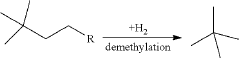Neopentane's Role in Pharmaceutical Synthesis Processes
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane in Pharma: Background and Objectives
Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, has emerged as a significant compound in pharmaceutical synthesis processes. This highly branched alkane, with its unique structural properties, has garnered attention in the pharmaceutical industry due to its potential to enhance drug development and manufacturing techniques.
The evolution of pharmaceutical synthesis has been marked by continuous efforts to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. In this context, neopentane's role has grown from a niche compound to a versatile tool in various synthetic pathways. Its compact, symmetrical structure and relative stability make it an attractive candidate for use in pharmaceutical applications.
Historically, the use of neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis was limited due to its perceived lack of reactivity and the challenges associated with its handling. However, recent advancements in organic chemistry and process engineering have unlocked new possibilities for its application. The pharmaceutical industry's increasing focus on green chemistry and sustainable practices has further propelled interest in neopentane as a potential alternative to more environmentally harmful solvents and reagents.
The primary objective of exploring neopentane's role in pharmaceutical synthesis is to leverage its unique properties to develop more efficient and sustainable drug manufacturing processes. Researchers aim to exploit its low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and inert nature to improve reaction conditions, enhance product purity, and facilitate easier separation and purification steps.
One of the key technical goals is to establish neopentane as a viable solvent or reagent in specific pharmaceutical synthesis reactions. This involves investigating its compatibility with various drug precursors and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), as well as its potential to improve reaction yields and selectivity. Additionally, researchers are exploring neopentane's potential in crystallization processes, where its properties could lead to better control over crystal morphology and polymorphism – critical factors in drug formulation and bioavailability.
Another important objective is to develop novel synthetic routes that incorporate neopentane as a key building block or intermediate. This could potentially lead to the creation of new drug molecules with improved pharmacological properties or enable more efficient synthesis of existing drugs. The exploration of neopentane-based chemistry may also open up new avenues for the modification of complex natural products, an area of significant interest in drug discovery.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of neopentane in synthesis processes represents a promising frontier. By understanding its potential and overcoming the technical challenges associated with its use, researchers aim to contribute to the development of more sustainable, cost-effective, and innovative drug manufacturing methods. This aligns with the broader industry trends towards greener chemistry, process intensification, and the pursuit of novel molecular entities to address unmet medical needs.
The evolution of pharmaceutical synthesis has been marked by continuous efforts to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. In this context, neopentane's role has grown from a niche compound to a versatile tool in various synthetic pathways. Its compact, symmetrical structure and relative stability make it an attractive candidate for use in pharmaceutical applications.
Historically, the use of neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis was limited due to its perceived lack of reactivity and the challenges associated with its handling. However, recent advancements in organic chemistry and process engineering have unlocked new possibilities for its application. The pharmaceutical industry's increasing focus on green chemistry and sustainable practices has further propelled interest in neopentane as a potential alternative to more environmentally harmful solvents and reagents.
The primary objective of exploring neopentane's role in pharmaceutical synthesis is to leverage its unique properties to develop more efficient and sustainable drug manufacturing processes. Researchers aim to exploit its low boiling point, high vapor pressure, and inert nature to improve reaction conditions, enhance product purity, and facilitate easier separation and purification steps.
One of the key technical goals is to establish neopentane as a viable solvent or reagent in specific pharmaceutical synthesis reactions. This involves investigating its compatibility with various drug precursors and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), as well as its potential to improve reaction yields and selectivity. Additionally, researchers are exploring neopentane's potential in crystallization processes, where its properties could lead to better control over crystal morphology and polymorphism – critical factors in drug formulation and bioavailability.
Another important objective is to develop novel synthetic routes that incorporate neopentane as a key building block or intermediate. This could potentially lead to the creation of new drug molecules with improved pharmacological properties or enable more efficient synthesis of existing drugs. The exploration of neopentane-based chemistry may also open up new avenues for the modification of complex natural products, an area of significant interest in drug discovery.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of neopentane in synthesis processes represents a promising frontier. By understanding its potential and overcoming the technical challenges associated with its use, researchers aim to contribute to the development of more sustainable, cost-effective, and innovative drug manufacturing methods. This aligns with the broader industry trends towards greener chemistry, process intensification, and the pursuit of novel molecular entities to address unmet medical needs.
Market Analysis: Neopentane-Based Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry has shown a growing interest in neopentane-based synthesis processes, driven by the compound's unique properties and potential applications. Market analysis reveals a steady increase in demand for neopentane in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly in the production of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates.
The global market for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall pharmaceutical industry average. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increased research and development activities, and the expanding geriatric population worldwide.
