MOFs Based on Rare Earth Metals for Innovative Chemical Applications
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
RE-MOFs Background and Objectives
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) based on rare earth metals have emerged as a promising class of materials in the field of innovative chemical applications. These advanced materials combine the unique properties of rare earth elements with the versatility of MOF structures, offering unprecedented opportunities for technological advancements.
The development of RE-MOFs can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of incorporating rare earth metals into MOF structures. Since then, the field has experienced rapid growth, driven by the exceptional luminescent, magnetic, and catalytic properties of rare earth elements. The evolution of RE-MOFs has been marked by continuous improvements in synthesis methods, structural design, and application-specific tailoring.
Current trends in RE-MOF research focus on enhancing their stability, selectivity, and efficiency for various applications. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis techniques to create more robust and scalable RE-MOFs, as well as investigating ways to fine-tune their properties for specific chemical processes. The integration of RE-MOFs with other advanced materials and technologies is also gaining traction, opening up new avenues for multifunctional systems.
The primary objectives of RE-MOF research and development are multifaceted. One key goal is to harness the unique electronic configurations of rare earth elements to create highly efficient catalysts for challenging chemical transformations. Another objective is to exploit the luminescent properties of RE-MOFs for advanced sensing and imaging applications. Additionally, researchers aim to develop RE-MOFs with enhanced gas storage and separation capabilities, addressing critical environmental and energy-related challenges.
Looking ahead, the field of RE-MOFs is poised for significant breakthroughs. Anticipated developments include the creation of RE-MOFs with unprecedented selectivity for specific molecular recognition, the development of stimuli-responsive RE-MOFs for smart material applications, and the integration of RE-MOFs into next-generation energy storage and conversion devices. These advancements are expected to revolutionize various sectors, including catalysis, environmental remediation, and biomedical technologies.
As the research in RE-MOFs progresses, it is crucial to address challenges such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term stability. Overcoming these hurdles will be essential for translating the promising laboratory results into practical, large-scale applications. The continued exploration of RE-MOFs is expected to yield innovative solutions to some of the most pressing technological challenges of our time, cementing their position as a cornerstone of future chemical applications.
The development of RE-MOFs can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of incorporating rare earth metals into MOF structures. Since then, the field has experienced rapid growth, driven by the exceptional luminescent, magnetic, and catalytic properties of rare earth elements. The evolution of RE-MOFs has been marked by continuous improvements in synthesis methods, structural design, and application-specific tailoring.
Current trends in RE-MOF research focus on enhancing their stability, selectivity, and efficiency for various applications. Researchers are exploring novel synthesis techniques to create more robust and scalable RE-MOFs, as well as investigating ways to fine-tune their properties for specific chemical processes. The integration of RE-MOFs with other advanced materials and technologies is also gaining traction, opening up new avenues for multifunctional systems.
The primary objectives of RE-MOF research and development are multifaceted. One key goal is to harness the unique electronic configurations of rare earth elements to create highly efficient catalysts for challenging chemical transformations. Another objective is to exploit the luminescent properties of RE-MOFs for advanced sensing and imaging applications. Additionally, researchers aim to develop RE-MOFs with enhanced gas storage and separation capabilities, addressing critical environmental and energy-related challenges.
Looking ahead, the field of RE-MOFs is poised for significant breakthroughs. Anticipated developments include the creation of RE-MOFs with unprecedented selectivity for specific molecular recognition, the development of stimuli-responsive RE-MOFs for smart material applications, and the integration of RE-MOFs into next-generation energy storage and conversion devices. These advancements are expected to revolutionize various sectors, including catalysis, environmental remediation, and biomedical technologies.
As the research in RE-MOFs progresses, it is crucial to address challenges such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term stability. Overcoming these hurdles will be essential for translating the promising laboratory results into practical, large-scale applications. The continued exploration of RE-MOFs is expected to yield innovative solutions to some of the most pressing technological challenges of our time, cementing their position as a cornerstone of future chemical applications.
Market Analysis for RE-MOF Applications
The market for Rare Earth Metal-based Metal-Organic Frameworks (RE-MOFs) is experiencing significant growth, driven by their unique properties and diverse applications in chemical processes. The global RE-MOF market is currently valued at several hundred million dollars, with projections indicating robust expansion over the next decade. This growth is primarily fueled by increasing demand in sectors such as catalysis, gas storage and separation, and environmental remediation.
