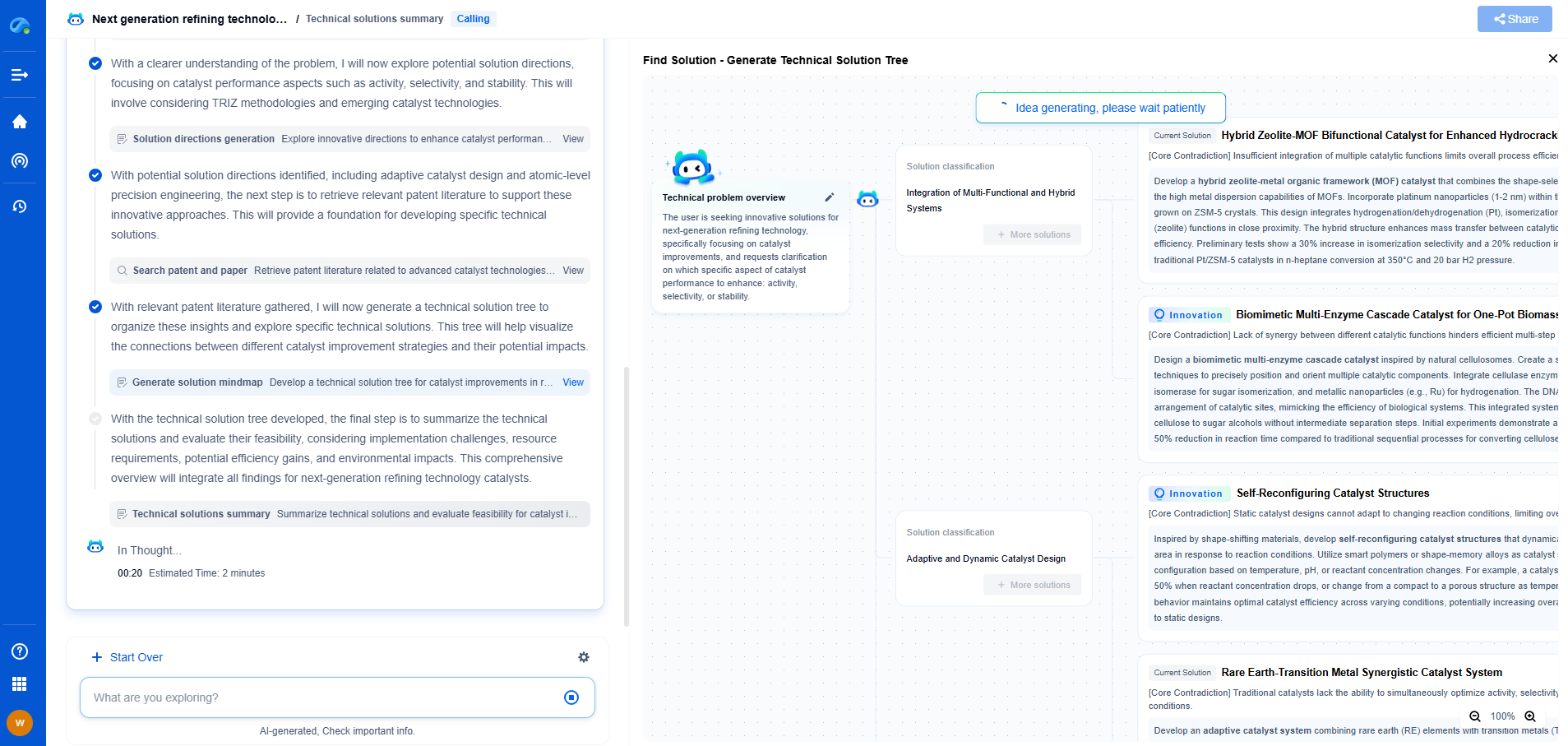
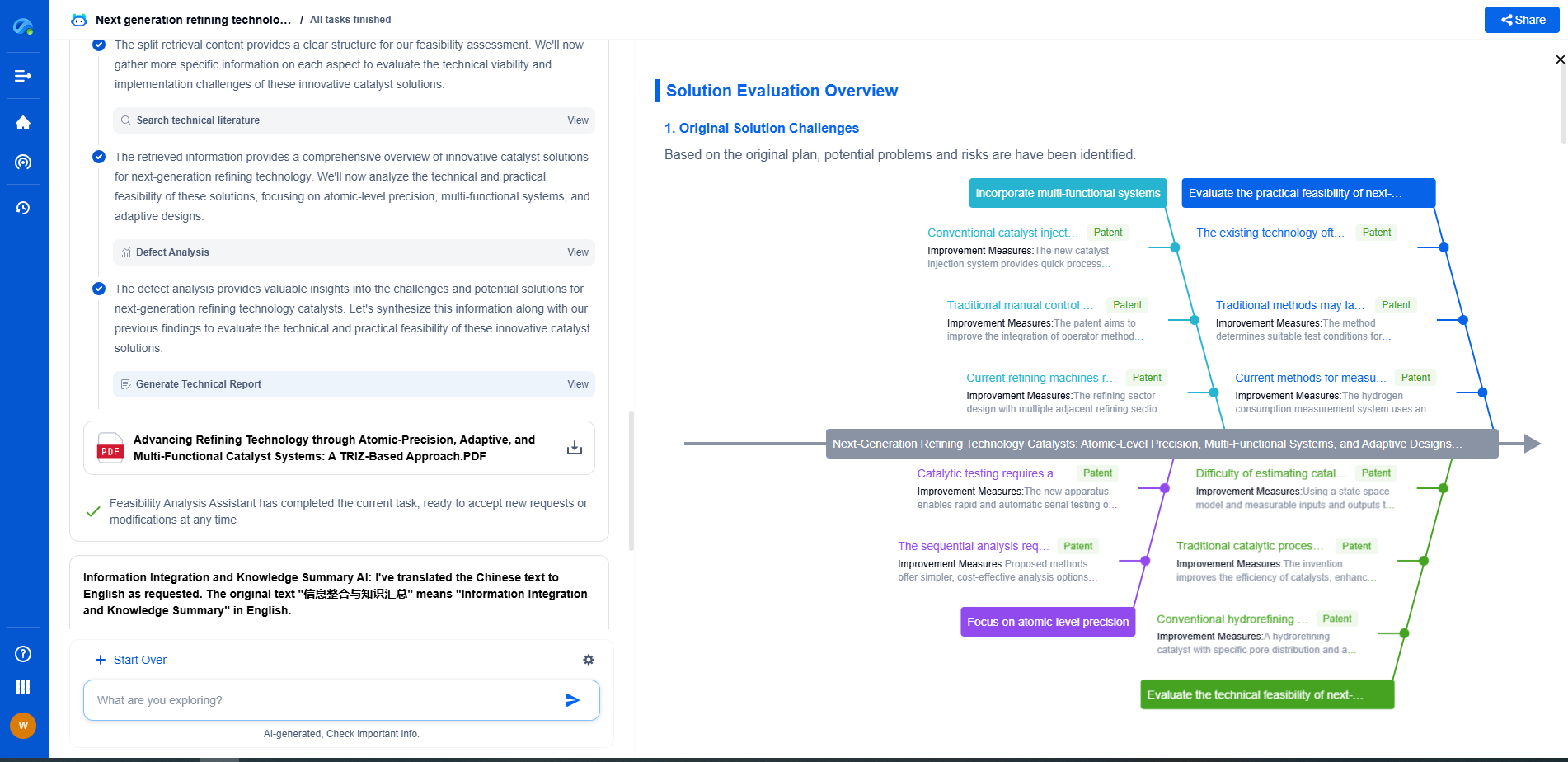
Acceleration vs. Velocity vs. Displacement: Key Differences in Vibration Analysis
JUL 16, 2025 |
Vibration analysis is a critical component of many fields, including engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance. It helps in diagnosing issues related to machinery and structural health. At its core, vibration analysis revolves around three fundamental concepts: acceleration, velocity, and displacement. These parameters are instrumental in assessing the condition of machinery and identifying potential problems before they escalate. Understanding the differences between these parameters is crucial for effective vibration analysis and can vastly improve the maintenance processes of mechanical systems.
What is Displacement?
Displacement refers to the change in position of an object. In vibration analysis, it measures how much a vibrating object moves from its equilibrium position. Displacement is typically expressed in units of micrometers (µm) or mils (1 mil = 1/1000 of an inch). It is most useful in situations where low-frequency vibrations are of concern, such as in large rotating machinery. Monitoring displacement can be particularly beneficial in detecting misalignment, imbalance, or looseness in equipment. By understanding how much a component moves during operation, engineers can identify excessive wear or other mechanical issues that may affect performance.
Unpacking Velocity
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. In vibration analysis, it provides information about the speed at which an object moves back and forth. Velocity is typically measured in millimeters per second (mm/s) or inches per second (in/s). It is a crucial parameter for evaluating medium-frequency vibrations typically found in motors, pumps, and other industrial machines. Monitoring velocity helps in identifying problems related to resonance and ensures that machinery operates within safe limits. It is a preferred parameter for many applications because it provides a balance between low and high-frequency components, making it an effective indicator of overall machine condition.
The Role of Acceleration