Key market segments for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals include oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and central nervous system disorders. These therapeutic areas have shown the most promising applications for neopentane-derived compounds, with several drugs in late-stage clinical trials or recently approved for market use.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neopentane-based pharmaceutical market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, high R&D investments, and favorable regulatory environments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing government support for pharmaceutical research.
The competitive landscape of the neopentane-based pharmaceutical market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to leverage neopentane's potential in drug synthesis, aiming to create more efficient and cost-effective production processes.
Market trends indicate a shift towards green chemistry practices, with neopentane offering potential advantages in terms of reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvents used in pharmaceutical synthesis. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry and may drive further adoption of neopentane-based processes.
Challenges in the market include regulatory hurdles, as new synthesis processes using neopentane must undergo rigorous safety and efficacy evaluations. Additionally, the volatility of neopentane prices, influenced by fluctuations in the petrochemical industry, poses a potential risk to manufacturers.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel drug delivery systems present new opportunities for neopentane applications in pharmaceutical synthesis. As research continues to uncover new potential uses for neopentane in drug manufacturing, the market is expected to expand further, attracting more investment and driving innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
The global market for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall pharmaceutical industry average. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increased research and development activities, and the expanding geriatric population worldwide.
Key market segments for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals include oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and central nervous system disorders. These therapeutic areas have shown the most promising applications for neopentane-derived compounds, with several drugs in late-stage clinical trials or recently approved for market use.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the neopentane-based pharmaceutical market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, high R&D investments, and favorable regulatory environments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing government support for pharmaceutical research.
The competitive landscape of the neopentane-based pharmaceutical market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and innovative biotech startups. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to leverage neopentane's potential in drug synthesis, aiming to create more efficient and cost-effective production processes.
Market trends indicate a shift towards green chemistry practices, with neopentane offering potential advantages in terms of reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvents used in pharmaceutical synthesis. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the pharmaceutical industry and may drive further adoption of neopentane-based processes.
Challenges in the market include regulatory hurdles, as new synthesis processes using neopentane must undergo rigorous safety and efficacy evaluations. Additionally, the volatility of neopentane prices, influenced by fluctuations in the petrochemical industry, poses a potential risk to manufacturers.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for neopentane-based pharmaceuticals remains positive. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel drug delivery systems present new opportunities for neopentane applications in pharmaceutical synthesis. As research continues to uncover new potential uses for neopentane in drug manufacturing, the market is expected to expand further, attracting more investment and driving innovation in the pharmaceutical industry.
Current Challenges in Neopentane Synthesis
The synthesis of neopentane presents several significant challenges in pharmaceutical processes. One of the primary obstacles is the high energy requirement for its production. The conventional methods of synthesizing neopentane often involve energy-intensive processes, which can be costly and environmentally unfriendly. This energy demand not only impacts the economic viability of neopentane synthesis but also raises concerns about sustainability in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Another major challenge lies in the control of reaction selectivity. Neopentane's unique structure, with a quaternary carbon center, makes it difficult to achieve high selectivity in its synthesis. Side reactions and the formation of unwanted isomers are common issues, leading to reduced yields and increased purification costs. This selectivity problem is particularly critical in pharmaceutical applications, where product purity is of utmost importance.
The scalability of neopentane synthesis processes poses another significant hurdle. While laboratory-scale production might be feasible, scaling up to industrial levels presents numerous engineering and safety challenges. The volatile nature of neopentane and its precursors requires specialized equipment and stringent safety measures, which can be complex and expensive to implement at larger scales.
Furthermore, the availability and cost of starting materials for neopentane synthesis can be problematic. Many synthetic routes rely on specific precursors that may not be readily available or are expensive, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of the process. This challenge is particularly acute in the pharmaceutical industry, where cost considerations play a crucial role in drug development and production.
Environmental concerns also present a significant challenge in neopentane synthesis. Many traditional methods involve the use of harsh reagents or generate substantial waste, which is increasingly unacceptable in the face of stricter environmental regulations. Developing greener, more sustainable synthesis routes for neopentane is a pressing need, especially in the environmentally conscious pharmaceutical sector.
Lastly, the optimization of reaction conditions for neopentane synthesis remains a complex task. Factors such as temperature, pressure, catalyst selection, and reaction time all play critical roles in the efficiency and yield of the process. Finding the optimal balance of these parameters, particularly for pharmaceutical-grade production, requires extensive research and development efforts, often involving costly and time-consuming experimentation.