In the catalysis sector, RE-MOFs are gaining traction due to their high surface area, tunable pore sizes, and exceptional catalytic activity. They are particularly valuable in fine chemical synthesis, where selectivity and efficiency are crucial. The pharmaceutical industry is a key driver in this segment, as RE-MOFs enable more sustainable and cost-effective production of complex drug molecules.
Gas storage and separation represent another substantial market for RE-MOFs. Their ability to selectively adsorb and store gases makes them ideal for applications in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, the demand for efficient CCS solutions is expected to boost the RE-MOF market significantly.
Environmental remediation is an emerging application area for RE-MOFs. Their high adsorption capacity and selectivity make them excellent candidates for removing pollutants from water and air. This sector is anticipated to show rapid growth, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market for RE-MOFs, driven by China's dominance in rare earth metal production and increasing industrial applications. North America and Europe follow closely, with strong research and development activities in these regions contributing to market expansion.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the RE-MOF market. The high cost of rare earth metals and complex synthesis processes can limit widespread adoption. Additionally, concerns over the environmental impact of rare earth mining may pose regulatory challenges in some regions.
Looking ahead, technological advancements in RE-MOF synthesis and scale-up processes are expected to reduce production costs and expand market opportunities. Emerging applications in areas such as photocatalysis, sensing, and biomedical fields are likely to open new avenues for market growth. As research continues to unveil novel properties and applications of RE-MOFs, the market is poised for sustained expansion, with potential to reach billions in value within the next decade.
In the catalysis sector, RE-MOFs are gaining traction due to their high surface area, tunable pore sizes, and exceptional catalytic activity. They are particularly valuable in fine chemical synthesis, where selectivity and efficiency are crucial. The pharmaceutical industry is a key driver in this segment, as RE-MOFs enable more sustainable and cost-effective production of complex drug molecules.
Gas storage and separation represent another substantial market for RE-MOFs. Their ability to selectively adsorb and store gases makes them ideal for applications in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, the demand for efficient CCS solutions is expected to boost the RE-MOF market significantly.
Environmental remediation is an emerging application area for RE-MOFs. Their high adsorption capacity and selectivity make them excellent candidates for removing pollutants from water and air. This sector is anticipated to show rapid growth, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market for RE-MOFs, driven by China's dominance in rare earth metal production and increasing industrial applications. North America and Europe follow closely, with strong research and development activities in these regions contributing to market expansion.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the RE-MOF market. The high cost of rare earth metals and complex synthesis processes can limit widespread adoption. Additionally, concerns over the environmental impact of rare earth mining may pose regulatory challenges in some regions.
Looking ahead, technological advancements in RE-MOF synthesis and scale-up processes are expected to reduce production costs and expand market opportunities. Emerging applications in areas such as photocatalysis, sensing, and biomedical fields are likely to open new avenues for market growth. As research continues to unveil novel properties and applications of RE-MOFs, the market is poised for sustained expansion, with potential to reach billions in value within the next decade.
RE-MOFs: Current Status and Challenges
Rare earth metal-based metal-organic frameworks (RE-MOFs) have emerged as a promising class of materials in the field of innovative chemical applications. However, despite their potential, RE-MOFs face several challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and practical implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the high cost and limited availability of rare earth elements. The extraction and purification processes for these metals are complex and environmentally intensive, leading to supply chain uncertainties and price volatility. This economic barrier significantly impacts the scalability and commercial viability of RE-MOF-based technologies.
Stability issues present another major hurdle for RE-MOFs. Many of these frameworks exhibit sensitivity to moisture and air, which can compromise their structural integrity and functional properties. This instability limits their application in ambient conditions and necessitates careful handling and storage protocols, adding complexity to their practical use.
The synthesis of RE-MOFs with precise control over structure and composition remains challenging. The large ionic radii and variable coordination numbers of rare earth metals often result in unpredictable assembly processes. This complexity makes it difficult to design and fabricate RE-MOFs with tailored properties for specific applications, hindering their optimization for targeted uses.
