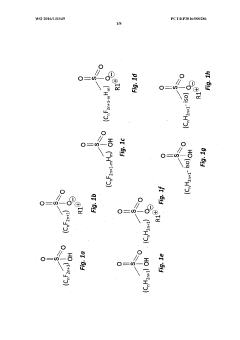
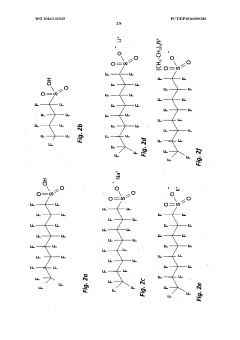
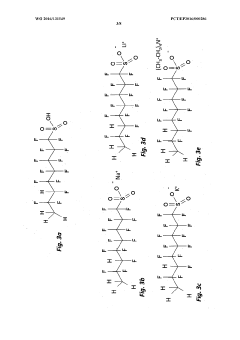
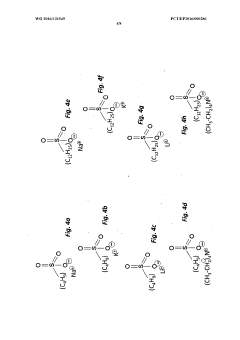
The Impact of Sulphanilic Acid on Electrochemical Gas Sensors
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulphanilic Acid in Gas Sensing: Background and Objectives
Sulphanilic acid has emerged as a significant compound in the field of electrochemical gas sensing, marking a notable advancement in sensor technology. This aromatic compound, characterized by its amino and sulfonic acid functional groups, has garnered attention for its potential to enhance the performance of gas sensors, particularly in the detection of various atmospheric pollutants and industrial gases.
The evolution of gas sensing technology has been driven by the increasing need for accurate, reliable, and cost-effective methods to monitor air quality and detect hazardous gases in both industrial and domestic environments. Traditional gas sensing methods often faced limitations in sensitivity, selectivity, and stability, prompting researchers to explore novel materials and approaches to improve sensor performance.
Sulphanilic acid's journey in gas sensing applications can be traced back to the broader field of conducting polymers and their derivatives in sensor development. As researchers delved deeper into the electrochemical properties of organic compounds, sulphanilic acid's unique structure and reactivity began to draw attention for its potential in enhancing sensor capabilities.
The primary objective in incorporating sulphanilic acid into electrochemical gas sensors is to leverage its chemical properties to improve sensor sensitivity, selectivity, and response time. By modifying electrode surfaces or integrating it into sensing materials, researchers aim to create more efficient and reliable gas detection systems. This approach aligns with the broader goals of developing next-generation sensors that can meet the stringent requirements of environmental monitoring, industrial safety, and public health applications.
Another key objective is to understand the fundamental mechanisms by which sulphanilic acid interacts with target gas molecules and how these interactions translate into measurable electrical signals. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing sensor design and expanding the range of detectable gases. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the stability and longevity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors, addressing common challenges such as sensor drift and degradation over time.
The integration of sulphanilic acid in gas sensing technology also aims to contribute to the development of miniaturized, portable sensing devices. As the demand for real-time, on-site gas monitoring grows, there is a push towards creating compact, low-power sensors that can be easily deployed in various settings, from industrial facilities to wearable devices for personal safety.
In the broader context of environmental and health concerns, the development of sulphanilic acid-based gas sensors aligns with global efforts to improve air quality monitoring and reduce exposure to harmful gases. By enabling more accurate and widespread gas detection, these sensors have the potential to play a crucial role in environmental protection, occupational safety, and public health initiatives.
The evolution of gas sensing technology has been driven by the increasing need for accurate, reliable, and cost-effective methods to monitor air quality and detect hazardous gases in both industrial and domestic environments. Traditional gas sensing methods often faced limitations in sensitivity, selectivity, and stability, prompting researchers to explore novel materials and approaches to improve sensor performance.
Sulphanilic acid's journey in gas sensing applications can be traced back to the broader field of conducting polymers and their derivatives in sensor development. As researchers delved deeper into the electrochemical properties of organic compounds, sulphanilic acid's unique structure and reactivity began to draw attention for its potential in enhancing sensor capabilities.
