What are the Risks of Muriatic Acid Exposure in Industrial Settings?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muriatic Acid Hazards
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, poses significant hazards in industrial settings due to its corrosive nature and potential for severe health impacts. The primary risks associated with muriatic acid exposure include severe chemical burns to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Even brief contact can cause immediate and painful tissue damage, potentially leading to permanent scarring or blindness if not promptly treated.
Inhalation of muriatic acid vapors presents another critical hazard. The fumes can cause respiratory irritation, coughing, and shortness of breath. Prolonged or high-concentration exposure may result in pulmonary edema, a potentially life-threatening condition where fluid accumulates in the lungs. Workers in poorly ventilated areas are particularly vulnerable to these respiratory risks.
Ingestion of muriatic acid, though less common in industrial settings, can have catastrophic consequences. It can cause severe internal burns to the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach, potentially leading to perforation of these organs and long-term health complications or death.
The corrosive properties of muriatic acid also present significant material hazards. It can rapidly deteriorate metal surfaces, leading to equipment damage, structural weakening, and potential leaks or spills. This corrosion risk extends to storage containers, pipelines, and processing equipment, necessitating careful material selection and regular maintenance protocols.
Environmental concerns are another aspect of muriatic acid hazards. Accidental releases can severely impact soil and water ecosystems, altering pH levels and potentially harming flora and fauna. Proper containment and disposal procedures are crucial to mitigate these environmental risks.
In industrial settings, the reactivity of muriatic acid with other chemicals poses additional hazards. When mixed with certain substances, it can generate toxic gases or cause violent reactions. For instance, its interaction with bleach produces chlorine gas, which is highly toxic and potentially fatal if inhaled.
Long-term occupational exposure to low levels of muriatic acid vapors can lead to chronic health issues. These may include dental erosion, chronic bronchitis, and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. Workers in industries such as metal processing, chemical manufacturing, and pool maintenance are at higher risk for these cumulative effects.
To address these hazards, comprehensive safety measures are essential. These include proper personal protective equipment (PPE), adequate ventilation systems, emergency eyewash and shower stations, and rigorous handling and storage protocols. Regular safety training, risk assessments, and emergency response planning are also critical components of managing muriatic acid hazards in industrial environments.
Inhalation of muriatic acid vapors presents another critical hazard. The fumes can cause respiratory irritation, coughing, and shortness of breath. Prolonged or high-concentration exposure may result in pulmonary edema, a potentially life-threatening condition where fluid accumulates in the lungs. Workers in poorly ventilated areas are particularly vulnerable to these respiratory risks.
Ingestion of muriatic acid, though less common in industrial settings, can have catastrophic consequences. It can cause severe internal burns to the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach, potentially leading to perforation of these organs and long-term health complications or death.
The corrosive properties of muriatic acid also present significant material hazards. It can rapidly deteriorate metal surfaces, leading to equipment damage, structural weakening, and potential leaks or spills. This corrosion risk extends to storage containers, pipelines, and processing equipment, necessitating careful material selection and regular maintenance protocols.
Environmental concerns are another aspect of muriatic acid hazards. Accidental releases can severely impact soil and water ecosystems, altering pH levels and potentially harming flora and fauna. Proper containment and disposal procedures are crucial to mitigate these environmental risks.
In industrial settings, the reactivity of muriatic acid with other chemicals poses additional hazards. When mixed with certain substances, it can generate toxic gases or cause violent reactions. For instance, its interaction with bleach produces chlorine gas, which is highly toxic and potentially fatal if inhaled.
Long-term occupational exposure to low levels of muriatic acid vapors can lead to chronic health issues. These may include dental erosion, chronic bronchitis, and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. Workers in industries such as metal processing, chemical manufacturing, and pool maintenance are at higher risk for these cumulative effects.
To address these hazards, comprehensive safety measures are essential. These include proper personal protective equipment (PPE), adequate ventilation systems, emergency eyewash and shower stations, and rigorous handling and storage protocols. Regular safety training, risk assessments, and emergency response planning are also critical components of managing muriatic acid hazards in industrial environments.
