supporting mitochondrial processes. This compound shows potential in treating conditions associated with mitochondrial dysfunction.- Lithium orotate's effect on mitochondrial function: Lithium orotate has been found to positively influence mitochondrial function. It may help regulate energy production, reduce oxidative stress, and improve overall cellular health by supporting mitochondrial processes. This compound could potentially be used in treatments targeting mitochondrial dysfunction-related disorders.
- Neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate: Lithium orotate exhibits neuroprotective properties, potentially through its interaction with mitochondrial function. It may help prevent neuronal damage, support brain health, and could be beneficial in the treatment or prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium forms contributes to its effectiveness.
- Lithium orotate in metabolic regulation: Research suggests that lithium orotate plays a role in metabolic regulation, possibly through its effects on mitochondrial function. It may influence energy metabolism, glucose utilization, and lipid metabolism. This property could make it a potential candidate for treating metabolic disorders or improving overall metabolic health.
- Combination therapies involving lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is being studied in combination with other compounds to enhance its effects on mitochondrial function and overall health. These combination therapies may provide synergistic benefits, potentially improving treatment outcomes for various conditions related to mitochondrial dysfunction or cellular energy production.
- Lithium orotate in cellular stress response: Studies indicate that lithium orotate may play a role in modulating cellular stress responses, particularly in relation to mitochondrial function. It could help cells adapt to various stressors, potentially enhancing resilience and longevity. This property might be leveraged in developing treatments for stress-related disorders or age-related conditions.
02 Neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate
Lithium orotate exhibits neuroprotective effects, potentially through its impact on mitochondrial function. It may help prevent neuronal damage, support brain health, and show promise in treating neurodegenerative disorders. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium forms contributes to its effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate in metabolic regulation
Research suggests that lithium orotate plays a role in metabolic regulation, potentially through its effects on mitochondrial function. It may influence glucose metabolism, lipid homeostasis, and energy balance. This property makes it a candidate for investigating metabolic disorders and related conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies involving lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is being studied in combination with other compounds to enhance its effects on mitochondrial function and overall health. These combination therapies may offer synergistic benefits in treating various disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and cellular energy production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Diagnostic and therapeutic applications
The effects of lithium orotate on mitochondrial function are being explored for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications. This includes developing new methods for assessing mitochondrial health, as well as novel treatments for conditions associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, such as neurodegenerative diseases, mood disorders, and metabolic syndromes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Neuropharmacology Players
The field of lithium orotate's effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in neurological health and mitochondrial medicine. The technology's maturity is still evolving, as evidenced by ongoing research at institutions like Arizona State University and Harvard College. Companies such as Khondrion BV and Amazentis SA are at the forefront of developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies, indicating a competitive landscape with both academic and commercial players. The involvement of established pharmaceutical companies like Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. suggests potential for market expansion, while specialized firms like Abliva AB focus specifically on mitochondrial diseases, highlighting the niche but promising nature of this field.
Khondrion BV
Technical Solution: Khondrion BV has developed a novel approach to target mitochondrial function in neuronal cells using sonlicromanol (KH176), a small molecule that acts as a potent intracellular redox modulator. This compound has shown promise in improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress in cellular models of mitochondrial disease[1]. In the context of lithium orotate's effects, Khondrion's research could provide valuable insights into how different compounds interact with mitochondrial processes. Their technology platform allows for the screening of compounds that may enhance mitochondrial function, potentially including lithium orotate or related molecules[2]. By utilizing advanced imaging techniques and metabolic profiling, Khondrion can assess the impact of various compounds on mitochondrial membrane potential, ATP production, and redox balance in neuronal cells[3].
Strengths: Specialized focus on mitochondrial diseases and therapies; advanced screening platform for mitochondrial function. Weaknesses: Limited public data on specific lithium orotate research; primary focus on proprietary compounds may limit broader applications.
The General Hospital Corp.