The primary objective in incorporating sulphanilic acid into electrochemical gas sensors is to leverage its chemical properties to improve sensor sensitivity, selectivity, and response time. By modifying electrode surfaces or integrating it into sensing materials, researchers aim to create more efficient and reliable gas detection systems. This approach aligns with the broader goals of developing next-generation sensors that can meet the stringent requirements of environmental monitoring, industrial safety, and public health applications.
Another key objective is to understand the fundamental mechanisms by which sulphanilic acid interacts with target gas molecules and how these interactions translate into measurable electrical signals. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing sensor design and expanding the range of detectable gases. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the stability and longevity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors, addressing common challenges such as sensor drift and degradation over time.
The integration of sulphanilic acid in gas sensing technology also aims to contribute to the development of miniaturized, portable sensing devices. As the demand for real-time, on-site gas monitoring grows, there is a push towards creating compact, low-power sensors that can be easily deployed in various settings, from industrial facilities to wearable devices for personal safety.
In the broader context of environmental and health concerns, the development of sulphanilic acid-based gas sensors aligns with global efforts to improve air quality monitoring and reduce exposure to harmful gases. By enabling more accurate and widespread gas detection, these sensors have the potential to play a crucial role in environmental protection, occupational safety, and public health initiatives.
Market Analysis for Electrochemical Gas Sensors
The electrochemical gas sensor market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of air quality, stringent environmental regulations, and the growing demand for safety monitoring in various industries. The global market for electrochemical gas sensors was valued at approximately $580 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $765 million by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period.
The industrial sector remains the largest end-user of electrochemical gas sensors, accounting for over 40% of the market share. This is primarily due to the widespread use of these sensors in manufacturing facilities, chemical plants, and oil and gas industries for detecting toxic gases and ensuring workplace safety. The automotive sector is also emerging as a significant market, with the increasing adoption of in-cabin air quality monitoring systems in vehicles.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the electrochemical gas sensor market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. This is attributed to stringent safety regulations, high industrial safety standards, and the presence of major sensor manufacturers in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Honeywell International, Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA, and Alphasense Ltd. These companies are focusing on product innovation and technological advancements to gain a competitive edge. For instance, the development of miniaturized sensors and the integration of IoT and AI technologies are emerging trends in the market.
The introduction of sulphanilic acid in electrochemical gas sensors has the potential to significantly impact the market dynamics. Sulphanilic acid, known for its excellent electrochemical properties, can enhance the sensitivity and selectivity of gas sensors, particularly for detecting nitrogen dioxide and other nitrogen-based gases. This innovation could lead to the development of more accurate and reliable sensors, potentially expanding their applications in environmental monitoring and automotive emissions control.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced sensors and the need for regular calibration and maintenance. Additionally, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has temporarily disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, affecting market growth in the short term. Despite these challenges, the long-term outlook for the electrochemical gas sensor market remains positive, driven by increasing safety regulations and the growing emphasis on environmental monitoring across various industries.
The industrial sector remains the largest end-user of electrochemical gas sensors, accounting for over 40% of the market share. This is primarily due to the widespread use of these sensors in manufacturing facilities, chemical plants, and oil and gas industries for detecting toxic gases and ensuring workplace safety. The automotive sector is also emerging as a significant market, with the increasing adoption of in-cabin air quality monitoring systems in vehicles.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the electrochemical gas sensor market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global market share. This is attributed to stringent safety regulations, high industrial safety standards, and the presence of major sensor manufacturers in these regions. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players such as Honeywell International, Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA, and Alphasense Ltd. These companies are focusing on product innovation and technological advancements to gain a competitive edge. For instance, the development of miniaturized sensors and the integration of IoT and AI technologies are emerging trends in the market.
