Silicone Rubber for Sustainable Packaging Development
JUL 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Silicone Rubber Packaging Evolution and Objectives
Silicone rubber has emerged as a promising material for sustainable packaging solutions, evolving significantly over the past decades. Initially developed in the 1940s, silicone rubber's unique properties, including flexibility, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures, have made it increasingly attractive for various industries, including packaging.
The evolution of silicone rubber in packaging began with its use in specialized applications, such as medical device packaging and high-temperature food containers. As environmental concerns grew, researchers and manufacturers recognized the potential of silicone rubber to address sustainability challenges in the packaging industry. This led to a shift in focus towards developing silicone rubber formulations specifically tailored for sustainable packaging applications.
In recent years, the packaging industry has faced mounting pressure to reduce plastic waste and improve recyclability. Silicone rubber has gained attention as a potential alternative to traditional plastics due to its long lifespan, reusability, and potential for recycling. The material's ability to withstand multiple use cycles without degradation aligns well with circular economy principles, driving further research and development in this area.
The objectives of current research on silicone rubber for sustainable packaging development are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to enhance the material's eco-friendly properties while maintaining its desirable characteristics. This includes improving biodegradability without compromising durability, developing more efficient recycling processes, and reducing the environmental impact of silicone rubber production.
Another key objective is to expand the range of applications for silicone rubber in packaging. This involves creating new formulations that can replace single-use plastics in various packaging formats, from food containers to shipping materials. Researchers are also exploring ways to combine silicone rubber with other sustainable materials to create hybrid solutions that offer the best of both worlds.
Furthermore, there is a strong focus on optimizing the production processes of silicone rubber packaging to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing techniques, exploring renewable energy sources for production, and implementing closed-loop systems to recapture and reuse materials throughout the manufacturing cycle.
As the packaging industry continues to evolve, the objectives for silicone rubber research extend to meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and consumer demands for sustainable packaging solutions. This drives ongoing efforts to improve the material's performance, reduce costs, and enhance its overall sustainability profile, positioning silicone rubber as a key player in the future of eco-friendly packaging.
The evolution of silicone rubber in packaging began with its use in specialized applications, such as medical device packaging and high-temperature food containers. As environmental concerns grew, researchers and manufacturers recognized the potential of silicone rubber to address sustainability challenges in the packaging industry. This led to a shift in focus towards developing silicone rubber formulations specifically tailored for sustainable packaging applications.
In recent years, the packaging industry has faced mounting pressure to reduce plastic waste and improve recyclability. Silicone rubber has gained attention as a potential alternative to traditional plastics due to its long lifespan, reusability, and potential for recycling. The material's ability to withstand multiple use cycles without degradation aligns well with circular economy principles, driving further research and development in this area.
The objectives of current research on silicone rubber for sustainable packaging development are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to enhance the material's eco-friendly properties while maintaining its desirable characteristics. This includes improving biodegradability without compromising durability, developing more efficient recycling processes, and reducing the environmental impact of silicone rubber production.
Another key objective is to expand the range of applications for silicone rubber in packaging. This involves creating new formulations that can replace single-use plastics in various packaging formats, from food containers to shipping materials. Researchers are also exploring ways to combine silicone rubber with other sustainable materials to create hybrid solutions that offer the best of both worlds.
Furthermore, there is a strong focus on optimizing the production processes of silicone rubber packaging to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing techniques, exploring renewable energy sources for production, and implementing closed-loop systems to recapture and reuse materials throughout the manufacturing cycle.
As the packaging industry continues to evolve, the objectives for silicone rubber research extend to meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and consumer demands for sustainable packaging solutions. This drives ongoing efforts to improve the material's performance, reduce costs, and enhance its overall sustainability profile, positioning silicone rubber as a key player in the future of eco-friendly packaging.
