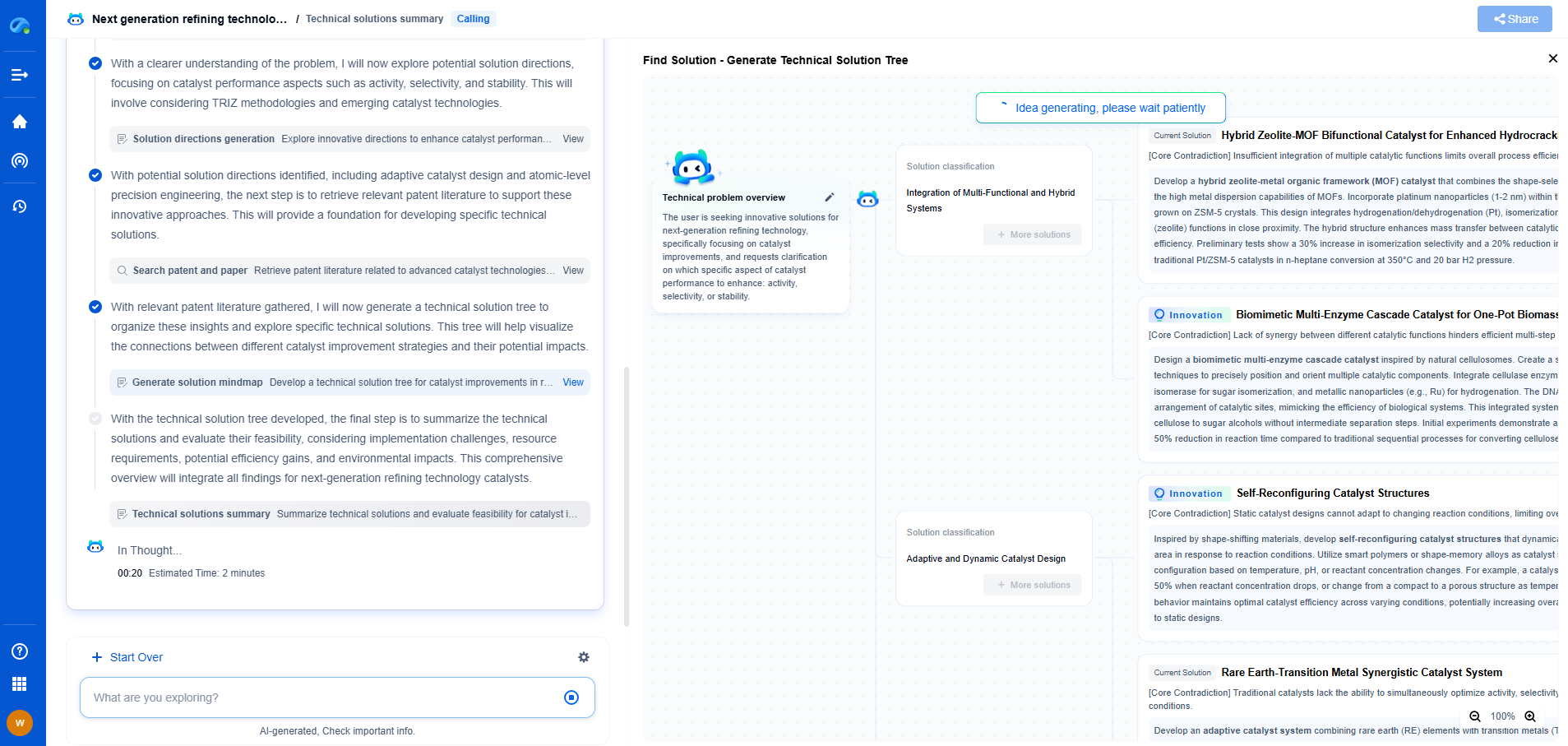
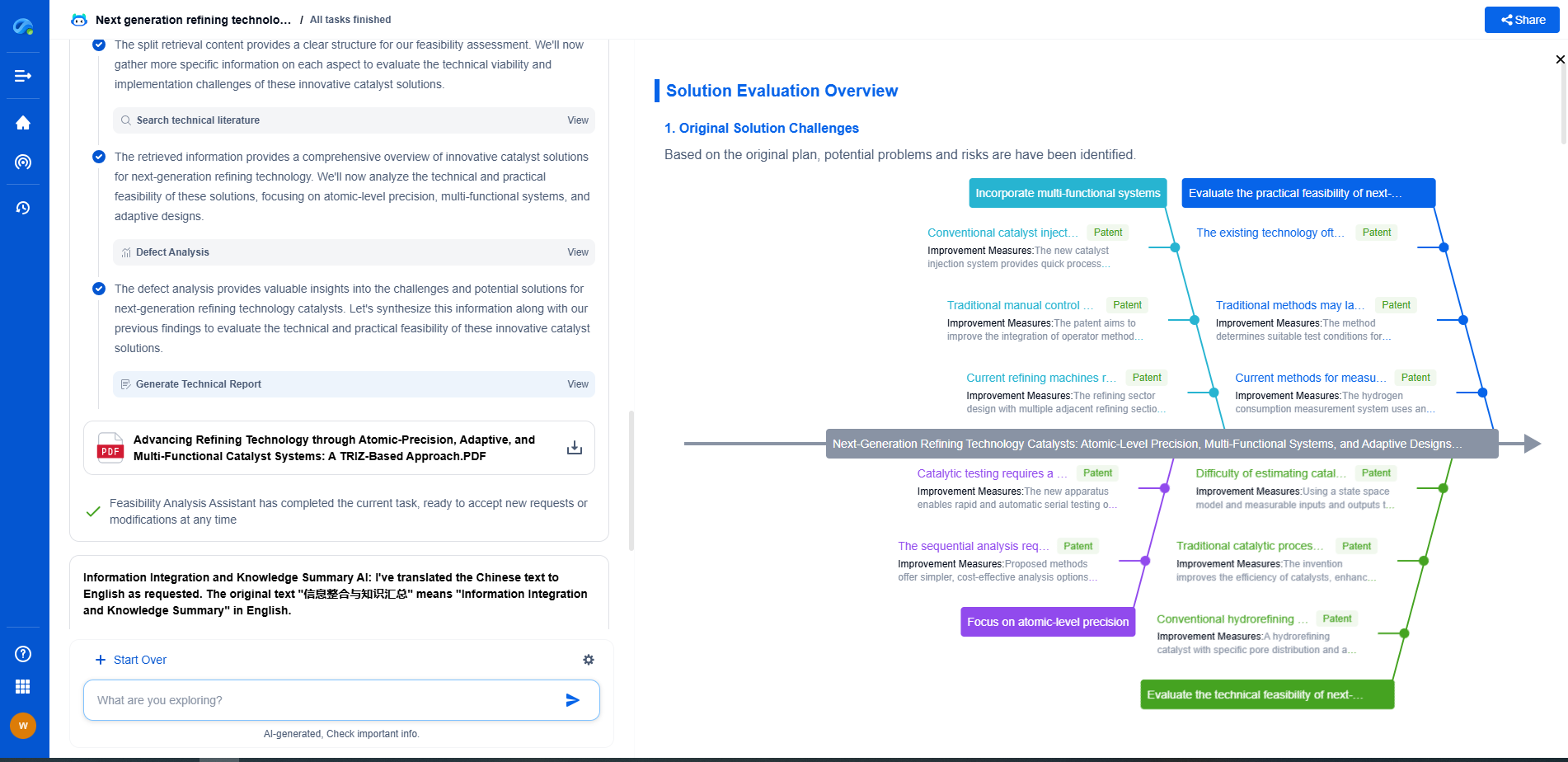
Analog (4–20mA) vs Digital Output: When to Choose Each for Process Control
JUL 14, 2025 |
Process control is essential in various industries, allowing operators to monitor and adjust processes to ensure efficiency, safety, and quality. When choosing between analog and digital outputs, particularly the analog 4–20mA and digital outputs, it is crucial to understand the differences and the specific applications where each excels.
Analog 4–20mA Output
The 4–20mA current loop has been a longstanding standard in process control systems. It is a robust method for transmitting analog signals over long distances. Here's why it is preferred in certain applications:
1. **Simplicity and Reliability**: The 4–20mA signal is inherently simple, with the current flowing through a circuit directly proportional to the measured parameter. It is less susceptible to electrical noise compared to voltage signals, making it reliable in harsh industrial environments.
2. **Long-distance Transmission**: Current signals do not degrade over long distances, unlike voltage signals. This makes the 4–20mA output ideal for large-scale facilities where sensors are spread out over sizeable areas.
3. **Failure Detection**: The range of 4–20mA allows for easy detection of faults. A current less than 4mA typically indicates a wiring issue or a device malfunction, making troubleshooting more straightforward.
4. **Compatibility**: Many legacy systems in industries like petrochemical, oil and gas, and manufacturing are designed around the 4–20mA standard. Integrating new sensors and transmitters using this output is seamless.
Digital Output
Digital outputs offer precise and fast data transmission, which is increasingly essential in modern process control systems. Here's why you might choose digital over analog:
1. **Precision and Accuracy**: Digital signals provide exact values, reducing the chance of errors associated with signal conversion. This is particularly important in applications requiring high precision, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing and high-tech electronics production.
