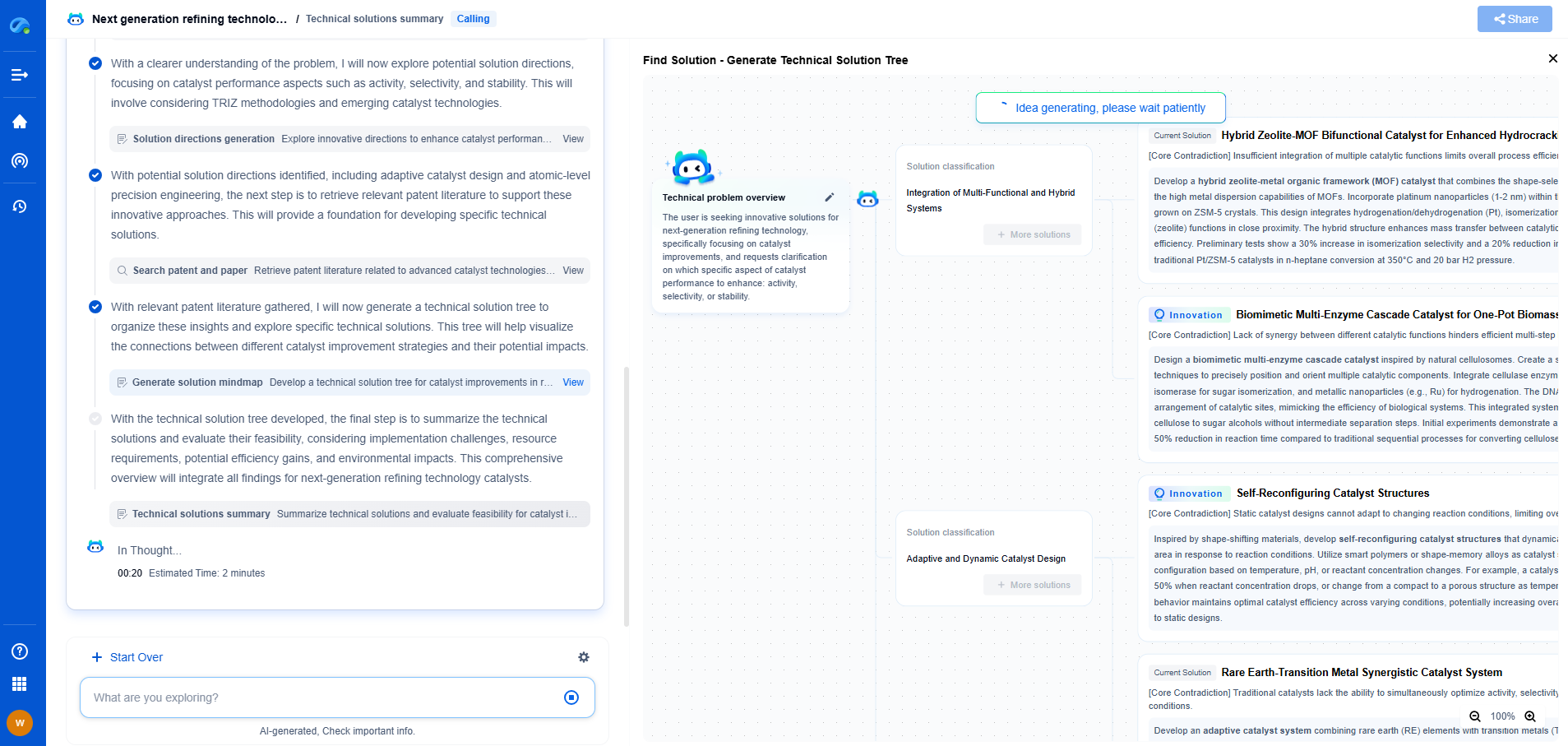
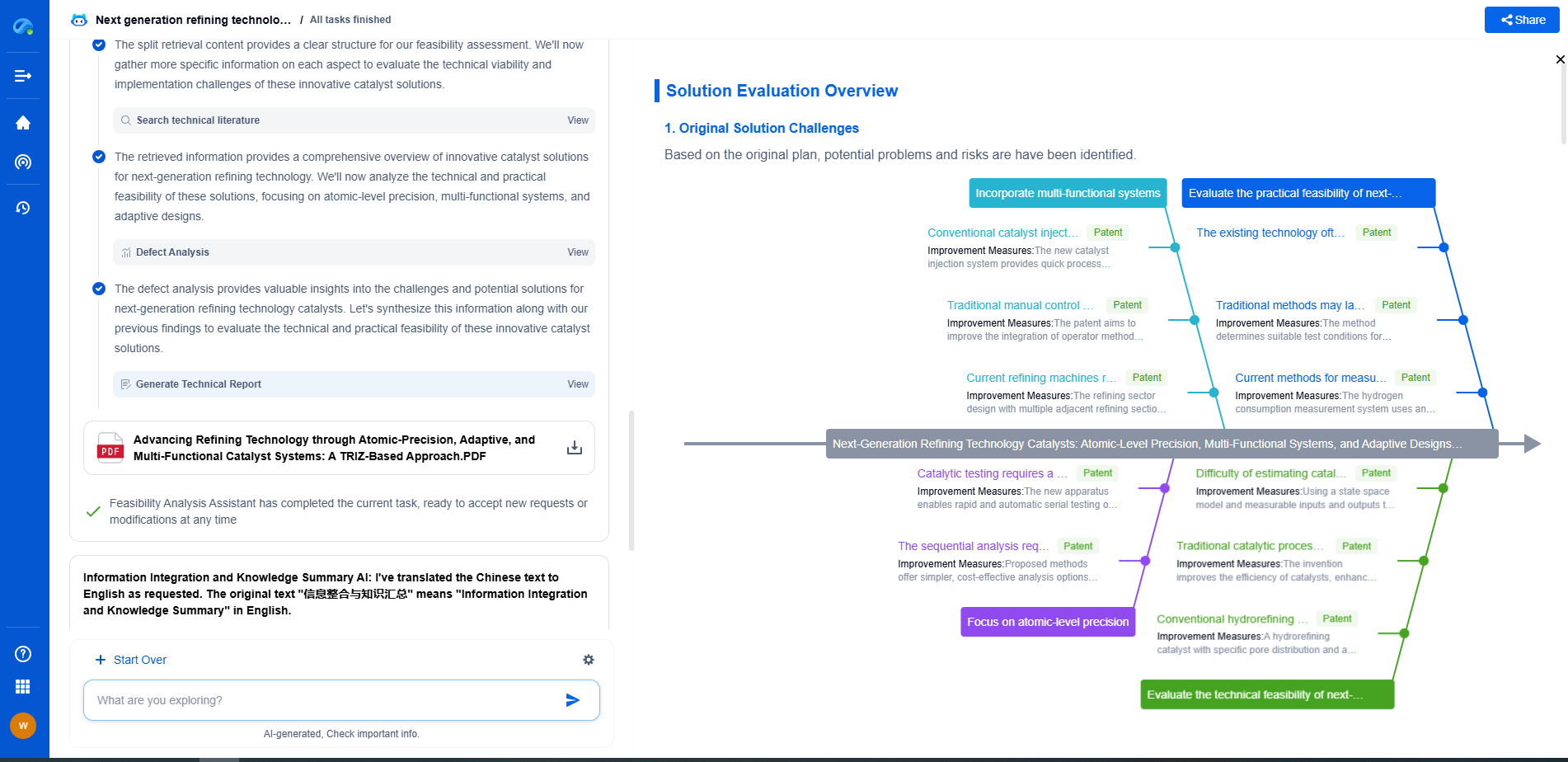
49 CFR Part 192 vs. 195: How PHMSA Treats Natural Gas Differently From Crude Oil
JUN 20, 2025 |
The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) plays a critical role in regulating the safe transportation of energy products. Within its purview, PHMSA enforces specific rules under Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), particularly Parts 192 and 195. These parts outline the standards applicable to natural gas and crude oil pipelines respectively, underscoring their unique regulatory approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for industry stakeholders and those interested in energy transportation.
Distinguishing Natural Gas and Crude Oil Regulations
At its core, 49 CFR Part 192 governs the safety of natural gas pipelines, whereas Part 195 pertains to hazardous liquid pipelines, which include crude oil. The divergence in regulatory frameworks between these two parts stems from the inherent differences in the physical and chemical properties of natural gas and crude oil, as well as their distinct transportation risks.
Material Specifications and Pipeline Construction
One of the primary differentiators between Parts 192 and 195 is the specification of materials and construction standards for pipelines. Natural gas pipelines must adhere to stringent guidelines to withstand high-pressure environments, given the gaseous state of the product. These guidelines are detailed in Part 192, which emphasizes the necessity for durable materials that can prevent leaks and withstand environmental stresses.
Conversely, crude oil pipelines are governed by Part 195, which takes into account the liquid nature of the product and its potential for spills. The regulation requires pipelines to be constructed using materials that minimize corrosion and facilitate easy detection and repair of leaks. While both parts prioritize safety, the methodologies and materials specified often differ to address the unique challenges posed by transporting gas versus liquid.
Operational and Maintenance Standards
Operational and maintenance standards also vary between natural gas and crude oil pipelines. Part 192 mandates regular inspections, pressure testing, and maintenance activities tailored to the high-pressure conditions of gas pipelines. These measures ensure that any anomalies are promptly addressed to prevent catastrophic failures.