Sustainable Packaging Market Analysis
The sustainable packaging market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations. The global sustainable packaging market was valued at $274.15 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $470.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period. This robust growth is attributed to the rising demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions across various industries, including food and beverage, healthcare, and consumer goods.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards environmentally responsible products, with 74% of consumers willing to pay more for sustainable packaging. This trend has prompted major corporations to commit to sustainable packaging goals, further driving market expansion. For instance, Coca-Cola aims to make 100% of its packaging recyclable by 2025, while Unilever plans to halve its use of virgin plastic by 2025.
The food and beverage sector dominates the sustainable packaging market, accounting for over 40% of the total market share. This is due to the increasing demand for biodegradable and compostable packaging materials in this industry. The healthcare sector is also emerging as a significant contributor to market growth, with a focus on reducing plastic waste in medical packaging.
Geographically, Europe leads the sustainable packaging market, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Europe's dominance is attributed to strict regulations on single-use plastics and high consumer awareness. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
Key trends shaping the sustainable packaging market include the adoption of bioplastics, the development of recyclable and compostable materials, and the implementation of circular economy principles. The use of silicone rubber in sustainable packaging is gaining traction due to its durability, reusability, and potential for recycling.
However, challenges such as higher production costs and limited recycling infrastructure persist. The average cost of sustainable packaging materials is 25-30% higher than conventional alternatives, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, the lack of standardized recycling processes for some sustainable materials, including certain types of silicone rubber, poses challenges for widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, the sustainable packaging market is poised for continued growth. Innovations in material science, advancements in recycling technologies, and increasing collaborations between packaging manufacturers and recycling companies are expected to drive the market forward. The integration of smart packaging technologies with sustainable materials is also emerging as a promising trend, offering opportunities for enhanced product traceability and reduced food waste.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards environmentally responsible products, with 74% of consumers willing to pay more for sustainable packaging. This trend has prompted major corporations to commit to sustainable packaging goals, further driving market expansion. For instance, Coca-Cola aims to make 100% of its packaging recyclable by 2025, while Unilever plans to halve its use of virgin plastic by 2025.
The food and beverage sector dominates the sustainable packaging market, accounting for over 40% of the total market share. This is due to the increasing demand for biodegradable and compostable packaging materials in this industry. The healthcare sector is also emerging as a significant contributor to market growth, with a focus on reducing plastic waste in medical packaging.
Geographically, Europe leads the sustainable packaging market, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Europe's dominance is attributed to strict regulations on single-use plastics and high consumer awareness. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
Key trends shaping the sustainable packaging market include the adoption of bioplastics, the development of recyclable and compostable materials, and the implementation of circular economy principles. The use of silicone rubber in sustainable packaging is gaining traction due to its durability, reusability, and potential for recycling.
However, challenges such as higher production costs and limited recycling infrastructure persist. The average cost of sustainable packaging materials is 25-30% higher than conventional alternatives, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, the lack of standardized recycling processes for some sustainable materials, including certain types of silicone rubber, poses challenges for widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, the sustainable packaging market is poised for continued growth. Innovations in material science, advancements in recycling technologies, and increasing collaborations between packaging manufacturers and recycling companies are expected to drive the market forward. The integration of smart packaging technologies with sustainable materials is also emerging as a promising trend, offering opportunities for enhanced product traceability and reduced food waste.
Silicone Rubber Technology: Current State and Challenges
Silicone rubber technology has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in the context of sustainable packaging development. However, it still faces several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential in this field. The current state of silicone rubber technology is characterized by its versatility, durability, and eco-friendly properties, making it an attractive option for sustainable packaging solutions.
One of the primary advantages of silicone rubber is its excellent thermal stability and resistance to extreme temperatures. This property allows for the creation of packaging materials that can withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, from freezing to high heat, without degrading or releasing harmful substances. Additionally, silicone rubber exhibits remarkable flexibility and elasticity, enabling the production of packaging that can be easily molded into various shapes and sizes while maintaining its structural integrity.
Despite these advantages, the widespread adoption of silicone rubber in sustainable packaging faces several challenges. One significant issue is the relatively high cost of production compared to traditional packaging materials. This cost factor often limits its use to high-end or specialized applications, hindering its broader implementation in everyday consumer goods packaging.