2. **Multi-parameter Transmission**: Unlike 4–20mA, which typically transmits a single parameter, digital outputs can carry multiple data points, including diagnostics and status information. This ability to convey comprehensive data supports advanced process control strategies.
3. **Integration with Modern Systems**: Digital outputs are more compatible with modern control systems, which frequently use fieldbus protocols like Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP. This facilitates seamless integration into smart factory environments and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
4. **Remote Monitoring and Control**: Digital outputs enable remote monitoring and control via network connections, allowing operators to manage processes from centralized control rooms or even remote locations.
When to Choose Each
The decision between analog 4–20mA and digital outputs often depends on the specific requirements of the process and the existing infrastructure.
1. **Existing Infrastructure**: If your facility has an established analog system, it may be cost-effective and practical to continue using 4–20mA outputs. This avoids the need for substantial upgrades or new equipment.
2. **Environmental Conditions**: In environments with high electromagnetic interference or long cable runs, the 4–20mA output may be more reliable due to its immunity to noise and loss over distance.
3. **Measurement Precision**: For applications needing high precision and accuracy, digital outputs are preferable. They minimize errors inherent in analog-to-digital conversion processes.
4. **Data Requirements**: If your process benefits from the transmission of multiple data types or requires remote monitoring capabilities, digital outputs provide a more comprehensive solution.
Conclusion
Choosing between analog 4–20mA and digital outputs for process control involves considering the specific needs of your operation, existing systems, and future goals. While 4–20mA offers simplicity, reliability, and ease of integration with legacy systems, digital outputs provide precision, multi-parameter data transmission, and compatibility with modern control systems. Understanding the advantages of each will guide you to make the best choice for optimizing process control in your facility.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com