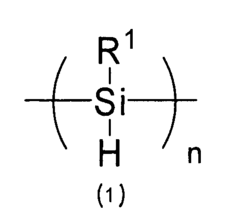
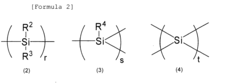
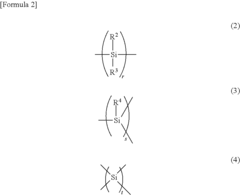Polysilane Optical Properties for Improved Signal Transmission
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Optics Background and Objectives
Polysilanes have emerged as a promising class of materials for advanced optical applications, particularly in the realm of signal transmission. The evolution of polysilane research can be traced back to the 1980s when their unique electronic and optical properties were first recognized. Since then, the field has witnessed significant advancements, driven by the growing demand for high-performance optical materials in telecommunications, photonics, and optoelectronics.
The primary objective of research on polysilane optical properties is to enhance signal transmission efficiency and reliability in optical communication systems. This goal aligns with the broader trend in the telecommunications industry towards faster, more robust data transfer capabilities. Polysilanes offer several advantages over traditional materials, including their tunable optical properties, ease of processing, and potential for integration with existing silicon-based technologies.
One of the key areas of focus in polysilane optics research is the manipulation of their molecular structure to optimize light transmission characteristics. By altering the side chains and backbone composition of polysilanes, researchers aim to achieve precise control over refractive indices, optical absorption, and emission properties. This tailoring of molecular architecture opens up possibilities for creating materials with specific optical responses suited for various applications in signal transmission.
Another critical aspect of polysilane research is the investigation of their nonlinear optical properties. These properties are particularly relevant for applications in optical switching and signal processing, where rapid and efficient manipulation of light signals is essential. The exploration of nonlinear effects in polysilanes could lead to the development of novel devices for all-optical signal processing, potentially revolutionizing the field of optical communications.
The study of polysilane thin films and nanostructures represents a significant trend in the field. These structures offer unique opportunities for enhancing light-matter interactions and improving signal transmission efficiency. Research in this area aims to develop advanced waveguides, optical modulators, and other photonic components that can leverage the unique properties of polysilanes at the nanoscale.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing focus on integrating polysilane-based materials with existing optical technologies. This integration presents both challenges and opportunities, driving research towards developing compatible processing techniques and exploring hybrid material systems. The ultimate goal is to create seamless, high-performance optical systems that can meet the ever-growing demands of modern communication networks.
In conclusion, the research on polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission is a dynamic and multifaceted field with significant potential for technological advancement. By addressing current limitations and exploring new frontiers in material design and application, this research aims to pave the way for next-generation optical communication systems with enhanced performance and capabilities.
The primary objective of research on polysilane optical properties is to enhance signal transmission efficiency and reliability in optical communication systems. This goal aligns with the broader trend in the telecommunications industry towards faster, more robust data transfer capabilities. Polysilanes offer several advantages over traditional materials, including their tunable optical properties, ease of processing, and potential for integration with existing silicon-based technologies.
One of the key areas of focus in polysilane optics research is the manipulation of their molecular structure to optimize light transmission characteristics. By altering the side chains and backbone composition of polysilanes, researchers aim to achieve precise control over refractive indices, optical absorption, and emission properties. This tailoring of molecular architecture opens up possibilities for creating materials with specific optical responses suited for various applications in signal transmission.
Another critical aspect of polysilane research is the investigation of their nonlinear optical properties. These properties are particularly relevant for applications in optical switching and signal processing, where rapid and efficient manipulation of light signals is essential. The exploration of nonlinear effects in polysilanes could lead to the development of novel devices for all-optical signal processing, potentially revolutionizing the field of optical communications.
The study of polysilane thin films and nanostructures represents a significant trend in the field. These structures offer unique opportunities for enhancing light-matter interactions and improving signal transmission efficiency. Research in this area aims to develop advanced waveguides, optical modulators, and other photonic components that can leverage the unique properties of polysilanes at the nanoscale.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing focus on integrating polysilane-based materials with existing optical technologies. This integration presents both challenges and opportunities, driving research towards developing compatible processing techniques and exploring hybrid material systems. The ultimate goal is to create seamless, high-performance optical systems that can meet the ever-growing demands of modern communication networks.
