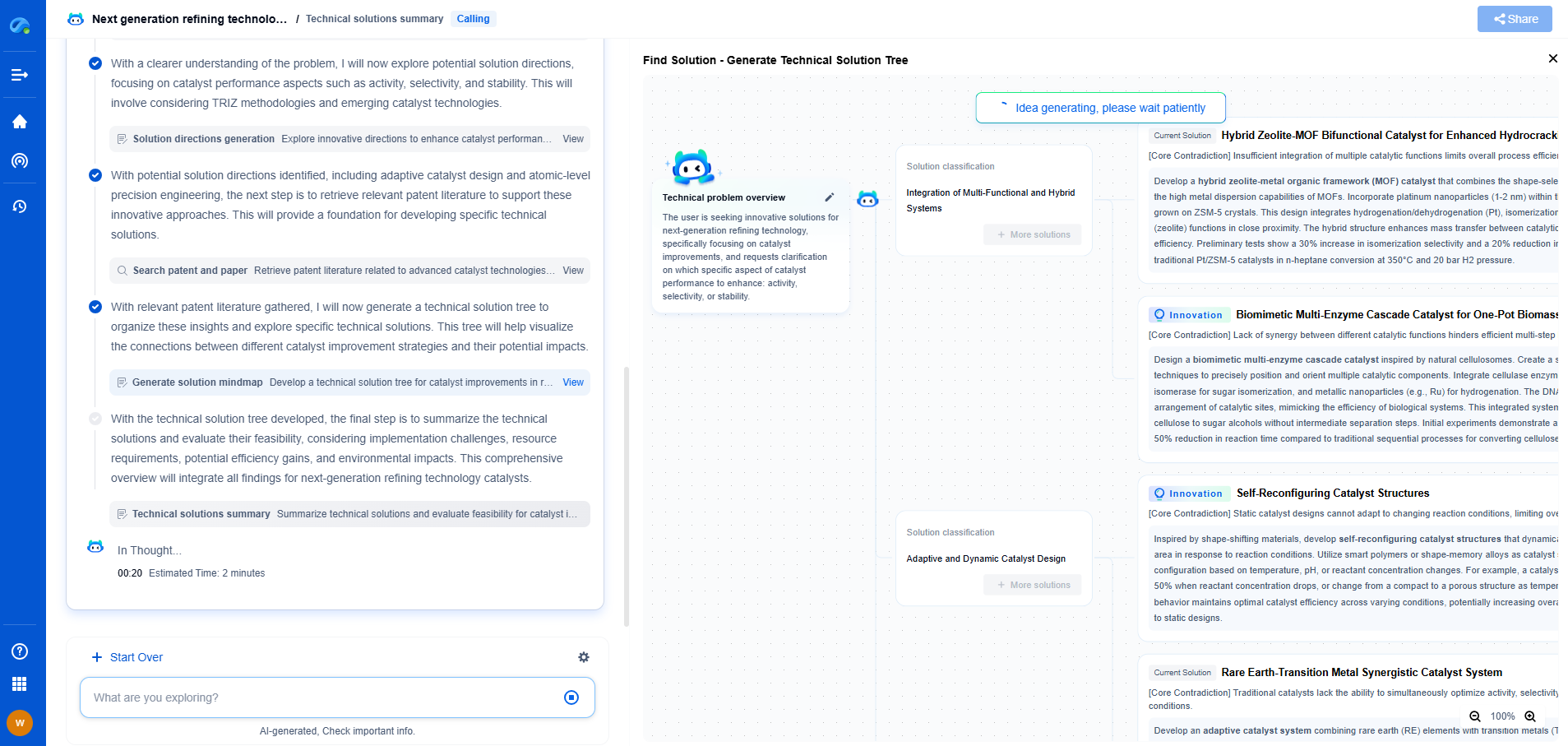
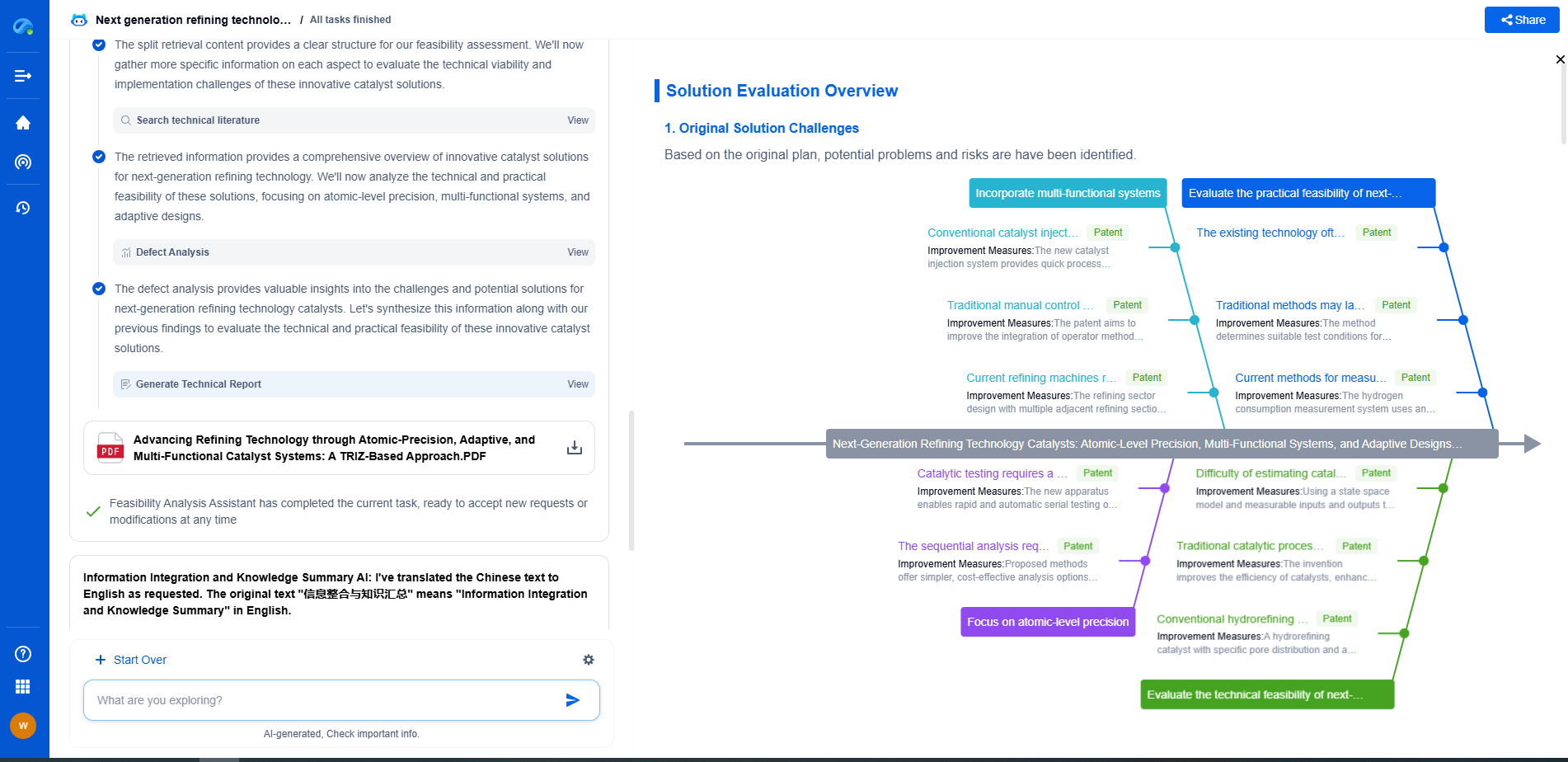
Ammonia Pipelines: Next-Gen Hydrogen Carrier Infrastructure?
JUN 20, 2025 |
As the world pivots towards a sustainable energy future, hydrogen stands out as a promising candidate due to its potential to decarbonize various sectors, including transportation, industry, and energy production. However, transporting hydrogen efficiently and safely remains a significant challenge. Enter ammonia, a chemical compound emerging as a potential next-gen hydrogen carrier infrastructure. Ammonia offers a compelling solution due to its ability to store and transport hydrogen in a stable and energy-dense form.
Why Consider Ammonia Pipelines?
The use of ammonia pipelines presents several advantages compared to traditional hydrogen transportation methods. Firstly, ammonia is easier to liquefy and store than pure hydrogen, making it more economically viable for long-distance transport. Unlike hydrogen, which requires cryogenic conditions for liquefaction, ammonia can be liquefied at moderate pressures and temperatures. This characteristic drastically reduces infrastructure costs and complexity.
Moreover, ammonia pipelines can leverage existing natural gas infrastructure with minimal modifications, enabling a quicker and more cost-effective transition. Repurposing existing pipelines to transport ammonia means less capital investment and faster deployment, potentially accelerating the adoption of hydrogen energy solutions.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While ammonia pipelines offer promising benefits, safety and environmental considerations are paramount. Ammonia is a hazardous material that can pose environmental and health risks if not properly managed. The potential for leaks and accidental releases necessitates stringent safety protocols and monitoring systems.
To mitigate these risks, implementing advanced sensor technologies and automated response systems can ensure early detection and rapid containment of any leaks. Additionally, extensive training for personnel and adherence to international safety standards will be crucial in maintaining safe operations.