Industrial Demand
The industrial demand for muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, remains robust across various sectors due to its versatile applications and cost-effectiveness. In the chemical manufacturing industry, muriatic acid serves as a crucial raw material for producing numerous chemicals, including PVC, water treatment chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. The growing demand for these end products directly drives the need for muriatic acid in industrial processes.
The metal processing and surface treatment sector represents another significant consumer of muriatic acid. Steel pickling, a process used to remove rust and scale from metal surfaces, heavily relies on muriatic acid solutions. As the global steel industry continues to expand, particularly in developing economies, the demand for muriatic acid in this application is expected to grow correspondingly.
In the oil and gas industry, muriatic acid plays a vital role in well acidizing and stimulation processes. These techniques are employed to enhance oil and gas production by improving the permeability of reservoir rocks. With the ongoing exploration of unconventional oil and gas resources, such as shale formations, the demand for muriatic acid in this sector is projected to remain strong.
The water treatment industry also contributes significantly to the industrial demand for muriatic acid. It is widely used for pH adjustment in water and wastewater treatment processes, as well as in the regeneration of ion exchange resins. As global water scarcity concerns intensify and regulations on water quality become more stringent, the demand for muriatic acid in this sector is expected to increase.
The food processing industry utilizes muriatic acid for various applications, including pH control in food products and as a cleaning agent for equipment. With the growing global population and increasing food production, this sector's demand for muriatic acid is likely to rise steadily.
Despite its widespread use, the industrial demand for muriatic acid is not without challenges. Increasing awareness of the potential health and environmental risks associated with its exposure has led to stricter regulations and safety protocols in many industries. This has prompted some companies to explore alternative chemicals or processes that may reduce their reliance on muriatic acid.
Furthermore, the circular economy concept and sustainability initiatives are driving efforts to recover and recycle hydrochloric acid from industrial processes. While this may impact the overall demand for fresh muriatic acid, it also presents opportunities for innovative recycling technologies and more efficient use of the chemical in industrial settings.
The metal processing and surface treatment sector represents another significant consumer of muriatic acid. Steel pickling, a process used to remove rust and scale from metal surfaces, heavily relies on muriatic acid solutions. As the global steel industry continues to expand, particularly in developing economies, the demand for muriatic acid in this application is expected to grow correspondingly.
In the oil and gas industry, muriatic acid plays a vital role in well acidizing and stimulation processes. These techniques are employed to enhance oil and gas production by improving the permeability of reservoir rocks. With the ongoing exploration of unconventional oil and gas resources, such as shale formations, the demand for muriatic acid in this sector is projected to remain strong.
The water treatment industry also contributes significantly to the industrial demand for muriatic acid. It is widely used for pH adjustment in water and wastewater treatment processes, as well as in the regeneration of ion exchange resins. As global water scarcity concerns intensify and regulations on water quality become more stringent, the demand for muriatic acid in this sector is expected to increase.
The food processing industry utilizes muriatic acid for various applications, including pH control in food products and as a cleaning agent for equipment. With the growing global population and increasing food production, this sector's demand for muriatic acid is likely to rise steadily.
Despite its widespread use, the industrial demand for muriatic acid is not without challenges. Increasing awareness of the potential health and environmental risks associated with its exposure has led to stricter regulations and safety protocols in many industries. This has prompted some companies to explore alternative chemicals or processes that may reduce their reliance on muriatic acid.
Furthermore, the circular economy concept and sustainability initiatives are driving efforts to recover and recycle hydrochloric acid from industrial processes. While this may impact the overall demand for fresh muriatic acid, it also presents opportunities for innovative recycling technologies and more efficient use of the chemical in industrial settings.
Exposure Risks
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, poses significant risks in industrial settings due to its corrosive and toxic nature. The primary exposure routes include inhalation, skin contact, and ingestion, each presenting unique hazards to workers and the environment.
Inhalation of muriatic acid vapors can cause severe respiratory irritation, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, and in extreme cases, pulmonary edema. Prolonged exposure may result in chronic respiratory issues and damage to the lungs. The concentration of acid fumes in poorly ventilated areas can quickly reach dangerous levels, making proper ventilation systems crucial in industrial facilities handling this chemical.