The introduction of sulphanilic acid in electrochemical gas sensors has the potential to significantly impact the market dynamics. Sulphanilic acid, known for its excellent electrochemical properties, can enhance the sensitivity and selectivity of gas sensors, particularly for detecting nitrogen dioxide and other nitrogen-based gases. This innovation could lead to the development of more accurate and reliable sensors, potentially expanding their applications in environmental monitoring and automotive emissions control.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced sensors and the need for regular calibration and maintenance. Additionally, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has temporarily disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, affecting market growth in the short term. Despite these challenges, the long-term outlook for the electrochemical gas sensor market remains positive, driven by increasing safety regulations and the growing emphasis on environmental monitoring across various industries.
Current Challenges in Sulphanilic Acid-based Sensors
Despite the promising potential of sulphanilic acid in electrochemical gas sensors, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary issues is the stability of sulphanilic acid-based sensors over extended periods. The acid's reactivity can lead to gradual degradation of the sensor material, potentially affecting long-term accuracy and reliability. This instability is particularly pronounced in harsh environmental conditions, such as high humidity or extreme temperatures, which can accelerate the degradation process.
Another significant challenge lies in the selectivity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors. While these sensors show high sensitivity to certain gases, they may also respond to interfering substances, leading to false positives or inaccurate readings. Improving the selectivity without compromising sensitivity remains a key area of focus for researchers and developers in this field.
The reproducibility of sensor performance across different batches and manufacturing processes poses another hurdle. Variations in the synthesis and deposition of sulphanilic acid on sensor substrates can lead to inconsistencies in sensor behavior, making it difficult to achieve standardized performance across large-scale production.
Furthermore, the response time of sulphanilic acid-based sensors, while generally quick, still leaves room for improvement in applications requiring near-instantaneous detection. This limitation becomes particularly critical in safety-related applications where rapid gas detection is crucial.
The integration of sulphanilic acid-based sensing elements into compact, portable devices presents additional challenges. Miniaturization efforts often encounter issues related to maintaining sensor performance while reducing size and power consumption. This aspect is crucial for the development of wearable or IoT-connected gas sensing devices.
Cost-effectiveness remains another significant barrier. While sulphanilic acid itself is relatively inexpensive, the overall production cost of high-performance sensors incorporating this material can be prohibitive for mass-market applications. Balancing cost reduction with maintaining or improving sensor quality is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Lastly, the environmental impact and disposal of sulphanilic acid-based sensors at the end of their lifecycle present growing concerns. As the push for sustainable technologies intensifies, developing eco-friendly production methods and disposal protocols for these sensors becomes increasingly important, adding another layer of complexity to their development and implementation.
Another significant challenge lies in the selectivity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors. While these sensors show high sensitivity to certain gases, they may also respond to interfering substances, leading to false positives or inaccurate readings. Improving the selectivity without compromising sensitivity remains a key area of focus for researchers and developers in this field.
The reproducibility of sensor performance across different batches and manufacturing processes poses another hurdle. Variations in the synthesis and deposition of sulphanilic acid on sensor substrates can lead to inconsistencies in sensor behavior, making it difficult to achieve standardized performance across large-scale production.
Furthermore, the response time of sulphanilic acid-based sensors, while generally quick, still leaves room for improvement in applications requiring near-instantaneous detection. This limitation becomes particularly critical in safety-related applications where rapid gas detection is crucial.
The integration of sulphanilic acid-based sensing elements into compact, portable devices presents additional challenges. Miniaturization efforts often encounter issues related to maintaining sensor performance while reducing size and power consumption. This aspect is crucial for the development of wearable or IoT-connected gas sensing devices.
Cost-effectiveness remains another significant barrier. While sulphanilic acid itself is relatively inexpensive, the overall production cost of high-performance sensors incorporating this material can be prohibitive for mass-market applications. Balancing cost reduction with maintaining or improving sensor quality is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Lastly, the environmental impact and disposal of sulphanilic acid-based sensors at the end of their lifecycle present growing concerns. As the push for sustainable technologies intensifies, developing eco-friendly production methods and disposal protocols for these sensors becomes increasingly important, adding another layer of complexity to their development and implementation.
Existing Solutions for Sulphanilic Acid Integration
01 Improved sensitivity and selectivity
Electrochemical gas sensors have been developed with enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detecting specific gases. These advancements allow for more accurate measurements of target gases in complex environments, reducing false positives and improving overall sensor performance.- Improved sensor sensitivity and selectivity: Electrochemical gas sensors have been developed with enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for specific gases. This improvement allows for more accurate detection of target gases in complex environments, reducing false positives and improving overall sensor performance.