Environmental impacts must also be addressed, particularly regarding ammonia production. The traditional Haber-Bosch process, used to produce ammonia, relies heavily on fossil fuels. Transitioning to green ammonia production, using renewable energy sources, can significantly reduce carbon emissions and enhance the overall sustainability of this hydrogen carrier method.
Ammonia vs. Other Hydrogen Carriers
Ammonia is not the only candidate vying to become the preferred hydrogen carrier. Competing technologies include liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) and compressed hydrogen gas transport. Each method has its own strengths and challenges, but ammonia offers distinct advantages.
In terms of energy density, ammonia outperforms compressed hydrogen, allowing for more efficient storage and transport. Additionally, ammonia's established industrial uses provide a familiar framework for scaling its application as a hydrogen carrier. The global ammonia market is well-developed, providing a robust supply chain that can be leveraged for hydrogen transport.
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of ammonia pipelines as a hydrogen carrier is promising, yet several challenges must be overcome. Technological advancements in ammonia synthesis, transport, and conversion back to hydrogen are essential. Research into more efficient catalytic processes for ammonia synthesis and cracking will drive down costs and improve efficiency.
Moreover, policy and regulatory support are crucial to facilitate the development and deployment of ammonia pipeline infrastructure. Governments must implement clear guidelines and financial incentives to promote investment in ammonia-based hydrogen transport solutions. Collaborative efforts between industry, academia, and policymakers will be vital in addressing technical, economic, and environmental challenges.
Conclusion
Ammonia pipelines represent a promising next-gen hydrogen carrier infrastructure, offering a feasible solution to the transportation and storage challenges of hydrogen. While there are hurdles to overcome, the potential benefits in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and efficiency make ammonia an attractive option. Through continued research, innovation, and collaborative efforts, ammonia pipelines could play a pivotal role in realizing a hydrogen-powered sustainable energy future.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com