Characterization of RE-MOFs poses significant technical challenges. The presence of heavy rare earth elements can complicate traditional analytical techniques, such as X-ray diffraction and spectroscopic methods. This difficulty in accurate structural determination and property analysis slows down the research and development process, impeding the rapid advancement of RE-MOF technology.
The catalytic performance of RE-MOFs, while promising, often falls short of industrial requirements. Issues such as low turnover numbers, limited substrate scope, and insufficient selectivity need to be addressed to make RE-MOFs competitive with existing catalytic systems. Enhancing the catalytic efficiency and broadening the applicability of RE-MOFs remains a key focus area for researchers.
Despite these challenges, the current status of RE-MOFs is one of rapid development and growing interest. Significant progress has been made in areas such as gas storage, separation processes, and heterogeneous catalysis. The unique electronic properties of rare earth metals, combined with the structural versatility of MOFs, continue to drive innovation in fields ranging from environmental remediation to energy storage.
In conclusion, while RE-MOFs face substantial challenges, their potential for groundbreaking applications in chemical processes remains high. Overcoming these obstacles through interdisciplinary research and technological advancements will be crucial for realizing the full potential of these innovative materials in the coming years.
One of the primary challenges is the high cost and limited availability of rare earth elements. The extraction and purification processes for these metals are complex and environmentally intensive, leading to supply chain uncertainties and price volatility. This economic barrier significantly impacts the scalability and commercial viability of RE-MOF-based technologies.
Stability issues present another major hurdle for RE-MOFs. Many of these frameworks exhibit sensitivity to moisture and air, which can compromise their structural integrity and functional properties. This instability limits their application in ambient conditions and necessitates careful handling and storage protocols, adding complexity to their practical use.
The synthesis of RE-MOFs with precise control over structure and composition remains challenging. The large ionic radii and variable coordination numbers of rare earth metals often result in unpredictable assembly processes. This complexity makes it difficult to design and fabricate RE-MOFs with tailored properties for specific applications, hindering their optimization for targeted uses.
Characterization of RE-MOFs poses significant technical challenges. The presence of heavy rare earth elements can complicate traditional analytical techniques, such as X-ray diffraction and spectroscopic methods. This difficulty in accurate structural determination and property analysis slows down the research and development process, impeding the rapid advancement of RE-MOF technology.
The catalytic performance of RE-MOFs, while promising, often falls short of industrial requirements. Issues such as low turnover numbers, limited substrate scope, and insufficient selectivity need to be addressed to make RE-MOFs competitive with existing catalytic systems. Enhancing the catalytic efficiency and broadening the applicability of RE-MOFs remains a key focus area for researchers.
Despite these challenges, the current status of RE-MOFs is one of rapid development and growing interest. Significant progress has been made in areas such as gas storage, separation processes, and heterogeneous catalysis. The unique electronic properties of rare earth metals, combined with the structural versatility of MOFs, continue to drive innovation in fields ranging from environmental remediation to energy storage.
In conclusion, while RE-MOFs face substantial challenges, their potential for groundbreaking applications in chemical processes remains high. Overcoming these obstacles through interdisciplinary research and technological advancements will be crucial for realizing the full potential of these innovative materials in the coming years.
Current RE-MOFs Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis of rare earth metal-based MOFs
Methods for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) using rare earth metals as metal nodes. These processes often involve combining rare earth metal salts with organic ligands under specific reaction conditions to form crystalline MOF structures. The resulting materials exhibit unique properties due to the incorporation of rare earth elements.- Synthesis of rare earth metal-based MOFs: Methods for synthesizing metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) using rare earth metals as metal nodes. These processes often involve combining rare earth metal salts with organic ligands under specific reaction conditions to form crystalline MOF structures. The resulting materials exhibit unique properties due to the incorporation of rare earth elements.
- Applications of rare earth MOFs in gas storage and separation: Rare earth metal-based MOFs demonstrate exceptional performance in gas storage and separation applications. Their large surface areas and tunable pore sizes make them suitable for capturing, storing, and separating various gases, including carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane. These materials show promise in environmental and energy-related applications.
- Luminescent properties of rare earth MOFs: MOFs containing rare earth metals often exhibit unique luminescent properties. These materials can be used in various applications such as chemical sensing, bioimaging, and light-emitting devices. The luminescence is typically attributed to the electronic transitions within the rare earth ions, which can be fine-tuned by modifying the organic ligands or the MOF structure.