Acceleration measures the rate of change of velocity over time. In vibration analysis, it indicates how quickly the speed of an object’s vibration is changing and is usually measured in terms of gravitational force (g) or meters per second squared (m/s²). Acceleration is particularly useful for detecting high-frequency vibrations often associated with bearing faults or gear mesh issues. Because it is sensitive to rapid changes, acceleration is an excellent parameter for identifying early signs of component failure. By observing acceleration data, maintenance teams can proactively address potential problems before they result in costly downtime or catastrophic failures.
Comparing Acceleration, Velocity, and Displacement
While acceleration, velocity, and displacement are interrelated, they serve different purposes in vibration analysis. Displacement is best for identifying issues at lower frequencies, such as structural failures or misalignment. Velocity provides a balance and is suitable for medium-frequency problems, offering a comprehensive view of machine health. Acceleration focuses on high-frequency issues, making it ideal for detecting bearing or gear faults.
Selecting the appropriate parameter depends on the specific application and the type of faults being monitored. Understanding these differences allows engineers to tailor their vibration analysis approach to match the operational needs of their machinery, ultimately leading to more efficient maintenance strategies and improved machine reliability.
Applications in Industry
In industrial applications, the choice between displacement, velocity, and acceleration depends on the machinery and the nature of the vibrations being analyzed. For example, in large turbines, displacement might be monitored to check for rotor imbalances. In contrast, in a high-speed motor, acceleration could be the focus to detect potential bearing failures. Many industries maintain a comprehensive vibration analysis program that incorporates all three parameters to ensure no potential issue goes undetected.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between acceleration, velocity, and displacement is fundamental to effective vibration analysis. Each parameter provides unique insights into the condition of machinery, allowing for targeted maintenance strategies. By effectively utilizing these parameters, industries can enhance equipment performance, prevent unexpected failures, and optimize maintenance resources. As technology advances, the integration of sophisticated data analysis tools with traditional vibration analysis parameters will likely lead to even more precise and effective maintenance strategies in the future.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com