In conclusion, the research on polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission is a dynamic and multifaceted field with significant potential for technological advancement. By addressing current limitations and exploring new frontiers in material design and application, this research aims to pave the way for next-generation optical communication systems with enhanced performance and capabilities.
Signal Transmission Market Analysis
The signal transmission market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-speed data transfer and reliable communication systems across various industries. This market encompasses a wide range of technologies, including optical fiber, wireless, and satellite communications, with optical fiber transmission playing a crucial role in meeting the ever-growing bandwidth requirements.
The global optical fiber market, which is closely related to signal transmission, was valued at approximately $4.48 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $6.81 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of 5G networks, increasing internet penetration, and the growing demand for high-speed connectivity in both developed and developing economies.
In the context of polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission, there is a growing interest in exploring novel materials that can enhance the efficiency and performance of optical communication systems. Polysilanes, with their unique electronic and optical properties, have shown potential in various optoelectronic applications, including signal transmission.
The demand for improved signal transmission technologies is driven by several factors. First, the exponential growth in data traffic, fueled by the proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), requires more efficient and higher-capacity transmission systems. Second, the ongoing deployment of 5G networks and the future development of 6G technologies necessitate advanced materials and transmission methods to support ultra-high-speed and low-latency communications.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of cloud computing, edge computing, and artificial intelligence applications is creating a surge in data center traffic, which in turn drives the demand for high-performance signal transmission solutions. The data center interconnect market, a subset of the signal transmission market, is expected to grow from $8.2 billion in 2020 to $17.9 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 13.9%.
The automotive and aerospace industries are also contributing to the growth of the signal transmission market. The rise of autonomous vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) requires robust and reliable signal transmission technologies to ensure safe and efficient operation. Similarly, the aerospace sector demands high-performance communication systems for both commercial and military applications.
In terms of geographical distribution, North America and Asia-Pacific are the leading regions in the signal transmission market. North America benefits from early technology adoption and significant investments in research and development, while Asia-Pacific is driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major electronics manufacturing hubs.
The global optical fiber market, which is closely related to signal transmission, was valued at approximately $4.48 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $6.81 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of 5G networks, increasing internet penetration, and the growing demand for high-speed connectivity in both developed and developing economies.
In the context of polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission, there is a growing interest in exploring novel materials that can enhance the efficiency and performance of optical communication systems. Polysilanes, with their unique electronic and optical properties, have shown potential in various optoelectronic applications, including signal transmission.
The demand for improved signal transmission technologies is driven by several factors. First, the exponential growth in data traffic, fueled by the proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), requires more efficient and higher-capacity transmission systems. Second, the ongoing deployment of 5G networks and the future development of 6G technologies necessitate advanced materials and transmission methods to support ultra-high-speed and low-latency communications.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of cloud computing, edge computing, and artificial intelligence applications is creating a surge in data center traffic, which in turn drives the demand for high-performance signal transmission solutions. The data center interconnect market, a subset of the signal transmission market, is expected to grow from $8.2 billion in 2020 to $17.9 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 13.9%.
The automotive and aerospace industries are also contributing to the growth of the signal transmission market. The rise of autonomous vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) requires robust and reliable signal transmission technologies to ensure safe and efficient operation. Similarly, the aerospace sector demands high-performance communication systems for both commercial and military applications.
In terms of geographical distribution, North America and Asia-Pacific are the leading regions in the signal transmission market. North America benefits from early technology adoption and significant investments in research and development, while Asia-Pacific is driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major electronics manufacturing hubs.
Polysilane Optical Properties: Current Status and Challenges
Polysilanes have emerged as promising materials for optical applications, particularly in signal transmission. However, the current status of polysilane optical properties presents both significant advancements and notable challenges. Recent research has demonstrated the potential of polysilanes to exhibit unique optical characteristics, including high photosensitivity, tunable refractive indices, and efficient light emission.