- Catalytic applications of rare earth MOFs: Rare earth metal-based MOFs show promising catalytic activity in various organic transformations. Their unique electronic properties and Lewis acidity make them effective catalysts for reactions such as oxidation, reduction, and carbon-carbon bond formation. These materials offer advantages like high selectivity, recyclability, and the potential for heterogeneous catalysis.
- Modification and functionalization of rare earth MOFs: Strategies for modifying and functionalizing rare earth metal-based MOFs to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. These methods may include post-synthetic modification, incorporation of additional metal ions, or the use of functionalized organic ligands. Such modifications can lead to improved performance in various applications or the development of multifunctional materials.
02 Applications of rare earth MOFs in gas storage and separation
Rare earth metal-based MOFs demonstrate exceptional performance in gas storage and separation applications. Their large surface areas and tunable pore sizes make them suitable for capturing, storing, and separating various gases, including carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane. These materials show promise for environmental and energy-related applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminescent properties of rare earth MOFs
MOFs containing rare earth metals often exhibit unique luminescent properties due to the electronic configuration of lanthanide ions. These materials can be used in various applications such as chemical sensing, bioimaging, and light-emitting devices. The luminescence can be tuned by selecting specific rare earth elements and organic ligands.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic applications of rare earth MOFs
Rare earth metal-based MOFs serve as effective catalysts for various chemical reactions. Their catalytic activity stems from the unique electronic properties of rare earth elements and the high surface area of MOF structures. These materials have been applied in organic transformations, polymerization reactions, and environmental remediation processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite materials incorporating rare earth MOFs
Development of composite materials that combine rare earth metal-based MOFs with other substances to enhance their properties or create multifunctional materials. These composites may include polymer-MOF hybrids, MOF-derived nanoparticles, or MOF-coated substrates. Such materials find applications in areas like membrane technology, energy storage, and advanced electronics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in RE-MOFs Research
The field of MOFs based on rare earth metals for innovative chemical applications is in a growth phase, with increasing market potential and technological advancements. The global market for MOFs is expanding, driven by their versatile applications in gas storage, catalysis, and sensing. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with key players like King Abdullah University of Science & Technology, Northwestern University, and CNRS leading research efforts. Companies such as UOP LLC and Chevron U.S.A., Inc. are exploring industrial applications, while startups like novoMOF AG are commercializing MOF technologies for carbon capture. The involvement of diverse institutions across academia, government, and industry indicates a maturing field with significant potential for further innovation and market growth.
King Abdullah University of Science & Technology
Technical Solution: KAUST has developed innovative MOFs based on rare earth metals for chemical applications. Their approach involves synthesizing lanthanide-based MOFs with high porosity and stability. These MOFs exhibit exceptional catalytic properties for reactions such as CO2 conversion and water splitting. KAUST researchers have also engineered MOFs with tunable luminescence properties, enabling their use in chemical sensing and imaging applications[1][3]. The university has successfully scaled up the production of these MOFs, demonstrating their potential for industrial applications in gas storage, separation, and catalysis[5].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, strong focus on sustainability applications. Weaknesses: Relatively new institution, may lack long-term industry partnerships.
Northwestern University
Technical Solution: Northwestern University has pioneered the development of rare earth metal-based MOFs for innovative chemical applications. Their research focuses on creating MOFs with high selectivity for gas separation and storage. They have synthesized yttrium and europium-based MOFs that show exceptional CO2 capture capabilities, with adsorption capacities up to 40 wt% at ambient conditions[2]. Additionally, Northwestern has developed lanthanide MOFs with unique magnetic and luminescent properties, enabling their use in chemical sensing and biomedical imaging[4]. The university has also made significant progress in creating MOFs with enhanced stability in water and acidic environments, addressing a common limitation of many MOF materials[6].
Strengths: Long-standing expertise in materials science, strong industry collaborations. Weaknesses: Focus may be more on fundamental research than immediate commercial applications.