Another major challenge lies in the control of reaction selectivity. Neopentane's unique structure, with a quaternary carbon center, makes it difficult to achieve high selectivity in its synthesis. Side reactions and the formation of unwanted isomers are common issues, leading to reduced yields and increased purification costs. This selectivity problem is particularly critical in pharmaceutical applications, where product purity is of utmost importance.
The scalability of neopentane synthesis processes poses another significant hurdle. While laboratory-scale production might be feasible, scaling up to industrial levels presents numerous engineering and safety challenges. The volatile nature of neopentane and its precursors requires specialized equipment and stringent safety measures, which can be complex and expensive to implement at larger scales.
Furthermore, the availability and cost of starting materials for neopentane synthesis can be problematic. Many synthetic routes rely on specific precursors that may not be readily available or are expensive, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of the process. This challenge is particularly acute in the pharmaceutical industry, where cost considerations play a crucial role in drug development and production.
Environmental concerns also present a significant challenge in neopentane synthesis. Many traditional methods involve the use of harsh reagents or generate substantial waste, which is increasingly unacceptable in the face of stricter environmental regulations. Developing greener, more sustainable synthesis routes for neopentane is a pressing need, especially in the environmentally conscious pharmaceutical sector.
Lastly, the optimization of reaction conditions for neopentane synthesis remains a complex task. Factors such as temperature, pressure, catalyst selection, and reaction time all play critical roles in the efficiency and yield of the process. Finding the optimal balance of these parameters, particularly for pharmaceutical-grade production, requires extensive research and development efforts, often involving costly and time-consuming experimentation.
Current Neopentane Synthesis Methodologies
01 Production and purification of neopentane
Various methods for producing and purifying neopentane are described. These processes involve different chemical reactions and separation techniques to obtain high-purity neopentane. The methods may include catalytic reactions, distillation, and other purification steps to remove impurities and achieve the desired product quality.- Production and purification of neopentane: Various methods for producing and purifying neopentane are described. These include processes for separating neopentane from other hydrocarbons, such as using distillation or membrane separation techniques. The purification methods aim to obtain high-purity neopentane for industrial applications.
- Neopentane as a refrigerant or blowing agent: Neopentane is utilized as a refrigerant or blowing agent in various applications. Its properties make it suitable for use in cooling systems, foam production, and as an alternative to traditional refrigerants. The compound's low boiling point and environmental characteristics contribute to its effectiveness in these roles.
- Neopentane in chemical synthesis: Neopentane serves as a starting material or intermediate in various chemical synthesis processes. It is used in the production of other organic compounds, including polymers, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals. The unique structure of neopentane makes it valuable in certain synthetic routes.
- Neopentane in fuel compositions: Neopentane is incorporated into fuel compositions to enhance their properties. It can be used as an additive or component in gasoline, diesel, or other fuel blends to improve combustion characteristics, reduce emissions, or enhance cold-start performance in engines.
- Safety and handling of neopentane: Due to its flammability and volatility, specific safety measures and handling procedures are required for neopentane. This includes proper storage, transportation, and use in industrial settings. Guidelines and equipment for safe handling and minimizing risks associated with neopentane are discussed.
02 Applications of neopentane in chemical processes
Neopentane is utilized in various chemical processes as a reactant, solvent, or intermediate. It plays a role in the production of other chemicals, polymers, and materials. The compound's unique properties make it suitable for specific applications in the chemical industry.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant
The use of neopentane as a refrigerant or propellant is explored in several patents. Its properties, such as low boiling point and low global warming potential, make it an attractive alternative to traditional refrigerants and propellants in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neopentane in polymer production
Neopentane is used in the production of polymers and plastics. It can serve as a blowing agent, polymerization medium, or contribute to the properties of the final polymer product. The compound's role in improving polymer characteristics or processing is described in several patents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Separation and analysis of neopentane
Methods for separating neopentane from mixtures and analyzing its purity are discussed in various patents. These techniques may involve chromatography, spectroscopy, or other analytical methods to identify and quantify neopentane in complex mixtures or to ensure product quality in industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neopentane-Based Drug Synthesis
The competitive landscape for neopentane's role in pharmaceutical synthesis processes is evolving rapidly. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by the expanding pharmaceutical sector. The technology is maturing, with major players like Novartis AG, Glaxo Group Ltd., and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. investing in research and development. Academic institutions such as the University of Michigan and Colorado State University are also contributing to advancements. The market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized chemical firms, indicating a diverse and competitive environment. As the technology matures, we can expect increased efficiency and novel applications in drug synthesis processes.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has developed innovative approaches for utilizing neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis processes. Their method involves using neopentane as a key intermediate in the synthesis of complex drug molecules, particularly those with branched carbon structures. The process employs a novel catalytic system that enables selective functionalization of neopentane's methyl groups, allowing for the efficient creation of quaternary carbon centers[1]. This approach has been successfully applied in the synthesis of several potential drug candidates, including novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer compounds[3]. Novartis has also explored the use of neopentane-derived building blocks in fragment-based drug discovery, leveraging the unique spatial properties of the neopentane core to access previously challenging chemical space[5].
