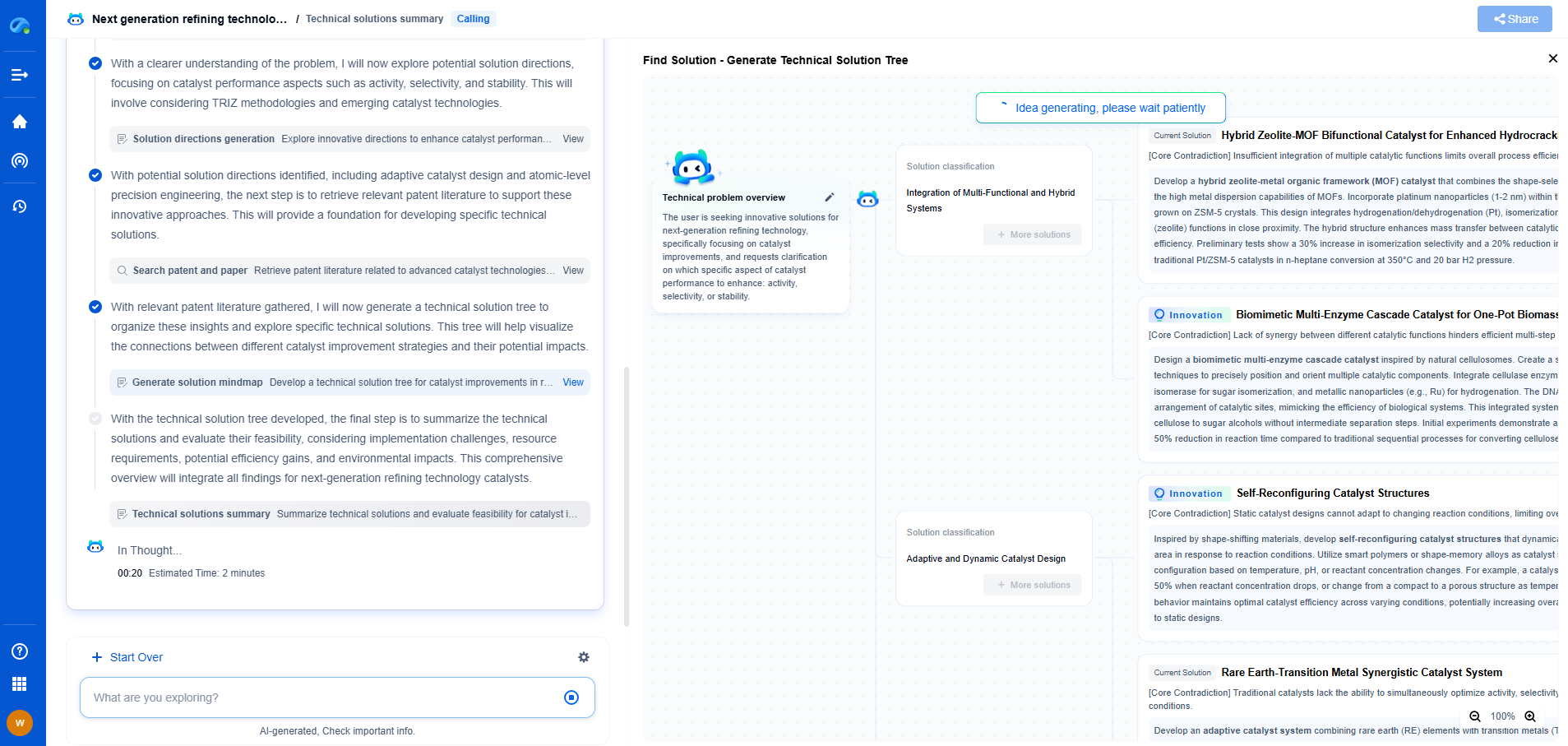
Analog vs. Digital Signal Output: Pros and Cons for Sensor Integration
JUL 14, 2025 |
In the realm of sensor integration, the choice between analog and digital signal output is crucial, impacting the efficiency, accuracy, and complexity of the overall system. Each type of signal output has its distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it vital to understand their characteristics to make informed decisions. This blog delves into the pros and cons of analog and digital signal outputs, aiding you in selecting the most suitable option for your application.
Understanding Analog Signal Output
Analog signals are continuous waveforms that vary in amplitude or frequency. These signals are analogous to physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, or sound, making them a natural choice for measuring and transmitting these forms of information.
Pros of Analog Signal Output
1. Simplicity: Analog systems can be simpler and less expensive to implement, especially for basic applications. They often require fewer components, making them relatively straightforward to design and maintain.
2. Real-time Processing: Analog signals provide instantaneous feedback, making them ideal for applications where real-time data processing is crucial.
3. Infinite Resolution: Since analog signals are continuous, they offer theoretically infinite resolution, capturing minute changes in the measured parameter without quantization error.
Cons of Analog Signal Output
1. Susceptibility to Noise: Analog signals are more prone to degradation from electrical noise and interference, which can lead to inaccuracies in the measurements.
2. Limited Range: The dynamic range of analog signals is constrained by the physical properties of the system, making it challenging to measure extremely high or low values without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Calibration Challenges: Analog systems often require frequent calibration to ensure accuracy, adding to the maintenance burden.