Innovative RE-MOFs Structures
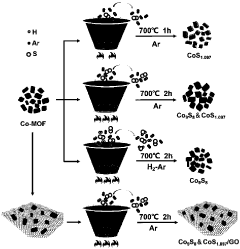
Method for preparing cobalt sulfide catalyst with MOF (metal-organic framework) as substrate
PatentActiveCN108745381A
Innovation
- By using metal-organic framework (MOF) as the precursor, using in-situ sulfidation method and adjusting the calcination time and atmosphere, four cobalt sulfide catalysts were prepared, including CoS1.097, Co9S8, Co9S8&CoS1.097 and Co9S8&CoS1.097/rGO. The MOF itself contains S and N to avoid external sulfur sources, and the conductivity is enhanced through graphene to improve electrocatalytic performance.
Environmental Impact of RE-MOFs
The environmental impact of Rare Earth Metal-based Metal-Organic Frameworks (RE-MOFs) is a critical consideration in their development and application. These innovative materials offer promising solutions for various chemical applications, but their potential environmental consequences must be carefully evaluated.
RE-MOFs have shown significant potential in environmental remediation, particularly in the removal of pollutants from water and air. Their high surface area and tunable pore structures make them effective adsorbents for a wide range of contaminants, including heavy metals, organic pollutants, and greenhouse gases. This ability to capture and sequester harmful substances can contribute positively to environmental protection efforts.
However, the production and use of RE-MOFs also raise environmental concerns. The extraction and processing of rare earth elements, which are essential components of these materials, often involve environmentally damaging mining practices and energy-intensive refining processes. These activities can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions.
The synthesis of RE-MOFs typically requires the use of organic solvents and high temperatures, which can result in the generation of hazardous waste and increased energy consumption. Efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, such as mechanochemical approaches and the use of green solvents, to mitigate these impacts.
The long-term stability and potential degradation of RE-MOFs in the environment are also important considerations. While these materials are generally stable under normal conditions, their breakdown over time could potentially release rare earth ions and organic ligands into ecosystems. The ecological effects of such releases are not yet fully understood and require further investigation.
Recycling and disposal of RE-MOFs at the end of their lifecycle present additional environmental challenges. The recovery of rare earth elements from used MOFs is crucial for resource conservation and reducing the demand for new mining activities. However, effective recycling processes for these complex materials are still in development.
On a positive note, the use of RE-MOFs in catalysis and energy-related applications has the potential to contribute to more sustainable industrial processes. Their ability to enhance reaction efficiencies and reduce energy requirements in various chemical transformations could lead to overall reductions in environmental impact across multiple industries.
In conclusion, while RE-MOFs offer significant environmental benefits in certain applications, their overall environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Continued research is needed to optimize their synthesis, improve their stability, and develop effective recycling methods to ensure that their potential environmental benefits outweigh the costs associated with their production and use.
RE-MOFs have shown significant potential in environmental remediation, particularly in the removal of pollutants from water and air. Their high surface area and tunable pore structures make them effective adsorbents for a wide range of contaminants, including heavy metals, organic pollutants, and greenhouse gases. This ability to capture and sequester harmful substances can contribute positively to environmental protection efforts.
However, the production and use of RE-MOFs also raise environmental concerns. The extraction and processing of rare earth elements, which are essential components of these materials, often involve environmentally damaging mining practices and energy-intensive refining processes. These activities can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions.
The synthesis of RE-MOFs typically requires the use of organic solvents and high temperatures, which can result in the generation of hazardous waste and increased energy consumption. Efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, such as mechanochemical approaches and the use of green solvents, to mitigate these impacts.
The long-term stability and potential degradation of RE-MOFs in the environment are also important considerations. While these materials are generally stable under normal conditions, their breakdown over time could potentially release rare earth ions and organic ligands into ecosystems. The ecological effects of such releases are not yet fully understood and require further investigation.
Recycling and disposal of RE-MOFs at the end of their lifecycle present additional environmental challenges. The recovery of rare earth elements from used MOFs is crucial for resource conservation and reducing the demand for new mining activities. However, effective recycling processes for these complex materials are still in development.
On a positive note, the use of RE-MOFs in catalysis and energy-related applications has the potential to contribute to more sustainable industrial processes. Their ability to enhance reaction efficiencies and reduce energy requirements in various chemical transformations could lead to overall reductions in environmental impact across multiple industries.