Part 195, on the other hand, focuses on protecting the environment from the adverse effects of oil spills. It includes stringent regulations on spill containment systems, leak detection technologies, and emergency response protocols. Regular inspections and maintenance activities are required to ensure pipelines operate within safe limits and any potential spills are swiftly managed.
Safety Management Systems
Safety Management Systems (SMS) are integral to both Parts 192 and 195, albeit with different focal points. Part 192 emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and management related to high-pressure gas environments. Operators are required to implement comprehensive SMS that incorporate regular risk analysis, employee training, and incident response planning.
In contrast, Part 195 places significant emphasis on environmental protection and spill management. Operators must develop SMS that prioritize safeguarding wildlife and ecosystems in the event of a spill. These systems are designed to ensure rapid response and minimal environmental impact, reflecting the unique risks associated with transporting crude oil.
Compliance and Enforcement
Compliance with PHMSA regulations is non-negotiable for pipeline operators. Part 192 and Part 195 both outline rigorous compliance requirements, although their enforcement focuses differ. Natural gas operators face stringent inspections and audits to ensure adherence to safety standards, with penalties for non-compliance aimed at preventing accidents.
Crude oil operators, under Part 195, are similarly held accountable for compliance, with an added emphasis on environmental protection. PHMSA actively monitors spill response readiness and ecological impact assessments, ensuring operators prioritize environmental safety alongside pipeline integrity.
Conclusion: Tailored Approaches for Different Resources
The contrasting approaches of Parts 192 and 195 highlight PHMSA's commitment to tailoring regulations based on the unique properties and risks associated with natural gas and crude oil transportation. Through these specialized regulatory frameworks, PHMSA aims to safeguard public safety and environmental health, ensuring that energy products are delivered reliably and responsibly.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for pipeline operators, who must navigate the complexities of compliance to maintain operational integrity and secure the trust of the communities they serve. As the energy landscape evolves, PHMSA's regulations will likely continue to adapt, reflecting ongoing advancements in technology and safety practices.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com