Skin contact with muriatic acid can cause severe burns and tissue damage. Even dilute solutions can irritate the skin, while concentrated forms can lead to deep, painful burns that may require extensive medical treatment. The risk of splash incidents during handling, transfer, or equipment maintenance is a constant concern in industrial settings.
Accidental ingestion, though less common, presents a severe risk of internal burns to the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. This can lead to long-term health complications or even be fatal in extreme cases. Proper labeling, storage, and handling protocols are essential to mitigate this risk.
The corrosive nature of muriatic acid also poses risks to equipment and infrastructure. It can damage metal surfaces, leading to equipment failure, leaks, or structural weaknesses in storage tanks and piping systems. This not only presents a safety hazard but can also result in significant economic losses due to equipment damage and production downtime.
Environmental risks are another critical concern. Accidental spills or improper disposal of muriatic acid can lead to soil and water contamination, harming ecosystems and potentially affecting nearby communities. The acid's ability to react with other chemicals can create additional hazards, including the generation of toxic gases or explosive reactions when mixed with incompatible substances.
Long-term occupational exposure to muriatic acid, even at low levels, may lead to chronic health issues. These can include dental erosion, chronic respiratory problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Implementing comprehensive safety protocols, including regular health monitoring for exposed workers, is crucial for mitigating these long-term risks.
Inhalation of muriatic acid vapors can cause severe respiratory irritation, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, and in extreme cases, pulmonary edema. Prolonged exposure may result in chronic respiratory issues and damage to the lungs. The concentration of acid fumes in poorly ventilated areas can quickly reach dangerous levels, making proper ventilation systems crucial in industrial facilities handling this chemical.
Skin contact with muriatic acid can cause severe burns and tissue damage. Even dilute solutions can irritate the skin, while concentrated forms can lead to deep, painful burns that may require extensive medical treatment. The risk of splash incidents during handling, transfer, or equipment maintenance is a constant concern in industrial settings.
Accidental ingestion, though less common, presents a severe risk of internal burns to the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. This can lead to long-term health complications or even be fatal in extreme cases. Proper labeling, storage, and handling protocols are essential to mitigate this risk.
The corrosive nature of muriatic acid also poses risks to equipment and infrastructure. It can damage metal surfaces, leading to equipment failure, leaks, or structural weaknesses in storage tanks and piping systems. This not only presents a safety hazard but can also result in significant economic losses due to equipment damage and production downtime.
Environmental risks are another critical concern. Accidental spills or improper disposal of muriatic acid can lead to soil and water contamination, harming ecosystems and potentially affecting nearby communities. The acid's ability to react with other chemicals can create additional hazards, including the generation of toxic gases or explosive reactions when mixed with incompatible substances.
Long-term occupational exposure to muriatic acid, even at low levels, may lead to chronic health issues. These can include dental erosion, chronic respiratory problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Implementing comprehensive safety protocols, including regular health monitoring for exposed workers, is crucial for mitigating these long-term risks.
Handling Protocols
01 Health and safety risks of muriatic acid exposure
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, poses significant health and safety risks upon exposure. It can cause severe burns to skin and eyes, respiratory irritation, and damage to the digestive system if ingested. Prolonged exposure may lead to chronic health issues. Proper safety measures and personal protective equipment are essential when handling this corrosive substance.- Health and safety risks of muriatic acid exposure: Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, poses significant health and safety risks upon exposure. It can cause severe burns to skin and eyes, respiratory irritation, and damage to the digestive system if ingested. Prolonged exposure may lead to chronic health issues. Proper safety measures and personal protective equipment are essential when handling this corrosive substance.
- Environmental impact and disposal considerations: Improper handling and disposal of muriatic acid can have severe environmental consequences. It can contaminate soil and water sources, affecting ecosystems and wildlife. Proper neutralization and disposal methods are crucial to minimize environmental risks. Regulations and guidelines for the safe disposal of muriatic acid must be strictly followed to prevent ecological damage.