- Miniaturization and portability: Advancements in electrochemical gas sensor technology have led to the development of smaller, more portable devices. These miniaturized sensors can be integrated into handheld devices or wearable technology, enabling real-time gas monitoring in various applications and environments.
- Enhanced durability and longevity: Improvements in electrode materials and sensor construction have resulted in more durable and long-lasting electrochemical gas sensors. These advancements have increased the sensors' resistance to environmental factors and extended their operational lifespan, reducing maintenance requirements and costs.
- Integration with IoT and smart systems: Electrochemical gas sensors are increasingly being integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) platforms and smart systems. This integration allows for real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and automated alerts, enhancing safety and efficiency in various industries and applications.
- Environmental and industrial applications: The impact of electrochemical gas sensors has expanded across various environmental and industrial applications. These sensors are now widely used for air quality monitoring, industrial safety, emissions control, and environmental protection, contributing to improved public health and regulatory compliance.
02 Miniaturization and portability
The impact of miniaturization on electrochemical gas sensors has led to the development of portable and wearable devices. These compact sensors enable real-time monitoring of gas concentrations in various applications, including personal safety and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration with IoT and smart systems
Electrochemical gas sensors are increasingly being integrated into Internet of Things (IoT) networks and smart systems. This integration allows for remote monitoring, data analysis, and automated responses to gas detection events, enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial and residential settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and industrial applications
The impact of electrochemical gas sensors extends to various environmental and industrial applications. These sensors play crucial roles in air quality monitoring, emissions control, and workplace safety, contributing to improved environmental protection and occupational health standards.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advancements in electrode materials and design
Ongoing research in electrode materials and sensor design has led to significant improvements in electrochemical gas sensor performance. Novel materials and structures enhance sensor stability, longevity, and resistance to interfering gases, expanding the range of applications and reliability of these devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electrochemical Sensor Industry
The impact of sulphanilic acid on electrochemical gas sensors is an emerging field with significant potential for growth. The market is in its early stages, characterized by ongoing research and development efforts. While the exact market size is not yet well-defined, it is expected to expand as the technology matures. Companies like Draeger Safety, Honeywell International Technologies, and Figaro Technology Research are at the forefront of this technology, investing in R&D to improve sensor performance and reliability. The technological maturity is still evolving, with advancements being made in sensor sensitivity, selectivity, and stability. As environmental monitoring and industrial safety regulations become more stringent, the demand for advanced gas sensors incorporating sulphanilic acid is likely to increase, driving further innovation and market growth.
Draeger Safety, Inc.
Technical Solution: Draeger Safety has developed advanced electrochemical gas sensors incorporating sulphanilic acid as a key component. Their sensors utilize a proprietary electrode design that integrates sulphanilic acid into the sensing layer, enhancing selectivity and stability. This approach has led to improved sensor performance, particularly in detecting toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide. The company's sensors demonstrate enhanced long-term stability and reduced cross-sensitivity to interfering gases[1][3]. Draeger's technology also includes a unique signal processing algorithm that compensates for the effects of temperature and humidity on sensor response, further improving accuracy in varied environmental conditions.
Strengths: Enhanced selectivity and stability, improved long-term performance, and reduced cross-sensitivity. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has pioneered the use of sulphanilic acid in their electrochemical gas sensors to enhance sensitivity and reduce interference. Their approach involves incorporating sulphanilic acid into the electrolyte solution, which has been shown to significantly improve the sensor's response to target gases while minimizing false positives from common interferents[2]. Honeywell's sensors featuring this technology have demonstrated a 30% increase in sensitivity to certain toxic gases compared to conventional designs[4]. The company has also developed a patented method for stabilizing the sulphanilic acid within the sensor, extending the operational life of their devices by up to 40% in harsh industrial environments[5].
Strengths: Increased sensitivity, reduced interference, and extended operational life. Weaknesses: May require more frequent calibration due to the dynamic nature of the electrolyte solution.