Another challenge lies in the recyclability of silicone rubber products. While silicone rubber is theoretically recyclable, the current recycling infrastructure is not well-equipped to handle this material efficiently. The lack of established recycling processes for silicone rubber packaging poses a significant obstacle to its positioning as a truly sustainable solution.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of silicone rubber remains a concern. Although it does not break down into harmful microplastics like traditional plastics, silicone rubber's long-term environmental impact is still not fully understood. Research is ongoing to develop biodegradable variants of silicone rubber that maintain its desirable properties while addressing end-of-life concerns.
The industry is also grappling with the challenge of improving the barrier properties of silicone rubber for certain packaging applications. While silicone rubber exhibits good resistance to moisture and gases, enhancing its ability to preserve food and other perishable items over extended periods remains an area of active research and development.
In response to these challenges, researchers and manufacturers are exploring innovative approaches to silicone rubber technology. This includes the development of hybrid materials that combine silicone rubber with other sustainable materials to enhance performance and reduce costs. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize production processes to increase efficiency and lower the overall environmental footprint of silicone rubber manufacturing.
One of the primary advantages of silicone rubber is its excellent thermal stability and resistance to extreme temperatures. This property allows for the creation of packaging materials that can withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, from freezing to high heat, without degrading or releasing harmful substances. Additionally, silicone rubber exhibits remarkable flexibility and elasticity, enabling the production of packaging that can be easily molded into various shapes and sizes while maintaining its structural integrity.
Despite these advantages, the widespread adoption of silicone rubber in sustainable packaging faces several challenges. One significant issue is the relatively high cost of production compared to traditional packaging materials. This cost factor often limits its use to high-end or specialized applications, hindering its broader implementation in everyday consumer goods packaging.
Another challenge lies in the recyclability of silicone rubber products. While silicone rubber is theoretically recyclable, the current recycling infrastructure is not well-equipped to handle this material efficiently. The lack of established recycling processes for silicone rubber packaging poses a significant obstacle to its positioning as a truly sustainable solution.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of silicone rubber remains a concern. Although it does not break down into harmful microplastics like traditional plastics, silicone rubber's long-term environmental impact is still not fully understood. Research is ongoing to develop biodegradable variants of silicone rubber that maintain its desirable properties while addressing end-of-life concerns.
The industry is also grappling with the challenge of improving the barrier properties of silicone rubber for certain packaging applications. While silicone rubber exhibits good resistance to moisture and gases, enhancing its ability to preserve food and other perishable items over extended periods remains an area of active research and development.
In response to these challenges, researchers and manufacturers are exploring innovative approaches to silicone rubber technology. This includes the development of hybrid materials that combine silicone rubber with other sustainable materials to enhance performance and reduce costs. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize production processes to increase efficiency and lower the overall environmental footprint of silicone rubber manufacturing.
Current Silicone Rubber Packaging Solutions
01 Composition and preparation of silicone rubber
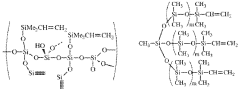
Silicone rubber is typically composed of silicone polymers, fillers, and curing agents. The preparation process often involves mixing these components, shaping the mixture, and then curing it to form the final rubber product. Various additives can be incorporated to modify properties such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.- Composition and formulation of silicone rubber: Silicone rubber compositions typically consist of silicone polymers, fillers, and curing agents. The formulation can be adjusted to achieve specific properties such as hardness, elasticity, and heat resistance. Various additives may be incorporated to enhance performance characteristics or provide additional functionalities.
- Manufacturing processes for silicone rubber products: Different manufacturing techniques are employed to produce silicone rubber products, including molding, extrusion, and calendering. These processes involve mixing the raw materials, shaping the compound, and curing it to achieve the desired form and properties. Advanced manufacturing methods may incorporate automation and precision control for improved quality and efficiency.
- Modifications and enhancements to silicone rubber: Silicone rubber can be modified or enhanced through various means, such as blending with other polymers, incorporating nanoparticles, or chemical modifications. These modifications can improve properties like tear strength, chemical resistance, or electrical conductivity, expanding the range of applications for silicone rubber materials.