Technical Solution: The General Hospital Corporation, associated with Massachusetts General Hospital, has conducted extensive research on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. Their studies have explored the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases[1]. While not specifically focused on lithium orotate, their research methodologies are highly applicable. They have developed advanced imaging techniques to visualize mitochondrial dynamics in live neurons, allowing for real-time assessment of mitochondrial function[2]. In the context of lithium orotate research, these techniques could be used to observe its effects on mitochondrial morphology, distribution, and function in neuronal cells. The hospital's research teams have also investigated the neuroprotective effects of various compounds on mitochondrial function, which could provide a framework for studying lithium orotate's potential benefits[3]. Their expertise in mitochondrial bioenergetics and oxidative stress in neuronal cells is particularly relevant to understanding how lithium orotate might influence these processes.
Strengths: Cutting-edge imaging techniques for mitochondrial research; extensive experience in neurological disorders. Weaknesses: Broad research focus may limit depth in specific compounds like lithium orotate.
Orotate Mechanism Analysis
Composition for preventing and treating depressive and cognitive symptoms
PatentPendingEP3698777A1
Innovation
- A combination of N-acetylcysteine, omega-3 fatty acids, and crocin, either separately or together, is administered to target inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways, providing a synergistic antidepressant effect and improving cognitive functions while slowing cognitive decline.
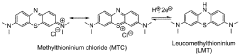
Methylthioninium compounds for use in the treatment of covid-19
PatentWO2021224144A1
Innovation
- The use of hydromethylthioninium salts (LMTX) as a monotherapy or combination therapy, providing specific dosages to achieve significant reductions in SARS-CoV-2 toxicity, enhance mitochondrial function, and improve blood oxygen capacity, which are administered orally or intravenously to ensure better absorption and distribution.
Safety and Dosage Protocols
The safety and dosage protocols for lithium orotate in relation to its effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells are crucial considerations for both research and potential therapeutic applications. Lithium orotate, a salt of orotic acid and lithium, has gained attention for its potential neuroprotective properties and lower toxicity compared to other lithium compounds.
Safety assessments for lithium orotate involve comprehensive toxicological studies, including acute and chronic exposure tests in various animal models. These studies evaluate potential adverse effects on organ systems, with particular emphasis on renal and thyroid function, as these are known targets of lithium toxicity. Neurological safety is a primary concern, given the compound's intended use in neuronal cells. Researchers employ a battery of behavioral and cognitive tests to assess any potential neurotoxic effects.
Dosage protocols for lithium orotate are typically established through dose-response studies in cellular and animal models. These studies aim to determine the optimal concentration range that maximizes beneficial effects on mitochondrial function while minimizing potential side effects. In vitro experiments with neuronal cell cultures help establish baseline effective concentrations, which are then translated to in vivo models for further refinement.
For human applications, dosage protocols must consider the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is more commonly used in clinical settings, lithium orotate may have different absorption and distribution profiles. This necessitates careful titration and monitoring of serum lithium levels to ensure therapeutic efficacy while avoiding toxicity.
Long-term safety monitoring protocols are essential for chronic administration of lithium orotate. These protocols typically include regular assessments of renal function, thyroid function, and serum lithium levels. Neurological examinations and cognitive assessments are also incorporated to detect any subtle changes in brain function over time. Additionally, monitoring for potential drug interactions is crucial, as lithium can interact with various medications, including NSAIDs and certain antidepressants.
In the context of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, specific safety considerations focus on maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Protocols may include assessments of ATP production, mitochondrial membrane potential, and reactive oxygen species generation to ensure that lithium orotate's effects on mitochondria do not lead to energetic stress or oxidative damage in neurons.
Safety assessments for lithium orotate involve comprehensive toxicological studies, including acute and chronic exposure tests in various animal models. These studies evaluate potential adverse effects on organ systems, with particular emphasis on renal and thyroid function, as these are known targets of lithium toxicity. Neurological safety is a primary concern, given the compound's intended use in neuronal cells. Researchers employ a battery of behavioral and cognitive tests to assess any potential neurotoxic effects.
Dosage protocols for lithium orotate are typically established through dose-response studies in cellular and animal models. These studies aim to determine the optimal concentration range that maximizes beneficial effects on mitochondrial function while minimizing potential side effects. In vitro experiments with neuronal cell cultures help establish baseline effective concentrations, which are then translated to in vivo models for further refinement.