- Occupational exposure assessment and monitoring: Assessing and monitoring occupational exposure to muriatic acid is critical in industrial settings. This involves implementing exposure limits, conducting regular air quality tests, and utilizing personal monitoring devices. Proper risk assessment and management strategies help minimize the potential for workplace accidents and long-term health effects on employees working with or around muriatic acid.
- Emergency response and first aid procedures: Establishing comprehensive emergency response and first aid procedures is essential for managing muriatic acid exposure incidents. This includes having readily available safety showers, eyewash stations, and appropriate neutralizing agents. Training personnel in proper emergency response techniques and ensuring quick access to medical assistance can significantly reduce the severity of exposure-related injuries.
- Risk mitigation through engineering controls and PPE: Implementing engineering controls and providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) are crucial for mitigating muriatic acid exposure risks. This includes using closed systems, proper ventilation, acid-resistant materials, and requiring the use of chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and protective clothing. Regular maintenance and inspection of equipment and PPE are essential to ensure their effectiveness in preventing exposure incidents.
02 Environmental impact and disposal considerations
Improper handling and disposal of muriatic acid can have severe environmental consequences. It can contaminate soil and water sources, affecting ecosystems and wildlife. Proper neutralization and disposal methods must be employed to minimize environmental risks. Regulations and guidelines for the safe disposal of muriatic acid should be strictly followed to prevent ecological damage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Workplace safety protocols and risk assessment
Implementing comprehensive workplace safety protocols is crucial when dealing with muriatic acid. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments, providing adequate training to employees, and establishing emergency response procedures. Regular safety audits and updates to protocols help minimize the potential for accidents and exposure risks in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements
Proper personal protective equipment is essential when handling muriatic acid. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, goggles or face shields, protective clothing, and respiratory protection in case of potential vapor exposure. The selection and use of appropriate PPE can significantly reduce the risk of injury from accidental exposure to muriatic acid.Expand Specific Solutions05 Storage and handling precautions
Proper storage and handling of muriatic acid are critical to prevent accidental exposure and spills. This includes using corrosion-resistant containers, storing in well-ventilated areas away from incompatible materials, and implementing spill containment measures. Clear labeling and restricted access to storage areas help minimize the risk of accidents and unauthorized handling.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The industrial use of muriatic acid presents significant risks, with the market for safety solutions in a mature stage but continually evolving. The global market size for industrial safety equipment is substantial, driven by stringent regulations and increasing awareness. Companies like Fluid Energy Group Ltd. and Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE are at the forefront of developing safer chemical handling technologies. The technical maturity of acid exposure prevention varies, with established methods like personal protective equipment coexisting with emerging innovations in acid neutralization and containment systems. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. and LG Chem Ltd. are investing in advanced safety protocols for their chemical-intensive processes, indicating a trend towards more sophisticated risk management strategies in high-tech industries.
Fluid Energy Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fluid Energy Group has developed alternative acid technologies that aim to reduce the risks associated with traditional muriatic acid use in industrial settings. Their HCl replacement products, such as the Enviro-Syn Modified Acid™ series, offer similar performance to muriatic acid but with significantly reduced corrosivity and vapour pressure[9]. These products are designed to be safer for workers, equipment, and the environment while maintaining effectiveness in applications such as well stimulation, scale removal, and industrial cleaning. The company's approach focuses on modifying the chemical structure of acids to reduce their hazardous properties without compromising their functional benefits[10].
Strengths: Innovative acid alternatives that reduce exposure risks while maintaining functionality, potentially applicable across multiple industries. Weaknesses: May require process adjustments and regulatory approvals for widespread adoption in various industrial applications.
VRTX Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: VRTX Technologies has developed innovative water treatment solutions that address the risks associated with muriatic acid use in industrial cooling systems. Their technology reduces or eliminates the need for muriatic acid in scale control, thereby minimizing exposure risks. The VRTX system uses a combination of hydrodynamic cavitation and chemical-free water treatment to control scale, corrosion, and biological growth in cooling towers[5]. This approach not only reduces the risks associated with acid handling but also improves overall system efficiency and reduces environmental impact. The company's solutions are particularly relevant in industries where large quantities of muriatic acid are traditionally used for water treatment[6].