Strengths: Enables access to complex molecular structures, improves efficiency in creating quaternary carbon centers, and expands chemical diversity in drug discovery. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and expertise, potentially increasing production costs.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group Ltd. has pioneered the use of neopentane derivatives in their pharmaceutical synthesis processes, focusing on improving the metabolic stability and bioavailability of drug candidates. Their approach involves incorporating neopentane-based moieties into drug scaffolds to create metabolically stable compounds with enhanced pharmacokinetic properties[2]. The company has developed a proprietary platform that utilizes neopentane-derived building blocks in the synthesis of novel protein kinase inhibitors, which have shown promise in oncology and immunology research[4]. Additionally, Glaxo has explored the use of neopentane as a solvent in green chemistry applications, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes[6].
Strengths: Improves drug metabolic stability and bioavailability, advances in targeted therapies, and promotes sustainable manufacturing practices. Weaknesses: May limit structural flexibility in some cases, potentially narrowing the range of accessible compound classes.
Innovative Neopentane Applications in Pharma
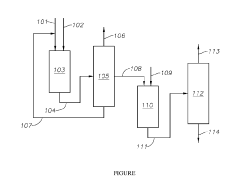
Production of Neopentane
PatentActiveUS20190169092A1
Innovation
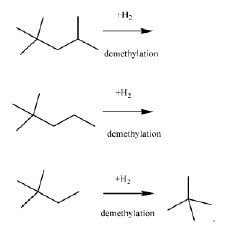
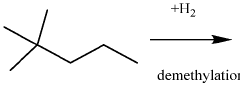
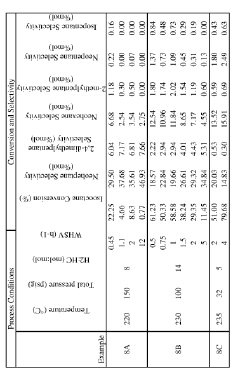
- A process involving the isomerization of C6-C7 paraffins to produce neohexane or neoheptane, followed by demethylation using a catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, to achieve high yields of neopentane from readily available C4-C7 paraffinic feed streams, such as light virgin naphtha.
Production of neopentane
PatentWO2018044596A1
Innovation
- A process involving the alkylation of isobutane with butylenes to produce isooctane, followed by demethylation in the presence of a catalyst, using a C4olefinic feed stream, such as a refinery raffinate, to achieve high yields of neopentane under mild conditions.
Environmental Impact of Neopentane Use
The use of neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis processes raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), neopentane can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone when released into the atmosphere. This can have detrimental effects on both human health and ecosystems, particularly in urban areas where VOC emissions are often concentrated.
Furthermore, the production of neopentane typically involves petroleum refining processes, which are energy-intensive and associated with greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon footprint of neopentane use in pharmaceutical synthesis extends beyond its direct application, encompassing its entire lifecycle from extraction to disposal.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact of neopentane use. Improper handling or accidental spills during pharmaceutical manufacturing processes can lead to contamination of water bodies. Neopentane's low water solubility means it can form a separate layer on water surfaces, potentially harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems.
In terms of waste management, the disposal of neopentane and neopentane-containing waste products poses challenges. Incineration, a common method for disposing of chemical waste, can result in the release of harmful combustion products if not properly controlled. Additionally, the potential for neopentane to contribute to the formation of hazardous waste streams in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes necessitates stringent waste management protocols.
The environmental persistence of neopentane is relatively low compared to some other organic compounds, as it tends to degrade in the atmosphere within days to weeks. However, its short-term effects on air quality and potential for contributing to smog formation remain significant concerns in areas with high industrial activity.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented measures to control VOC emissions, including those from pharmaceutical manufacturing. These regulations often require the implementation of best available techniques (BAT) for emission reduction, such as the use of closed systems, vapor recovery units, and efficient scrubbing technologies. Compliance with these regulations can lead to increased operational costs for pharmaceutical companies using neopentane in their synthesis processes.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. This has led to research into alternative solvents and reaction media that could potentially replace neopentane in certain synthesis processes, aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving process efficiency and product quality.