- Applications of silicone rubber in various industries: Silicone rubber finds extensive use across multiple industries due to its unique properties. It is commonly used in medical devices, automotive parts, electronics, construction materials, and consumer products. The material's biocompatibility, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures make it suitable for diverse applications.
- Environmental and sustainability aspects of silicone rubber: Research and development efforts are focused on improving the environmental profile of silicone rubber. This includes developing bio-based alternatives, enhancing recyclability, and reducing the environmental impact of production processes. Sustainable practices in the silicone rubber industry are becoming increasingly important to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demands.
02 Modification of silicone rubber properties
The properties of silicone rubber can be modified through the addition of specific compounds or by altering the polymer structure. This can include improving mechanical strength, enhancing thermal stability, or increasing chemical resistance. Techniques may involve blending with other polymers or incorporating nanoparticles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of silicone rubber
Silicone rubber finds wide applications across various industries due to its unique properties. It is used in medical devices, automotive parts, electrical insulation, and consumer products. Its biocompatibility, heat resistance, and flexibility make it suitable for diverse applications ranging from seals and gaskets to implantable medical devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Curing methods for silicone rubber
Various curing methods are employed for silicone rubber, including heat curing, room temperature vulcanization (RTV), and UV curing. The choice of curing method affects the final properties of the rubber and is often determined by the specific application requirements. Catalysts and curing agents play crucial roles in these processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Silicone rubber composites and blends
Silicone rubber can be combined with other materials to create composites or blends with enhanced properties. This includes reinforcing with fibers, blending with other elastomers, or incorporating functional fillers. These composites often exhibit improved mechanical properties, thermal stability, or specific functionalities not achievable with silicone rubber alone.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Silicone Rubber Packaging Industry
The research on silicone rubber for sustainable packaging development is in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by sustainability trends. The global silicone rubber market size is projected to reach $9.34 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%. Technologically, silicone rubber is relatively mature but continues to evolve for specialized applications. Key players like Shin-Etsu Chemical, Wacker Chemie, and Momentive Performance Materials are leading innovation in this space, focusing on developing eco-friendly formulations and enhancing material properties for packaging applications. Emerging companies from China, such as Zhejiang Xinan Chemical and Jiangxi Bluestar Xinghuo Silicones, are also making significant contributions to the field.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shin-Etsu Chemical has developed advanced silicone rubber compounds specifically for sustainable packaging applications. Their research focuses on improving the biodegradability and recyclability of silicone rubber materials while maintaining excellent mechanical properties and barrier performance. The company has introduced a new grade of silicone rubber that incorporates bio-based materials, reducing the carbon footprint of the final product[1]. Additionally, Shin-Etsu has developed a proprietary crosslinking technology that allows for easier separation and recycling of silicone rubber components from multi-material packaging systems[2]. This innovation addresses the challenge of recycling complex packaging structures, contributing to a more circular economy for silicone-based packaging materials.
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in silicone chemistry, strong R&D capabilities, and a wide range of product offerings. Weaknesses: Higher costs associated with advanced sustainable solutions may limit adoption in price-sensitive markets.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has made significant strides in developing sustainable silicone rubber solutions for packaging applications. Their research focuses on creating silicone elastomers with reduced environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. Wacker has introduced ELASTOSIL® eco, a series of silicone rubber compounds that incorporate renewable raw materials, reducing reliance on fossil-based resources[3]. The company has also developed a novel curing system that allows for lower processing temperatures, resulting in reduced energy consumption during manufacturing[4]. Furthermore, Wacker's research includes the development of silicone additives that enhance the recyclability of plastic packaging materials, improving the overall sustainability of packaging solutions that combine silicone and conventional plastics[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive product portfolio, strong focus on sustainability, and extensive global presence. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production of eco-friendly silicone rubber compounds to meet growing demand.