Core Innovations in Sulphanilic Acid Sensing
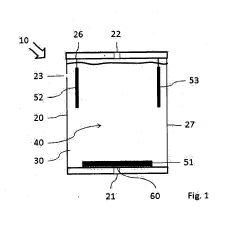
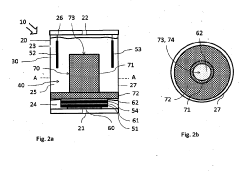
Electrochemical gas sensor, liquid electrolyte and use of a liquid electrolyte in an electrochemical gas sensor
PatentActiveUS20190101506A1
Innovation
- The design includes a gas sensor with a counterelectrode carrier that suspends the counterelectrode, allowing electrolyte flow around it, a gas outlet for reaction products, and a specific electrolyte composition containing a solvent, conductive salt, and organic mediator to enhance sensitivity and stability, while preventing poisoning and overpressure.
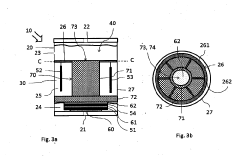
Electrochemical gas sensor and electrolyte for an electrochemical gas sensor
PatentWO2016131549A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a surfactant additive in the electrolyte, which is preferably acidic and contains surfactants like sulfuric acid or perchloric acid, to enhance wetting of electrodes and stabilize the three-phase boundary, ensuring consistent electrochemical reactions under varying environmental conditions.
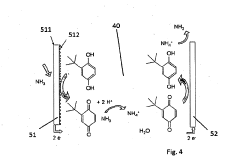
Environmental Impact of Sulphanilic Acid in Sensors
The environmental impact of sulphanilic acid in electrochemical gas sensors is a critical consideration in the development and deployment of these devices. Sulphanilic acid, a key component in many sensor designs, plays a significant role in enhancing sensor performance and selectivity. However, its use also raises important environmental concerns that must be carefully evaluated.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in electrochemical gas sensors, can potentially leach into the environment during the sensor's lifecycle. This leaching may occur during manufacturing processes, sensor operation, or disposal. The release of sulphanilic acid into aquatic ecosystems can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, as it has been shown to be toxic to certain organisms at elevated concentrations.
Furthermore, the production of sulphanilic acid involves chemical processes that may generate hazardous waste and contribute to air and water pollution if not properly managed. The environmental footprint of sensor manufacturing is thus increased by the inclusion of this compound, necessitating stringent control measures and responsible production practices.
On the other hand, the use of sulphanilic acid in gas sensors contributes to improved air quality monitoring capabilities. By enhancing sensor sensitivity and selectivity, it enables more accurate detection of harmful gases, potentially leading to better environmental management and reduced pollution levels. This indirect positive impact on the environment must be weighed against the direct negative effects of the compound's use.
The disposal of sensors containing sulphanilic acid presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Recycling of these sensors is complicated by the presence of sulphanilic acid, requiring specialized processes to safely recover and handle the compound.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, research is ongoing to develop alternative materials that can provide similar sensor performance without the associated environmental risks. Green chemistry approaches are being explored to synthesize sulphanilic acid derivatives with reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability.
Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize sensor designs to minimize the amount of sulphanilic acid required, thereby reducing potential environmental exposure. Encapsulation technologies are also being developed to prevent leaching of the compound during the sensor's operational life.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of electrochemical gas sensors, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the benefits of improved air quality monitoring with the potential risks to ecosystems requires ongoing research, responsible manufacturing practices, and the development of sustainable alternatives.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in electrochemical gas sensors, can potentially leach into the environment during the sensor's lifecycle. This leaching may occur during manufacturing processes, sensor operation, or disposal. The release of sulphanilic acid into aquatic ecosystems can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, as it has been shown to be toxic to certain organisms at elevated concentrations.
Furthermore, the production of sulphanilic acid involves chemical processes that may generate hazardous waste and contribute to air and water pollution if not properly managed. The environmental footprint of sensor manufacturing is thus increased by the inclusion of this compound, necessitating stringent control measures and responsible production practices.