In conclusion, while RE-MOFs offer significant environmental benefits in certain applications, their overall environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Continued research is needed to optimize their synthesis, improve their stability, and develop effective recycling methods to ensure that their potential environmental benefits outweigh the costs associated with their production and use.
RE-MOFs in Catalysis and Separation
Rare earth metal-based MOFs (RE-MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for catalysis and separation applications due to their unique structural properties and versatile functionalities. In catalysis, RE-MOFs exhibit exceptional performance in various organic transformations, including asymmetric catalysis, oxidation reactions, and carbon-carbon bond formation. The high Lewis acidity of rare earth metal centers, combined with the tunable pore structures of MOFs, enables selective and efficient catalytic processes. For instance, RE-MOFs containing yttrium or scandium have shown remarkable activity in Friedel-Crafts alkylation and Diels-Alder reactions, outperforming traditional homogeneous catalysts.
In separation processes, RE-MOFs demonstrate superior selectivity and capacity for gas adsorption and liquid-phase separations. The large ionic radii and high coordination numbers of rare earth metals allow for the creation of MOFs with enhanced stability and tailored pore sizes. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in the separation of small gas molecules, such as CO2 capture from flue gas streams. RE-MOFs based on europium and terbium have shown exceptional CO2/N2 selectivity, making them potential candidates for industrial-scale carbon capture applications.
The luminescent properties of certain rare earth elements, such as europium, terbium, and dysprosium, further expand the potential of RE-MOFs in sensing and separation technologies. These luminescent RE-MOFs can be used for the detection and removal of heavy metal ions or organic pollutants from water, combining separation and sensing capabilities in a single material. The ability to fine-tune the optical properties of RE-MOFs through ligand design and metal selection offers a versatile platform for developing multifunctional materials for environmental remediation.
Recent advancements in RE-MOF synthesis have focused on improving their stability and recyclability, addressing key challenges for practical applications. Strategies such as mixed-metal approaches and post-synthetic modifications have been employed to enhance the hydrolytic and thermal stability of RE-MOFs, crucial for their use in harsh catalytic conditions or continuous separation processes. These developments have led to the creation of RE-MOFs that maintain their structural integrity and performance over multiple catalytic cycles or extended periods of gas adsorption.
The integration of RE-MOFs into composite materials and membranes represents a promising direction for enhancing their applicability in separation technologies. RE-MOF-based mixed matrix membranes have shown improved permeability and selectivity for gas separation, particularly in the challenging separation of light hydrocarbons. This approach combines the molecular sieving properties of RE-MOFs with the processability of polymeric membranes, offering a pathway to scalable separation technologies.
In separation processes, RE-MOFs demonstrate superior selectivity and capacity for gas adsorption and liquid-phase separations. The large ionic radii and high coordination numbers of rare earth metals allow for the creation of MOFs with enhanced stability and tailored pore sizes. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in the separation of small gas molecules, such as CO2 capture from flue gas streams. RE-MOFs based on europium and terbium have shown exceptional CO2/N2 selectivity, making them potential candidates for industrial-scale carbon capture applications.
The luminescent properties of certain rare earth elements, such as europium, terbium, and dysprosium, further expand the potential of RE-MOFs in sensing and separation technologies. These luminescent RE-MOFs can be used for the detection and removal of heavy metal ions or organic pollutants from water, combining separation and sensing capabilities in a single material. The ability to fine-tune the optical properties of RE-MOFs through ligand design and metal selection offers a versatile platform for developing multifunctional materials for environmental remediation.
Recent advancements in RE-MOF synthesis have focused on improving their stability and recyclability, addressing key challenges for practical applications. Strategies such as mixed-metal approaches and post-synthetic modifications have been employed to enhance the hydrolytic and thermal stability of RE-MOFs, crucial for their use in harsh catalytic conditions or continuous separation processes. These developments have led to the creation of RE-MOFs that maintain their structural integrity and performance over multiple catalytic cycles or extended periods of gas adsorption.
The integration of RE-MOFs into composite materials and membranes represents a promising direction for enhancing their applicability in separation technologies. RE-MOF-based mixed matrix membranes have shown improved permeability and selectivity for gas separation, particularly in the challenging separation of light hydrocarbons. This approach combines the molecular sieving properties of RE-MOFs with the processability of polymeric membranes, offering a pathway to scalable separation technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!