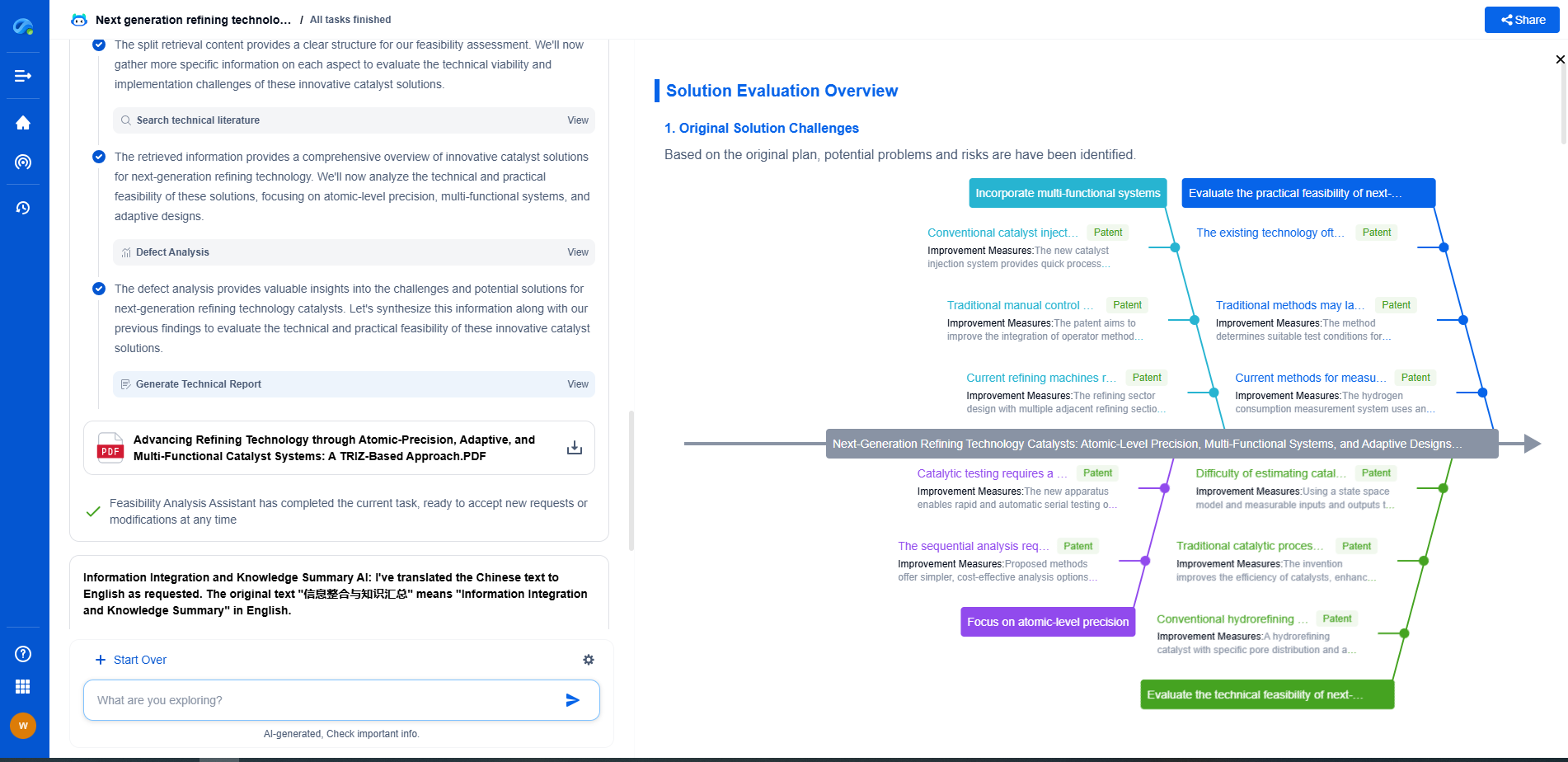
Exploring Digital Signal Output
Digital signals, in contrast, represent data in discrete binary form, typically as a series of 0s and 1s. This digitization process involves converting analog signals into a digital format using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
Pros of Digital Signal Output
1. Noise Immunity: Digital signals are less susceptible to noise and interference, ensuring higher accuracy and reliability in data transmission and processing.
2. Easy Integration: Modern digital systems are often easier to integrate with other digital devices and software, enhancing compatibility and expandability.
3. Consistent Quality: Digital signals maintain their integrity over long distances, providing consistent quality without the signal degradation common in analog systems.
4. Advanced Processing: Digital signals enable complex data processing techniques, such as filtering and error correction, improving overall system performance.
Cons of Digital Signal Output
1. Quantization Error: Digital signals can suffer from quantization error, as the continuous signal is approximated by discrete steps, potentially losing some information in the process.
2. Complexity and Cost: The initial setup of digital systems can be more complex and costly due to the need for ADCs, microcontrollers, and additional programming.
3. Latency: Digital systems can introduce latency, as the conversion and processing of signals take time, which might not be suitable for time-sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Signal Output for Your Application
The decision between analog and digital signal output should be guided by the specific requirements of your application. If you prioritize simplicity, low cost, and real-time performance, analog might be the right choice. However, if you need precision, noise immunity, and advanced processing capabilities, digital signal output could be more appropriate.
Consider factors such as the environment in which the sensors will operate, the level of accuracy needed, and the potential for future expansion. By weighing these elements alongside the pros and cons discussed, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals.
Conclusion
The debate between analog and digital signal output in sensor integration is ongoing, with each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these characteristics is essential for optimizing system performance and ensuring accurate data collection. By assessing your specific needs and constraints, you can choose the most effective signal output method, paving the way for successful sensor integration in your projects.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com