One of the primary advantages of polysilanes is their σ-conjugated backbone structure, which contributes to their exceptional optical properties. This structure allows for efficient electron delocalization along the silicon chain, resulting in strong absorption and emission in the ultraviolet region. Furthermore, the optical properties of polysilanes can be tailored by modifying the side groups attached to the silicon backbone, offering a high degree of versatility in their application.
Despite these promising features, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of polysilanes in optical applications. One significant obstacle is the stability of polysilanes under prolonged exposure to light and heat. The photodegradation of polysilanes can lead to a decrease in their optical performance over time, limiting their long-term reliability in signal transmission applications.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of polysilane thin film fabrication techniques. The optical properties of polysilanes are highly dependent on their molecular orientation and crystallinity, which can be significantly influenced by the deposition method and processing conditions. Achieving consistent and reproducible thin films with desired optical characteristics remains a key area of focus for researchers in the field.
The development of polysilanes with enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidation is another critical challenge. While progress has been made in synthesizing more stable polysilane derivatives, further improvements are necessary to meet the demanding requirements of advanced optical devices and systems.
Additionally, the integration of polysilanes into existing optical technologies poses challenges related to compatibility and interface engineering. Ensuring seamless integration without compromising the unique optical properties of polysilanes is crucial for their successful implementation in signal transmission applications.
In terms of geographical distribution, research on polysilane optical properties is primarily concentrated in advanced materials science centers across North America, Europe, and East Asia. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry partners have been instrumental in driving progress in this field.
One of the primary advantages of polysilanes is their σ-conjugated backbone structure, which contributes to their exceptional optical properties. This structure allows for efficient electron delocalization along the silicon chain, resulting in strong absorption and emission in the ultraviolet region. Furthermore, the optical properties of polysilanes can be tailored by modifying the side groups attached to the silicon backbone, offering a high degree of versatility in their application.
Despite these promising features, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of polysilanes in optical applications. One significant obstacle is the stability of polysilanes under prolonged exposure to light and heat. The photodegradation of polysilanes can lead to a decrease in their optical performance over time, limiting their long-term reliability in signal transmission applications.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of polysilane thin film fabrication techniques. The optical properties of polysilanes are highly dependent on their molecular orientation and crystallinity, which can be significantly influenced by the deposition method and processing conditions. Achieving consistent and reproducible thin films with desired optical characteristics remains a key area of focus for researchers in the field.
The development of polysilanes with enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidation is another critical challenge. While progress has been made in synthesizing more stable polysilane derivatives, further improvements are necessary to meet the demanding requirements of advanced optical devices and systems.
Additionally, the integration of polysilanes into existing optical technologies poses challenges related to compatibility and interface engineering. Ensuring seamless integration without compromising the unique optical properties of polysilanes is crucial for their successful implementation in signal transmission applications.
In terms of geographical distribution, research on polysilane optical properties is primarily concentrated in advanced materials science centers across North America, Europe, and East Asia. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry partners have been instrumental in driving progress in this field.
Existing Polysilane Optical Enhancement Techniques
01 Optical properties of polysilane films
Polysilane films exhibit unique optical properties, including high transparency and refractive index. These properties make them suitable for various optical applications, such as waveguides and optical coatings. The optical characteristics can be tuned by modifying the molecular structure and composition of the polysilane.- Optical properties of polysilane films: Polysilane films exhibit unique optical properties, including high transparency and refractive index. These properties make them suitable for various optical applications, such as waveguides and optical coatings. The optical characteristics can be tuned by modifying the molecular structure and composition of the polysilane.
- Nonlinear optical properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes demonstrate significant nonlinear optical properties, including high third-order nonlinear susceptibility. These properties make them promising materials for applications in optical switching, optical limiting, and other photonic devices. The nonlinear optical response can be enhanced by incorporating specific functional groups or dopants into the polysilane structure.