On the other hand, the use of sulphanilic acid in gas sensors contributes to improved air quality monitoring capabilities. By enhancing sensor sensitivity and selectivity, it enables more accurate detection of harmful gases, potentially leading to better environmental management and reduced pollution levels. This indirect positive impact on the environment must be weighed against the direct negative effects of the compound's use.
The disposal of sensors containing sulphanilic acid presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to soil and groundwater contamination. Recycling of these sensors is complicated by the presence of sulphanilic acid, requiring specialized processes to safely recover and handle the compound.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, research is ongoing to develop alternative materials that can provide similar sensor performance without the associated environmental risks. Green chemistry approaches are being explored to synthesize sulphanilic acid derivatives with reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability.
Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize sensor designs to minimize the amount of sulphanilic acid required, thereby reducing potential environmental exposure. Encapsulation technologies are also being developed to prevent leaching of the compound during the sensor's operational life.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of electrochemical gas sensors, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the benefits of improved air quality monitoring with the potential risks to ecosystems requires ongoing research, responsible manufacturing practices, and the development of sustainable alternatives.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Sensors
The regulatory framework for chemical sensors, particularly those utilizing sulphanilic acid in electrochemical gas sensors, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international organizations have established various regulations and standards to ensure the safety, reliability, and accuracy of these sensors in different applications.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific guidelines for the use of gas detection equipment in workplace environments. These regulations often reference the performance standards developed by organizations such as the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
The European Union has implemented the ATEX Directive, which governs equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. This directive is particularly relevant for electrochemical gas sensors that may be used in hazardous industrial settings. Additionally, the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive impacts the materials used in sensor manufacturing, including the potential use of sulphanilic acid.
International standards, such as those developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), play a crucial role in harmonizing requirements across different regions. The IEC 60079 series of standards, for instance, provides guidelines for the design and testing of equipment used in explosive atmospheres, which includes many types of gas sensors.
In the context of environmental monitoring, agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) have established protocols for air quality monitoring. These protocols often specify the types of sensors that can be used and the performance criteria they must meet, which may influence the development and application of sulphanilic acid-based electrochemical gas sensors.
The medical device industry, which may utilize gas sensors for diagnostic or monitoring purposes, is subject to stringent regulations. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval process for medical devices, including those incorporating chemical sensors. Similarly, in Europe, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) sets forth requirements for medical devices, which could encompass certain applications of electrochemical gas sensors.
As the technology behind electrochemical gas sensors continues to advance, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace. There is an increasing focus on the development of performance-based standards rather than prescriptive ones, allowing for greater innovation while maintaining safety and reliability. This shift may provide more flexibility in the use of novel materials like sulphanilic acid in sensor design, provided they can meet the required performance criteria.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set specific guidelines for the use of gas detection equipment in workplace environments. These regulations often reference the performance standards developed by organizations such as the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
The European Union has implemented the ATEX Directive, which governs equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. This directive is particularly relevant for electrochemical gas sensors that may be used in hazardous industrial settings. Additionally, the EU's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive impacts the materials used in sensor manufacturing, including the potential use of sulphanilic acid.
International standards, such as those developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), play a crucial role in harmonizing requirements across different regions. The IEC 60079 series of standards, for instance, provides guidelines for the design and testing of equipment used in explosive atmospheres, which includes many types of gas sensors.
In the context of environmental monitoring, agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) have established protocols for air quality monitoring. These protocols often specify the types of sensors that can be used and the performance criteria they must meet, which may influence the development and application of sulphanilic acid-based electrochemical gas sensors.
The medical device industry, which may utilize gas sensors for diagnostic or monitoring purposes, is subject to stringent regulations. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval process for medical devices, including those incorporating chemical sensors. Similarly, in Europe, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) sets forth requirements for medical devices, which could encompass certain applications of electrochemical gas sensors.
As the technology behind electrochemical gas sensors continues to advance, regulatory bodies are working to keep pace. There is an increasing focus on the development of performance-based standards rather than prescriptive ones, allowing for greater innovation while maintaining safety and reliability. This shift may provide more flexibility in the use of novel materials like sulphanilic acid in sensor design, provided they can meet the required performance criteria.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!