Furthermore, the production of neopentane typically involves petroleum refining processes, which are energy-intensive and associated with greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon footprint of neopentane use in pharmaceutical synthesis extends beyond its direct application, encompassing its entire lifecycle from extraction to disposal.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact of neopentane use. Improper handling or accidental spills during pharmaceutical manufacturing processes can lead to contamination of water bodies. Neopentane's low water solubility means it can form a separate layer on water surfaces, potentially harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems.
In terms of waste management, the disposal of neopentane and neopentane-containing waste products poses challenges. Incineration, a common method for disposing of chemical waste, can result in the release of harmful combustion products if not properly controlled. Additionally, the potential for neopentane to contribute to the formation of hazardous waste streams in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes necessitates stringent waste management protocols.
The environmental persistence of neopentane is relatively low compared to some other organic compounds, as it tends to degrade in the atmosphere within days to weeks. However, its short-term effects on air quality and potential for contributing to smog formation remain significant concerns in areas with high industrial activity.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented measures to control VOC emissions, including those from pharmaceutical manufacturing. These regulations often require the implementation of best available techniques (BAT) for emission reduction, such as the use of closed systems, vapor recovery units, and efficient scrubbing technologies. Compliance with these regulations can lead to increased operational costs for pharmaceutical companies using neopentane in their synthesis processes.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. This has led to research into alternative solvents and reaction media that could potentially replace neopentane in certain synthesis processes, aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving process efficiency and product quality.
Regulatory Framework for Neopentane in Pharma
The regulatory framework for neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis processes is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful navigation by industry stakeholders. At the global level, the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides guidelines that influence the use of solvents like neopentane in drug manufacturing. These guidelines, particularly ICH Q3C, categorize solvents based on their potential risks and set limits for residual solvents in pharmaceutical products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of neopentane and other solvents in pharmaceutical processes. The FDA's guidance on residual solvents aligns with ICH guidelines and requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their products meet safety standards. The agency also mandates that any changes in the manufacturing process, including solvent use, must be reported and may require approval through supplemental New Drug Applications (sNDAs) or Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) amendments.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) enforces similar regulations within the European Union. The EMA's guidelines on residual solvents in medicinal products closely follow ICH recommendations. Manufacturers must provide detailed information on the use of solvents like neopentane in their Marketing Authorization Applications (MAAs) and ensure compliance with established limits.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis. In many jurisdictions, including the United States and European Union, neopentane is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). As such, its use is subject to emissions controls and reporting requirements under clean air regulations. Pharmaceutical companies must implement appropriate containment and recovery systems to minimize environmental impact and comply with local and national environmental protection laws.
Occupational health and safety regulations further govern the handling and use of neopentane in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US and the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) set standards for workplace exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols when working with volatile solvents.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in pharmaceutical manufacturing, regulatory bodies are beginning to incorporate green chemistry principles into their frameworks. This trend may influence future regulations on the use of solvents like neopentane, potentially encouraging the adoption of more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes that minimize solvent use.
Compliance with these multifaceted regulations requires pharmaceutical companies to maintain robust quality management systems, conduct thorough risk assessments, and implement comprehensive documentation practices. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities ensure ongoing compliance and may lead to updates in regulatory requirements based on new scientific evidence or emerging safety concerns.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of neopentane and other solvents in pharmaceutical processes. The FDA's guidance on residual solvents aligns with ICH guidelines and requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their products meet safety standards. The agency also mandates that any changes in the manufacturing process, including solvent use, must be reported and may require approval through supplemental New Drug Applications (sNDAs) or Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) amendments.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) enforces similar regulations within the European Union. The EMA's guidelines on residual solvents in medicinal products closely follow ICH recommendations. Manufacturers must provide detailed information on the use of solvents like neopentane in their Marketing Authorization Applications (MAAs) and ensure compliance with established limits.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of neopentane in pharmaceutical synthesis. In many jurisdictions, including the United States and European Union, neopentane is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). As such, its use is subject to emissions controls and reporting requirements under clean air regulations. Pharmaceutical companies must implement appropriate containment and recovery systems to minimize environmental impact and comply with local and national environmental protection laws.
Occupational health and safety regulations further govern the handling and use of neopentane in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US and the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) set standards for workplace exposure limits, personal protective equipment, and safety protocols when working with volatile solvents.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration in pharmaceutical manufacturing, regulatory bodies are beginning to incorporate green chemistry principles into their frameworks. This trend may influence future regulations on the use of solvents like neopentane, potentially encouraging the adoption of more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes that minimize solvent use.
Compliance with these multifaceted regulations requires pharmaceutical companies to maintain robust quality management systems, conduct thorough risk assessments, and implement comprehensive documentation practices. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities ensure ongoing compliance and may lead to updates in regulatory requirements based on new scientific evidence or emerging safety concerns.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!