- Photoluminescence and electroluminescence of polysilanes: Polysilanes exhibit strong photoluminescence and electroluminescence properties, making them suitable for light-emitting applications. The emission wavelength can be tuned by modifying the polysilane structure or incorporating chromophores. These properties are particularly useful in the development of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and other optoelectronic devices.
- Optical sensing applications of polysilanes: The optical properties of polysilanes can be utilized for sensing applications. Changes in the optical characteristics of polysilanes in response to external stimuli, such as temperature, pressure, or chemical species, can be used to develop optical sensors. These sensors can be applied in various fields, including environmental monitoring and biomedical diagnostics.
- Polysilane-based optical waveguides and photonic devices: Polysilanes can be used to fabricate optical waveguides and other photonic devices due to their unique optical properties. The high refractive index and transparency of polysilanes make them suitable for light guiding and manipulation in integrated optical circuits. These materials can be processed into various structures, such as thin films, fibers, and patterned structures, for photonic applications.
02 Nonlinear optical properties of polysilanes
Polysilanes demonstrate significant nonlinear optical properties, including high third-order nonlinear susceptibility. These properties make them promising materials for applications in optical switching, optical limiting, and other photonic devices. The nonlinear optical response can be enhanced by incorporating specific functional groups or dopants into the polysilane structure.Expand Specific Solutions03 Photoluminescence and electroluminescence of polysilanes
Polysilanes exhibit strong photoluminescence and electroluminescence properties, making them suitable for light-emitting devices and displays. The emission wavelength can be tuned by modifying the polysilane structure or incorporating chromophores. These materials show potential for applications in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and other optoelectronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optical sensing applications of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be used in optical sensing applications due to their unique optical properties and sensitivity to environmental changes. They can be employed in chemical and biological sensors, as well as in temperature and pressure sensing devices. The optical response of polysilanes can be tailored to detect specific analytes or physical parameters.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane-based optical waveguides and photonic structures
Polysilanes can be used to fabricate optical waveguides and photonic structures due to their high refractive index and processability. These materials can be patterned using various techniques to create complex optical structures, such as gratings, resonators, and photonic crystals. Polysilane-based photonic devices show potential for applications in optical communications and integrated optics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Research and Development
The research on polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission is in a developing stage, with the market showing potential for growth. The technology's maturity is still evolving, as evidenced by ongoing research efforts from various players. Companies like Dow Silicones Corp., Momentive Performance Materials, and JSR Corp. are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in silicone-based materials. Academic institutions such as Wuhan University and East China Normal University are contributing to fundamental research. The involvement of major electronics firms like LG Electronics and ZTE Corp. suggests growing interest in practical applications. This competitive landscape indicates a dynamic field with opportunities for innovation and market expansion in optical signal transmission technologies.
Dow Silicones Corp.
Technical Solution: Dow Silicones Corp. has been actively researching polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission. Their approach focuses on developing high-performance polysilane materials for optical waveguides and photonic integrated circuits. They have patented several novel polysilane compositions with enhanced thermal stability and optical transparency in the near-infrared region[10]. Dow's research has also explored the use of polysilane-based nanocomposites, incorporating nanoparticles to fine-tune the refractive index and reduce optical losses[11]. Additionally, they have developed processing techniques to create ultra-smooth polysilane films, which are crucial for minimizing scattering losses in optical waveguides[12].
Strengths: Strong focus on practical applications and scalable manufacturing processes, extensive patent portfolio in polysilane materials. Weaknesses: May face competition from alternative materials in some applications, potential environmental concerns with certain polysilane compositions.
Momentive Performance Materials, Inc.
Technical Solution: Momentive Performance Materials has made significant strides in polysilane research for optical applications. Their approach focuses on developing polysilane-based materials with enhanced processability and optical performance. They have patented several polysilane copolymers that exhibit improved solubility and film-forming properties while maintaining excellent optical characteristics[13]. Momentive's research has also explored the use of polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide and silicon nitride optical materials, which show promise for high-temperature and harsh environment applications[14]. Additionally, they have developed surface modification techniques for polysilane nanoparticles, enabling their integration into various optical composite materials with tailored properties[15].