Strengths: Innovative technology that reduces or eliminates acid use, environmentally friendly approach, and improved system efficiency. Weaknesses: May require significant changes to existing industrial processes and initial investment costs.
Innovative Solutions
Stabilizing aqueous amino acid-hcl compositions
PatentWO2023223261A1
Innovation
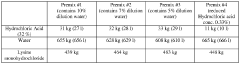
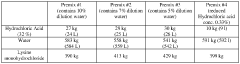
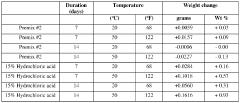
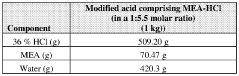
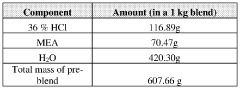
- A method to stabilize aqueous compositions of amino acid salts like lysine monohydrochloride by adding a first acidic component, which improves the stability of these compositions, allowing them to maintain effectiveness at high temperatures and reducing corrosion, thereby enabling the creation of a reconstituted modified acid that can be used for various oil and gas industry applications.
Stabilized modified acid pre-blends
PatentWO2023214360A1
Innovation
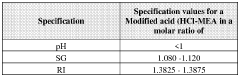
- A method to stabilize an aqueous composition of alkanolamine by adding a first acidic component, maintaining a pH between 7 and 11, and adjusting the molar ratio of alkanolamine to hydrochloric acid to achieve a stable modified acid composition that is resistant to temperature fluctuations, reduces corrosion, and is biodegradable, allowing for safer handling and more effective use in a wide range of oil and gas applications.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding muriatic acid exposure in industrial settings is comprehensive and multifaceted, designed to protect workers and the environment from the potential hazards associated with this corrosive substance. At the federal level in the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a pivotal role in establishing and enforcing standards for safe handling and exposure limits. OSHA's Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) for hydrogen chloride, the gaseous form of muriatic acid, is set at 5 parts per million (ppm) as a ceiling limit, meaning this concentration should not be exceeded at any time during a workday.
In addition to OSHA regulations, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) governs the environmental aspects of muriatic acid use and disposal under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA). These regulations mandate proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety.
On a state level, many jurisdictions have implemented their own regulations that may be more stringent than federal standards. For instance, California's Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that can cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm, which includes muriatic acid under certain conditions.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system has been adopted by many countries, including the European Union through its Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which impacts the import, manufacture, and use of muriatic acid in EU member states.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, industrial facilities must implement rigorous safety protocols, including proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, emergency response plans, and regular employee training programs. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be readily available, and proper labeling of containers and work areas is mandatory.
Regulatory bodies also require regular monitoring and reporting of workplace exposures, incidents, and near-misses related to muriatic acid. This data collection helps in refining safety standards and identifying areas for improvement in industrial hygiene practices. As scientific understanding of chemical hazards evolves, regulatory frameworks are periodically updated to reflect new findings and best practices in occupational health and safety.
In addition to OSHA regulations, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) governs the environmental aspects of muriatic acid use and disposal under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA). These regulations mandate proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety.
On a state level, many jurisdictions have implemented their own regulations that may be more stringent than federal standards. For instance, California's Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that can cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm, which includes muriatic acid under certain conditions.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system has been adopted by many countries, including the European Union through its Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which impacts the import, manufacture, and use of muriatic acid in EU member states.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, industrial facilities must implement rigorous safety protocols, including proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, emergency response plans, and regular employee training programs. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be readily available, and proper labeling of containers and work areas is mandatory.
Regulatory bodies also require regular monitoring and reporting of workplace exposures, incidents, and near-misses related to muriatic acid. This data collection helps in refining safety standards and identifying areas for improvement in industrial hygiene practices. As scientific understanding of chemical hazards evolves, regulatory frameworks are periodically updated to reflect new findings and best practices in occupational health and safety.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of muriatic acid exposure in industrial settings is a significant concern that requires careful consideration and management. Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is widely used in various industrial processes, including metal cleaning, pH adjustment, and chemical manufacturing. When released into the environment, it can have severe consequences on ecosystems, water bodies, and soil quality.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with muriatic acid exposure is its potential to alter the pH of water bodies. Even small quantities of the acid can significantly lower the pH of rivers, lakes, and groundwater, creating acidic conditions that are harmful to aquatic life. This acidification can lead to the death of fish, amphibians, and other water-dwelling organisms, disrupting entire ecosystems and food chains.