For human applications, dosage protocols must consider the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is more commonly used in clinical settings, lithium orotate may have different absorption and distribution profiles. This necessitates careful titration and monitoring of serum lithium levels to ensure therapeutic efficacy while avoiding toxicity.
Long-term safety monitoring protocols are essential for chronic administration of lithium orotate. These protocols typically include regular assessments of renal function, thyroid function, and serum lithium levels. Neurological examinations and cognitive assessments are also incorporated to detect any subtle changes in brain function over time. Additionally, monitoring for potential drug interactions is crucial, as lithium can interact with various medications, including NSAIDs and certain antidepressants.
In the context of mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, specific safety considerations focus on maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Protocols may include assessments of ATP production, mitochondrial membrane potential, and reactive oxygen species generation to ensure that lithium orotate's effects on mitochondria do not lead to energetic stress or oxidative damage in neurons.
Cognitive Enhancement Potential
Lithium orotate's potential for cognitive enhancement is an area of growing interest in neuroscience and psychiatric research. This compound, a combination of lithium and orotic acid, has shown promising effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells, which may translate to improved cognitive performance.
The cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate is primarily linked to its neuroprotective properties and its ability to optimize mitochondrial function. By enhancing mitochondrial efficiency, lithium orotate may increase energy production in neuronal cells, potentially leading to improved synaptic plasticity and overall cognitive function.
Studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can upregulate neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which plays a crucial role in neuronal survival, differentiation, and synaptic plasticity. This upregulation may contribute to enhanced learning and memory processes, as well as improved mood regulation.
Furthermore, lithium orotate has been shown to modulate various neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin. These modulations may result in improved cognitive flexibility, attention, and executive function. The compound's ability to stabilize mood and reduce anxiety may also indirectly contribute to enhanced cognitive performance by reducing cognitive interference from emotional distress.
Research has indicated that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are implicated in cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. By mitigating these harmful processes, lithium orotate could potentially slow cognitive aging and preserve cognitive function in the long term.
Clinical studies investigating the cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate have shown promising results in various populations, including healthy adults and individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Improvements have been observed in areas such as memory consolidation, information processing speed, and executive function.
However, it is important to note that while the cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate is promising, more extensive research is needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms of action and long-term effects. Additionally, optimal dosing strategies and potential interactions with other cognitive-enhancing compounds require further investigation to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
As research in this area continues to evolve, lithium orotate's cognitive enhancement potential may lead to novel therapeutic approaches for cognitive disorders and strategies for maintaining cognitive health in aging populations. The compound's unique effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells position it as a promising candidate for future cognitive enhancement interventions.
The cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate is primarily linked to its neuroprotective properties and its ability to optimize mitochondrial function. By enhancing mitochondrial efficiency, lithium orotate may increase energy production in neuronal cells, potentially leading to improved synaptic plasticity and overall cognitive function.
Studies have demonstrated that lithium orotate can upregulate neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which plays a crucial role in neuronal survival, differentiation, and synaptic plasticity. This upregulation may contribute to enhanced learning and memory processes, as well as improved mood regulation.
Furthermore, lithium orotate has been shown to modulate various neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin. These modulations may result in improved cognitive flexibility, attention, and executive function. The compound's ability to stabilize mood and reduce anxiety may also indirectly contribute to enhanced cognitive performance by reducing cognitive interference from emotional distress.
Research has indicated that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are implicated in cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. By mitigating these harmful processes, lithium orotate could potentially slow cognitive aging and preserve cognitive function in the long term.
Clinical studies investigating the cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate have shown promising results in various populations, including healthy adults and individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Improvements have been observed in areas such as memory consolidation, information processing speed, and executive function.
However, it is important to note that while the cognitive enhancement potential of lithium orotate is promising, more extensive research is needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms of action and long-term effects. Additionally, optimal dosing strategies and potential interactions with other cognitive-enhancing compounds require further investigation to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
As research in this area continues to evolve, lithium orotate's cognitive enhancement potential may lead to novel therapeutic approaches for cognitive disorders and strategies for maintaining cognitive health in aging populations. The compound's unique effects on mitochondrial function in neuronal cells position it as a promising candidate for future cognitive enhancement interventions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!