Strengths: Strong focus on material processability and integration into existing manufacturing processes, diverse range of polysilane-based materials for different optical applications. Weaknesses: Some specialized polysilane materials may have limited market size, potential regulatory challenges for certain applications.
Breakthrough Polysilane Optical Property Innovations
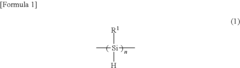
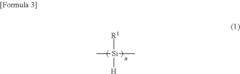
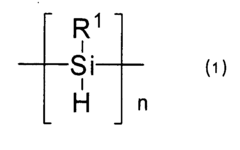
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Production
The production of polysilanes, while promising for their optical properties and potential in signal transmission, raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. The synthesis of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, which can have adverse effects on the environment if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental impacts of polysilane production is the energy consumption associated with the manufacturing process. The synthesis often requires high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy usage and consequent greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to the carbon footprint of the material and raises questions about its sustainability in the context of global climate change mitigation efforts.
Chemical waste generation is another critical environmental issue in polysilane production. The synthesis process may involve the use of toxic precursors and solvents, which can result in the creation of hazardous by-products. Proper disposal and treatment of these waste materials are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Additionally, the potential for accidental releases during production or transportation poses risks to local ecosystems and human health.
Water usage and pollution are also significant concerns in polysilane manufacturing. The production process may require substantial amounts of water for cooling and purification steps. Wastewater from these processes can contain trace amounts of chemicals and must be carefully treated before release to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources.
The raw materials used in polysilane production, particularly silicon-based compounds, often come from mining activities. This upstream impact on the environment includes land disturbance, habitat destruction, and potential water pollution associated with extractive industries. The sustainability of the supply chain for these raw materials is an important consideration in assessing the overall environmental footprint of polysilane technologies.
As research into polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly production methods. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less toxic reagents and solvents, are being explored to reduce the environmental impact of synthesis. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve energy efficiency in production processes and to implement closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation and resource consumption.
The potential for recycling and end-of-life management of polysilane-based products is another area of environmental concern. As these materials find applications in various technologies, considerations for their disposal or reuse become increasingly important. Developing effective recycling methods for polysilanes and their derivatives could significantly reduce their long-term environmental impact and improve the overall sustainability of their use in signal transmission applications.
One of the primary environmental impacts of polysilane production is the energy consumption associated with the manufacturing process. The synthesis often requires high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy usage and consequent greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to the carbon footprint of the material and raises questions about its sustainability in the context of global climate change mitigation efforts.
Chemical waste generation is another critical environmental issue in polysilane production. The synthesis process may involve the use of toxic precursors and solvents, which can result in the creation of hazardous by-products. Proper disposal and treatment of these waste materials are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Additionally, the potential for accidental releases during production or transportation poses risks to local ecosystems and human health.
Water usage and pollution are also significant concerns in polysilane manufacturing. The production process may require substantial amounts of water for cooling and purification steps. Wastewater from these processes can contain trace amounts of chemicals and must be carefully treated before release to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources.
The raw materials used in polysilane production, particularly silicon-based compounds, often come from mining activities. This upstream impact on the environment includes land disturbance, habitat destruction, and potential water pollution associated with extractive industries. The sustainability of the supply chain for these raw materials is an important consideration in assessing the overall environmental footprint of polysilane technologies.
As research into polysilane optical properties for improved signal transmission progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly production methods. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less toxic reagents and solvents, are being explored to reduce the environmental impact of synthesis. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve energy efficiency in production processes and to implement closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation and resource consumption.
The potential for recycling and end-of-life management of polysilane-based products is another area of environmental concern. As these materials find applications in various technologies, considerations for their disposal or reuse become increasingly important. Developing effective recycling methods for polysilanes and their derivatives could significantly reduce their long-term environmental impact and improve the overall sustainability of their use in signal transmission applications.