Innovative Silicone Rubber Formulations for Packaging
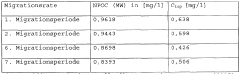
Silicone rubber compositions and their vulcanizates for use in potable water applications
PatentWO2021160238A1
Innovation
- A silicone rubber composition comprising polydiorganosiloxane, reinforcing fillers with a BET surface area of at least 50 m^2/g, and specific additives such as alkaline earth silicates, wollastonites, and magnesium hydroxide, which are processed into vulcanizates using peroxide or addition-crosslinking methods, reducing water-extractable fractions and avoiding critical ingredients that impair taste or smell.
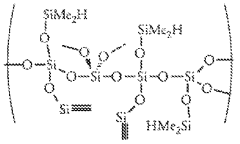
Silicone rubber material for soft lithography
PatentWO2009147602A2
Innovation
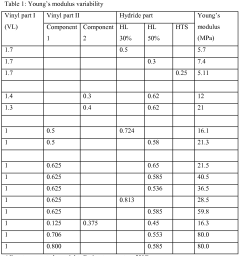
- A silicone rubber-like material comprising T branched and/or Q branched (poly)siloxane precursors crosslinked by linear polysiloxanes, with a Young's modulus ranging from 7 MPa to 80 MPa, allowing for flexible conformal contact and minimizing distortion during pattern formation, achieved through a method involving incubation at low temperatures and controlled crosslinking.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Silicone Packaging
The environmental impact assessment of silicone packaging is a crucial aspect of sustainable packaging development. Silicone rubber, known for its durability and versatility, offers potential advantages in reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. However, a comprehensive evaluation of its environmental footprint is necessary to ensure its sustainability credentials.
Silicone packaging materials generally exhibit lower environmental impacts compared to traditional plastic alternatives throughout their lifecycle. The production of silicone rubber requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions than many conventional plastics. Additionally, silicone's long lifespan and resistance to degradation contribute to reduced waste generation and extended product use.
One of the key environmental benefits of silicone packaging is its potential for reuse and recyclability. Unlike many single-use plastics, silicone products can be easily cleaned and reused multiple times, significantly reducing the demand for new packaging materials. When properly collected and processed, silicone can also be recycled into various industrial applications, further minimizing its environmental impact.
However, the environmental assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The production of silicone involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, which raises concerns about resource depletion and carbon footprint. While silicone is generally inert and non-toxic, improper disposal or incineration can lead to the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Water consumption and pollution during the manufacturing process of silicone rubber are additional factors that require careful evaluation. Implementing water-efficient production techniques and effective wastewater treatment systems is essential to mitigate these impacts.
The end-of-life management of silicone packaging presents both challenges and opportunities. While silicone products are not biodegradable, their durability allows for extended use and potential repurposing. Developing efficient collection and recycling systems for silicone packaging is crucial to maximize its environmental benefits and minimize waste accumulation in landfills or natural ecosystems.
To fully assess the environmental impact of silicone packaging, life cycle assessment (LCA) studies should be conducted, comparing silicone-based solutions with alternative packaging materials across various environmental indicators. These studies should consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life scenarios to provide a comprehensive understanding of silicone packaging's ecological footprint.
Silicone packaging materials generally exhibit lower environmental impacts compared to traditional plastic alternatives throughout their lifecycle. The production of silicone rubber requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions than many conventional plastics. Additionally, silicone's long lifespan and resistance to degradation contribute to reduced waste generation and extended product use.
One of the key environmental benefits of silicone packaging is its potential for reuse and recyclability. Unlike many single-use plastics, silicone products can be easily cleaned and reused multiple times, significantly reducing the demand for new packaging materials. When properly collected and processed, silicone can also be recycled into various industrial applications, further minimizing its environmental impact.
However, the environmental assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The production of silicone involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, which raises concerns about resource depletion and carbon footprint. While silicone is generally inert and non-toxic, improper disposal or incineration can lead to the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Water consumption and pollution during the manufacturing process of silicone rubber are additional factors that require careful evaluation. Implementing water-efficient production techniques and effective wastewater treatment systems is essential to mitigate these impacts.