Soil contamination is another critical environmental concern. When muriatic acid is spilled or improperly disposed of, it can seep into the soil, altering its chemical composition and pH levels. This can result in reduced soil fertility, impaired plant growth, and the potential leaching of heavy metals from the soil into groundwater. The long-term effects of soil acidification can persist for years, affecting agricultural productivity and natural habitats.
Air pollution is also a potential consequence of muriatic acid exposure in industrial settings. When the acid vaporizes or is released as an aerosol, it can contribute to the formation of acid rain. This phenomenon occurs when the acid combines with water vapor in the atmosphere, leading to precipitation with a lower pH. Acid rain can have far-reaching effects on forests, crops, and infrastructure, causing damage to vegetation, accelerating the corrosion of buildings and monuments, and further acidifying water bodies.
The impact on wildlife extends beyond aquatic ecosystems. Animals that come into contact with muriatic acid or consume contaminated water or vegetation can suffer from severe health issues, including burns, respiratory problems, and internal organ damage. This can lead to population declines and disruptions in local biodiversity.
To mitigate these environmental risks, industrial facilities must implement stringent safety measures and proper handling protocols. This includes the use of containment systems, neutralization procedures for spills, and appropriate disposal methods for acid waste. Additionally, regular environmental monitoring and impact assessments are crucial to detect and address any potential contamination promptly.
Regulatory compliance and adherence to environmental protection standards play a vital role in minimizing the environmental impact of muriatic acid exposure. Industries must follow guidelines set by environmental agencies regarding the storage, use, and disposal of hazardous chemicals. Implementing best practices and investing in technologies that reduce the risk of acid release can significantly contribute to environmental protection and sustainable industrial operations.
One of the primary environmental risks associated with muriatic acid exposure is its potential to alter the pH of water bodies. Even small quantities of the acid can significantly lower the pH of rivers, lakes, and groundwater, creating acidic conditions that are harmful to aquatic life. This acidification can lead to the death of fish, amphibians, and other water-dwelling organisms, disrupting entire ecosystems and food chains.
Soil contamination is another critical environmental concern. When muriatic acid is spilled or improperly disposed of, it can seep into the soil, altering its chemical composition and pH levels. This can result in reduced soil fertility, impaired plant growth, and the potential leaching of heavy metals from the soil into groundwater. The long-term effects of soil acidification can persist for years, affecting agricultural productivity and natural habitats.
Air pollution is also a potential consequence of muriatic acid exposure in industrial settings. When the acid vaporizes or is released as an aerosol, it can contribute to the formation of acid rain. This phenomenon occurs when the acid combines with water vapor in the atmosphere, leading to precipitation with a lower pH. Acid rain can have far-reaching effects on forests, crops, and infrastructure, causing damage to vegetation, accelerating the corrosion of buildings and monuments, and further acidifying water bodies.
The impact on wildlife extends beyond aquatic ecosystems. Animals that come into contact with muriatic acid or consume contaminated water or vegetation can suffer from severe health issues, including burns, respiratory problems, and internal organ damage. This can lead to population declines and disruptions in local biodiversity.
To mitigate these environmental risks, industrial facilities must implement stringent safety measures and proper handling protocols. This includes the use of containment systems, neutralization procedures for spills, and appropriate disposal methods for acid waste. Additionally, regular environmental monitoring and impact assessments are crucial to detect and address any potential contamination promptly.
Regulatory compliance and adherence to environmental protection standards play a vital role in minimizing the environmental impact of muriatic acid exposure. Industries must follow guidelines set by environmental agencies regarding the storage, use, and disposal of hazardous chemicals. Implementing best practices and investing in technologies that reduce the risk of acid release can significantly contribute to environmental protection and sustainable industrial operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!