Polysilane Integration in Photonic Devices
The integration of polysilanes into photonic devices represents a significant advancement in the field of optoelectronics. Polysilanes, with their unique optical properties, offer promising potential for enhancing signal transmission in various photonic applications. These silicon-based polymers exhibit strong σ-electron delocalization along their backbone, resulting in exceptional optical and electronic characteristics.
One of the primary advantages of incorporating polysilanes into photonic devices is their high photosensitivity and strong absorption in the ultraviolet region. This property makes them particularly suitable for use in photodetectors and optical sensors. By leveraging the UV absorption capabilities of polysilanes, researchers have developed highly sensitive photodetectors with improved response times and enhanced spectral selectivity.
Furthermore, polysilanes demonstrate remarkable photoluminescence properties, emitting light in the visible spectrum when excited by UV radiation. This characteristic has led to their application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and electroluminescent devices. The integration of polysilanes as active layers in organic LEDs has shown potential for improving device efficiency and color purity.
In the realm of optical waveguides, polysilanes have been explored as novel materials for signal transmission. Their high refractive index and low optical loss in certain wavelength ranges make them attractive candidates for waveguide fabrication. Researchers have successfully demonstrated polysilane-based waveguides with improved light propagation and reduced signal attenuation compared to conventional materials.
Another area where polysilane integration shows promise is in the development of nonlinear optical devices. The strong σ-electron delocalization in polysilanes contributes to their significant nonlinear optical response. This property has been exploited in the creation of optical switches and modulators with enhanced switching speeds and modulation depths.
The integration of polysilanes into photonic crystals has also garnered attention. By incorporating polysilanes into periodic structures, researchers have observed unique photonic bandgap effects and enhanced light-matter interactions. These polysilane-based photonic crystals offer potential applications in optical filtering, sensing, and light manipulation at the nanoscale.
Despite the promising advancements, challenges remain in the widespread integration of polysilanes in photonic devices. Issues such as long-term stability, processability, and compatibility with existing fabrication techniques need to be addressed. Ongoing research focuses on developing novel polysilane derivatives and optimizing integration methods to overcome these limitations and fully harness the potential of polysilanes in next-generation photonic devices.
One of the primary advantages of incorporating polysilanes into photonic devices is their high photosensitivity and strong absorption in the ultraviolet region. This property makes them particularly suitable for use in photodetectors and optical sensors. By leveraging the UV absorption capabilities of polysilanes, researchers have developed highly sensitive photodetectors with improved response times and enhanced spectral selectivity.
Furthermore, polysilanes demonstrate remarkable photoluminescence properties, emitting light in the visible spectrum when excited by UV radiation. This characteristic has led to their application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and electroluminescent devices. The integration of polysilanes as active layers in organic LEDs has shown potential for improving device efficiency and color purity.
In the realm of optical waveguides, polysilanes have been explored as novel materials for signal transmission. Their high refractive index and low optical loss in certain wavelength ranges make them attractive candidates for waveguide fabrication. Researchers have successfully demonstrated polysilane-based waveguides with improved light propagation and reduced signal attenuation compared to conventional materials.
Another area where polysilane integration shows promise is in the development of nonlinear optical devices. The strong σ-electron delocalization in polysilanes contributes to their significant nonlinear optical response. This property has been exploited in the creation of optical switches and modulators with enhanced switching speeds and modulation depths.
The integration of polysilanes into photonic crystals has also garnered attention. By incorporating polysilanes into periodic structures, researchers have observed unique photonic bandgap effects and enhanced light-matter interactions. These polysilane-based photonic crystals offer potential applications in optical filtering, sensing, and light manipulation at the nanoscale.
Despite the promising advancements, challenges remain in the widespread integration of polysilanes in photonic devices. Issues such as long-term stability, processability, and compatibility with existing fabrication techniques need to be addressed. Ongoing research focuses on developing novel polysilane derivatives and optimizing integration methods to overcome these limitations and fully harness the potential of polysilanes in next-generation photonic devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!