The end-of-life management of silicone packaging presents both challenges and opportunities. While silicone products are not biodegradable, their durability allows for extended use and potential repurposing. Developing efficient collection and recycling systems for silicone packaging is crucial to maximize its environmental benefits and minimize waste accumulation in landfills or natural ecosystems.
To fully assess the environmental impact of silicone packaging, life cycle assessment (LCA) studies should be conducted, comparing silicone-based solutions with alternative packaging materials across various environmental indicators. These studies should consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, transportation, use phase, and end-of-life scenarios to provide a comprehensive understanding of silicone packaging's ecological footprint.
Regulatory Framework for Sustainable Packaging Materials
The regulatory framework for sustainable packaging materials, particularly in the context of silicone rubber for sustainable packaging development, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international organizations are increasingly implementing stringent regulations to promote environmentally friendly packaging solutions and reduce waste.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials. The directive emphasizes the need for packaging to be designed, produced, and commercialized in a way that permits its reuse, recovery, and recycling. Silicone rubber, being a durable and potentially reusable material, aligns well with these objectives.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food contact materials, including silicone rubber used in packaging. The FDA's regulations ensure that materials used in food packaging are safe for their intended use and do not transfer harmful substances to food. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations through extensive testing and documentation.
Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations incentivize the use of sustainable materials like silicone rubber, which can be easily recycled or repurposed.
The Global Protocol on Packaging Sustainability (GPPS), developed by the Consumer Goods Forum, provides a common language and framework for the packaging supply chain to discuss and assess the relative sustainability of packaging. While not a regulation per se, it influences industry practices and can shape future regulatory developments.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on reducing single-use plastics. Regulations such as the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive aim to phase out certain single-use plastic items and promote more sustainable alternatives. This regulatory trend creates opportunities for materials like silicone rubber, which can offer durability and reusability in packaging applications.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards related to packaging and the environment, such as ISO 18601:2013, which provides a framework for assessing packaging sustainability. These standards, while voluntary, often inform regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
As concerns about microplastics and their environmental impact grow, regulators are beginning to scrutinize all types of polymers used in packaging, including silicone rubber. Future regulations may require more extensive testing and documentation regarding the environmental fate of these materials.
The regulatory landscape for sustainable packaging materials is dynamic, with new regulations and standards continually emerging. Companies involved in the development of silicone rubber for sustainable packaging must stay informed about these changes and proactively adapt their research and development efforts to ensure compliance and market acceptance.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials. The directive emphasizes the need for packaging to be designed, produced, and commercialized in a way that permits its reuse, recovery, and recycling. Silicone rubber, being a durable and potentially reusable material, aligns well with these objectives.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food contact materials, including silicone rubber used in packaging. The FDA's regulations ensure that materials used in food packaging are safe for their intended use and do not transfer harmful substances to food. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations through extensive testing and documentation.
Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations incentivize the use of sustainable materials like silicone rubber, which can be easily recycled or repurposed.
The Global Protocol on Packaging Sustainability (GPPS), developed by the Consumer Goods Forum, provides a common language and framework for the packaging supply chain to discuss and assess the relative sustainability of packaging. While not a regulation per se, it influences industry practices and can shape future regulatory developments.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on reducing single-use plastics. Regulations such as the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive aim to phase out certain single-use plastic items and promote more sustainable alternatives. This regulatory trend creates opportunities for materials like silicone rubber, which can offer durability and reusability in packaging applications.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards related to packaging and the environment, such as ISO 18601:2013, which provides a framework for assessing packaging sustainability. These standards, while voluntary, often inform regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
As concerns about microplastics and their environmental impact grow, regulators are beginning to scrutinize all types of polymers used in packaging, including silicone rubber. Future regulations may require more extensive testing and documentation regarding the environmental fate of these materials.
The regulatory landscape for sustainable packaging materials is dynamic, with new regulations and standards continually emerging. Companies involved in the development of silicone rubber for sustainable packaging must stay informed about these changes and proactively adapt their research and development efforts to ensure compliance and market acceptance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!